Patents
Literature
38 results about "Left half plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
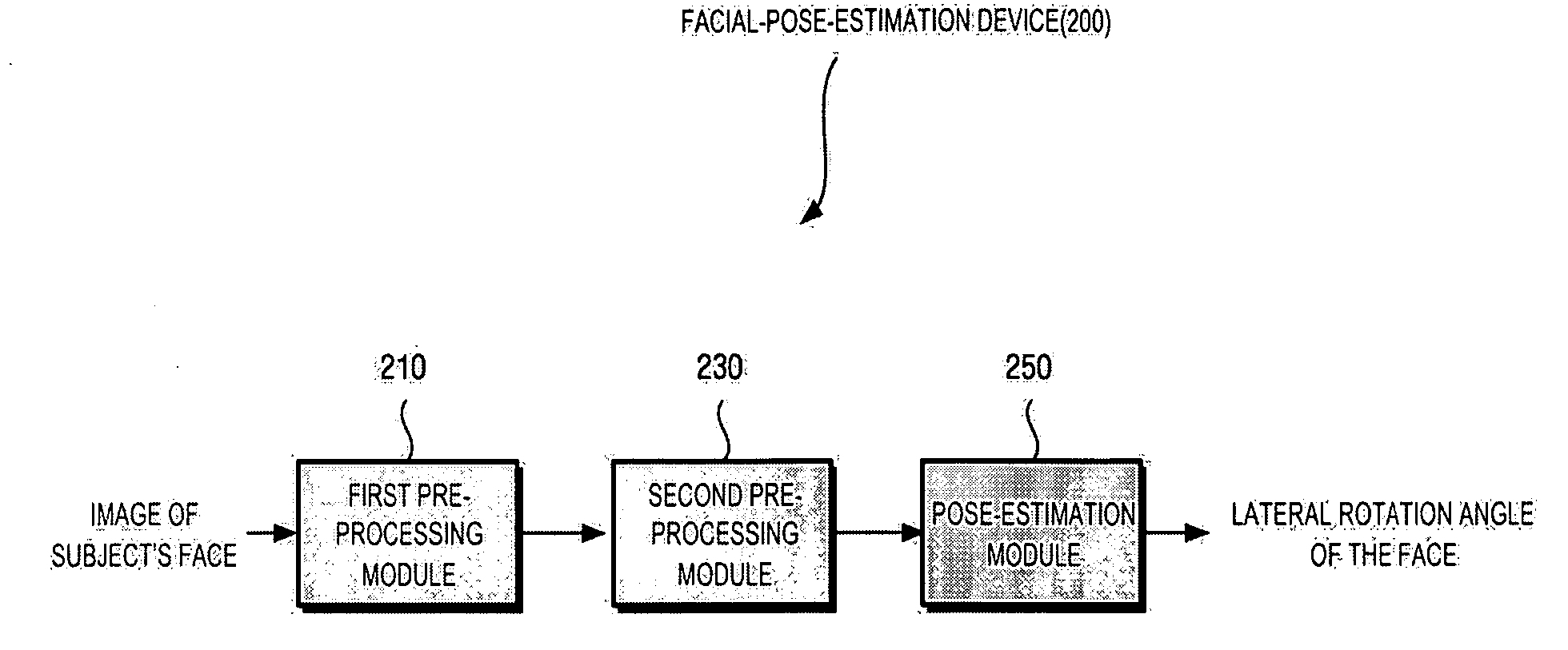
Apparatus and method for estimating a facial pose and a face recognition system using the method
An apparatus for estimating a facial pose. The apparatus includes a pre-processing module that provides feature points of a subject's face of a received image, and a pose-estimation module that computes sizes of a left half plane and a right half plane of the face from the provided feature points, and a lateral rotation angle of the face from the computed sizes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
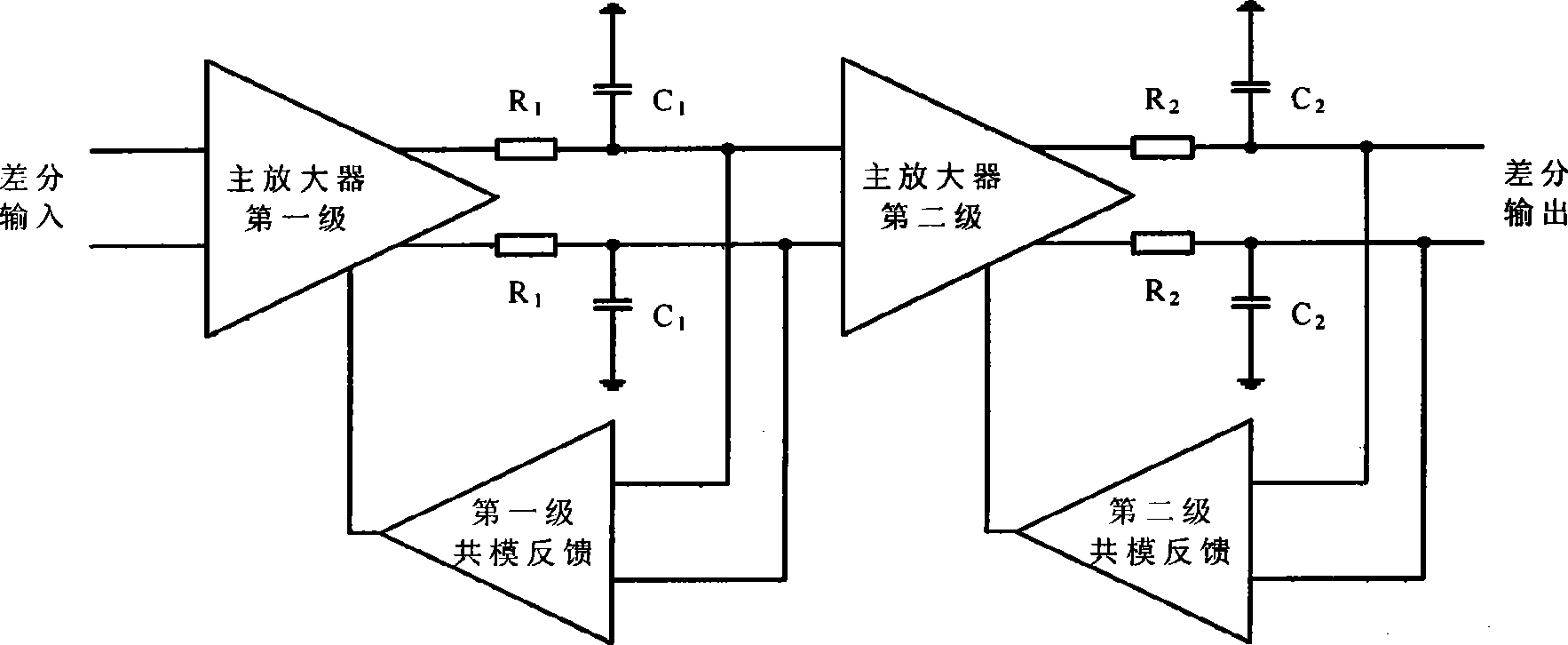
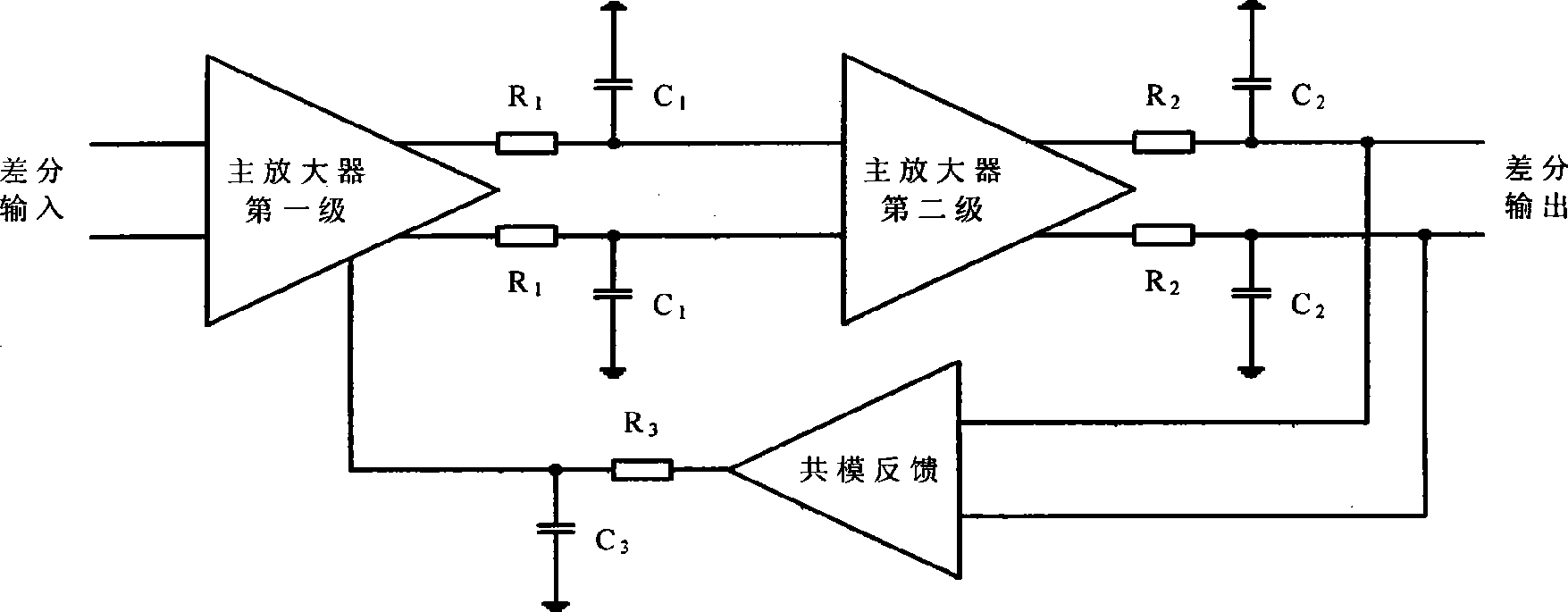
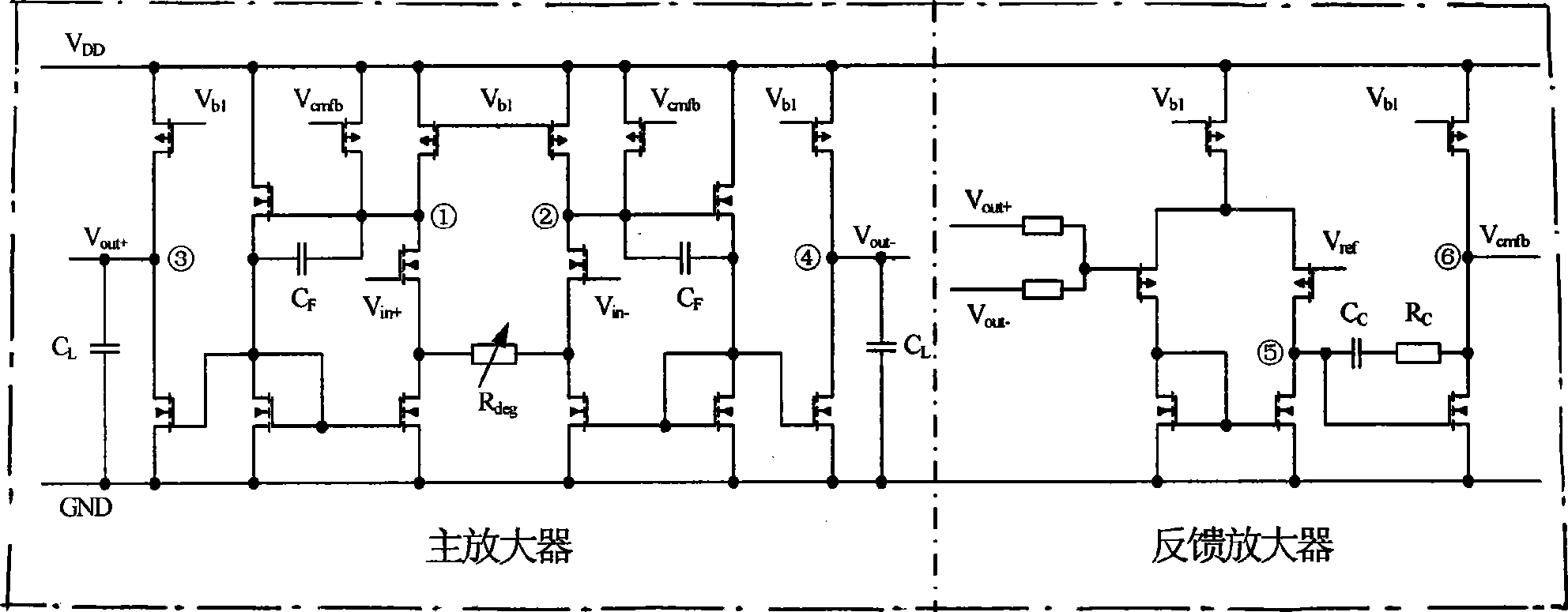
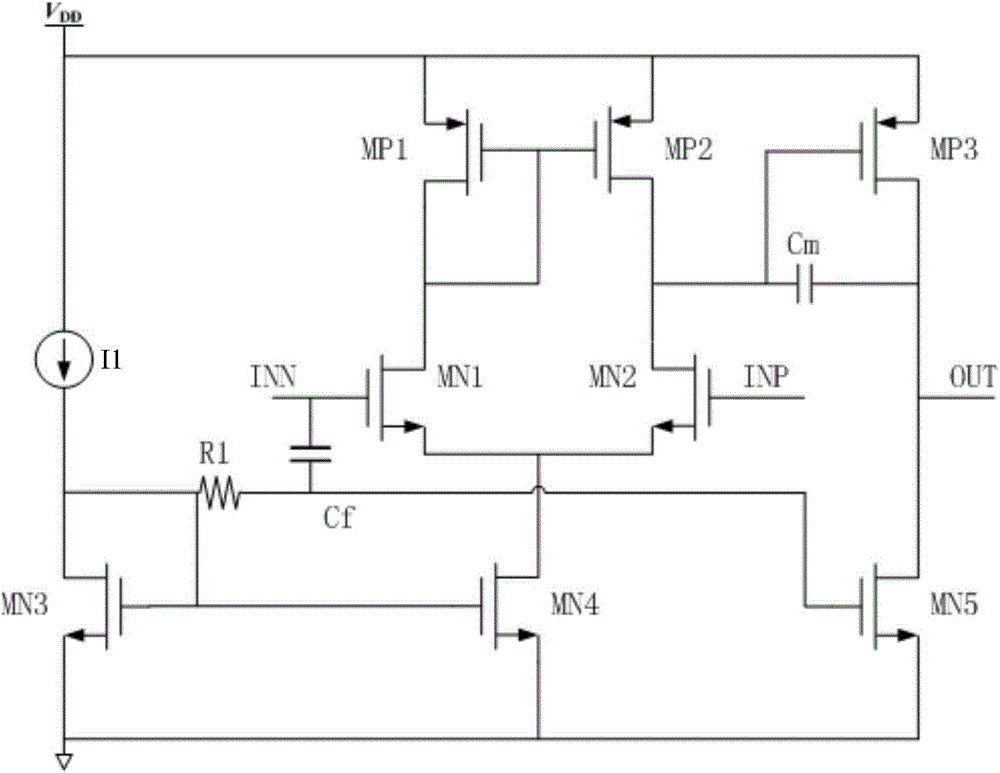
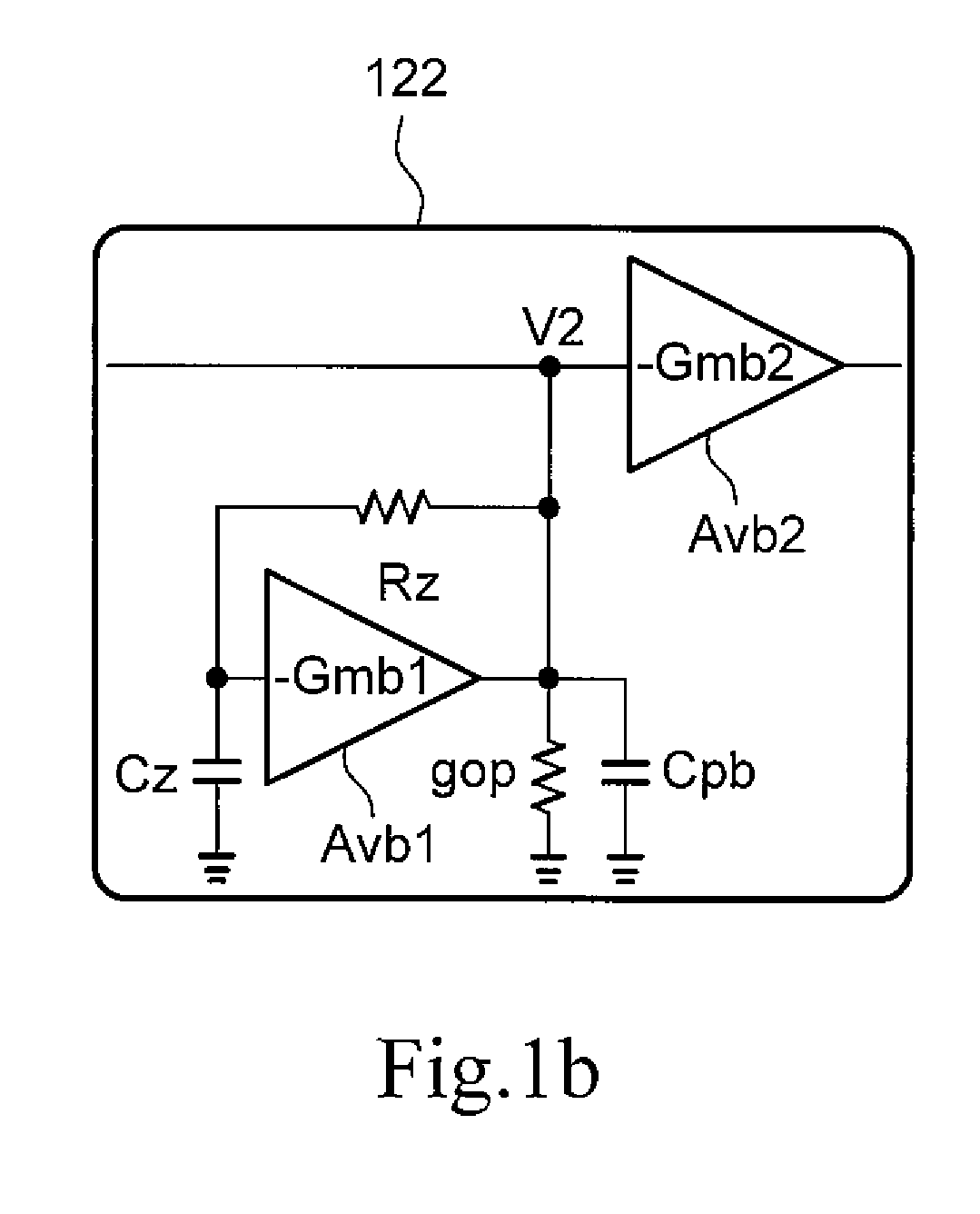
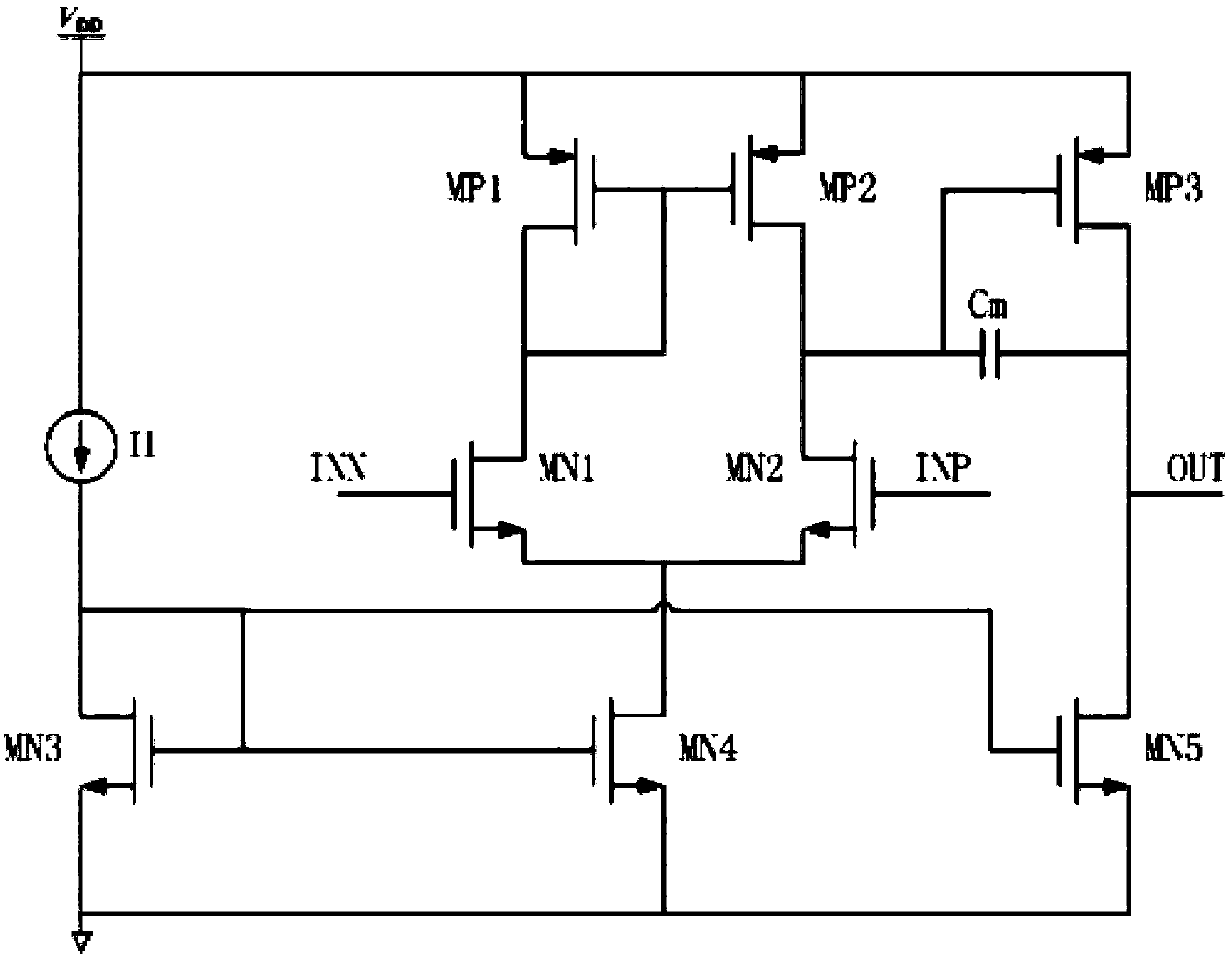
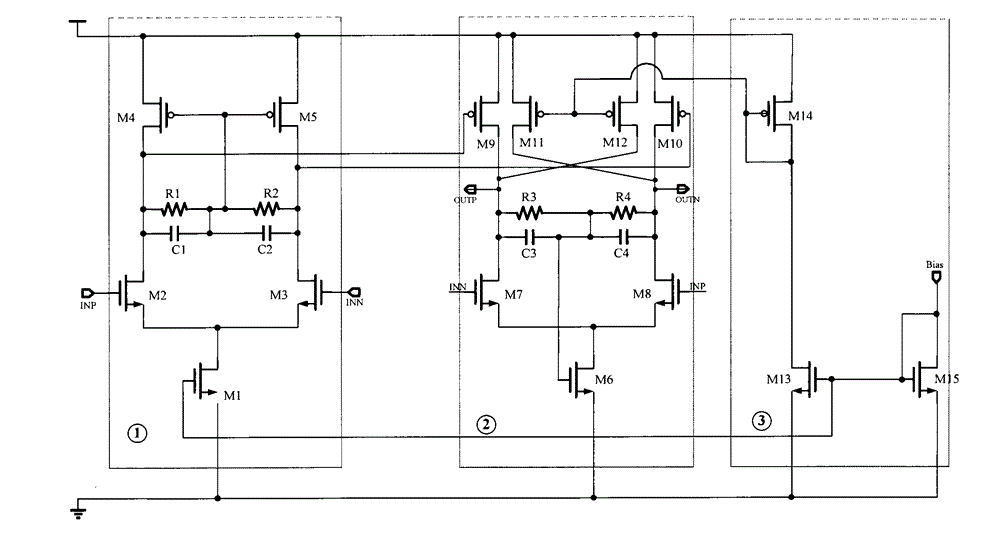
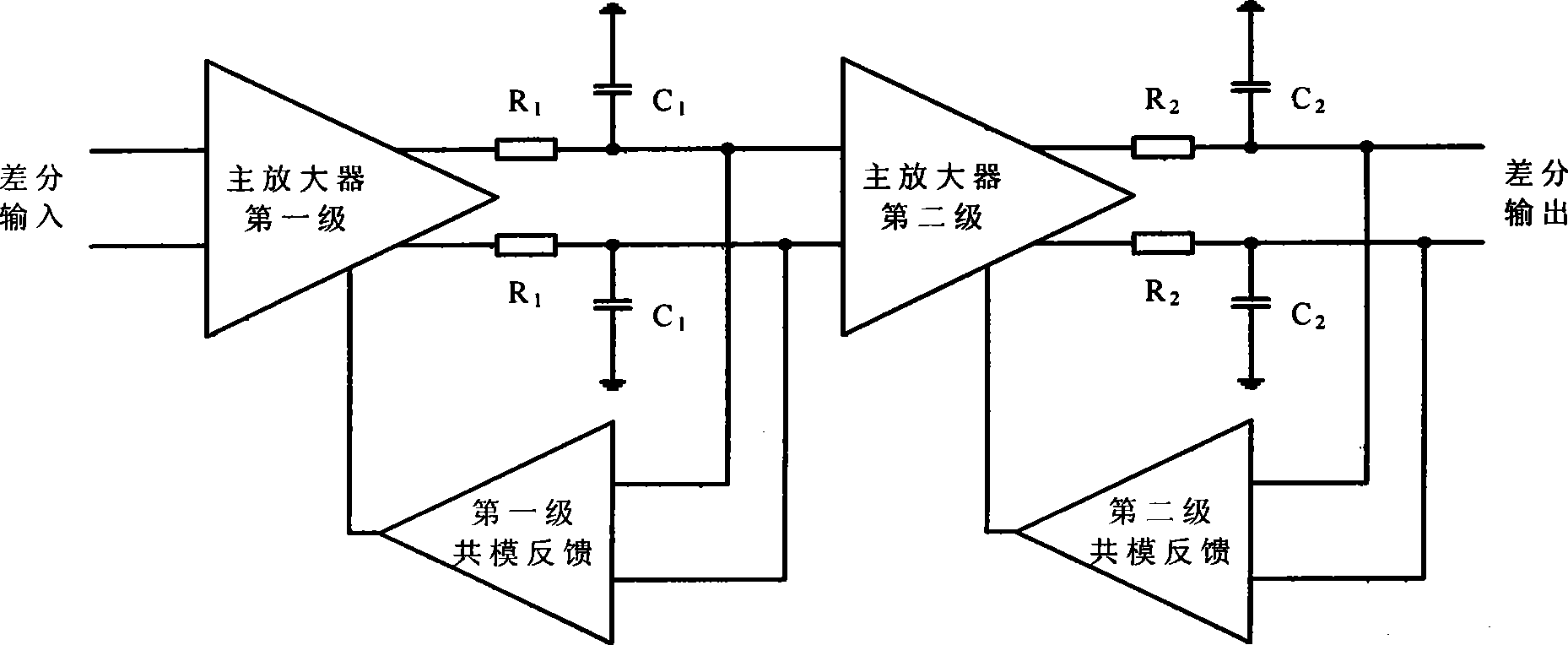
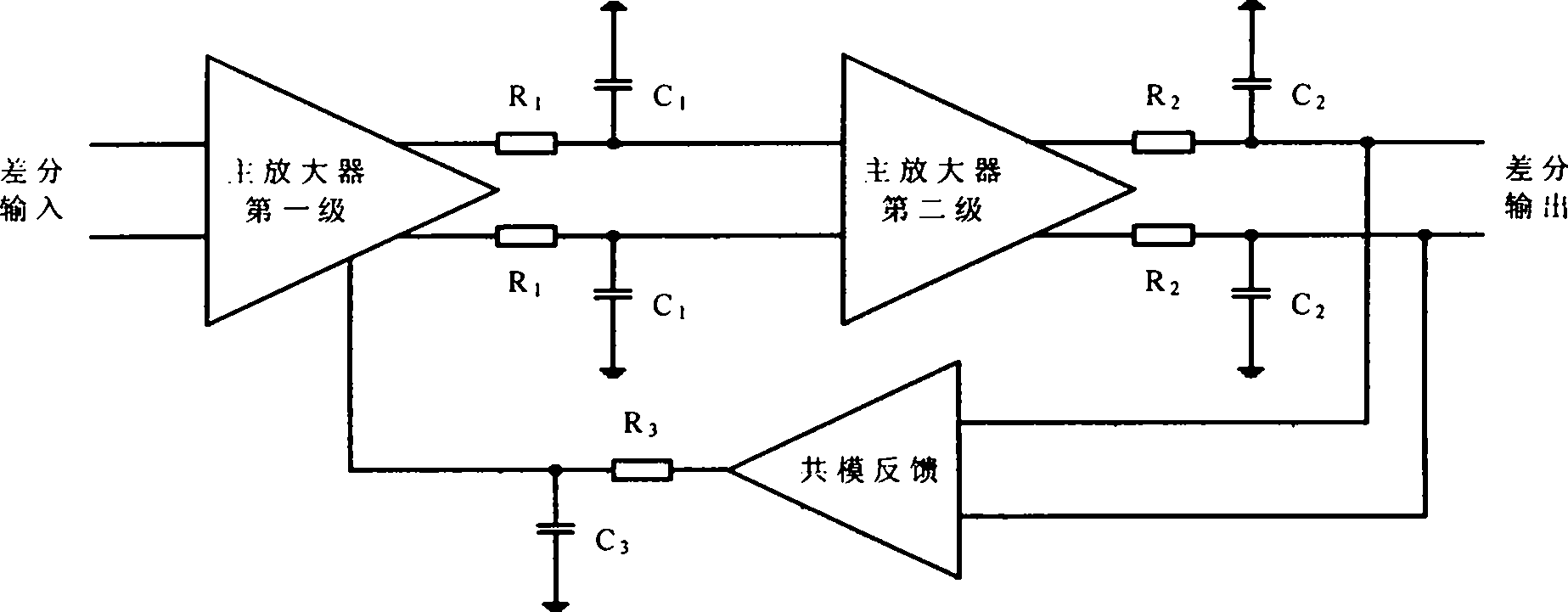
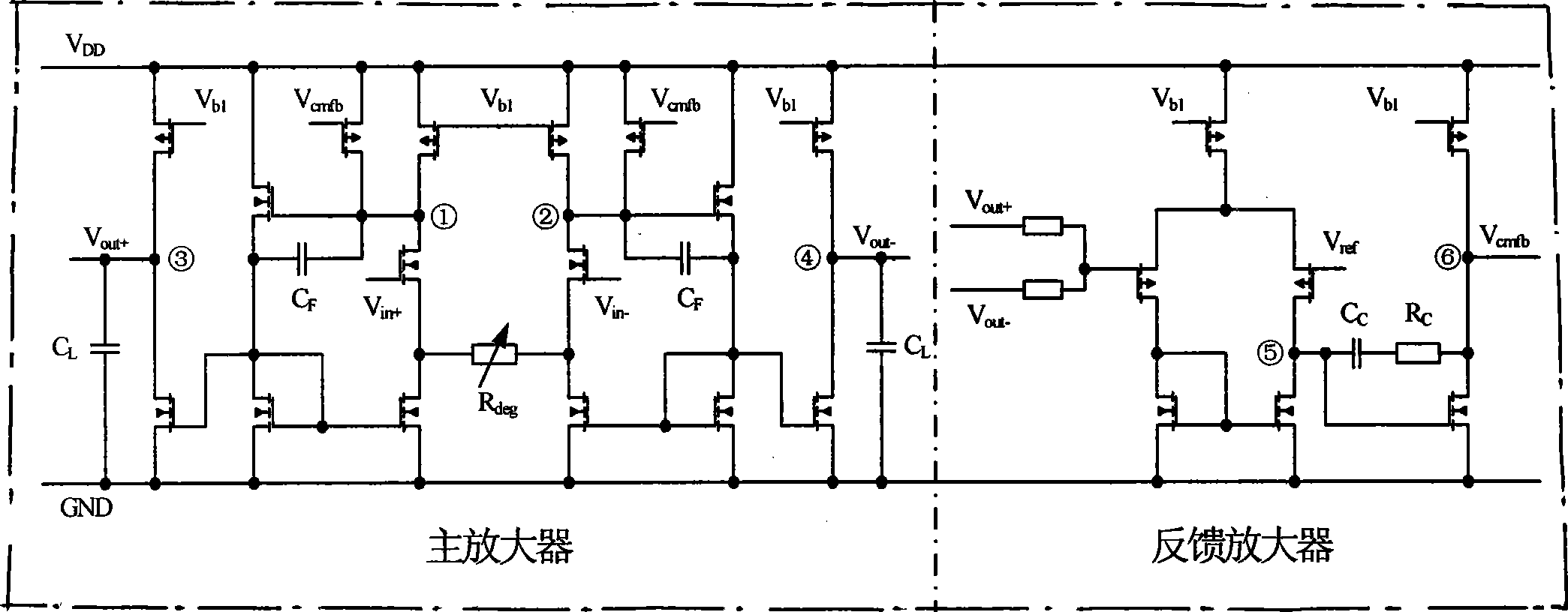
Method for compensating common mode feedback circuit frequency of two-stage amplifier
InactiveCN101373956AImprove phase marginImprove stabilityDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesDual stageControl signal
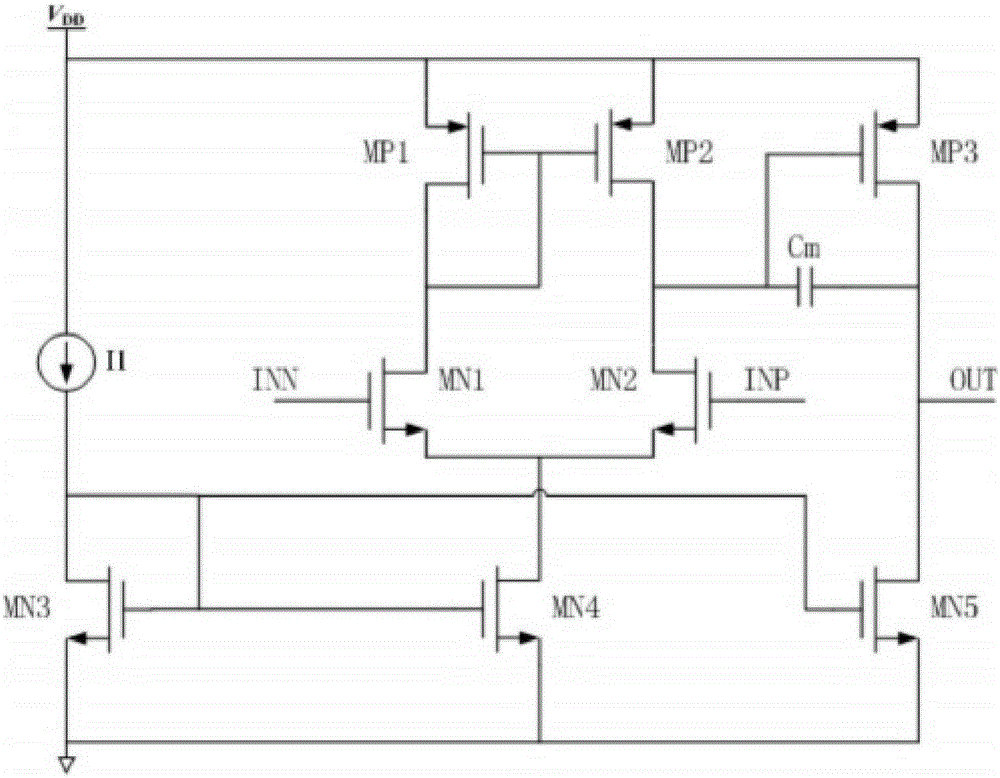
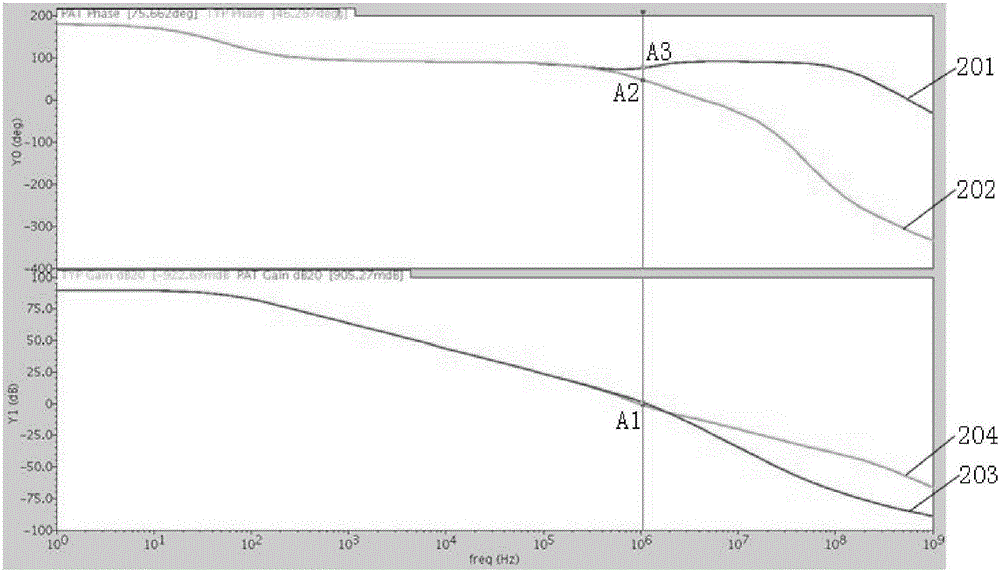
The invention discloses a common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method of a dual-stage amplifier, which belongs to the analog integrated circuit design field. One common-mode feedback circuit is adopted in the dual-stage amplifier to reduce the area and the power consumption of the feedback circuit; the dual-stage amplifier adopts a fully-differential input / output structure; a differential output terminal is used for sampling the common-mode output level; a first-stage amplifying circuit thereof comprises a