Compositions and methods for removing arsenic in water
A technology for pollutants and aqueous solutions, which can be used in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, solid adsorbent liquid separation, etc., and can solve problems such as expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1 Using Bottom Ash as a Representative Substrate
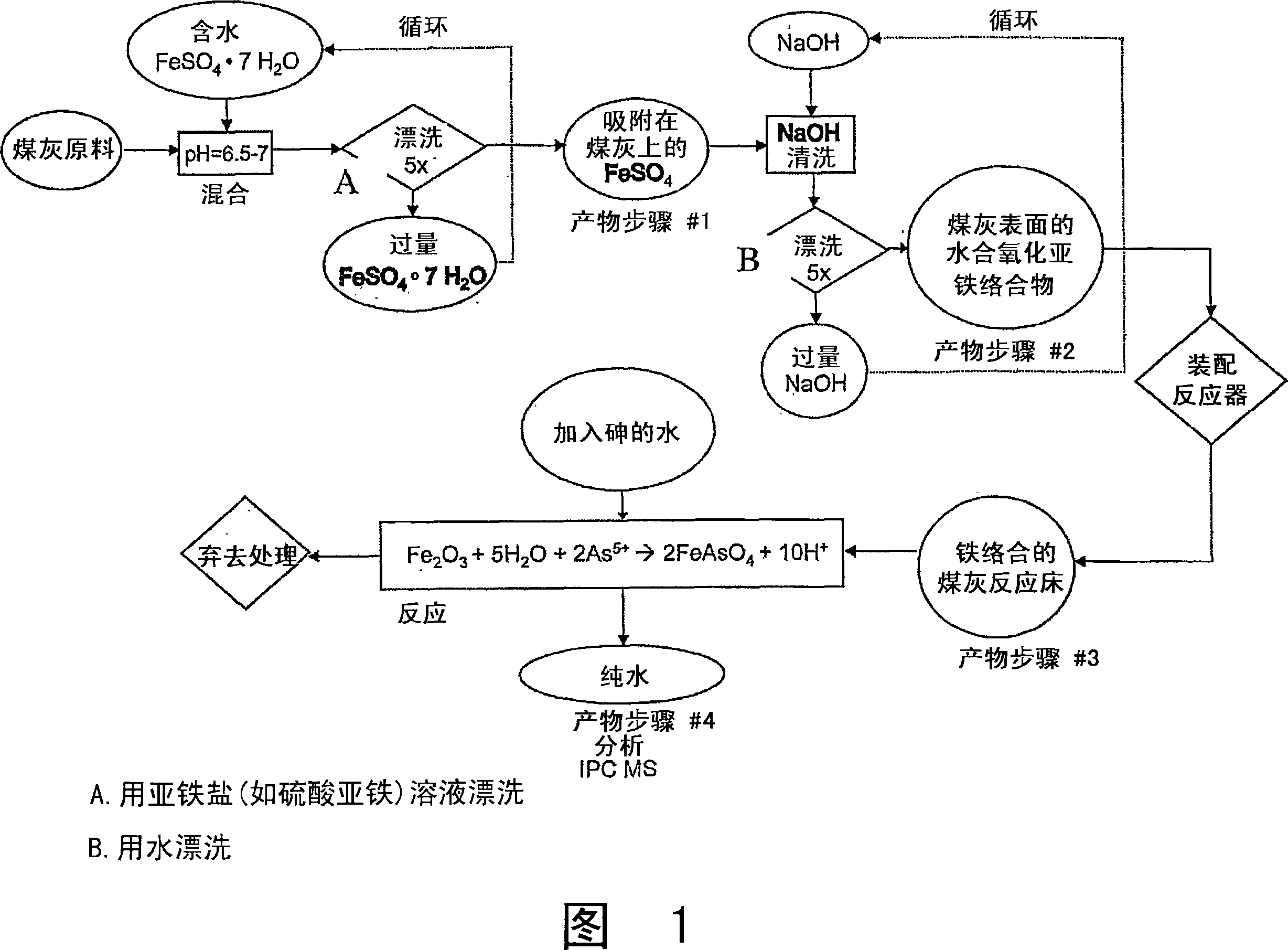
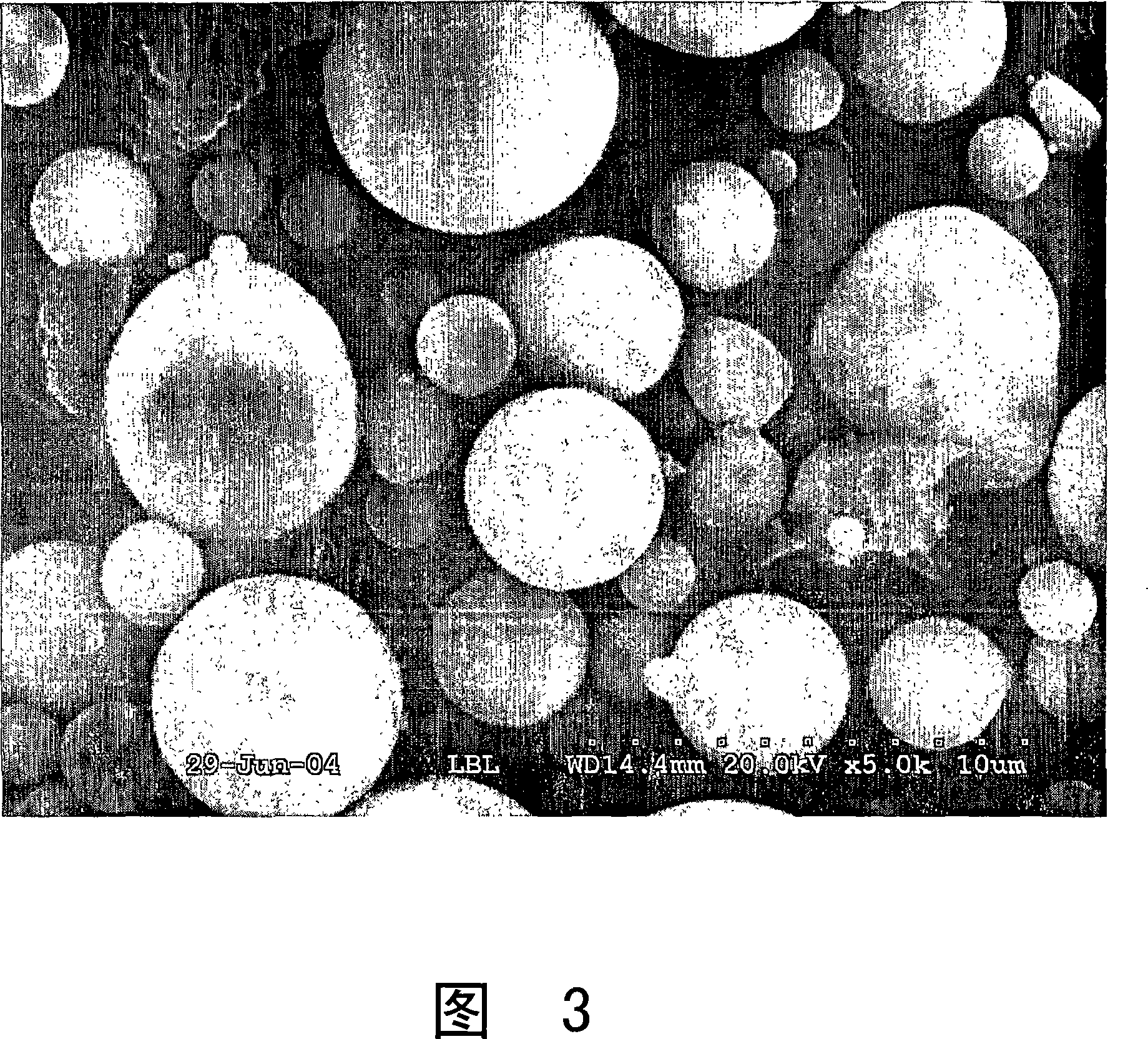
[0068] In one embodiment, bottom ash from a power plant in an area with water to be treated may be used. Coal-fired thermal power plants in South Asia, for example, produce large quantities of bottom ash suitable for use in the present invention. This bottom ash is a fine powder material of spherical particles without minerals, mainly containing silicates of iron, magnesium and aluminum. The particle size is generally 1-10 microns, providing a surface area to volume ratio of approximately 0.5m 2 / cm 3 . Disposal of bottom ash material from such thermal power plants cost US$ 5 per ton in 2005. The present invention can use a simple chemical method to coat the bottom ash with iron hydroxide and / or iron oxyhydroxide at room temperature, without using expensive raw materials and high energy consumption.
