Non-magnetic cemented carbide powder composed of nickel-tungsten and nickel-chromium binder phase and preparation
A technology of cemented carbide and hard phase powder, which is applied in the field of non-magnetic cemented carbide powder and coating preparation for thermal spraying, can solve the problems of large mold volume, difficult control of carbon content, easy cracking and deformation, etc. High bonding strength, high agglomeration density and good fluidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
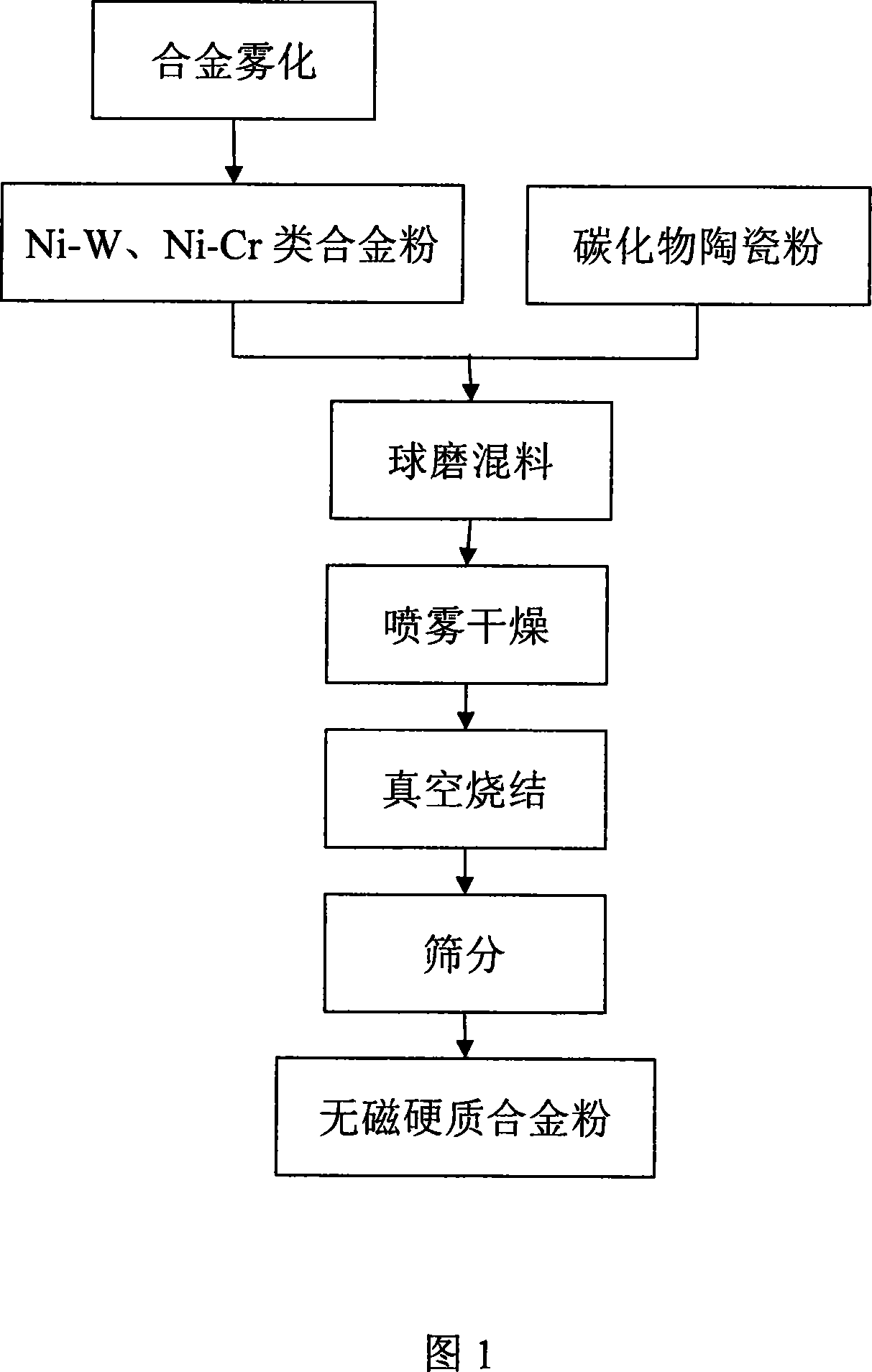
[0023] 1 Preparation of nickel-tungsten and nickel-chromium alloy binder phase powder
[0024] Metals or alloys such as nickel, tungsten, chromium and aluminum are placed in a smelting furnace according to the weight percentage of the required alloy powder (the vacuum atomization will be in the vacuum smelting furnace) to melt into an alloy solution and then atomized. Inert gas nitrogen or argon is used for vacuum atomization or ordinary gas atomization. The atomization gas pressure is generally controlled between 1.5-2.5MPa; the water atomization pressure is controlled at 20-40MPa. Non-magnetic nickel-tungsten and nickel-chromium alloy powders with a particle size of 104-2.5 μm can be produced by the above-mentioned smelting and atomization process. According to customer requirements, the non-magnetic alloy powder produced by the above-mentioned process can be sieved into different powders Particle size segment: such as 104-2.5 μm, 74-2.5 μm, or 38-2.5 μm.
[0025] 2 mix
...
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1 atomization
[0041] The nickel and tungsten metals are placed in a smelting furnace with a mass ratio of 4:1, smelted into an alloy solution, and then subjected to ordinary gas atomization. The inert gas for atomization is nitrogen, and the gas pressure is generally controlled between 1.5 and 2.5 MPa, and then the produced nickel-tungsten non-magnetic binder phase alloy powder is screened.
[0042] 2 mix
[0043] Nickel-tungsten alloy powder with a particle size of less than 30 μm (with a W content of 15 to 20 wt%) is selected as the binder phase powder, and tungsten carbide with a particle size of less than 2.7 μm is used as the hard phase powder. The mass of the two powders accounts for 12% and 88% respectively. Then carry out mixing ball milling. The ball milling medium is absolute ethanol, the ratio of balls, material and medium in the ball milling is 3:1:1, and the ball milling time is 48 hours.
[0044] 3 spray drying
[0045] The ball-milled powder is stir...
Embodiment 2
[0049] 1 atomization
[0050] The nickel and tungsten metals are placed in a melting furnace at a mass ratio of 4:1, smelted into an alloy solution, and then subjected to ordinary gas atomization. The inert gas for atomization is nitrogen, and the gas pressure is generally controlled between 1.5 and 2.5 MPa, and then the produced nickel-tungsten non-magnetic binder phase alloy powder is screened.
[0051] 2 mix
[0052]Nickel-tungsten alloy powder with a particle size of less than 30 μm (with a W content of 15 to 20 wt%) is selected as the binder phase powder, and tungsten carbide with a particle size of less than 2.7 μm is used as the hard phase powder. The mass of the two powders accounts for 20% and 80% respectively. Then carry out mixing ball milling. The ball milling medium is absolute ethanol, the ratio of balls, material and medium in the ball milling is 3:1:1, and the ball milling time is 48 hours.
[0053] 3 spray drying
[0054] The ball-milled powder is stirred ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Graininess | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Graininess | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com