controllable biasing circuit; a common-mode feedback control signal controls the first-stage common-mode output level and the second-stage common-mode output level of the amplifier at the same time through the controllable biasing circuit; a feedback amplifier is realized by adopting a dual-stage operational amplifier with miller compensation. The left half plane zero point generated by the feedback amplifier in a loop circuit counteracts a certain left half plane pole in a prime amplifier, thereby forming a stable compensation loop circuit. The common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method has the advantages of less feedback circuit elements, lower feedback circuit power consumption, high low-frequency loop gain and better compensation phase margin.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
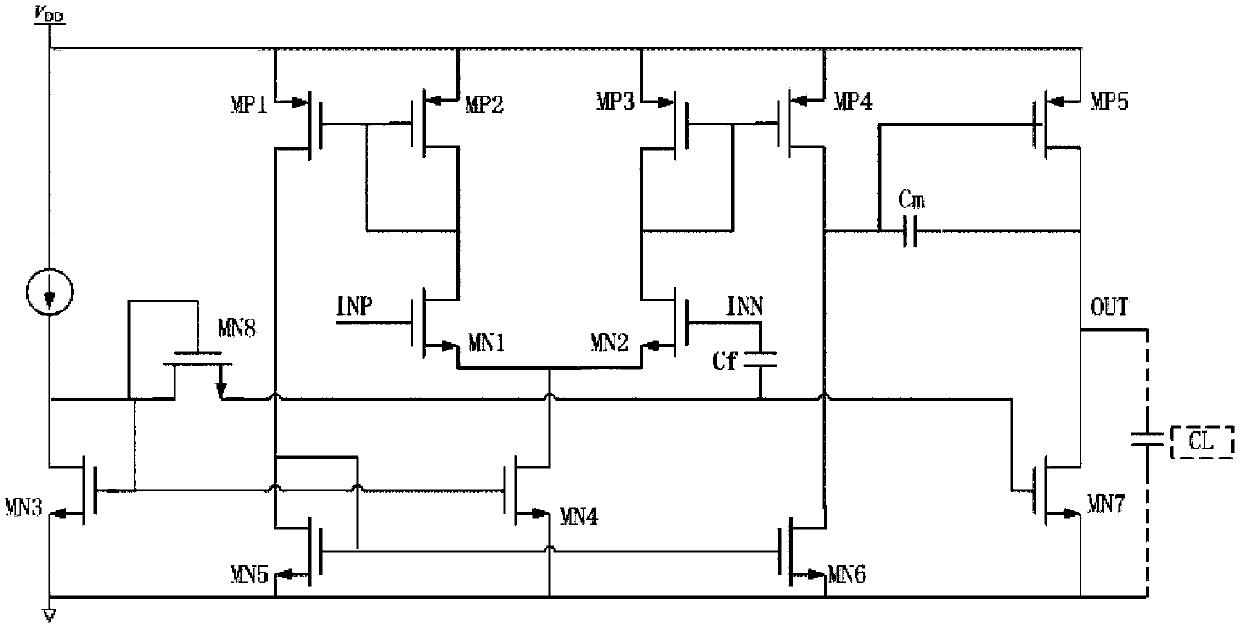
Operational amplifier
ActiveCN104393846AImprove stabilityDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses an operational amplifier. The operational amplifier comprises a first-stage amplification circuit and a second-stage amplification circuit, wherein the first-stage amplification circuit is a single-end output differential amplification circuit, the inverted phase output end of the single-end output differential amplification circuit serves as the output end of the first-stage amplification circuit, and a first-stage amplification signal is output; the input end of the second-stage amplification circuit is connected with the output end of the first-stage amplification signal, and a second-stage amplification signal is output; a first capacitor is connected between the input end and the output end of the second-stage amplification circuit; the second-stage amplification circuit comprises a first MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistor; the first MOS transistor is connected with the output end of the