Method of producing active material for lithium secondary battery, method of producing electrode for lithium secondary battery, method of producing lithium secondary battery, and method of monitoring
A technology for lithium secondary batteries and active materials, which is applied in the manufacture and quality supervision of active materials, the manufacture of lithium secondary batteries using the same, and the fields of electrodes for lithium secondary batteries, and can solve the problems of low sensitivity and precision, low battery capacity, etc. Reduction, uneven amount of impurities, etc., to achieve the effect of high quality and high energy density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
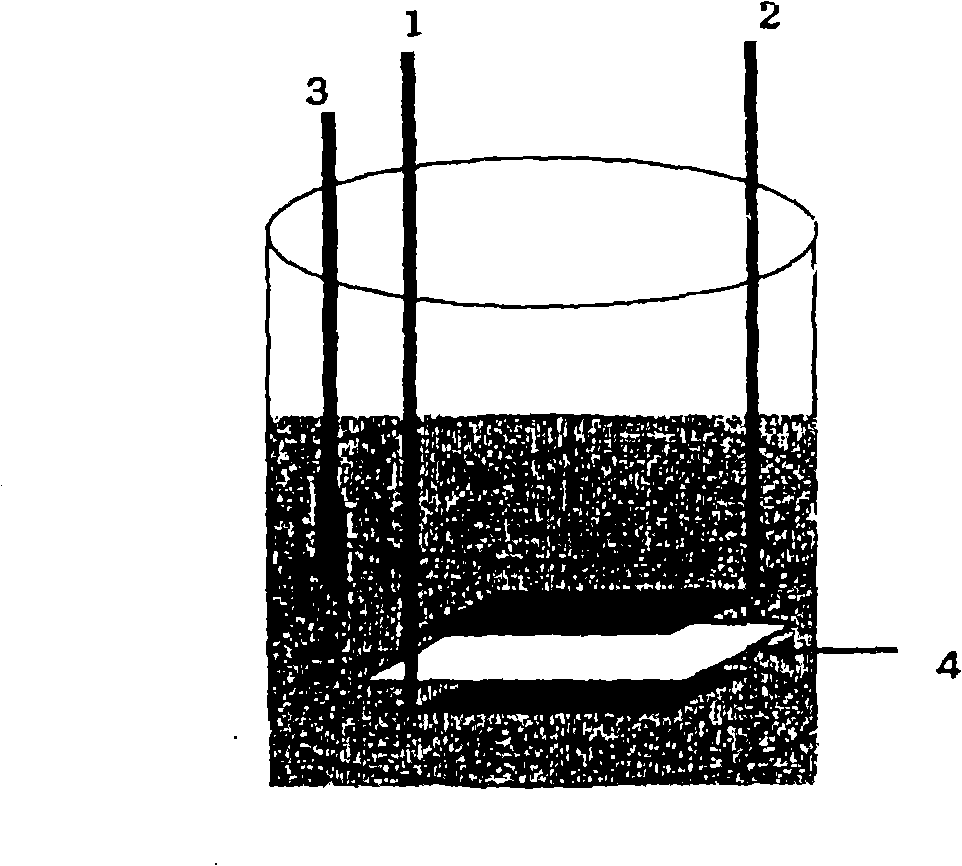
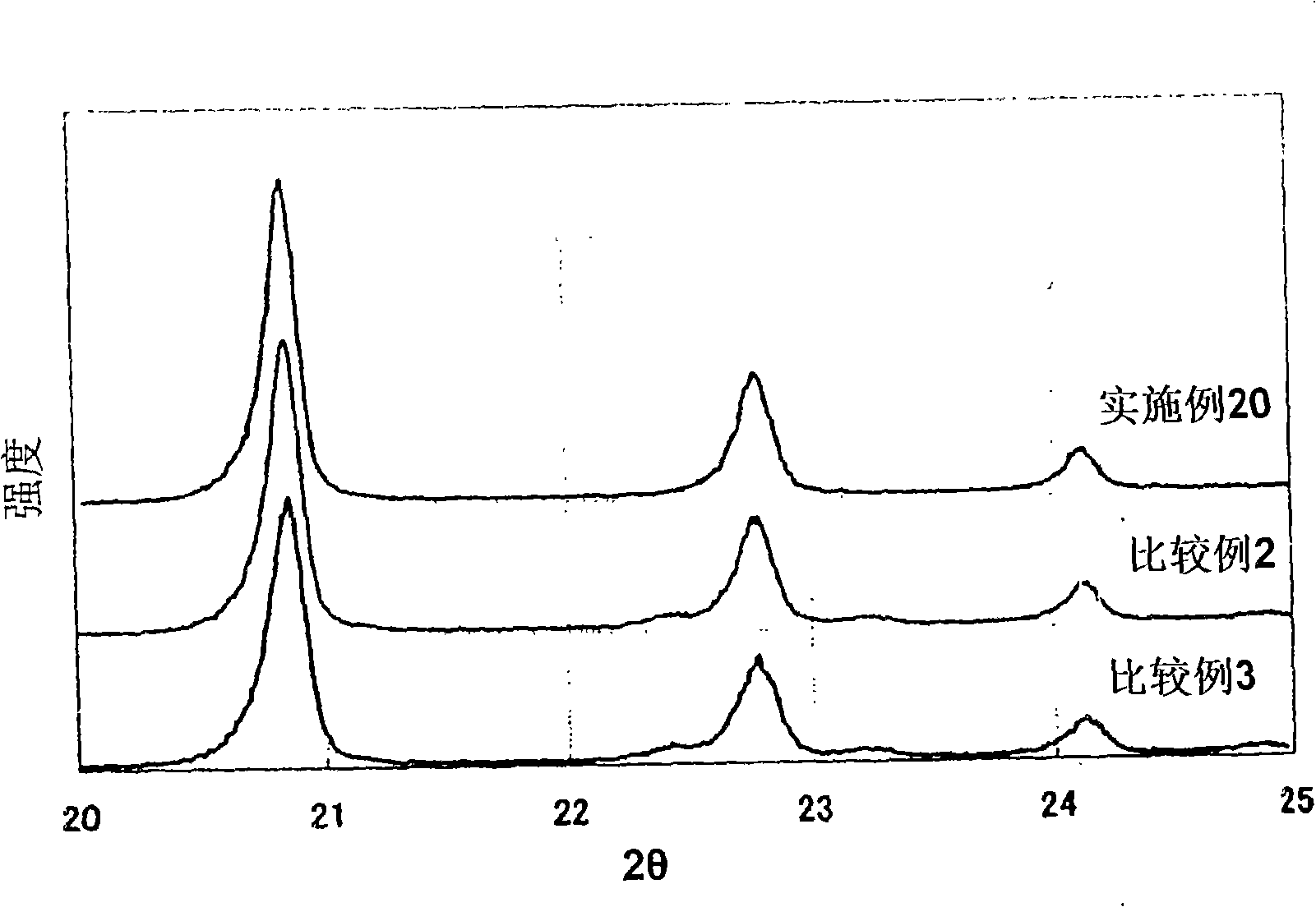
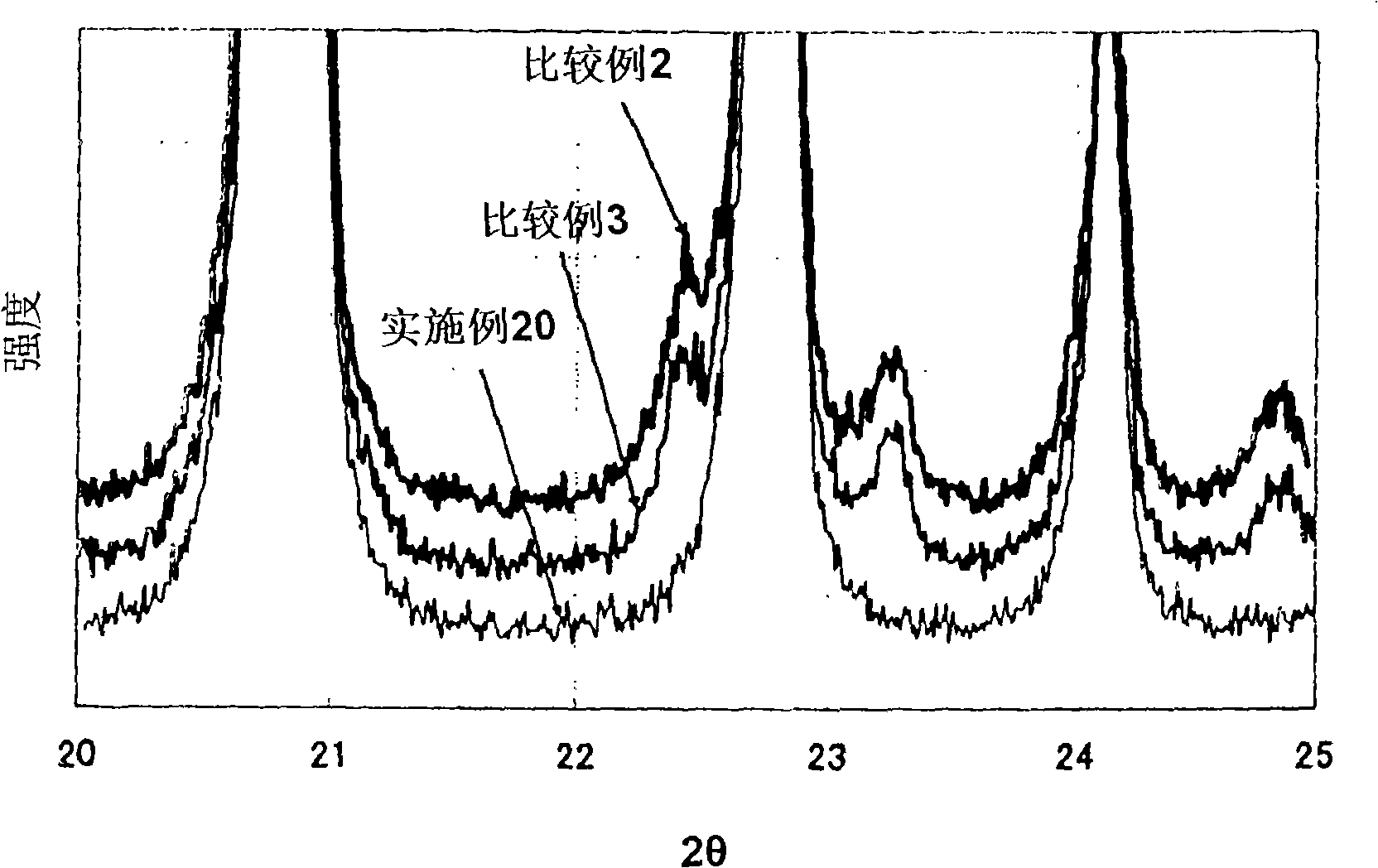
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045]
