Method for compensating common mode feedback circuit frequency of two-stage amplifier
A common-mode feedback and frequency compensation technology, applied in the direction of differential amplifiers, DC-coupled DC amplifiers, etc., can solve the problems of poor common-mode output level capability, gain reduction, and low-frequency gain reduction of common-mode feedback circuits, etc., to achieve large Effect of phase margin and stability improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
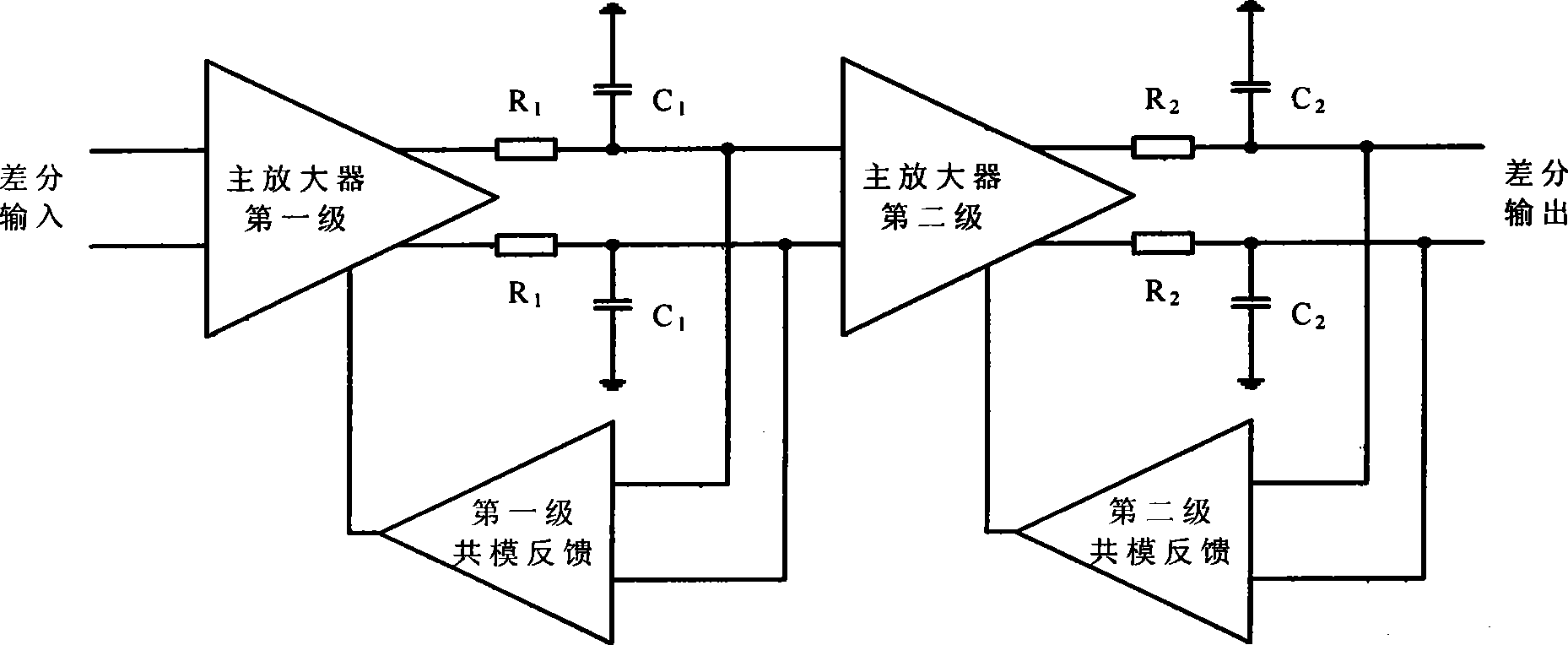
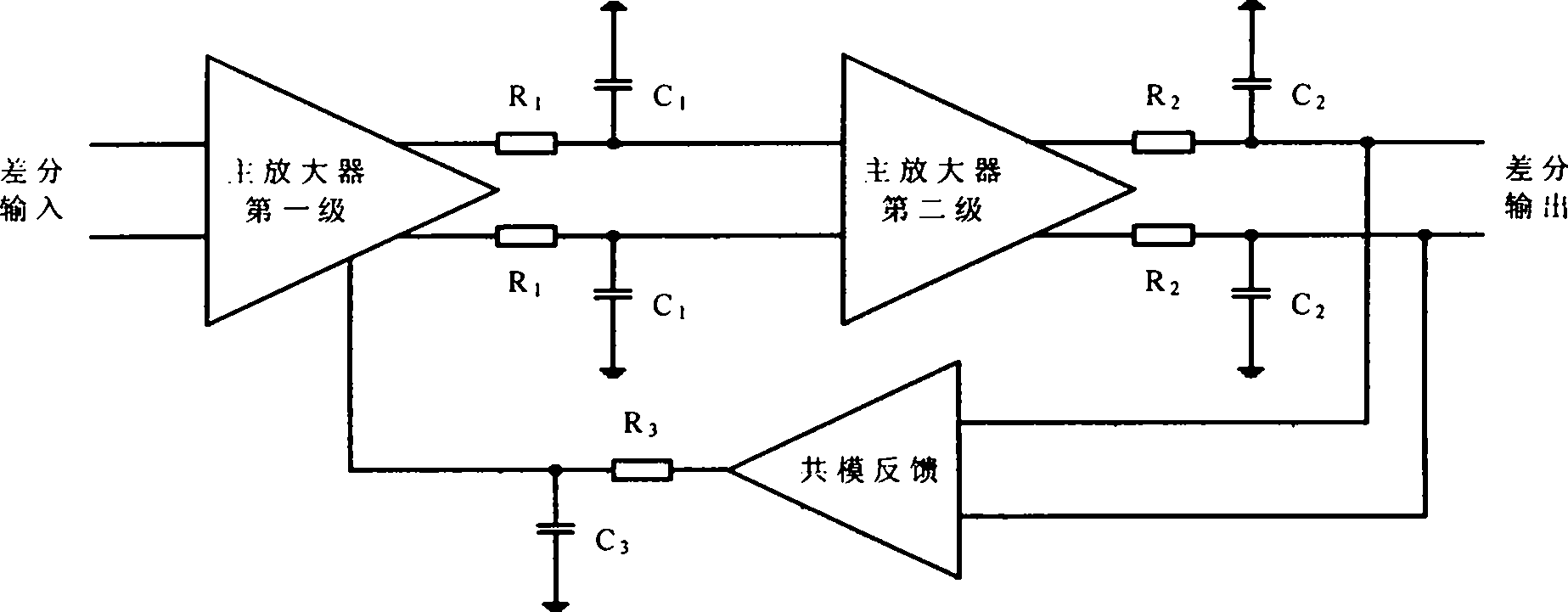
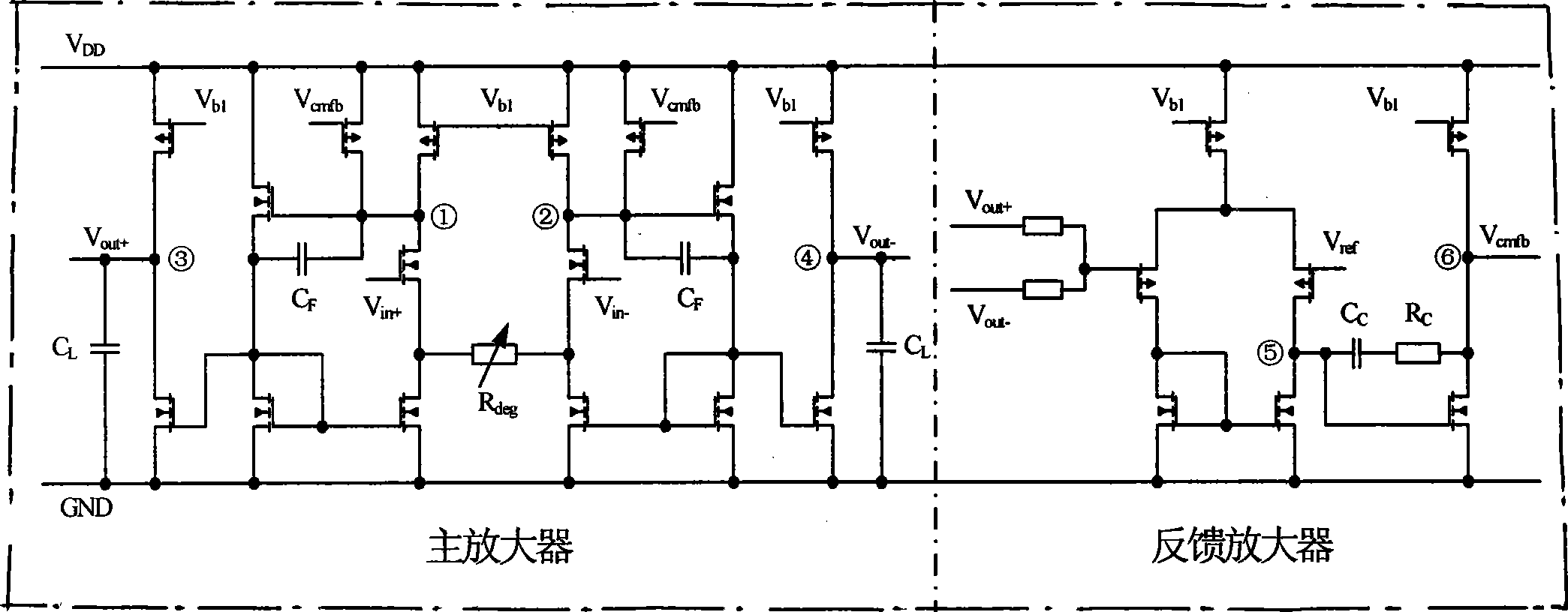
[0011] image 3 A schematic circuit of a two-stage amplifier with a common-mode feedback circuit is depicted. On the left is a two-stage amplifier structure, where V in+ and V in- is the differential input of the two-stage amplifier, V out+ and V out- is the differential output of the two-stage amplifier. The first stage of the two-stage amplifier uses a transconductance enhancement circuit to increase the equivalent transconductance of the input tube, and uses a source negative feedback resistor to reduce the distortion of the input tube transconductance. Nodes ① and ② are the outputs of the first stage amplifier. The second-stage amplifier adopts a common-source structure, and nodes ③ and ④ are the outputs of the second-stage amplifier. V cmfb It is the output control signal of the feedback amplifier in the common-mode feedback circuit. This signal is added to the gate of the MOS transistor of the two-stage amplifier, and at the same time realizes the control of the co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com