second-stage amplification circuit and provides a current source load for the second-stage amplification circuit; the inverted phase input end of the single-end output differential amplification circuit is connected to a gate of the first MOS transistor through a second capacitor to form a feed-forward path; the trans-conductance of the first MOS transistor is set to be greater than that of the first-stage amplification circuit, so that a left half plane zero point is formed by the operational amplifier. The stability of the operational amplifier can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Transconductance-capacitor compensation circuit for rolling over network
ActiveCN101425785ASimple in-phase transconductanceSimple structureDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceCMOS
The invention relates to a turning network transconductor, namely a capacitance compensating circuit which comprises a main signal transconductor, a feedforward compensating transconductor, a compensating capacitor and a loading capacitor, wherein the main signal transconductor comprises N+1 main signal transconductance units which are in step linkage to form a main signal path, the feedforward compensating conductance comprises N feedforward compensating conductance units which are used for forming a left half-plane zero point and improving the phase margin, the compensating capacitor comprises N capacitors used for improving the stability of a high-conductance amplifier because the Miller effect enables main poles are separated from non-main poles, and the loading capacitor comprises a capacitor forming the pole of a conductance amplifier with a loading resistor. An RNGCC circuit provided by the invention effectively improves the phase margin, has simple structure and is suitable for the necessary low power supply voltage of the future CMOS technology, and the applying prospect is wide.