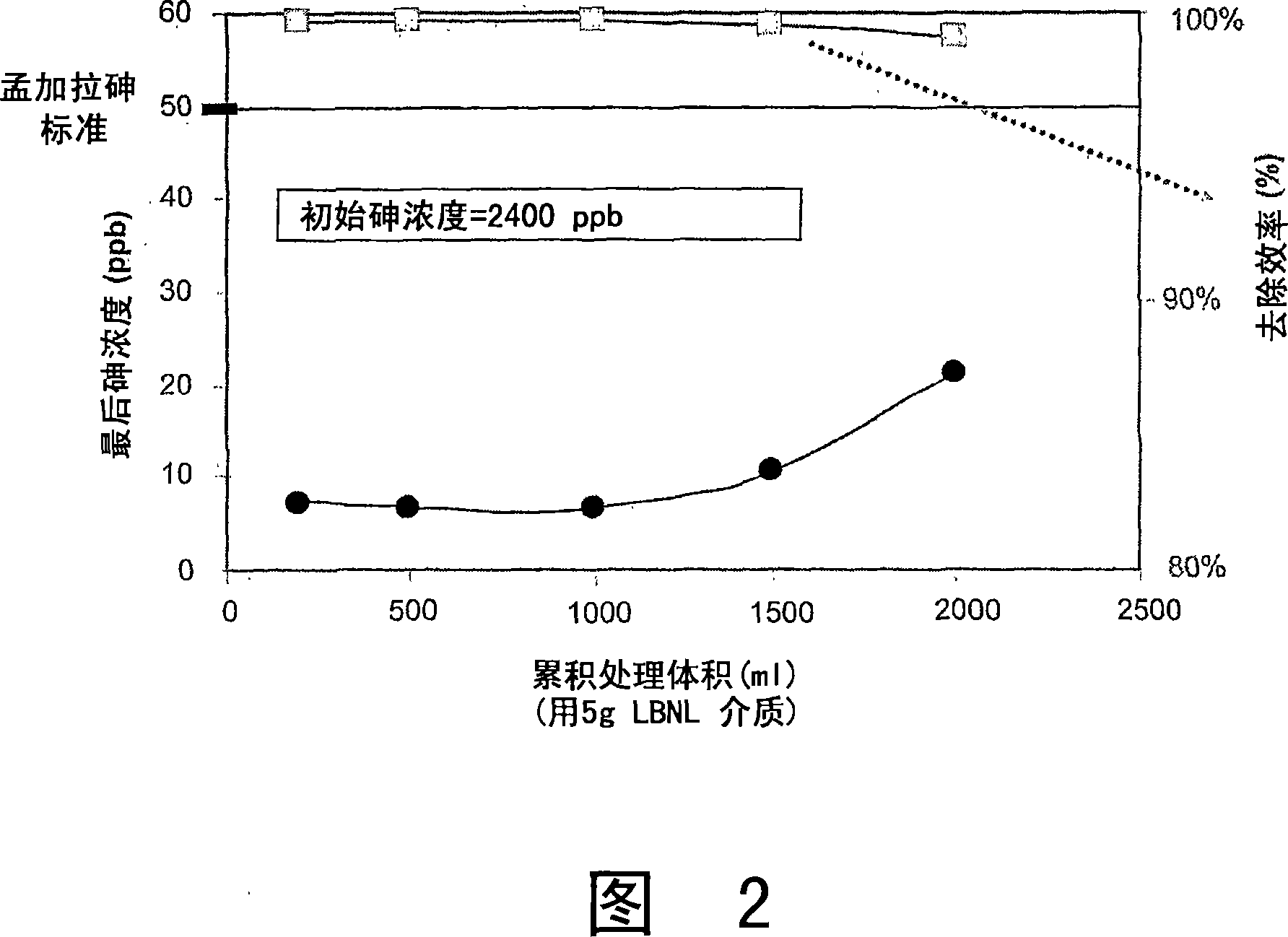
[0069] 1 kg of this medium can remove 0.7 g of elemental arsenic from drinking water, which is equivalent t...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The preparation of embodiment 2 5 grams of pretreatment bottom ash
[0080] First place 5 g of dry bottom ash in a collection container.
[0081]30ml of 0.6M FeSO 4 Mix with the bottom ash and continue stirring for 1 hour at a temperature close to room temperature, eg 10-40°C. Although this is FeSO 4 A saturated solution at room temperature, but lower concentrations may be used for lower surface coverage of the bottom ash or for smaller quantities of bottom ash. Available FeSO 4 The concentration is from 0.1M or greater.
[0082] After stirring, solid bottom ash particles are allowed to settle to the bottom of the collection container within about 5 minutes. At this point the superficial liquid was removed, this liquid was filtered, and the residue on the filter paper was added to the dense solid at the bottom of the collection vessel.
[0083] Then add 5ml of 0.5N aqueous NaOH to the collection vessel and stir to mix for 5 minutes. It can be considered that the ...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3 Removal of Arsenic Using Pretreated Bottom Ash
[0090] In practice, combining arsenic-containing water sources with Fe(OH) 3 The applied render is thoroughly mixed to reduce the arsenic content to acceptable levels. Currently, the acceptable level stipulated by the US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) is 50ppb, but since January 2006, the acceptable value has been reduced to 10ppb. The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced that the lower limit of the interim value for the recommended acceptable arsenic concentration in drinking water is changed to below 10 ppb.
[0091] The arsenic-containing water is pretreated with ultraviolet light, so that the state of arsenic in the water changes from As 3+ to As 5+ , can improve the adsorption performance. Normally, clear water lets UV light through without absorbing it. But after adding coloring agent or color core source, ultraviolet light will be absorbed, provide energy for ions, and change the va...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com