[0046] A phthalate pH standard solution (pH 4.01) manufactured by Kishida Chemical was used as a cleaning solution. The pH of the cleaning solution at this time was 4.0.
[0047]
[0048] Weigh out Li 3 PO 4 LiFePO 4 100 mg of the sample (sample A) was added with 10 mL of cleaning solution, placed in an ultrasonic pretreatment device, and cleaned by ultrasonic treatment for 1 hour.
[0049]
[0050] In order to remove undissolved samples by washing, the washing liquid after washing was filtered, and the amount of P dissolved in the washing liquid was quantified by inductively coupled high-frequency plasma emission spectrometry (ICP emission spectrometry).
[0051] The dissolved amount was calculated by the following calculation formula.
[0052] P dissolved amount (wt%) = (P dissolved in the cleaning solution (mg) × 100) / sample amount (mg)
[0053] In addition, in order to determine the pH of the cleaning solution after cleaning, the pH of the cleaning so...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Acetic acid and sodium acetate were mixed at a weight ratio of 1:1, pure water was added thereto, and a 1.0 wt% aqueous solution of the mixture was prepared as a cleaning solution. The pH of the cleaning solution at this time was 4.5. Except for using this cleaning solution, the sample was washed in the same manner as in Example 1, the amount of P dissolved in the cleaning solution was quantified, and the pH of the cleaning solution was measured.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Acetic acid and sodium acetate were mixed at a weight ratio of 1:10, pure water was added thereto, and a 1.0 wt% aqueous solution of the mixture was prepared as a cleaning solution. The pH of the cleaning solution at this time was 5.6. Except for using this cleaning solution, the sample was washed in the same manner as in Example 1, the amount of P dissolved in the cleaning solution was quantified, and the pH of the cleaning solution was measured.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com