Method for vaccination soybean with phytophthora sojae
A technology for Phytophthora sojae and soybeans, which is applied in horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problems of high risk, large space occupation, long time required, etc. The effect of small footprint and short experimental period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Embodiment 1, the determination of experimental procedure of zoospore root inoculation method and inoculation amount
[0015] In this example, the No. 1 physiological race of Phytophthora sojae (Xu Xiuhong, Lu Huiying, Qu Juanjuan, Yang Qingkai. Identification and toxicity analysis of physiological race of Phytophthora sojae root rot, Journal of Plant Protection, 2003, 30(2): 125 -128) is the experimental strain, and Suinong 10 (disease resistant variety) and sloan (susceptible variety) are used as experimental soybean varieties.
[0016] The specific operations are as follows:
[0017] (1) Preparation of soybean seedlings
[0018] Moisturize the sloan soybean seeds for 2-3 days until the radicle length is about 2cm, select the seedlings with the same radicle length, and divide them into ampoules (volume 10ml) containing the same amount of sterilized tap water. The shaft 1cm and the roots are all immersed in sterile water, and the cotyledons are left outside the bottl...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2. Application of the zoospore root inoculation method in the screening of antibiotics
[0034] The bacterial strains used in this example are as shown in Table 2 (Li Ying, Yang Mingxiu, Wen Jingzhi, Phytophthora soya bean 1st generation single zoospore strain population variation, Chinese Journal of Oil Crops, 2007(4): 460- 465). The soybean varieties used in this example are 9 internationally used Phytophthora sojae identification hosts and 11 commonly used varieties in production. The variety catalog is shown in Table 3.
[0035] Table 2. Phytophthora sojae physiological race and its corresponding toxicity formula (Li Ying, 2007)
[0036] serial number
Toxicity formula
physiological race
serial number
Toxicity formula
physiological race
1
2
3
1a, 7
1a
3a, 1b, 7
3
5
6
7
3a, 7
7
1b, 7
15
1
2
4
1a, 1c, 7
...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3. Screening of Antibiotics with Zoospore Root Inoculation Method
[0058] The 32 soybean varieties used in this example are commonly used varieties in production, and the other physiological races except No. 1 physiological race in Table 2 are used for testing respectively.
[0059] Infect the soybean seedlings of 32 varieties shown in Table 4 with the other physiological races except No. 1 physiological race in Table 2, wherein, the experimental method of each strain infecting the soybean seedlings of each variety, except the inoculation concentration Except for 250 spores / 1 soybean seedling, the other methods are the same as those described in Example 1.
[0060] The experiment was repeated three times, and the results are shown in Table 4.
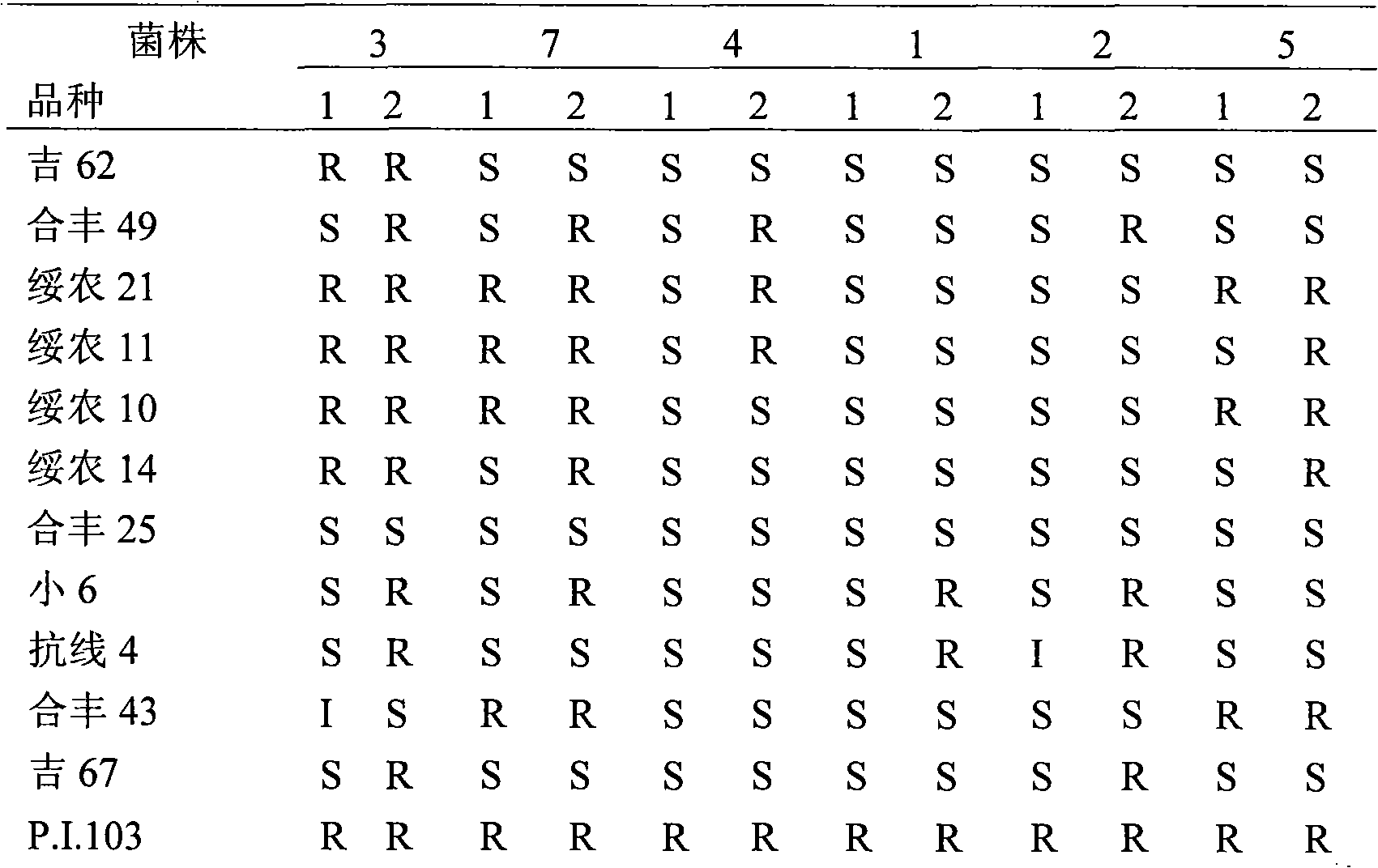
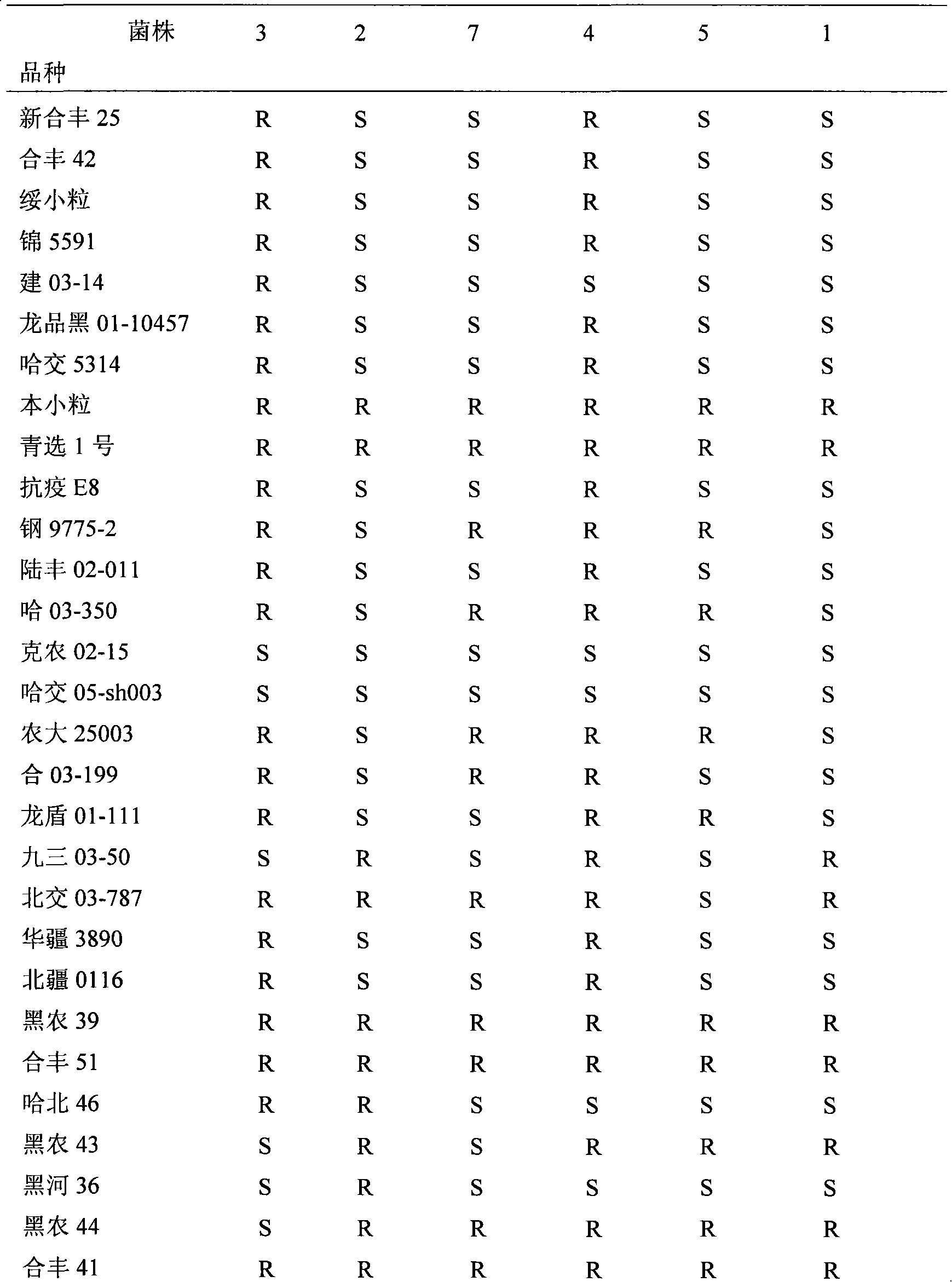
[0061] Table 4. Identification results of 32 soybean variety resources against Phytophthora root rot
[0062]
[0063]
[0064] Note: S is susceptible; R is resistant
[0065] The experimental results showed tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com