Owner:灿芯创智微电子技术(北京)有限公司
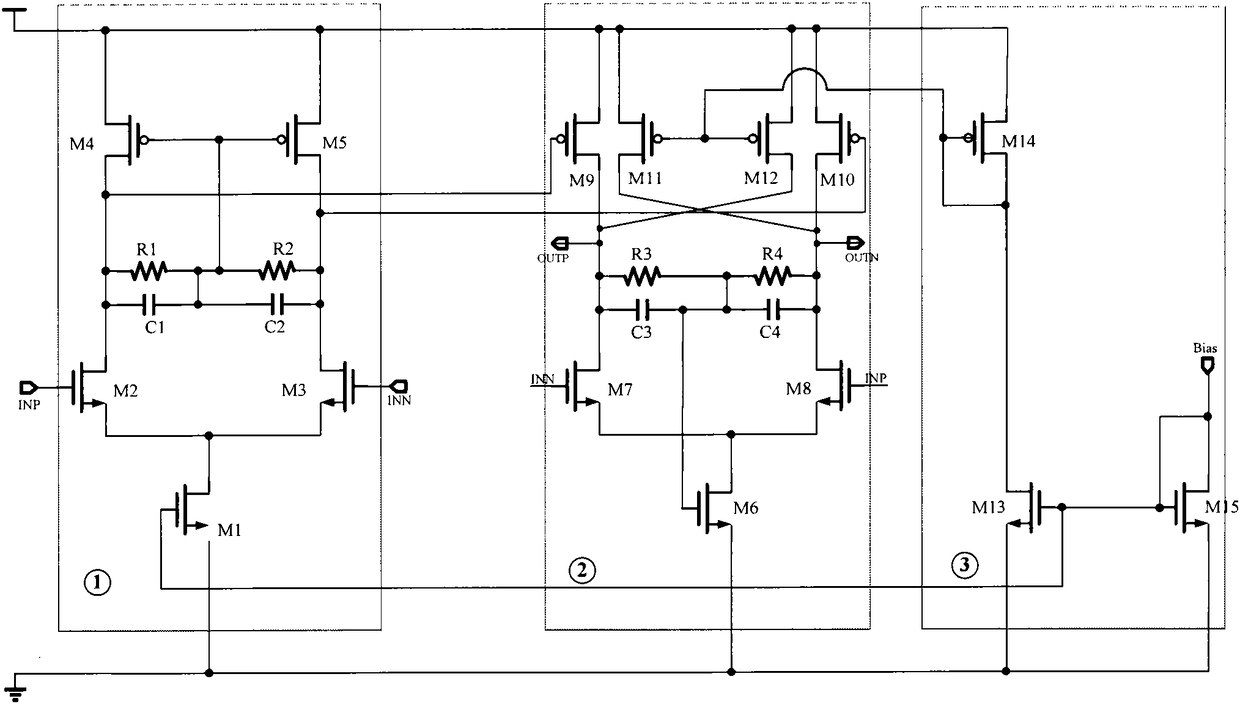
Operational amplifier
ActiveCN106160683AImprove stabilityNo power consumptionDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses an operational amplifier, which comprises a first-stage amplifier circuit and a second-stage amplifier circuit, wherein the first-stage amplifier circuit is a single-ended output differential amplifier circuit; a grid of a first MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistor and a grid of a second MOS transistor are respectively taken as a non-inverting input terminal and an inverting input terminal of the single-ended output differential amplifier circuit; a drain of an eleventh PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube is taken as an inverting output terminal and outputs a first-stage amplifying signal; an input end of the second-stage amplifier circuit is connected to the first-stage amplifying signal; and a seventh MOS transistor is connected to an output end of the second-stage amplifier circuit and provides current source load for the second-stage amplifier circuit. A second capacitor and the seventh MOS transistor form a feedforward path between the inverting input terminal of the single-ended output differential amplifier circuit and the output end of the second-stage amplifier circuit; the transconductance of the seventh transistor is arranged to be greater than the transconductance of the first-stage amplifier circuit, so that the operational amplifier forms left half plane zero to offset a pole in order to realize an effect of improving the stability of the circuit.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
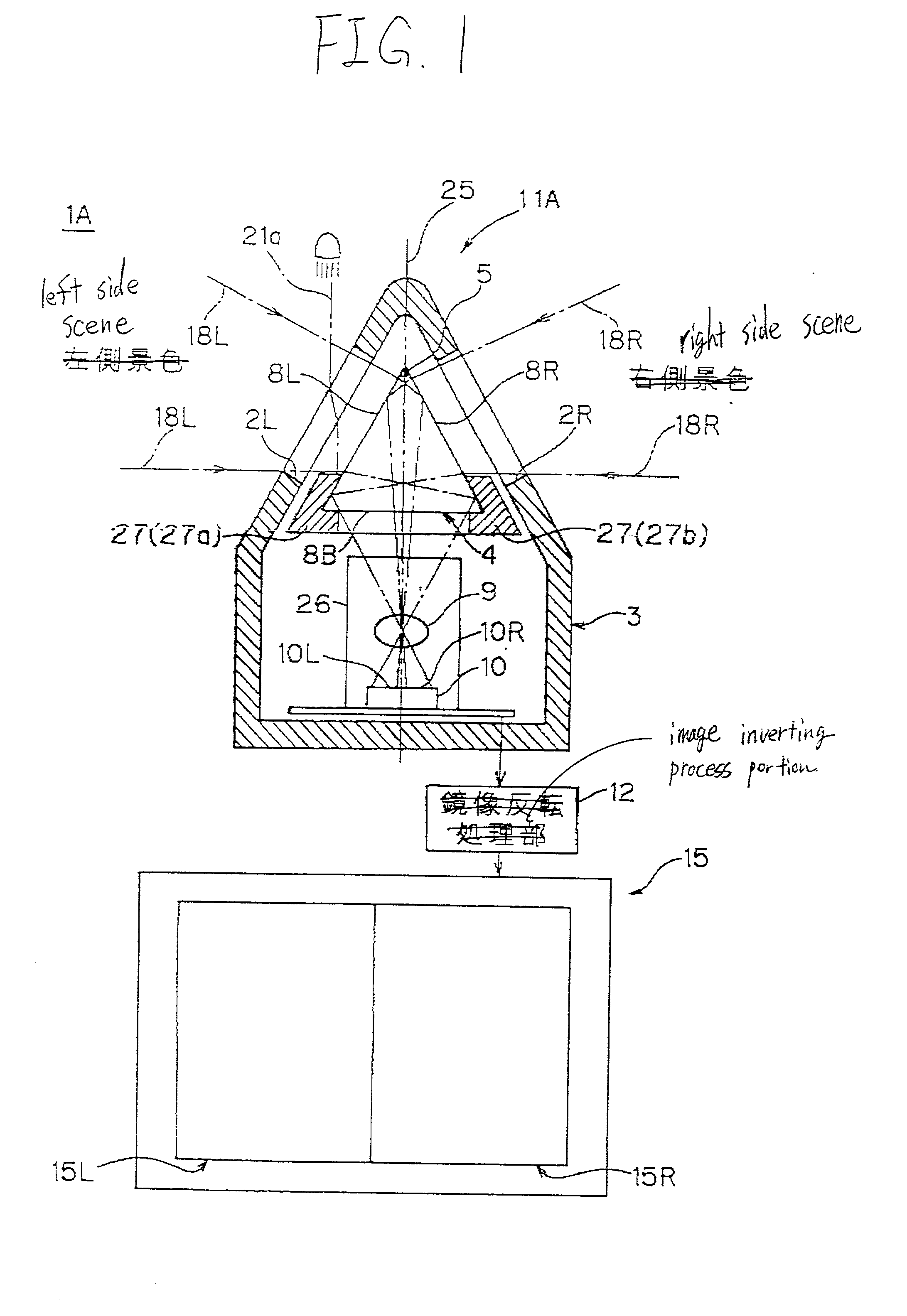
Vehicle surrounding viewing system
InactiveUS6472995B2Detection of traffic movementColor television detailsRight half-planeOptoelectronics
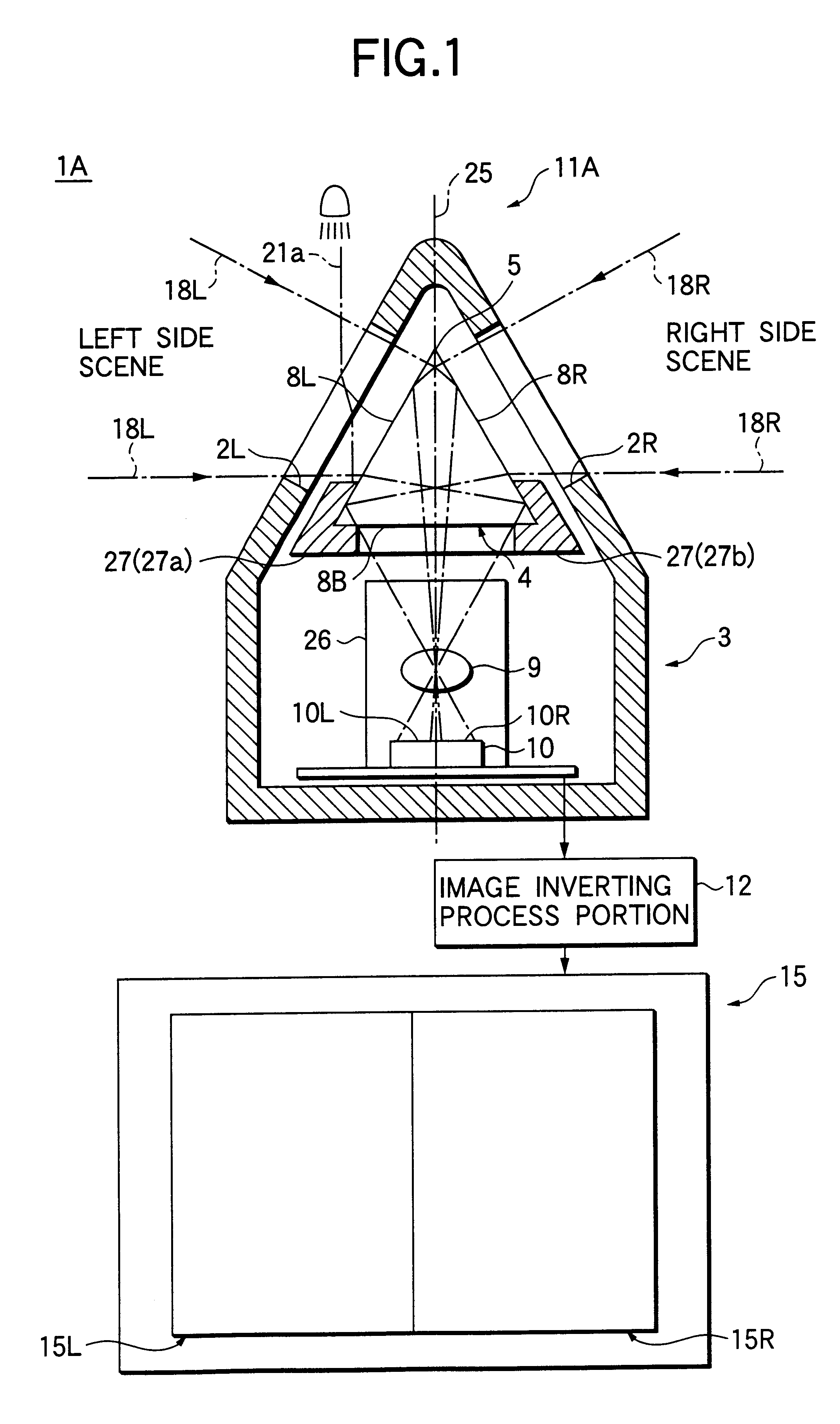
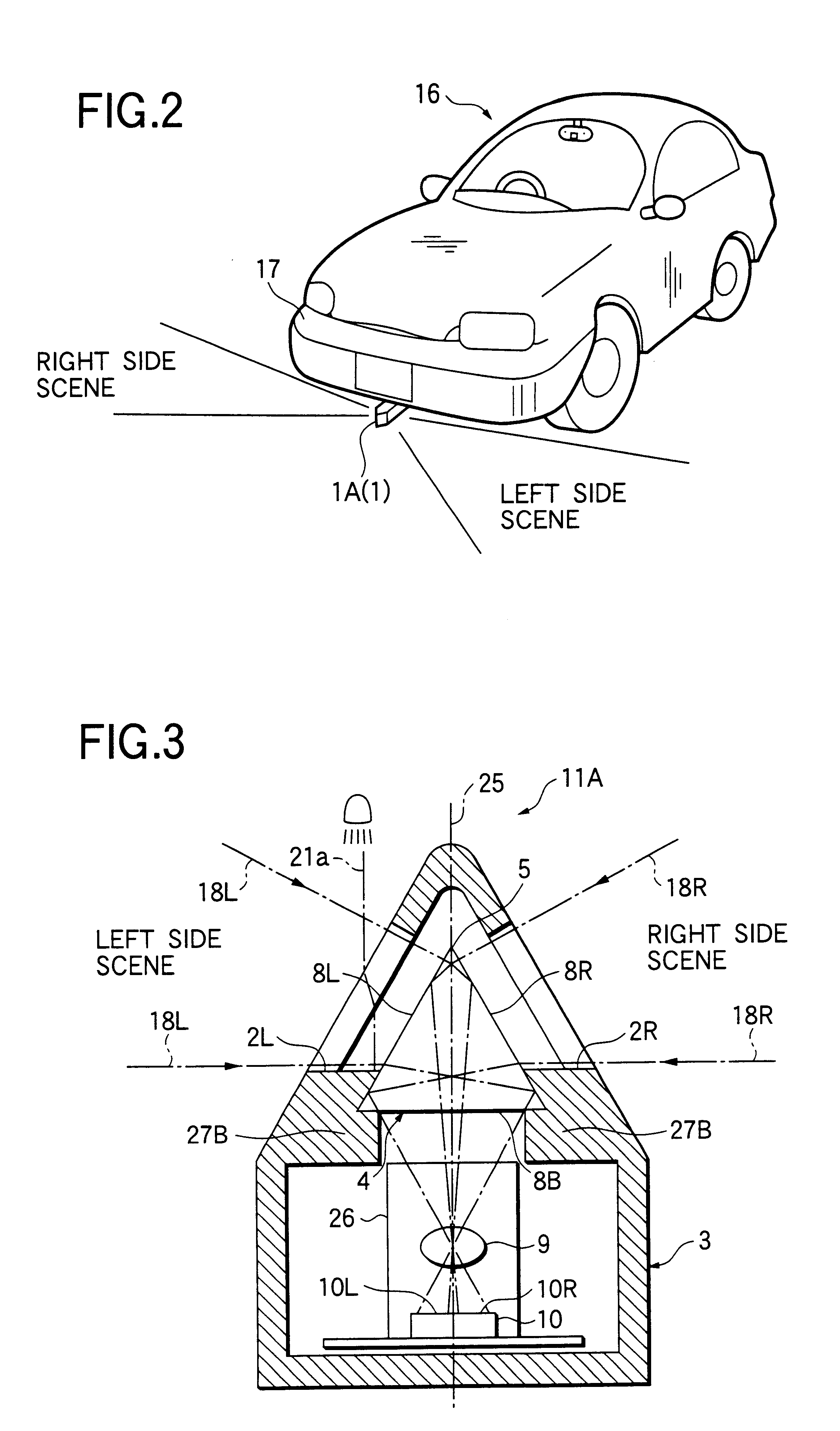
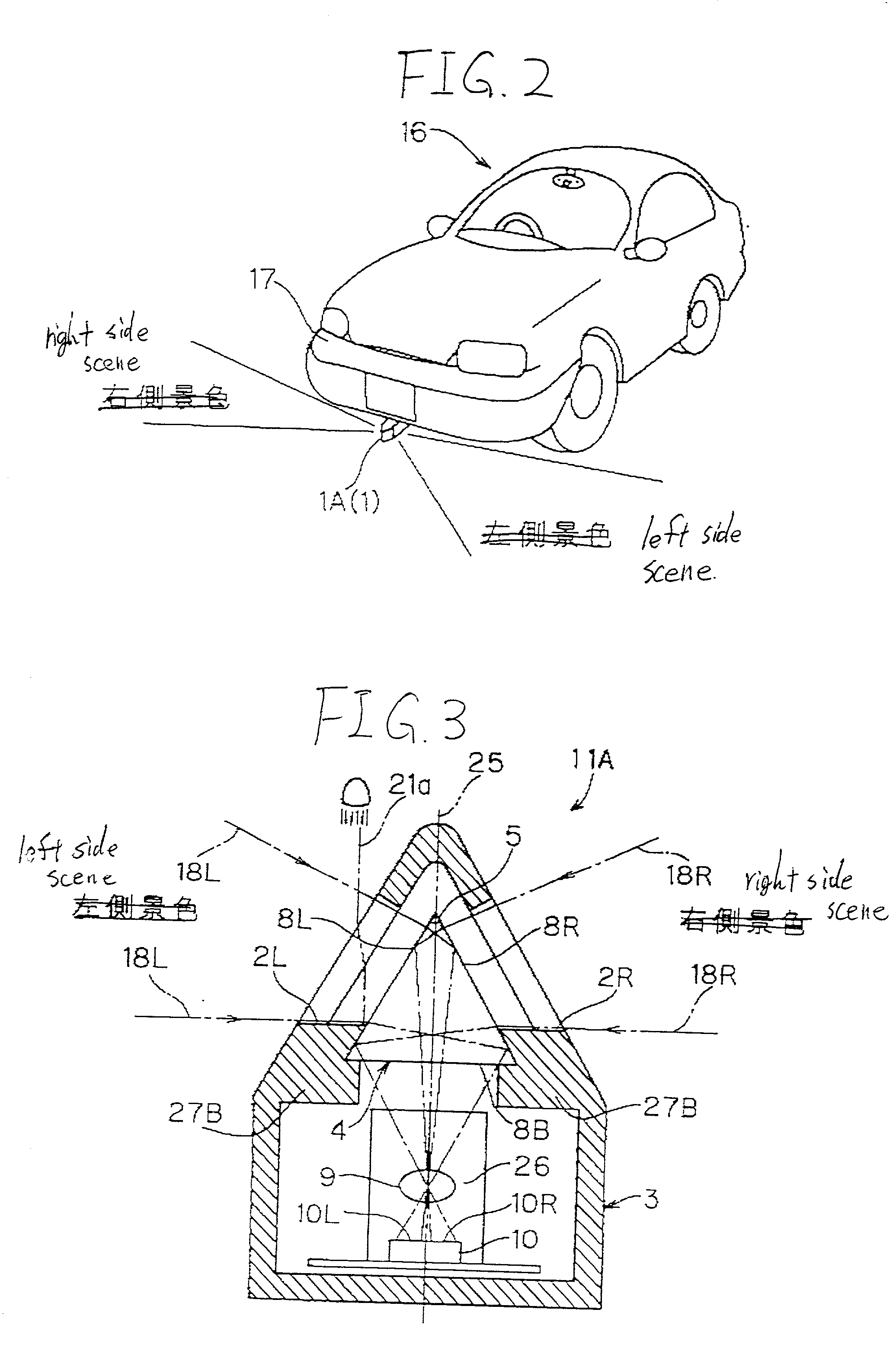
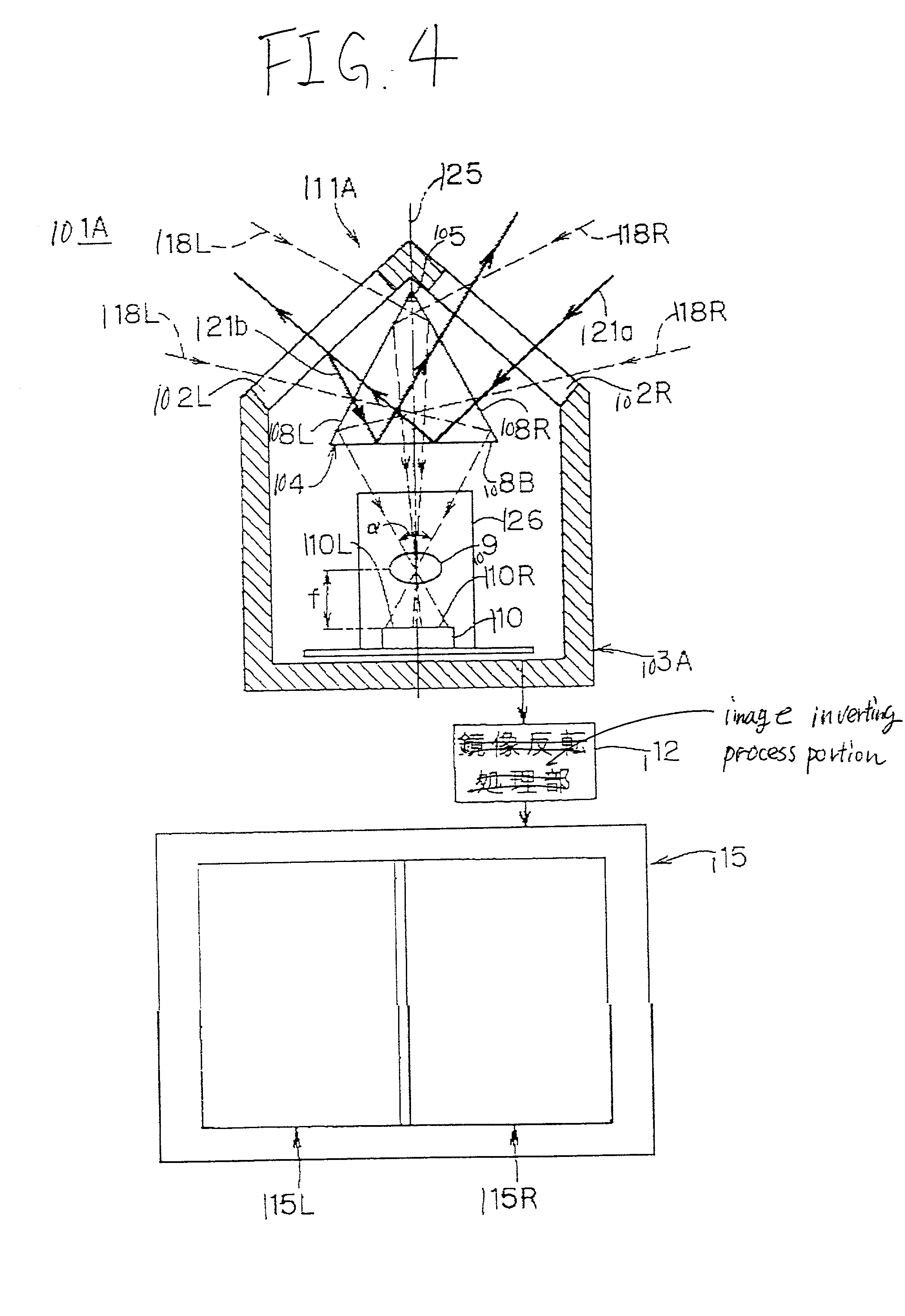
In the vehicle surrounding viewing system 1A, the light shielding member 27, that is coated on the areas other than the effective area of the surface of the prism 4 provided in the case 3, can transmit only the ray of light 18L, that enters into the transmit window 2L of the case 3, then passes through the prism side surface 8L, and then internally reflects at the prism side surface 8R, and subsequently is focused by the focusing lens 9 to be guided to the left half plane 10L of the image pick-up plane of the image pick-up element 10, and also the ray of light 18R, that enters into the transmit window 2R of the case 3, then passes through the prism side surface 8R, and then internally reflects at the prism side surface 8L, and subsequently is focused by the focusing lens 9 to be guided to the right half plane 10R of the image pick-up plane of the image pick-up element 10.
