Thin stator, axialclearance brushless vibrating motor with the stator
A type of stator and stator technology, applied in the field of axial gap type brushless vibration motor, can solve the problems that the deflection angle cannot be increased, the starting torque is reduced, the thickness of the hollow armature winding is reduced, and the torque is reduced, so as to improve reliability , strong impact resistance, reliable insulation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
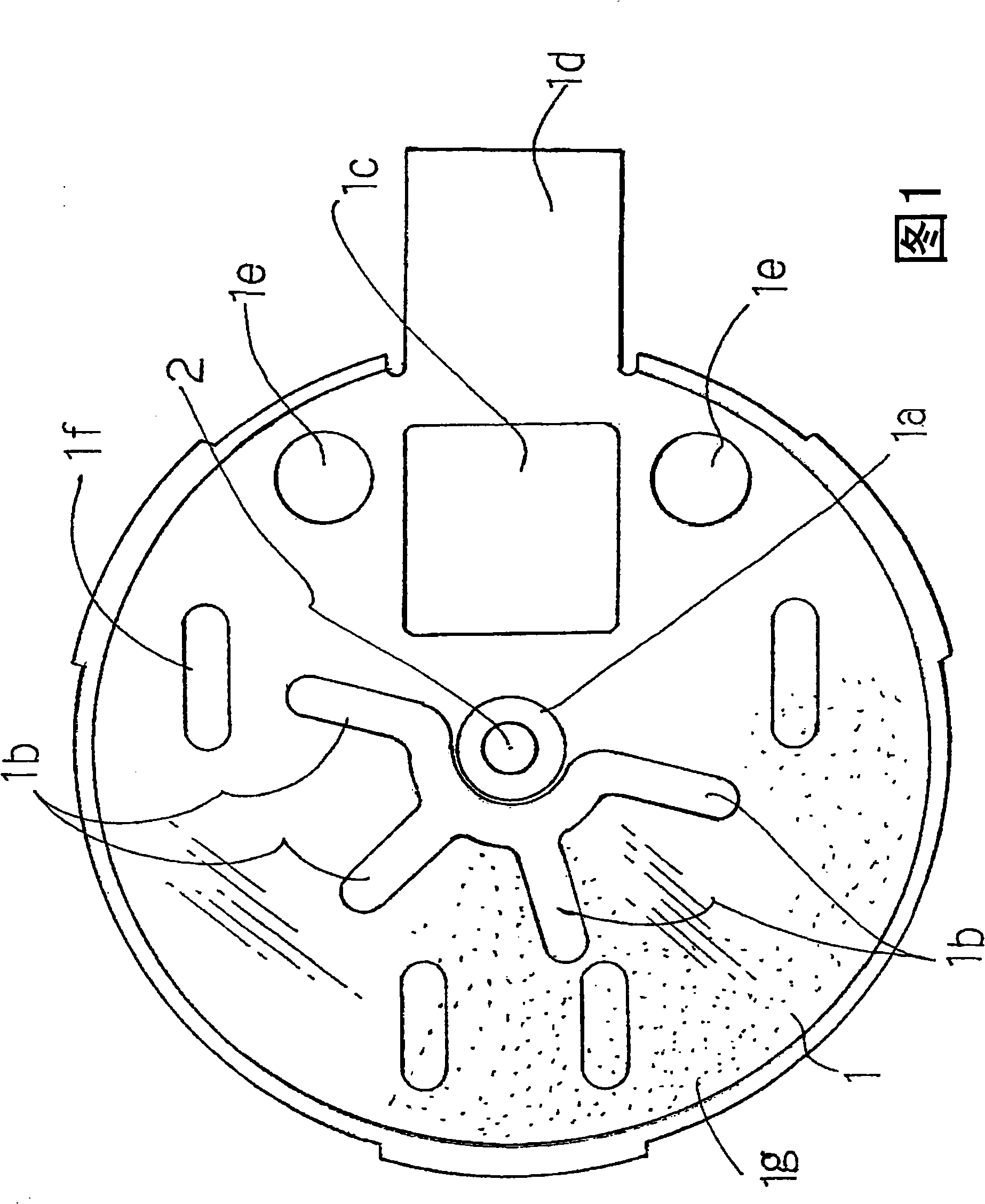
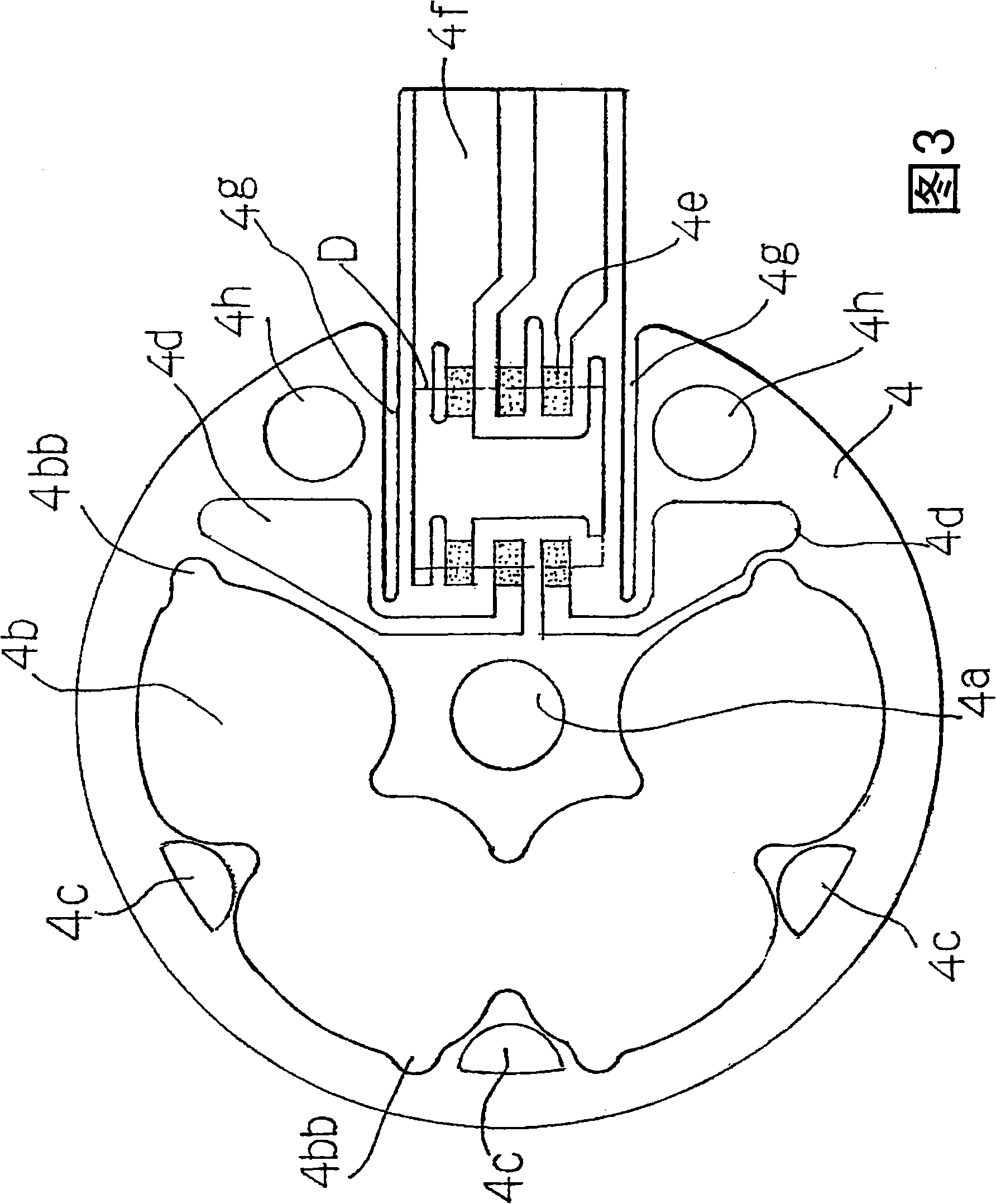
[0035] The bracket 1 constituting the stator according to the present embodiment shown in FIG. 1 is formed of a nonmagnetic or weakly magnetic stainless steel thin plate with a thickness of about 0.2 mm. Then, the proximal end of the shaft 2 is fixed to the shaft support portion 1a at the center of the bracket 1 from the outside (inside the drawing of FIG. 1 ) by laser welding L1 (see FIG. 5 described later). And, on the outside of the diameter direction of the shaft 2 of the bracket 1, there are four through holes 1b that are connected on one side of the center and expand into a V shape in the diameter direction. The magnetic pole opening angles (60°) of the axial gap magnets 10 (see FIG. 5 ) of the combined rotor described above are equal. In addition, the bracket 1 can also be a conductive or non-conductive material.
[0036] In order to start the rotor reliably even if either the center of the magnetic pole or the neutral region of the magnetic pole of the axial gap type ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0051] This embodiment is an example of an axial gap type brushless vibration motor using the stator S according to the first embodiment.
