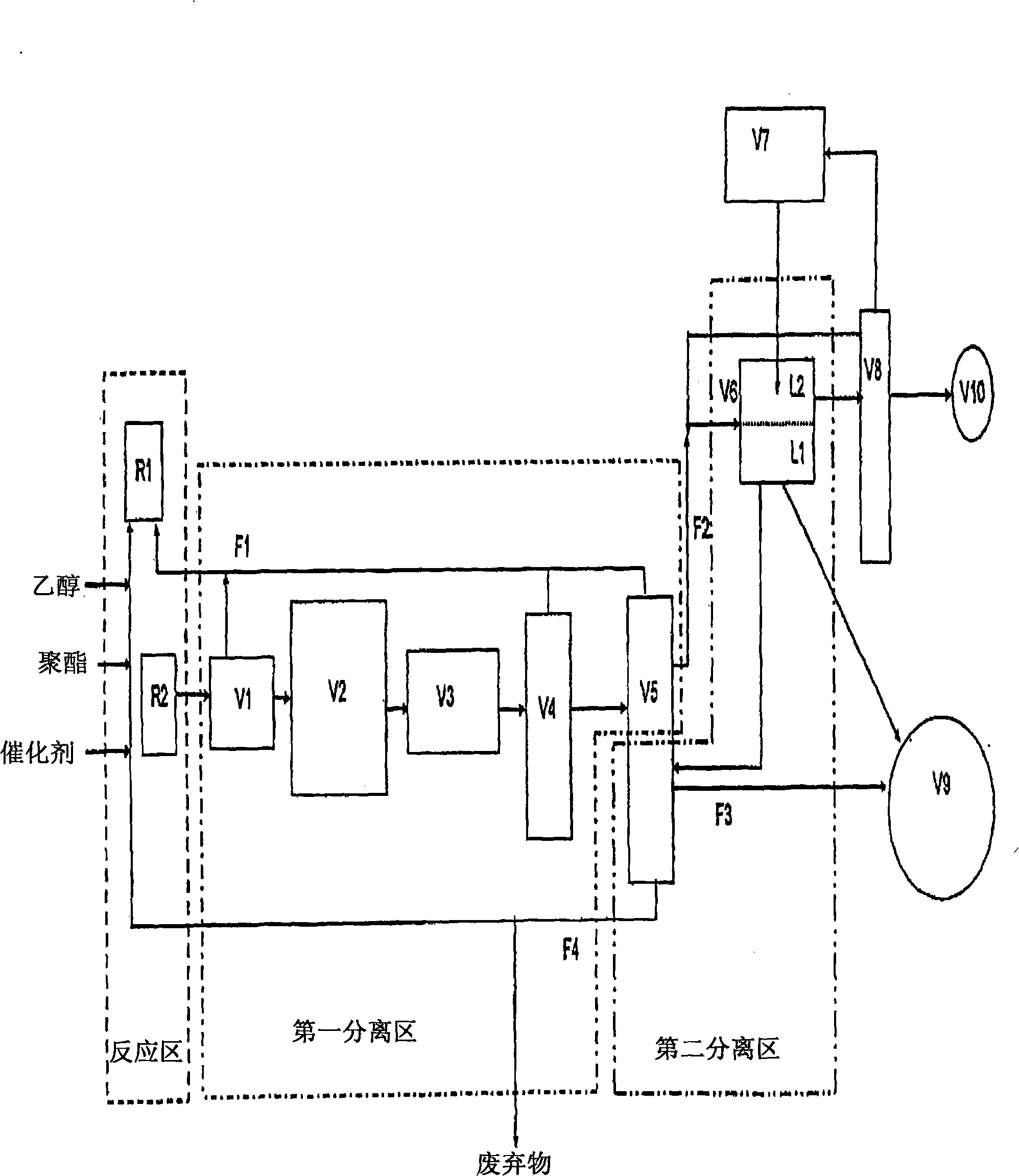
Ethanolysis of PET to form DET and oxidation thereof
A technology for ethanol and ethylene glycol, used in waste polymers and optional other polymers, raw materials for the preparation of aromatic carboxylic acids, other polymers of aryl ester monomers, preparation of acetic acid, preparation of terephthalic acid, preparation of Aromatic carboxylic acids, in the field of preparation of acetic acid and aromatic carboxylic acids, can solve problems such as inapplicability of DMT
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
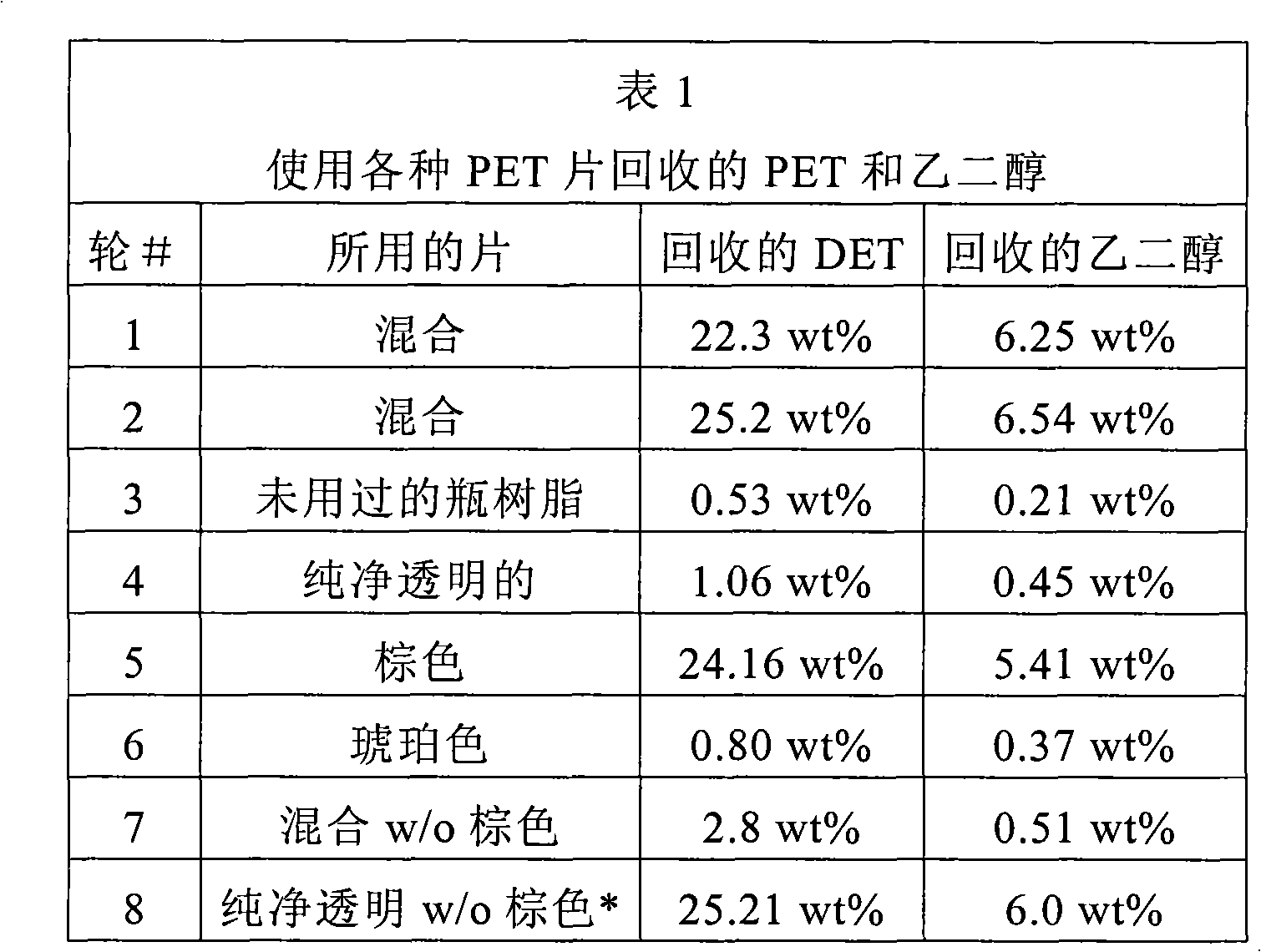
[0130] 300 g of PET flakes of the type shown in Table 1 were reacted with ethanol in an ethanol:PET weight ratio of 3:1 according to the above procedure. The water content of ethanol is 0.0734 wt%. No extraneous catalysts were added. Both mixed flakes and neat clear flakes were obtained through NAPCOR (National Association for PET Container Resource). The mixed flakes contained about 55 wt% brown flakes, with the remainder mainly green, amber and clear PET flakes. Virgin bottle resin was obtained from Wellman Inc. under product number 61802. The theoretical maximum percentages of DET and ethylene glycol in the reaction mixture are 28.86 wt% and 8.06 wt%, respectively.
[0131]
[0132] * 45 wt% pure transparent flakes and 55% brown flakes
[0133] The results obtained for rounds 1 and 2 in Table 1 demonstrate that even without adding any catalyst, the hybrid flakes still contain catalytic impurities that catalyze the ethanol decomposition reaction. Runs 3 to 8 reveale...