Owner:AUTONETWORKS TECH LTD +2
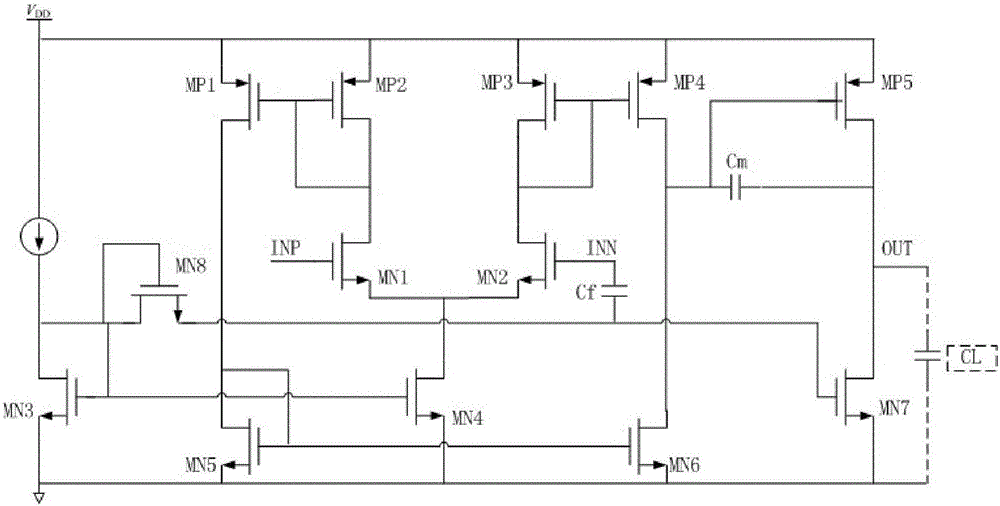
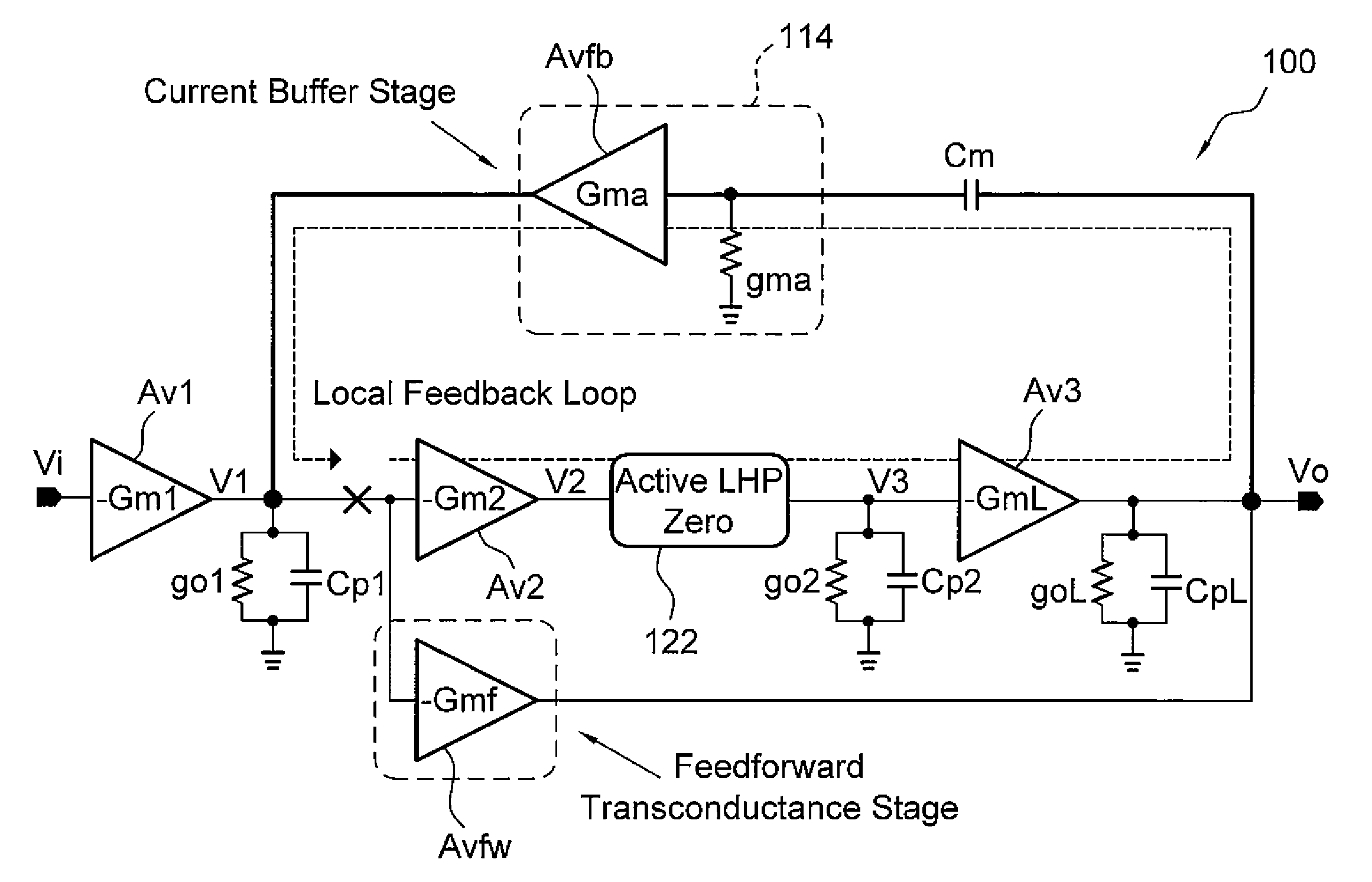
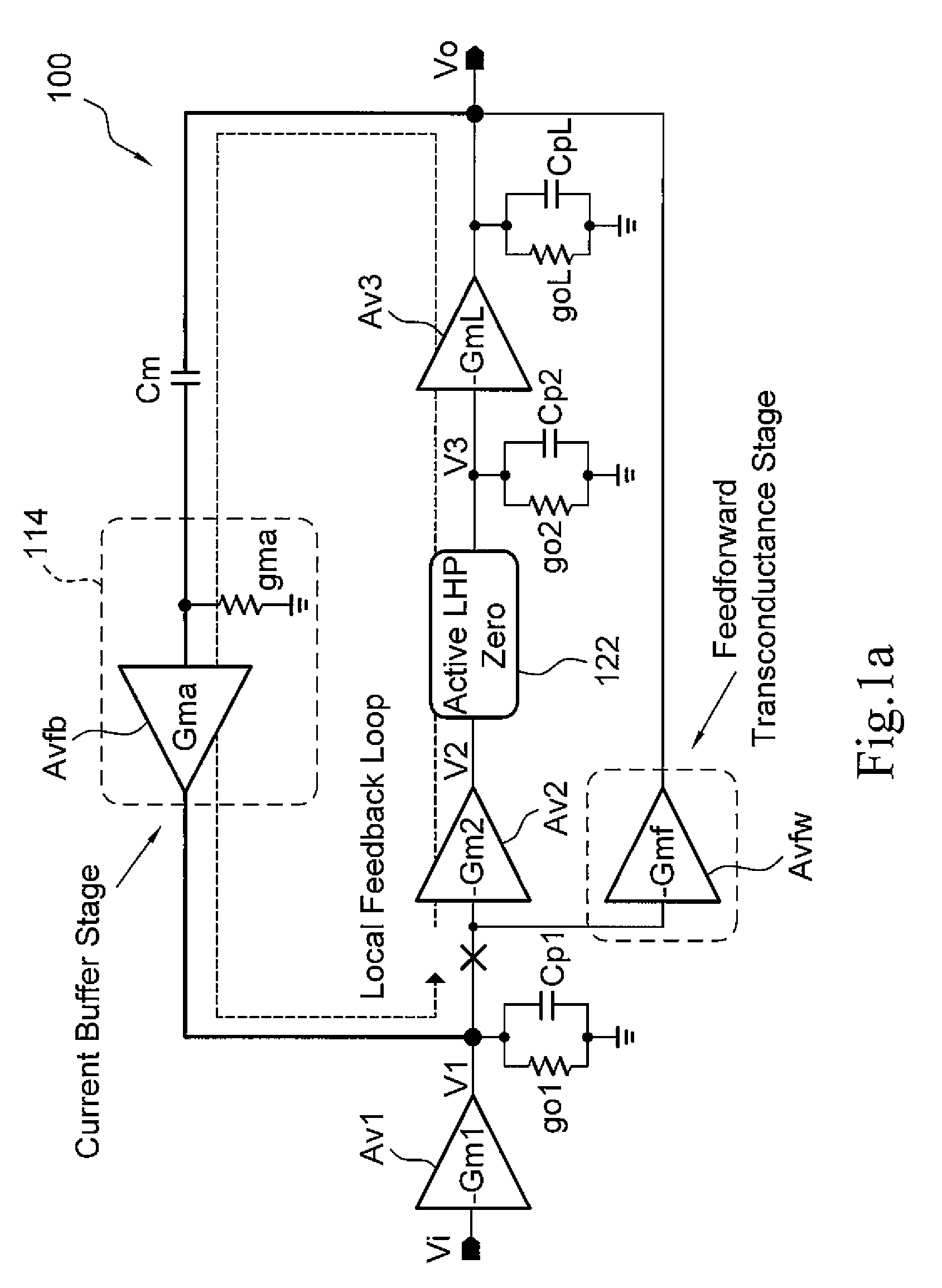
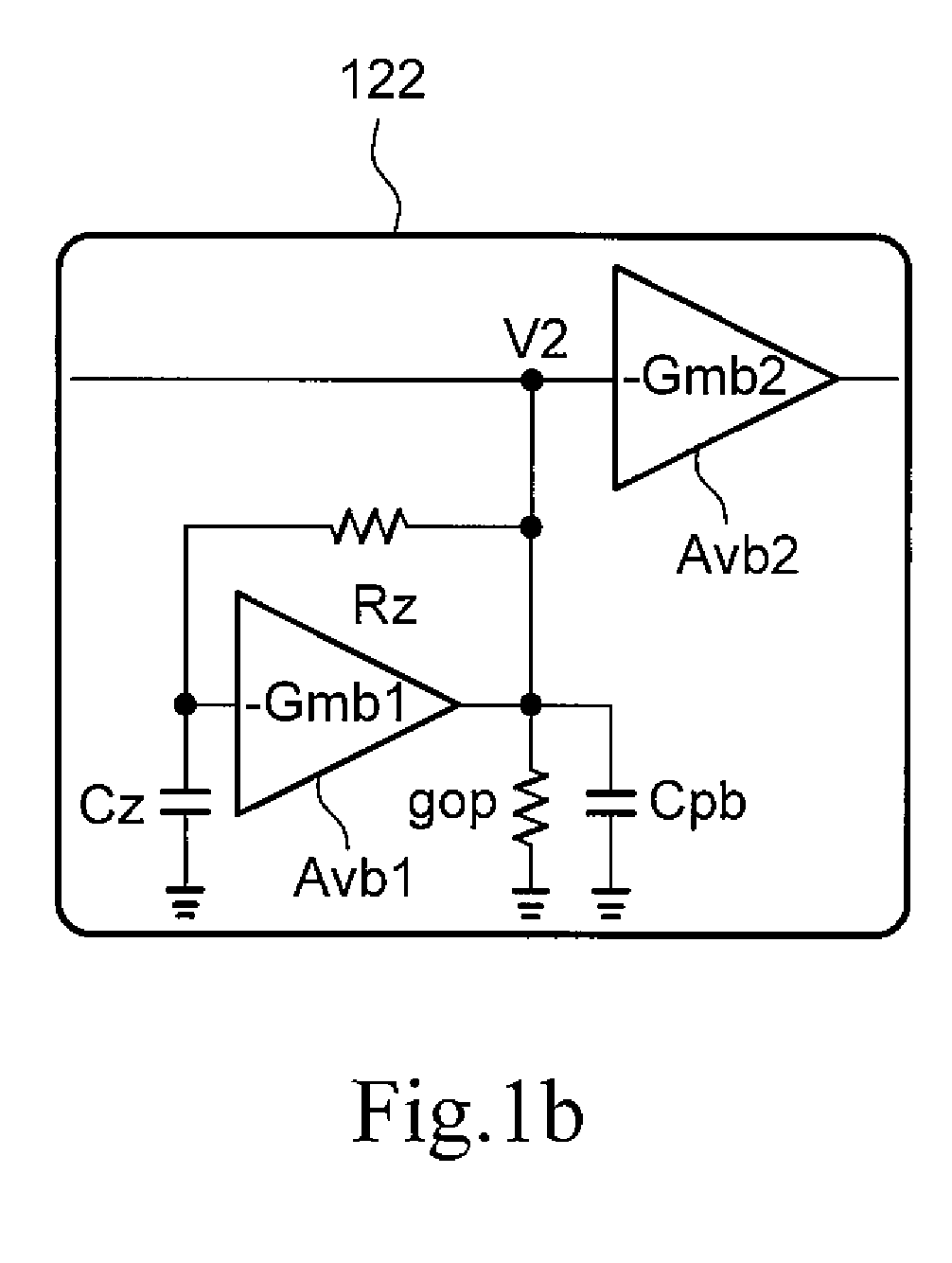
Frequency compensation techniques for low-power and small-area multistage amplifiers
ActiveUS20140232465A1Improve drivabilityDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceFrequency compensation
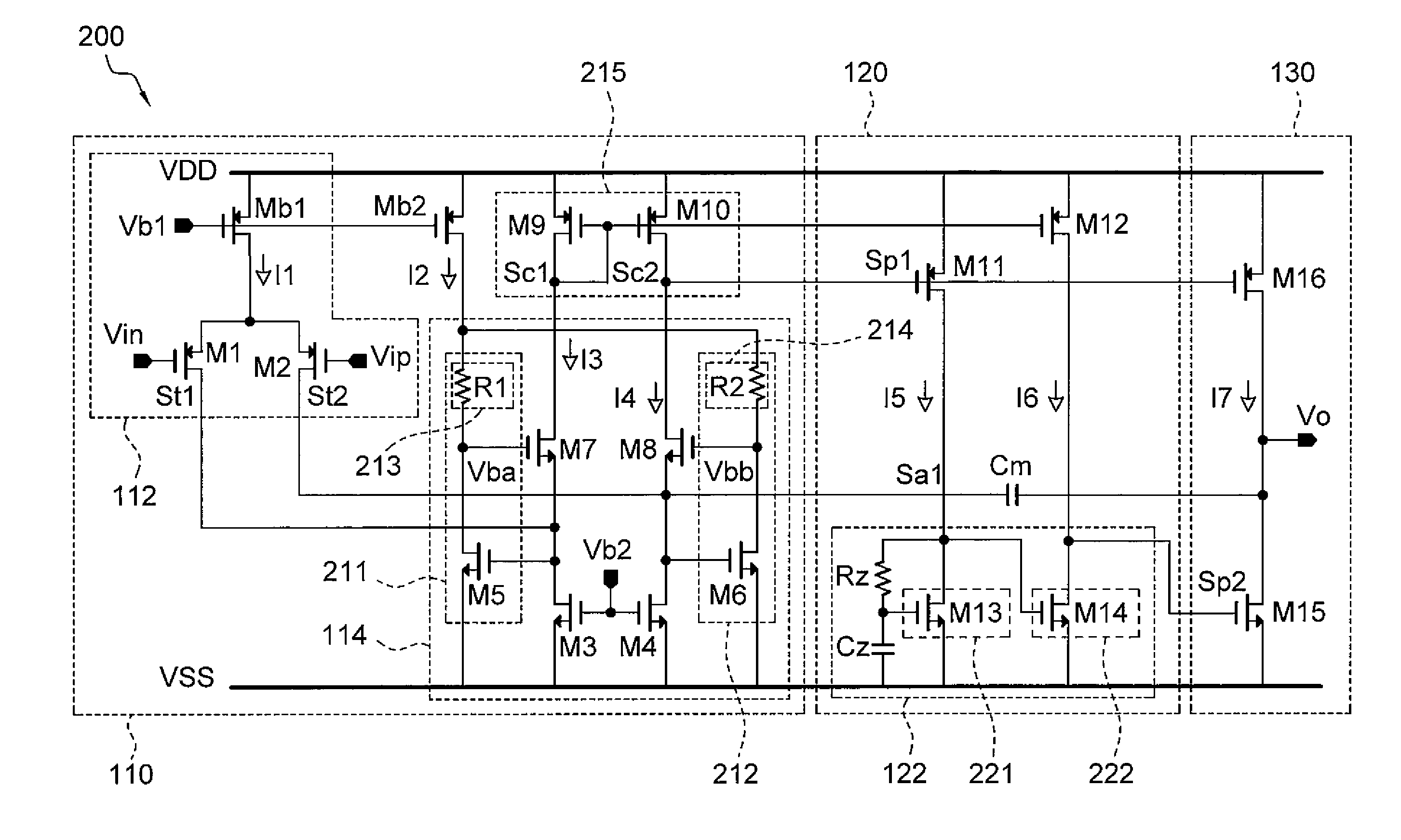
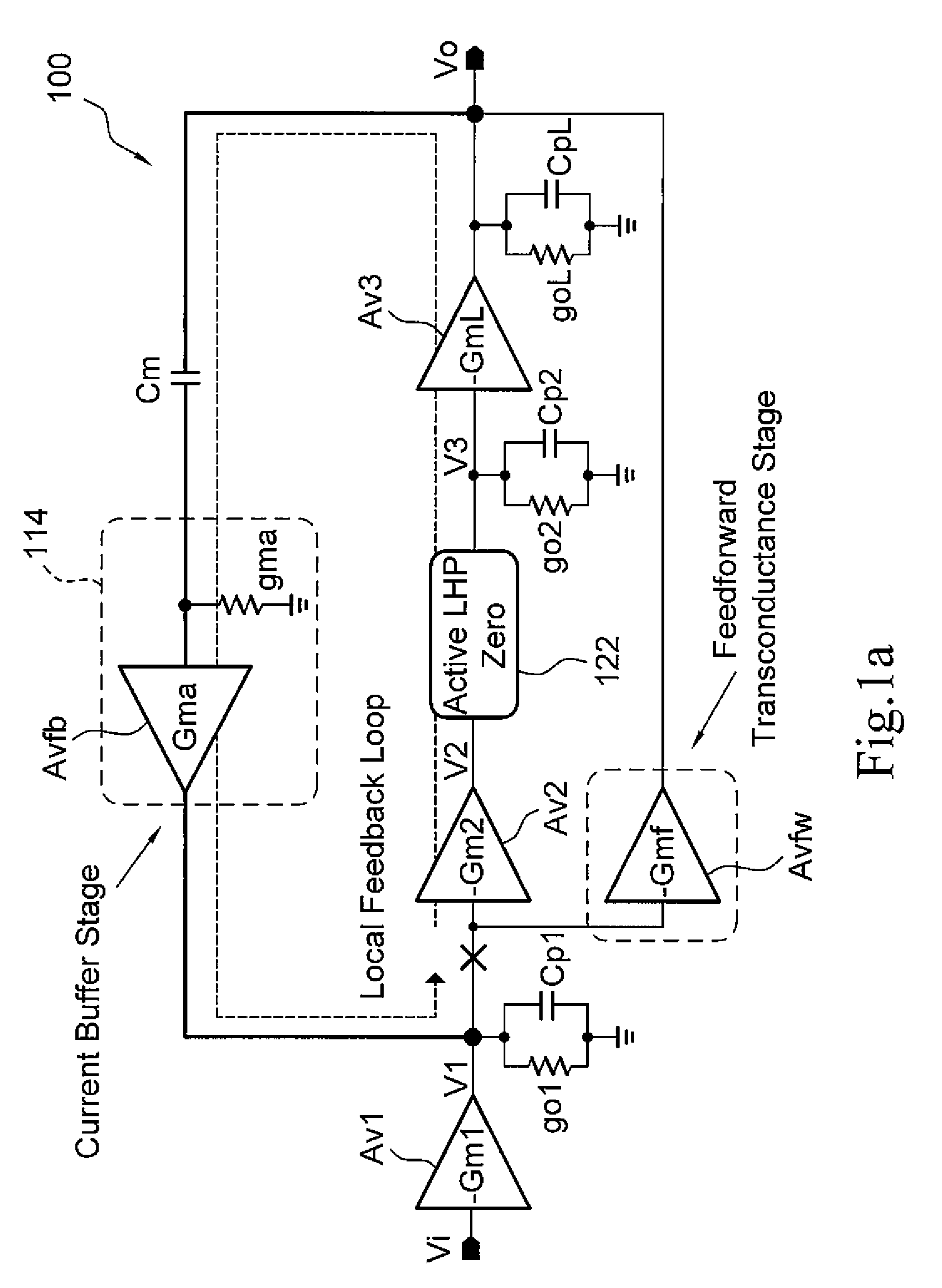
A three stage amplifier is provided and the three stage amplifier comprises a first gain stage, a second gain stage and a third gain stage wherein said first stage receives an amplifier input signal and said third gain stage outputs an amplifier output signal. The amplifier includes a feedback loop having a current buffer and a compensation capacitance provided from the output of said third gain stage to the output of the first gain stage. In addition, an active left half plane zero stage is embedded in said feedback loop for cancelling a parasitic pole of said feedback loop.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
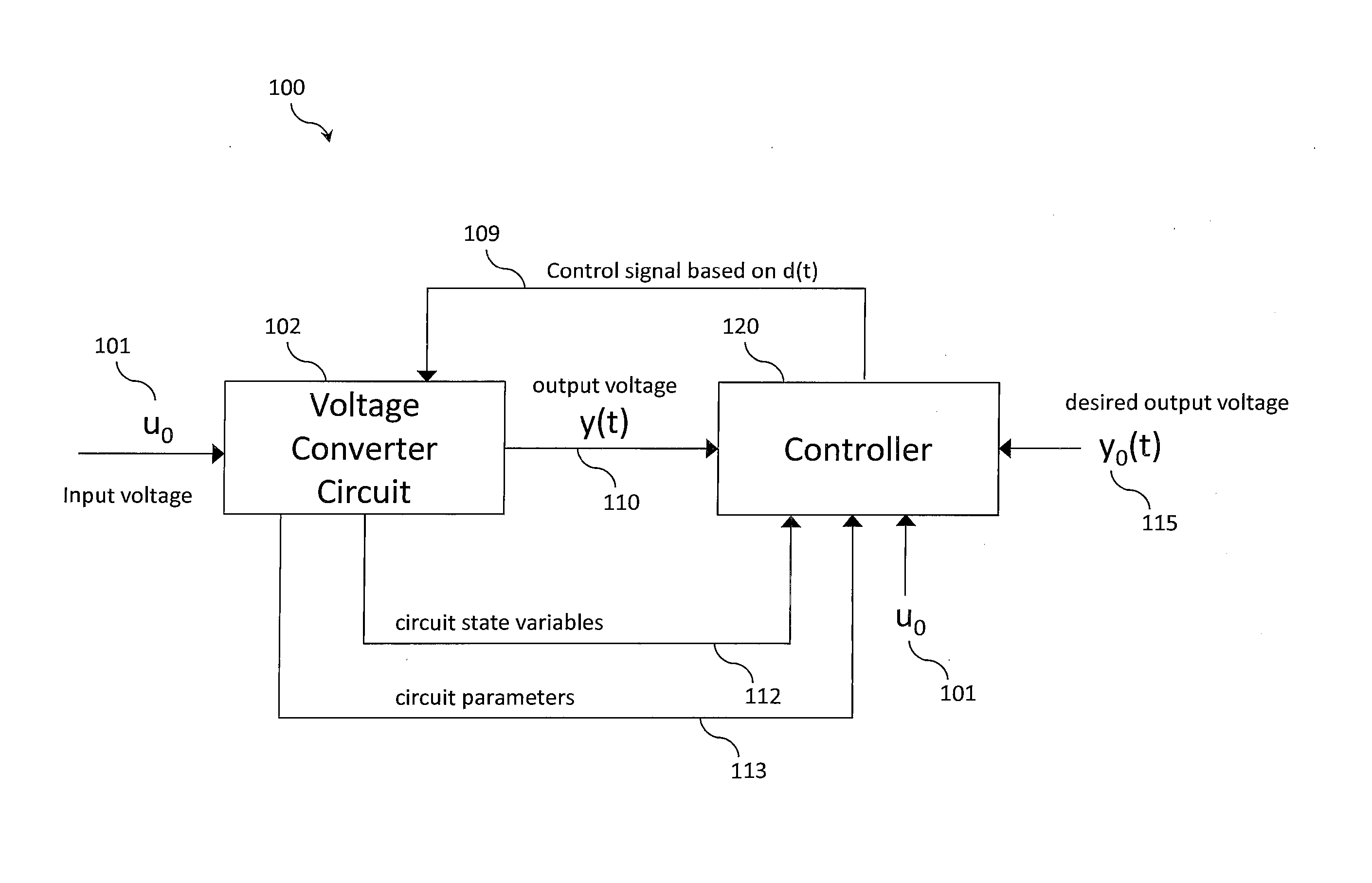
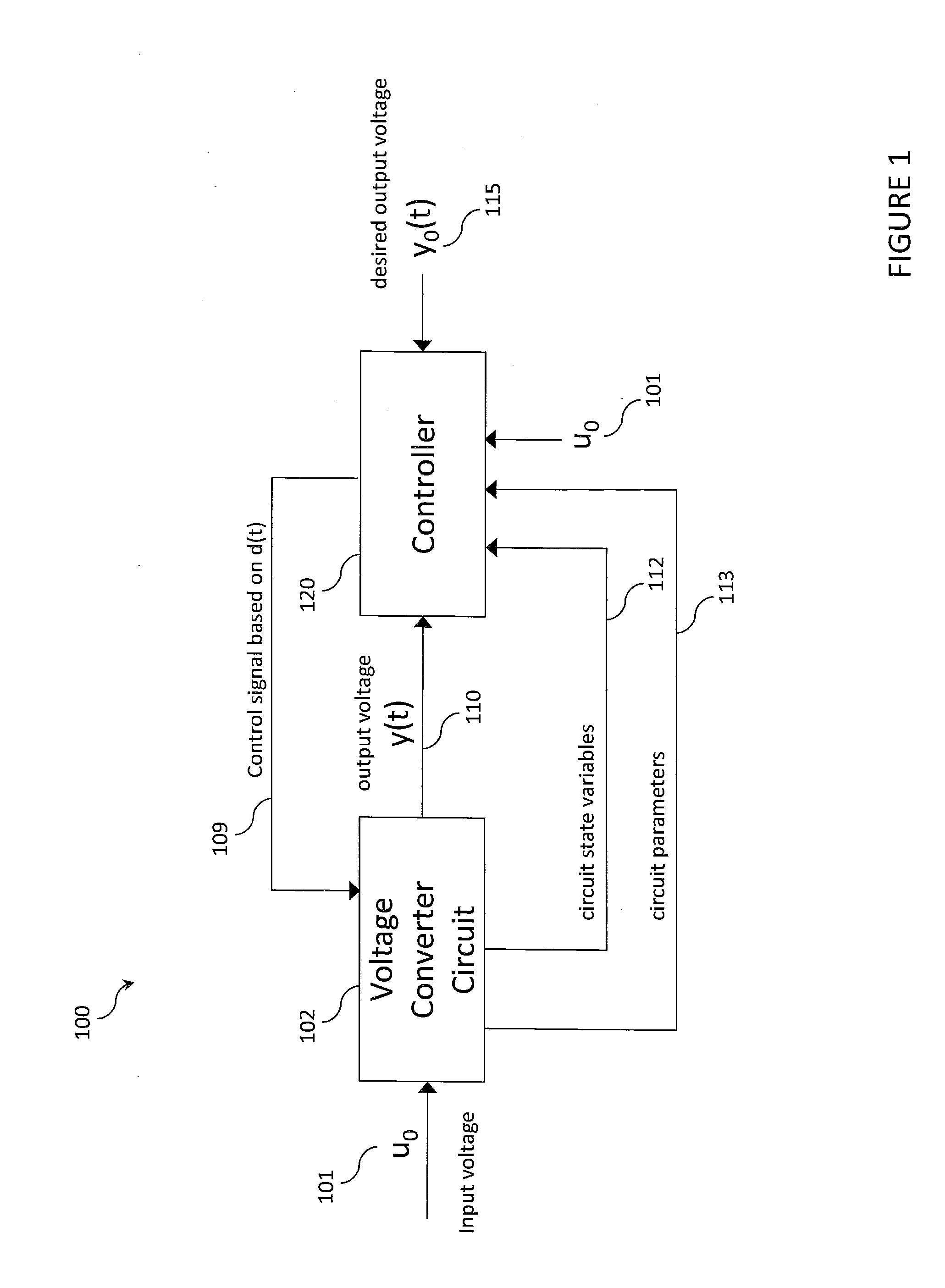
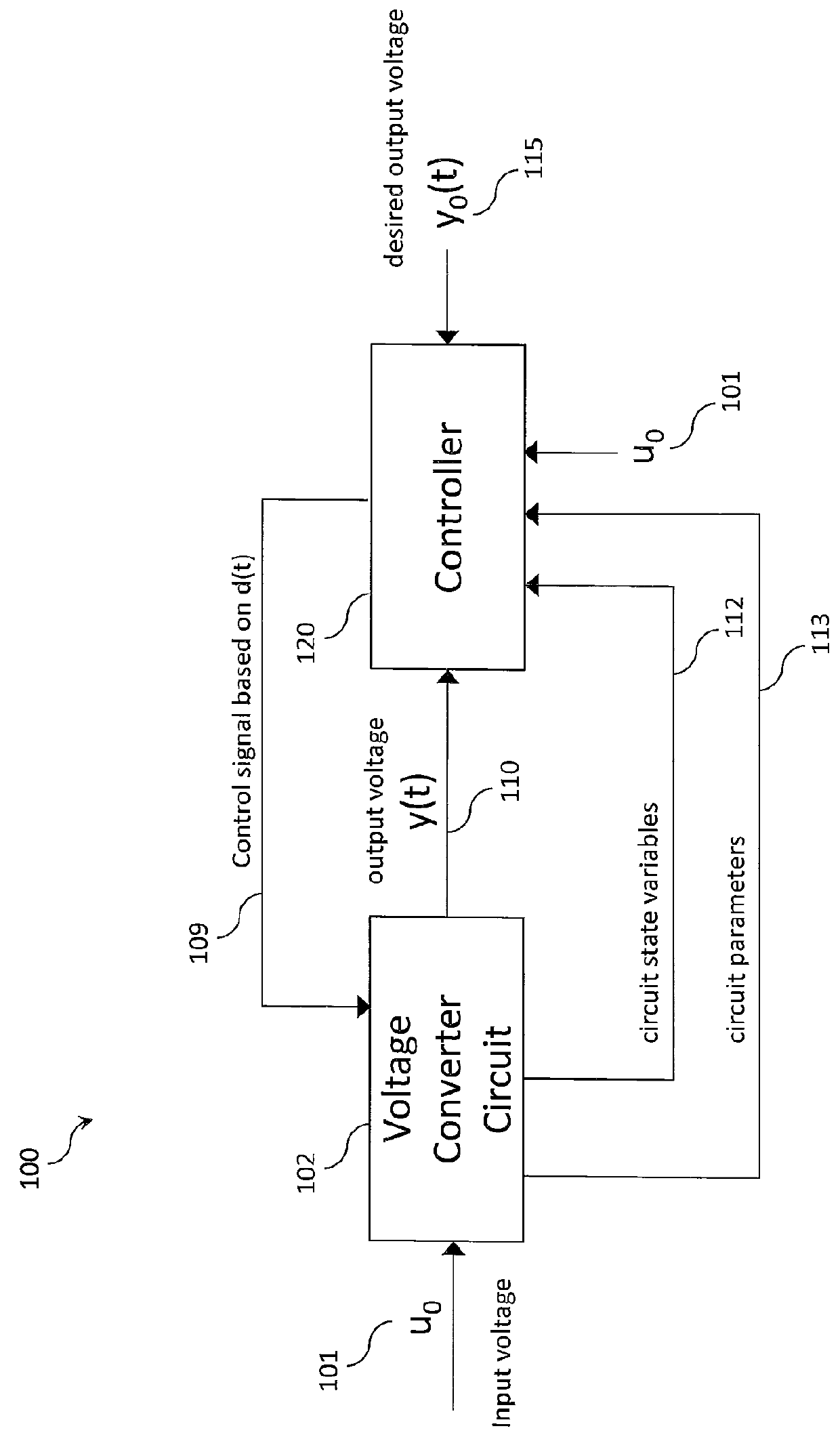
Tracking converters with input output linearization control
ActiveUS20130301321A1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionVoltage converterLeading edge
In a preferred embodiment, a voltage inverter comprises a voltage converter circuit and a controller. The voltage inverter produces a time-varying output voltage from an input voltage, which can be a DC input voltage or an AC input voltage. The controller provides a control signal at a duty ratio determined dynamically by a set of signals. The set of signals include the time-varying output voltage, a predetermined output voltage, a gain factor and an inductor current in the voltage converter circuit. The predetermined output voltage can have an AC waveform or an arbitrary time-varying waveform. The voltage inverter operates to match the time-varying output voltage to the predetermined output voltage. Input-output linearization is used to design a buck inverter, and input-output linearization with leading edge modulation is used to design boost and buck-boost inverters under conditions where left half plane zero effects are present.
Owner:CIRASYS
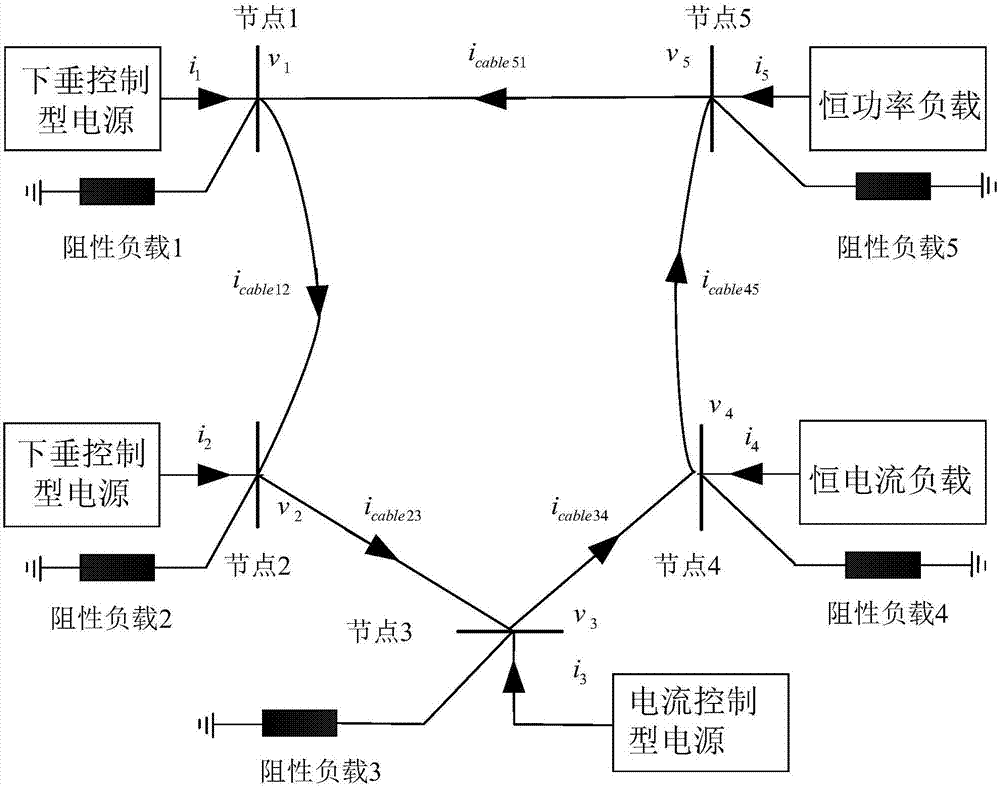
Stability determination method for DC micro-grid in master-slave control mode