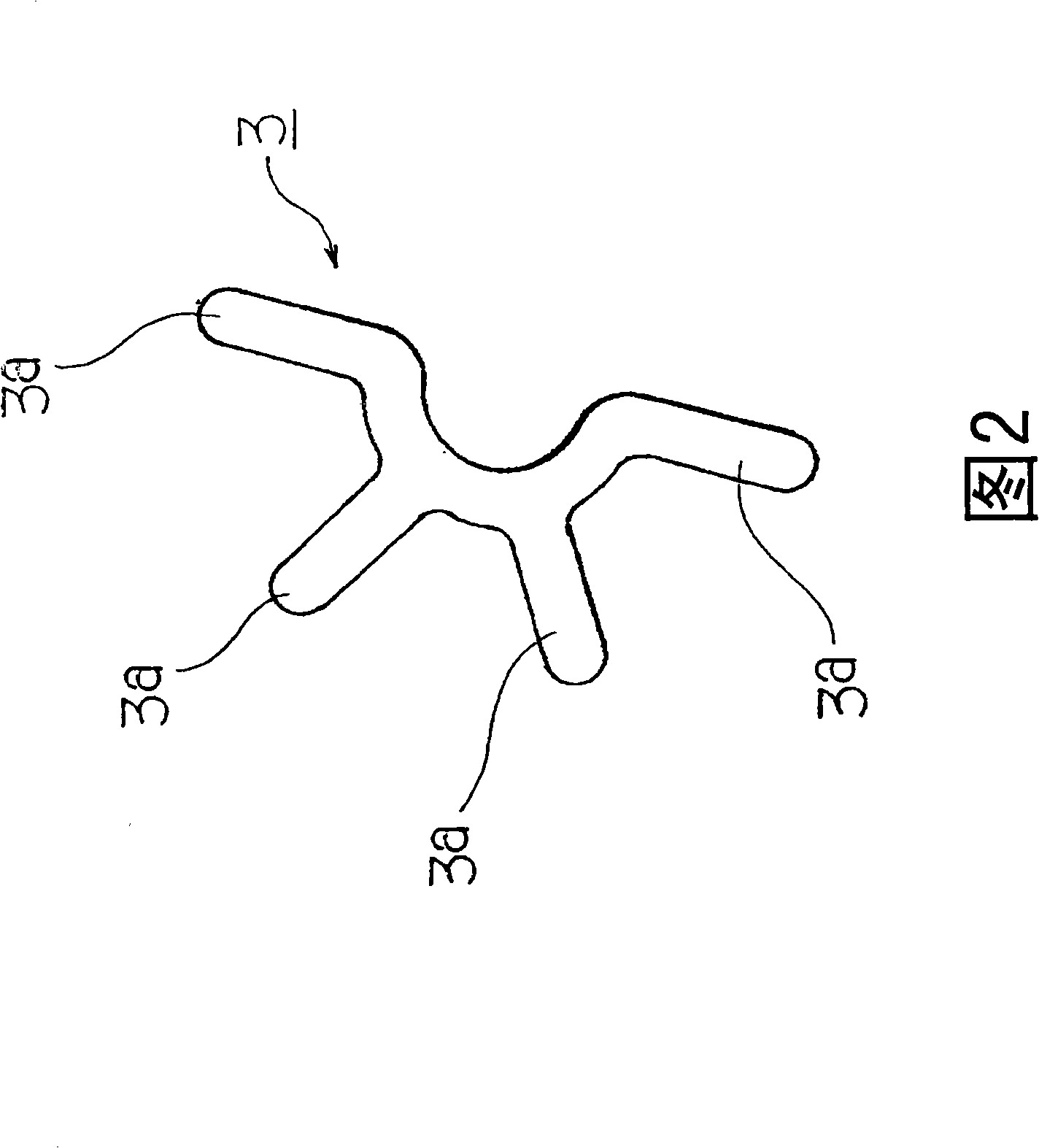
[0052] The eccentric rotor R combined to the stator S is shown in Fig. 5 . That is, the rotor case 7 is formed with a magnetic stainless steel flat portion 7a with a thickness of about 0.2 mm, an outer peripheral side hanging portion 7b, and an inner diameter side hanging portion 7c, and an arc-shaped tungsten eccentric weight 8 is fixed by soldering or laser welding. The sintered oil-impregnated bearing 9 is fixed to the radially inner hanging portion 7c on the outer peripheral side hanging portion 7b by caulking, laser welding, soldering, or the like. The axial gap magnet 10 magnetized into six poles is fixed inside the flat portion 7a by bonding or the like.
[0053] Furthermore, as a method of fixing the eccentric weight 8, besides the above-mentioned method, a method such as extending the outer periphery of the rotor case 7, riveting...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com