Method for preparation of plant extract
A manufacturing method and extract technology, applied in the field of plant extract manufacturing method, can solve problems such as insufficient reduction of turbidity, loss of polyphenols, long time consumption, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening the time and improving the recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
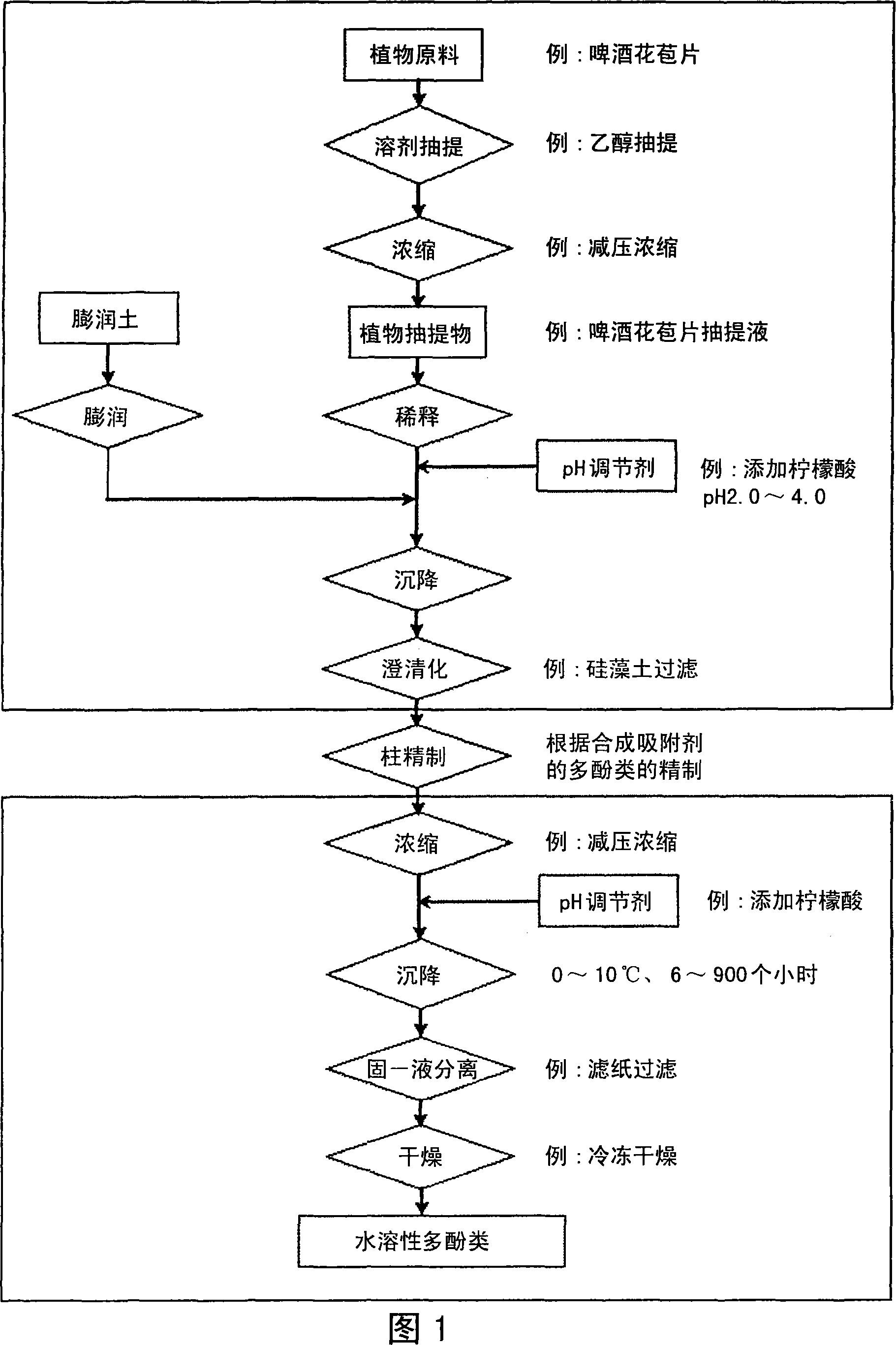
[0060] 400 g of a polyphenol-containing extract obtained by extracting 800 g of raw hop bracts with a 50% by volume alcohol aqueous solution was dissolved in pure water heated at 40° C., and mixed to 1200 mL (dilution rate 3 times v / w). Next, 200 mL of this solution was poured into a 250 mL graduated cylinder, respectively, to prepare five specimens.
[0061] On the other hand, 5 g of bentonite was added to 100 mL of pure water heated at 80° C., and stirred for 12 hours to swell, thereby preparing a suspension containing 5% of bentonite. This suspension was added to each of the above samples as shown in Table 1, and then all were adjusted to the same amount with pure water.
[0062] After standing still overnight, centrifugation was performed to obtain a supernatant. For this supernatant, the turbidity was obtained by measuring the absorbance at 650 nm with a spectrophotometer using a 10 mm long container, and the pH was measured with a pH meter. In addition, after filteri...
Embodiment 2
[0068] In the same manner as in Example 1, 400 g of a polyphenol-containing extract obtained by extracting 800 g of raw hop bracts with a 50% by volume alcohol aqueous solution was dissolved in pure water heated at 40°C, and mixed to 1200 mL (Dilution rate 3 times v / w). Next, 200 mL of this solution was poured into a 250 mL graduated cylinder, respectively, to prepare five specimens.
[0069] On the other hand, 5 g of bentonite was added to 100 mL of pure water heated at 80° C., and stirred for 12 hours to swell, thereby preparing a suspension containing 5% of bentonite. This suspension was added to each of the above samples as shown in Table 2, and then all were adjusted to the same amount with pure water.
[0070] After standing still overnight, centrifugation was performed to obtain a supernatant. This supernatant was treated in the same manner as in Example 1 above, and then the turbidity, pH, Cu concentration, Na concentration, and apparent polyphenol concentration were...
Embodiment 3
[0076] 2 kg of a polyphenol-containing extract obtained by extracting 4 kg of raw hop buds with a 50% by volume alcoholic solution was dissolved in pure water heated to 40° C., and mixed to 7.2 L (dilution rate 3.6 times v / w). Next, 1.8 mL of this solution was poured into 2 L graduated cylinders, respectively, to prepare four specimens. In addition, citric acid (anhydrous) was used for pH adjustment of the specimen.
[0077] On the other hand, 25 g of bentonite was added to 500 mL of pure water heated at 80° C., and stirred for 12 hours to swell, thereby preparing a suspension containing 5% of bentonite. This suspension was added to each of the above samples as shown in Table 3, and then all were adjusted to the same amount (2000 mL) with pure water.
[0078] After standing still overnight, centrifugation was performed to obtain a supernatant. For this supernatant, the turbidity was obtained by measuring the absorbance at 650 nm with a spectrophotometer using a 10 mm long ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com