Embodiment 2
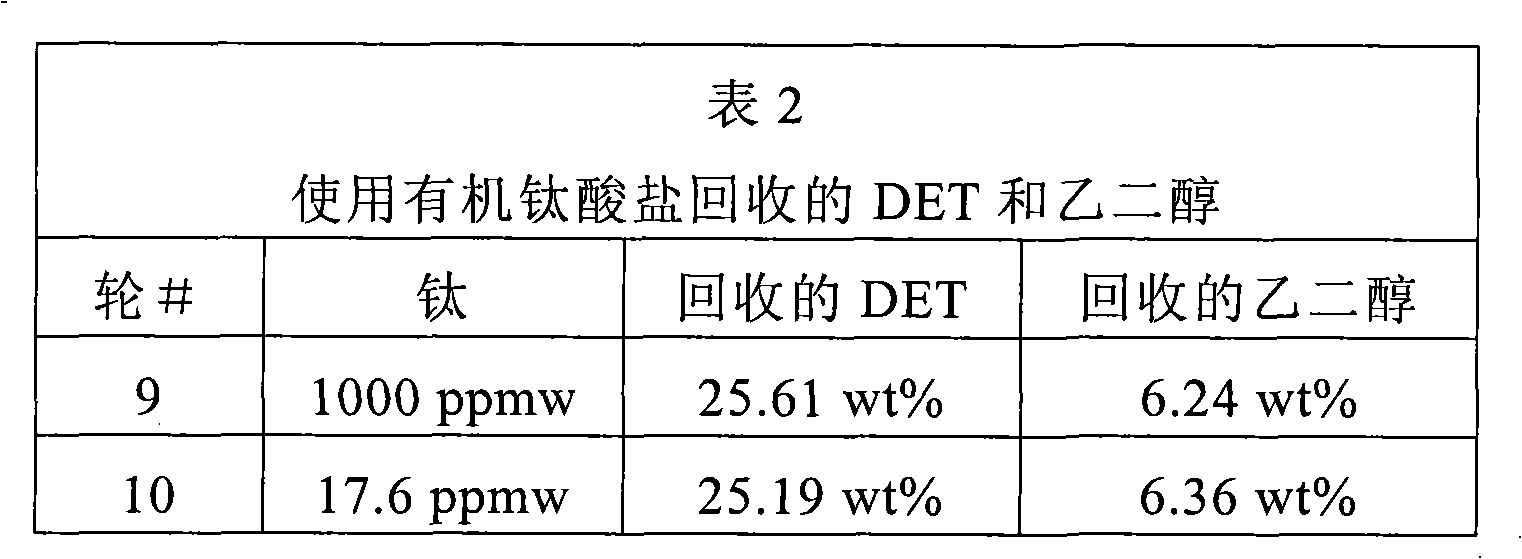
[0135] In the presence of titanium in the form of organotitanate, 300 g of clear transparent PET flakes were reacted with 900 g of ethanol according to the above procedure. The organic titanate TYZOR TPT from DuPont was used as titanium source. The water concentration of ethanol was 0.0734 wt%. The organic titanate was added in an amount equal to 1000 ppmw (based on PET) titanium. The results are reflected in Run 9 in Table 2 below. Run round 10 using 200 g of virgin clear PET flakes and 600 g of ethanol according to the above procedure. The amount of organic titanate added was equal to 17.6 ppmw titanium (based on PET). The results are reflected in Table 2 below.
[0136]
[0137] Table 2 illustrates the efficiency of organotitanates in catalyzing the ethanol decomposition of PET. Even a very small amount used in the 10th round is effective.
Embodiment 3
[0139] Ethanololysis was run according to the above procedure, without catalyst addition, and using mixed PET flakes as described in Example 1, with a water content of 0.0734 wt% ethanol. The ethanol:PET ratio was 3:1 and no extraneous catalyst was added. After distillation of the reaction product as described above, the distillation bottoms were used as a catalyst for further ethanol decomposition reactions. An additional ethanolysis reaction was run using 600 g of ethanol with a water content of 0.0734 wt%, 162 g of clear clear PET flakes and 38 g of distillation bottoms. No additional catalyst was used. The results are shown in Table 3 below.
[0140]
[0141] Table 3 shows that the catalytic impurities present in the mixing sheet feed remain active after distillation treatment and that a portion of the distillation bottoms can be recycled to effectively catalyze the ethanololysis of PET. The comparison between run 4 in Table 1 and run 11 in Table 3 especially highlig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com