ActiveCN106877309ASimple calculationImprove scalabilityEnergy industryDc source parallel operationConstant powerRight half-plane
The invention relates to the stability analysis technology in the DC micro-grid technologies, and aims to provide a stability determination method for a DC micro-grid in the master-slave control mode. The method comprises the following steps: using the unit connection method to carry on the Thevenin / Norton equivalent to the power modules of each power supply and each constant power load so as to obtain the corresponding impedance / admittance, and obtaining the impedance matrix of the main power supply, the admittance matrixes of the slave power source and the constant power load; according to the known resistive load size of each node, obtaining the resistive load admittance matrix, and obtaining the system node admittance matrix according to the inter-node cable parameter; placing each matrix into the stability criterion and calculating its pole; if all the poles are on the left half plane, determining that the system is stable; and if there is a pole on the right half plane, determining the system is unstable. The method is compatible with the inter-node impedance of the system, and has no specific requirement for the system structure, and has a wide application range. The calculation is simplified in the system-level stability analysis and the stability of the complex DC micro-grid can be effectively analyzed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGXIN POWER ENG CONSTR CO LTD +1
Frequency compensation techniques for low-power and small-area multistage amplifiers
ActiveUS8963639B2Improve drivabilityDifferential amplifiersAmplifier detailsCapacitanceFrequency compensation
A three stage amplifier is provided and the three stage amplifier comprises a first gain stage, a second gain stage and a third gain stage wherein said first stage receives an amplifier input signal and said third gain stage outputs an amplifier output signal. The amplifier includes a feedback loop having a current buffer and a compensation capacitance provided from the output of said third gain stage to the output of the first gain stage. In addition, an active left half plane zero stage is embedded in said feedback loop for cancelling a parasitic pole of said feedback loop.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
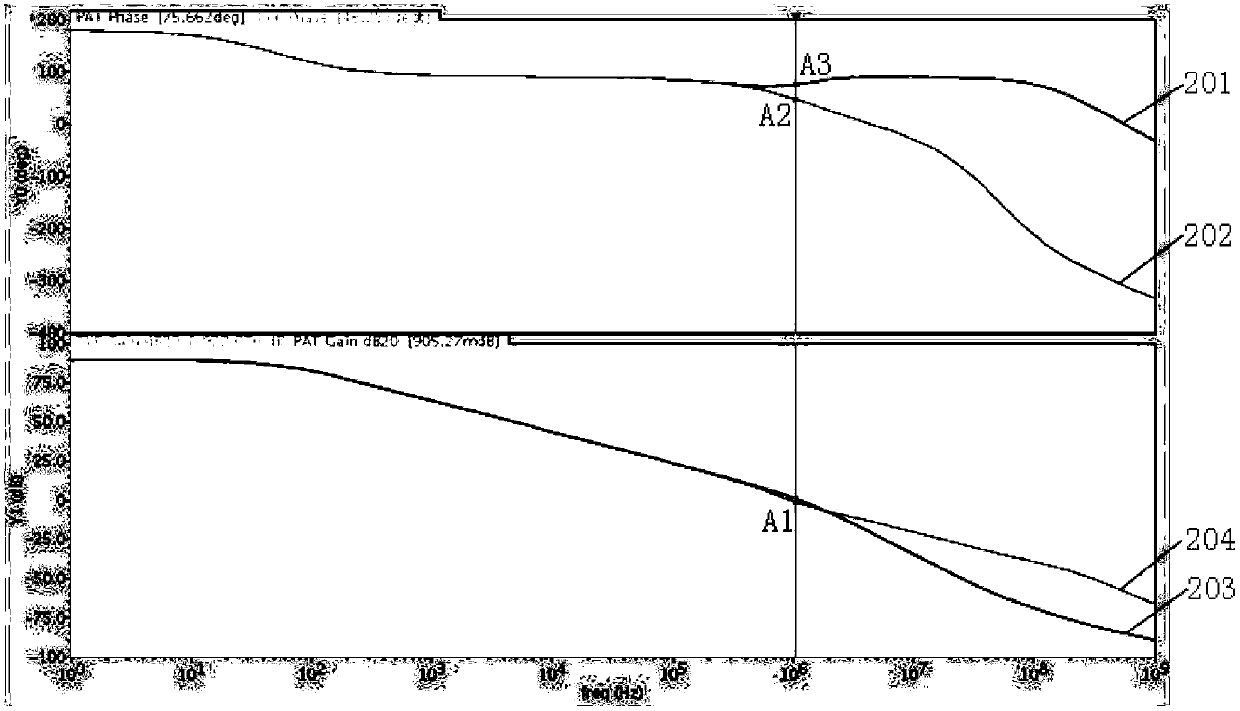
Frequency compensation circuit for operational amplifier
