Electrochemical device
An electrochemical and electrode technology, applied in the field of electrochemical devices, can solve the problems of high price and limited lithium resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
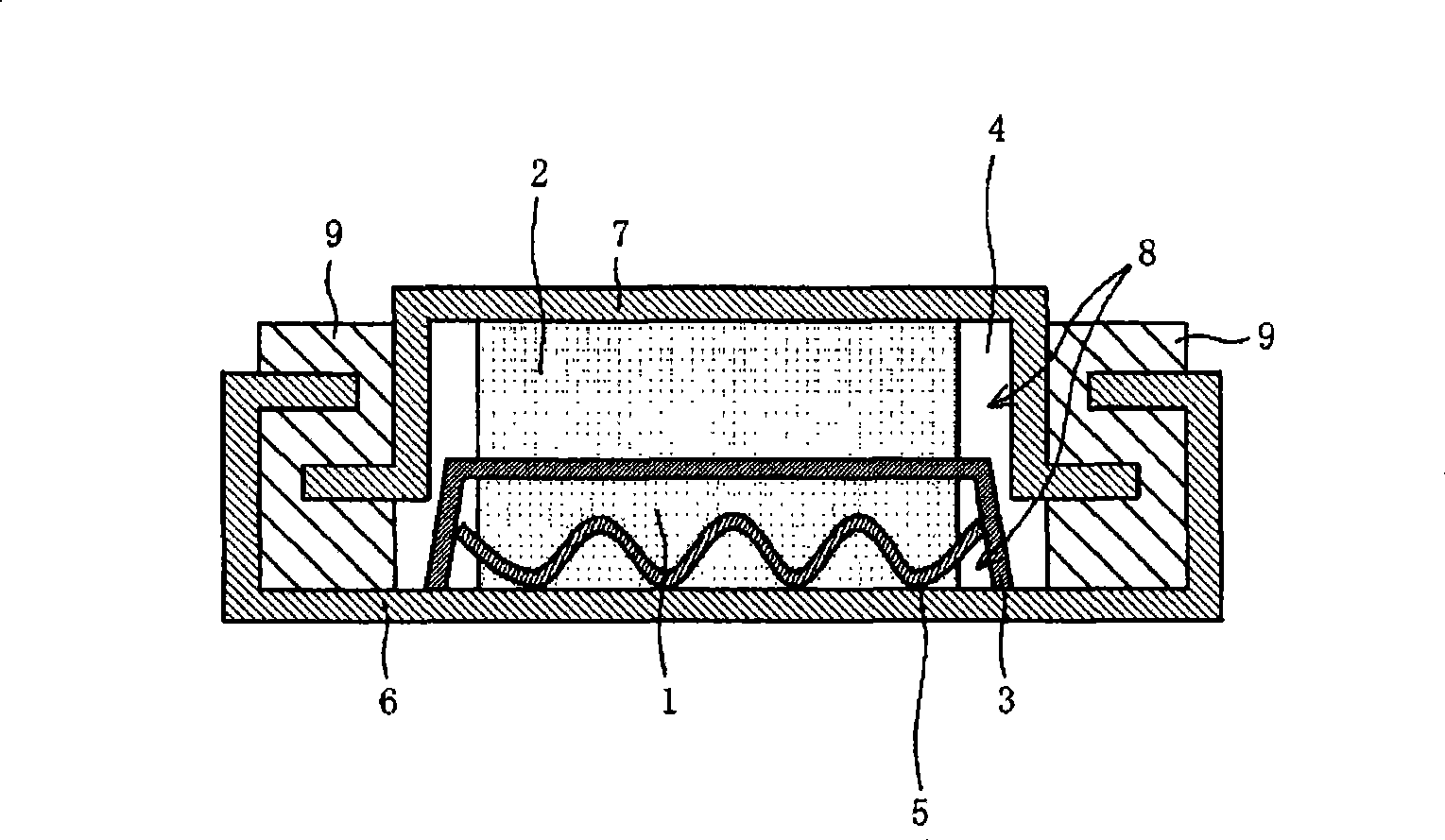
[0045] Using metal magnesium as the negative electrode active material, cobalt (II) chloride (CoCl 2 ) as the positive active material to manufacture figure 1 A coin-type magnesium secondary battery 10 is shown.
[0046]
[0047] First, a mixture is prepared as follows: cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl 2 , Sigma-AldrichCo. product), to which small particle size graphite was added as a conductive carbon material, and they were thoroughly mixed. Graphite is a product of Timcal Japan Co., Ltd., with a trade name of "KS6", and has an average particle diameter of 6 μm. The mixture contains cobalt(II) chloride and KS6 in a weight ratio of 1:1. This mixture was pressed onto a positive electrode collector grid 5 made of stainless steel (SAS), thereby forming a sheet-like positive electrode 1 .
[0048] In this embodiment, the polymer binder is omitted in order to maximize the energy capacity per unit weight and unit volume of the positive electrode 1 . However, it is desirable to use...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Figure 4 The measured discharge curves of different magnesium secondary batteries 10 prepared using other chlorides as positive electrode active materials are shown. Figure 4 CoCl used in Example 1 is also shown 2 The measured discharge curves are used for comparison. The materials used in this embodiment are CuCl, CuCl 2 、NiCl 2 , FeCl 2 , FeCl 3 , CrCl 2 and MnCl 2 . The materials used in this example are all products of Sigma-Aldrich Co., and the battery was manufactured and measured in the same manner as in Example 1. Figure 4 It shows that a variety of chloride materials can be used as positive electrode active materials for magnesium secondary batteries, among which NiCl with large current capacity is preferred 2 、CoCl 2 , FeCl 2 , CrCl 2 and CuCl 2 .
[0060] Reference (J. Electrochem. Soc., 149, p. 627-634 (2002)) discloses a lithium ion secondary battery using cobalt(II) oxide (CoO) as a positive electrode active material. It is disclosed that...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com