Preparation of organic-inorganic composite microballoons
An inorganic composite microsphere, organic technology, applied in the preparation of microspheres, microcapsule preparations, etc., can solve the problems of low mechanical strength, time-consuming, low embedding rate of inorganic particles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
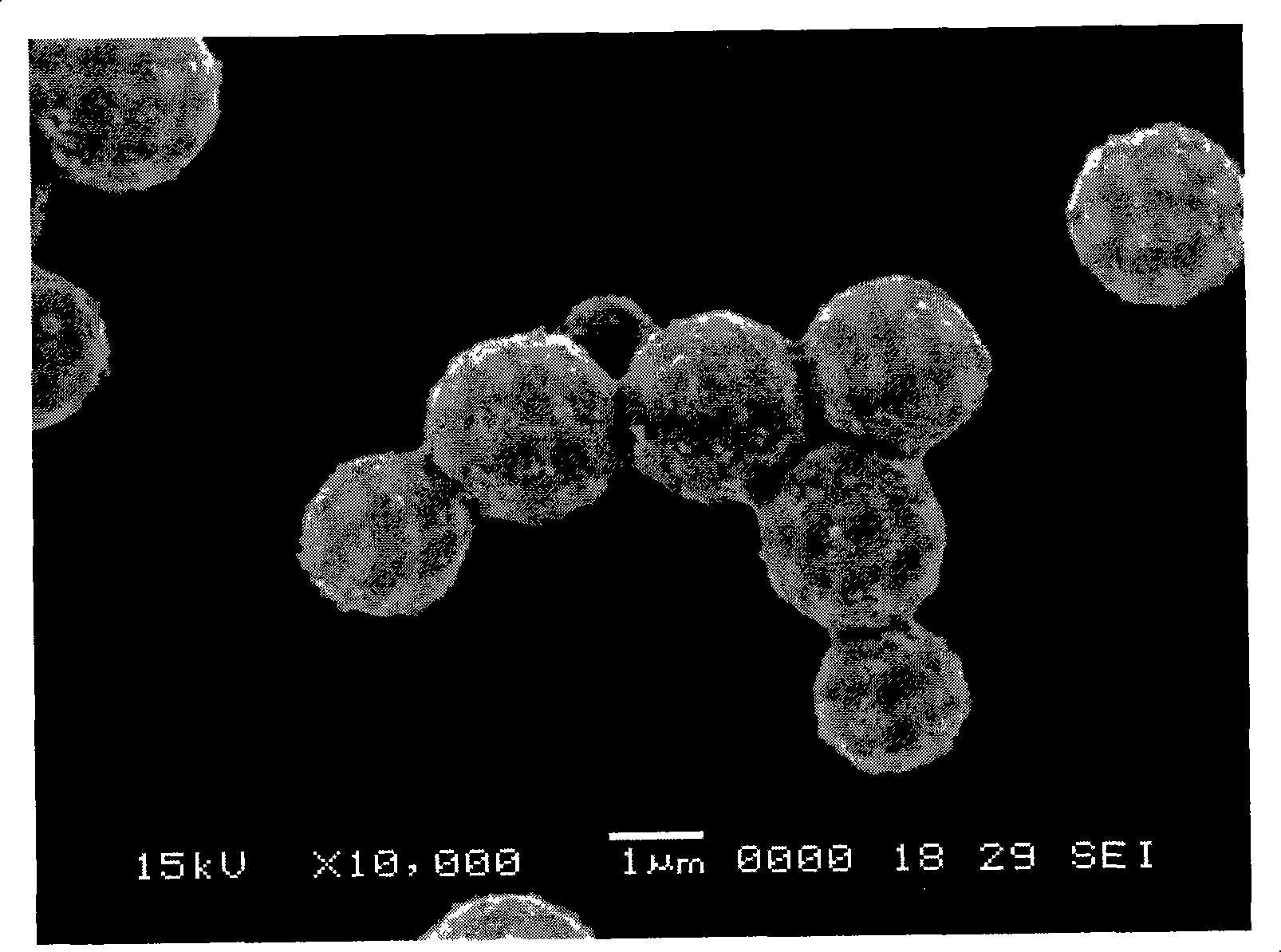
[0033] Polystyrene, Nylon 6 and TiO with a particle size of 30nm 2 After weighing according to the weight ratio of 80 / 20 / 10, it was added to a Haake rheometer for blending. The blending temperature was 240° C., the rotation speed was 100 rpm, and the time was 10 minutes. The resulting blend was heat-treated at 240°C for 10 minutes and then dissolved in toluene. After 2 hours, it was filtered with an acid-proof funnel under reduced pressure, washed, purified, and TiO was separated. 2 / Nylon 6 composite microspheres, the diameter of the obtained microspheres is about 2 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Polystyrene, hexamethylene adipamide prepolymer and Fe with a particle size of 20nm 3 o 4 After weighing according to the weight ratio of 60 / 40 / 15, it was added to a Haake rheometer for blending. The blending temperature was 240° C., the rotation speed was 100 rpm, and the time was 10 minutes. The resulting blend was heat-treated at 240°C for 10 minutes and then dissolved in toluene. After 2 hours, it was filtered with an acid-resistant funnel under reduced pressure, washed, purified, and separated to obtain nano-Fe 3 o 4 / Nylon 66 composite microspheres, the diameter of the obtained microspheres is 5-10 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0037] After weighing polystyrene, nylon 6 and carbon black with a particle size of 23nm in a weight ratio of 80 / 20 / 5, first add polystyrene and carbon black to a Haake rheometer for blending, and the blending temperature is 240°C , the rotation speed was 100 rpm, and the time was 5 minutes, and then nylon 6 was added to the Haake rheometer and blended for 5 minutes under the same conditions. Heat the obtained blend at 240°C for 10 minutes, put it into toluene and dissolve it for 2 hours, then use an acid-resistant funnel to filter it under reduced pressure, wash and purify, and separate carbon black / nylon 6 composite microspheres, the diameter of which is 5 μm about.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com