ActiveCN106026954AImplement frequency compensationImprove -3dB bandwidthDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a frequency compensation circuit for an operational amplifier. The frequency compensation circuit comprises a gain circuit, an output circuit and a tail current source bootstrap circuit of the gain circuit, wherein a grounding end of the gain circuit is connected with a first end and a second end of the tail current source bootstrap circuit; an output end of the gain circuit is connected with a first input end of the output circuit and an input end of the tail current source bootstrap circuit respectively; an output end of the tail current source bootstrap circuit is connected a bias voltage, and connected with a second input end of the output circuit through a first resistor; and the second input end of the output circuit is connected with the output end of the gain circuit through a first capacitor. Based on an RC network consisting of the first resistor and the first capacitor, the operational amplifier generates a left-half plane null point z, and the left-half plane null point z and a first non-main pole of the operational amplifier can be counteracted by adjustment of the magnitude of the RC, so that frequency compensation of the operational amplifier is realized. Meanwhile, the unit gain bandwidth of the operational amplifier can be increased remarkably.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
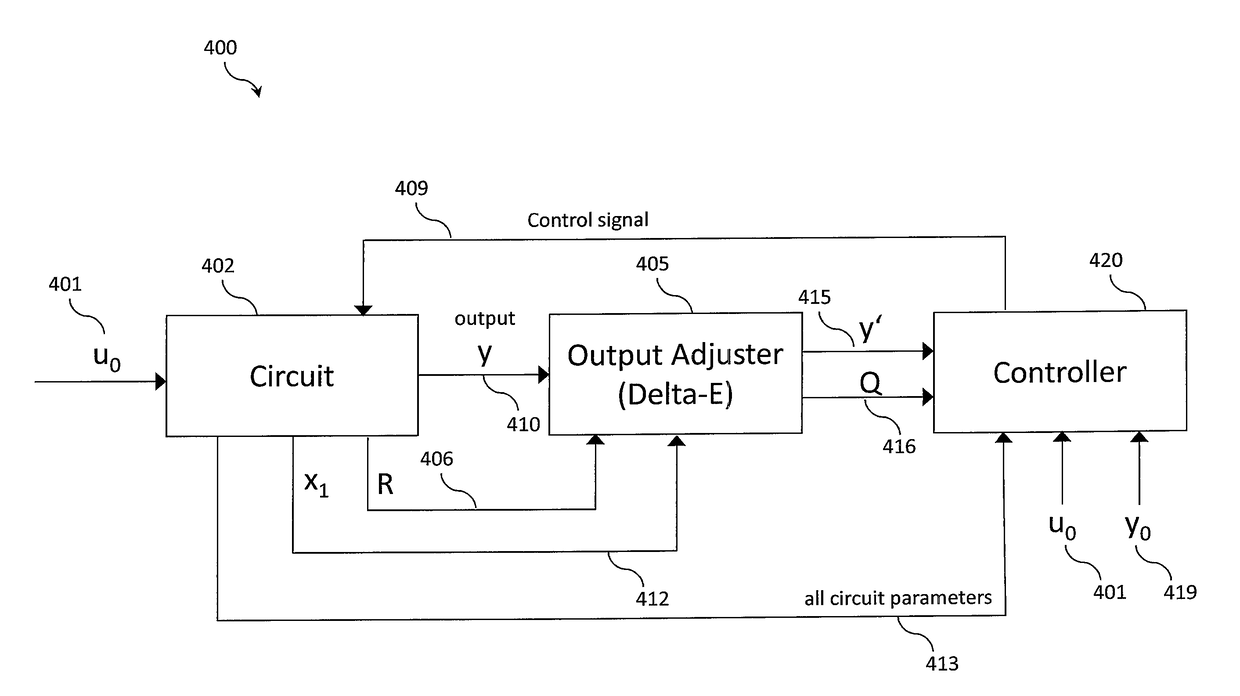
System and method for controlling output ripple of dc-dc converters with leading edge modulation control using current injection
In a preferred embodiment, a voltage converter comprises a voltage converter circuit, an output adjuster and a controller. The controller provides a control signal at a duty ratio determined dynamically by a set of input signals. The dynamic output adjuster determines the set of input signals by adjusting the ac component of an output voltage based on a gain Q. The dynamic output adjuster alleviates dependence on the value of Rc under leading edge modulation in either analog or digital converter systems. In addition to delivering the desired left half plane zero effects, dynamic output adjustment reduces the value of the output ripple. As a result, modern control methods such as input-output linearization can be used to design both boost and buck-boost PWM converters if only left half plane zero effects are present.
Owner:CIRASYS +1
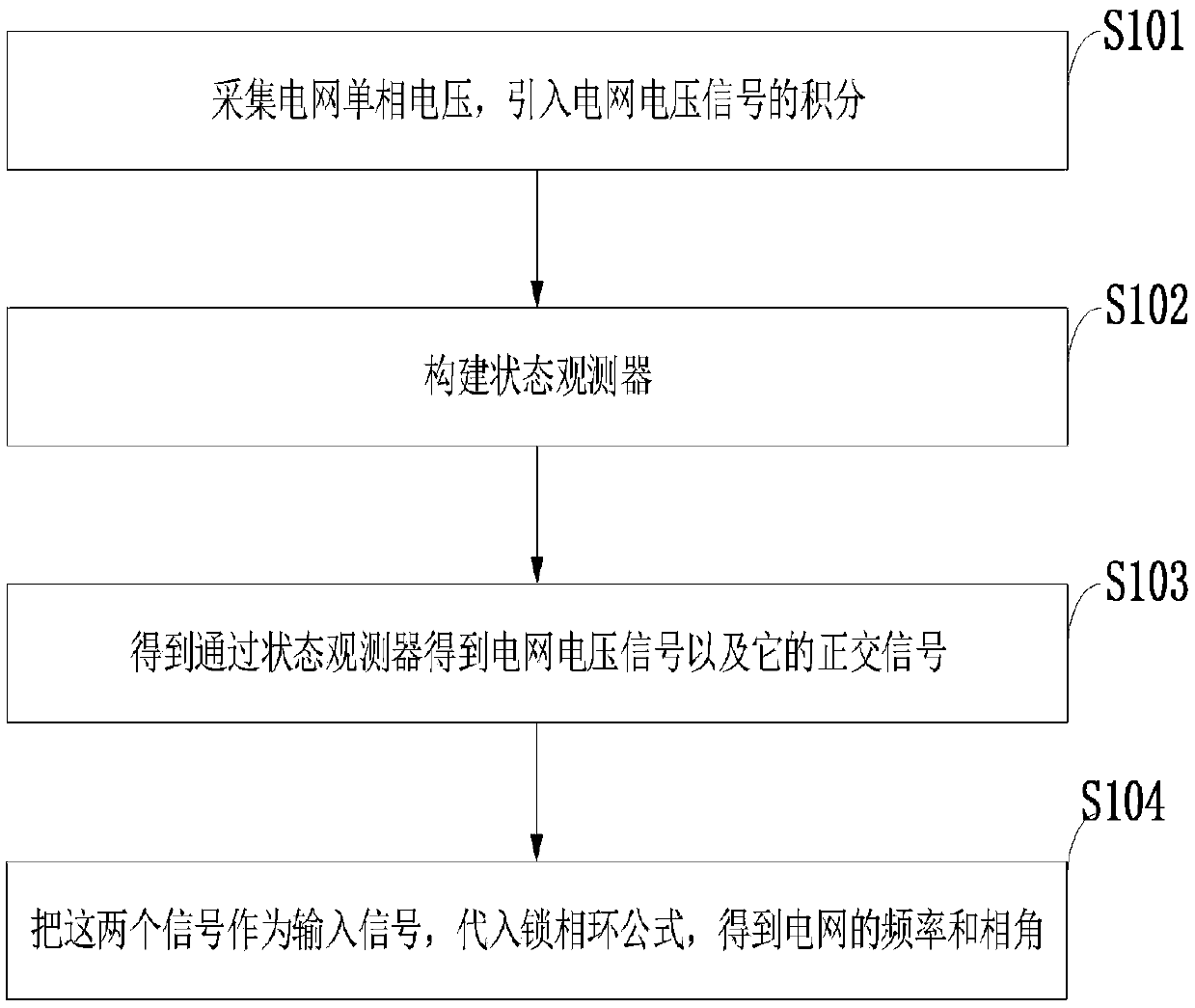
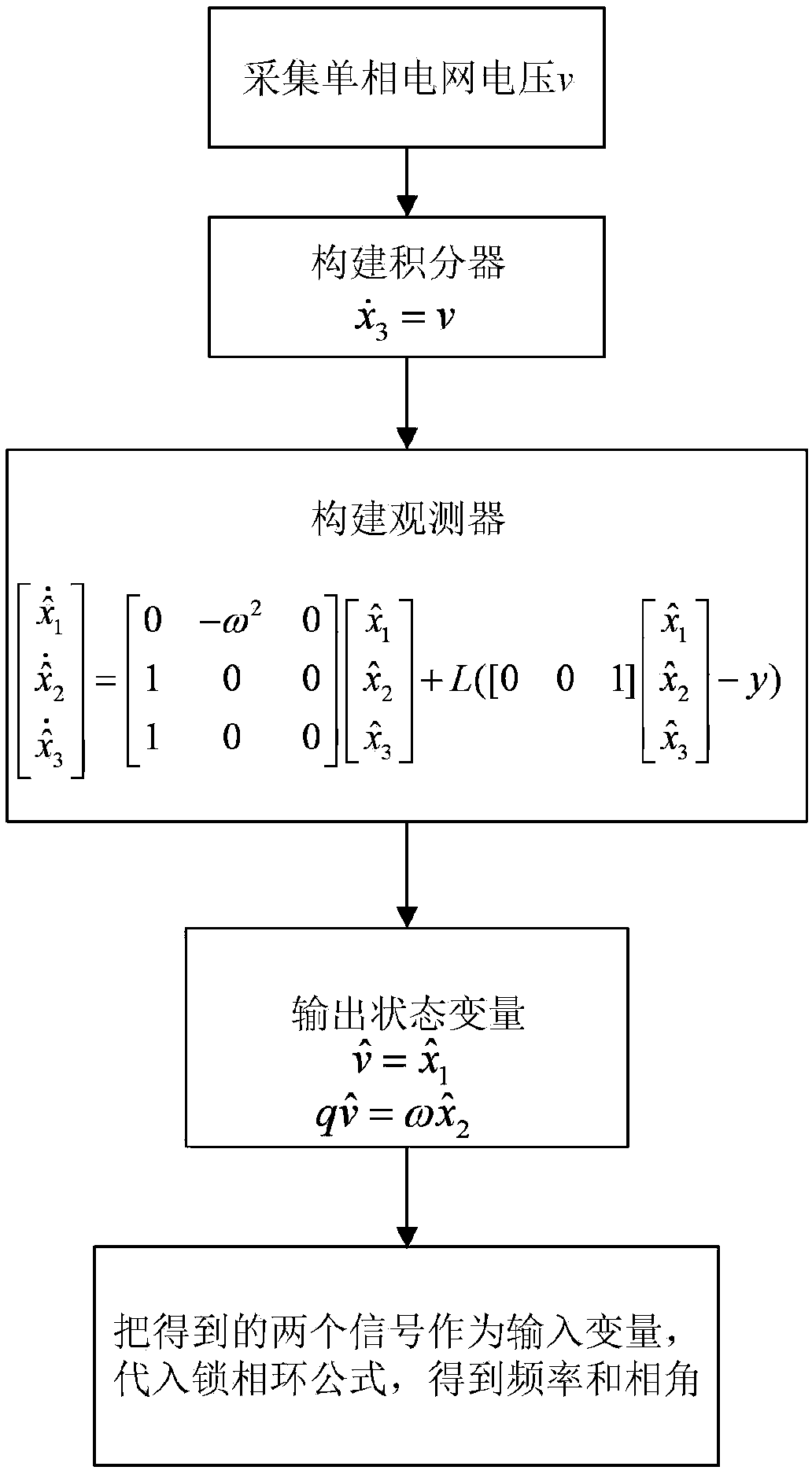
Power grid voltage frequency and phase angle detection method and system and single-phase power grid detection system
ActiveCN109557365AFlexible configurationFast dynamic responseVoltage-current phase angleFrequency measurement arrangementSingle phaseLeft half plane
The invention belongs to the technical fields of power grid performance testing devices and electrical fault detection devices, and discloses a power grid voltage frequency and phase angle detection method. The method comprises the steps that a single-phase power grid voltage signal is acquired, an integrator and a state observer are constructed, a power grid voltage signal and an orthogonal signal thereof are obtained and substituted into a phase-locked loop formula by serving as variables, and then frequency and phase angle information of a power grid is obtained. According to the method, key information such as the amplitude, the frequency and the phase angle of the power grid is measured by using a PLL; the dynamic response speed is high, and the excellent steady-state precision is achieved under the conditions of power grid frequency changes and harmonic interference; a QSG is designed from the angle of the observer, pole configuration is more flexible, poles can be configured ona left half plane arbitrarily, and the range that parameters can be adjusted is wider; and the dynamic response speed and the harmonic suppression capacity are high. When the method is used for measuring the power grid voltage, the better dynamic performance and the better harmonic suppression performance are achieved, the parameter configuration range is wider, and arbitrary configuration can beachieved on the left half plane.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Tracking converters with input output linearization control
ActiveUS9252683B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionVoltage converterLeading edge
In a preferred embodiment, a voltage inverter comprises a voltage converter circuit and a controller. The voltage inverter produces a time-varying output voltage from an input voltage, which can be a DC input voltage or an AC input voltage. The controller provides a control signal at a duty ratio determined dynamically by a set of signals. The set of signals include the time-varying output voltage, a predetermined output voltage, a gain factor and an inductor current in the voltage converter circuit. The predetermined output voltage can have an AC waveform or an arbitrary time-varying waveform. The voltage inverter operates to match the time-varying output voltage to the predetermined output voltage. Input-output linearization is used to design a buck inverter, and input-output linearization with leading edge modulation is used to design boost and buck-boost inverters under conditions where left half plane zero effects are present.
Owner:CIRASYS
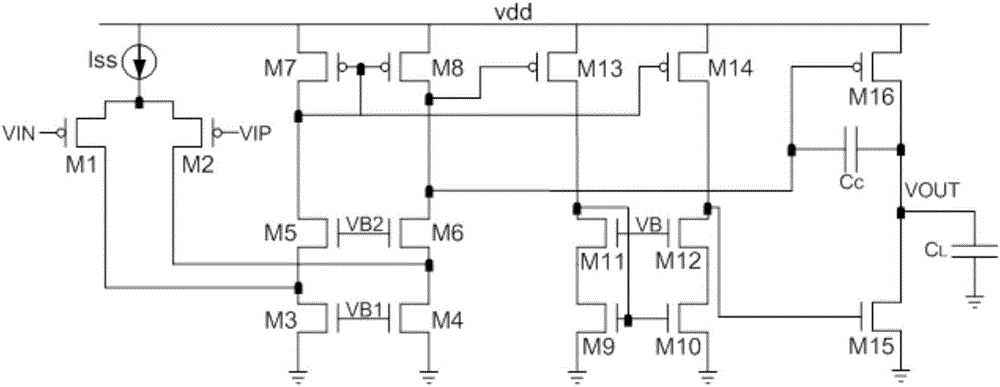
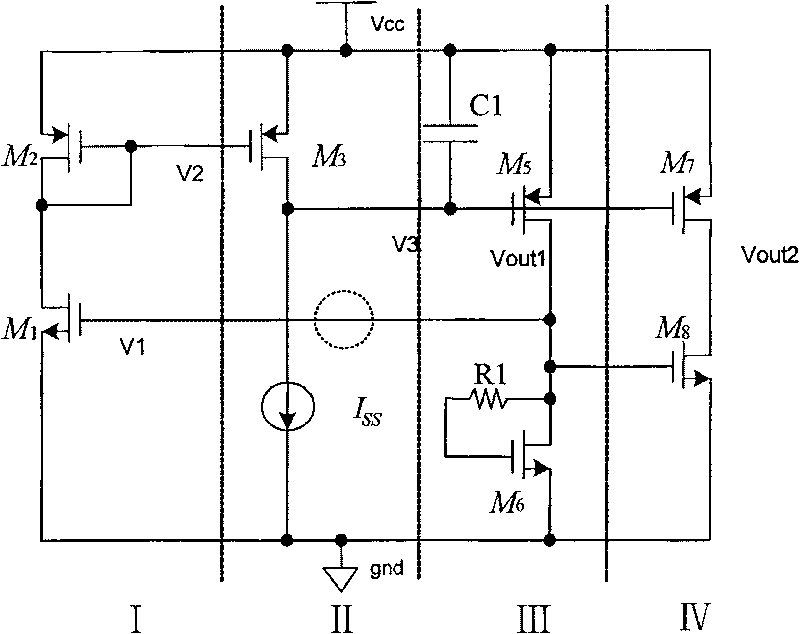
Three-stage transconductance amplifier
ActiveCN105897206ADoes not lower the dominant pole-3dB wide bandwidthDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a three-stage transconductance amplifier design. The three-stage transconductance amplifier is characterized in that NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tubes M3 / M4 / M5 / M6, PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tubes M1 / M2 / M7 / M8 and a tail current source Iss form a folding input structure and a first stage; NMOS tubes M9 / M10 / M11 / M12 and PMOS tubes M13 / M14 form a second stage; an NMOS tube M15 and a PMOS tube M16 form a third stage; NMOS tubes M17 / M18, PMOS tubes M19 / M20 and a capacitor Cc form a compensation structure; the input end of the compensation structure is connected to the output end of the second stage of the transconductance amplifier; and the output end of the compensation structure is connected to the output end of the transconductance amplifier. A power supply of the transconductance amplifier is vdd1, a power supply of the compensation structure is vdd2 and a capacitor CL represents a load capacitor of the transconductance amplifier. According to the three-stage transconductance amplifier, a left half plane zero is introduced into a product of a gain A of a gain stage and the capacitor Cc, so that a dominant pole of a transmission function of the three-stage transconductance amplifier is not reduced, and the transconductance amplifier is guaranteed to have relatively large -3dB bandwidth and unity-gain bandwidth.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
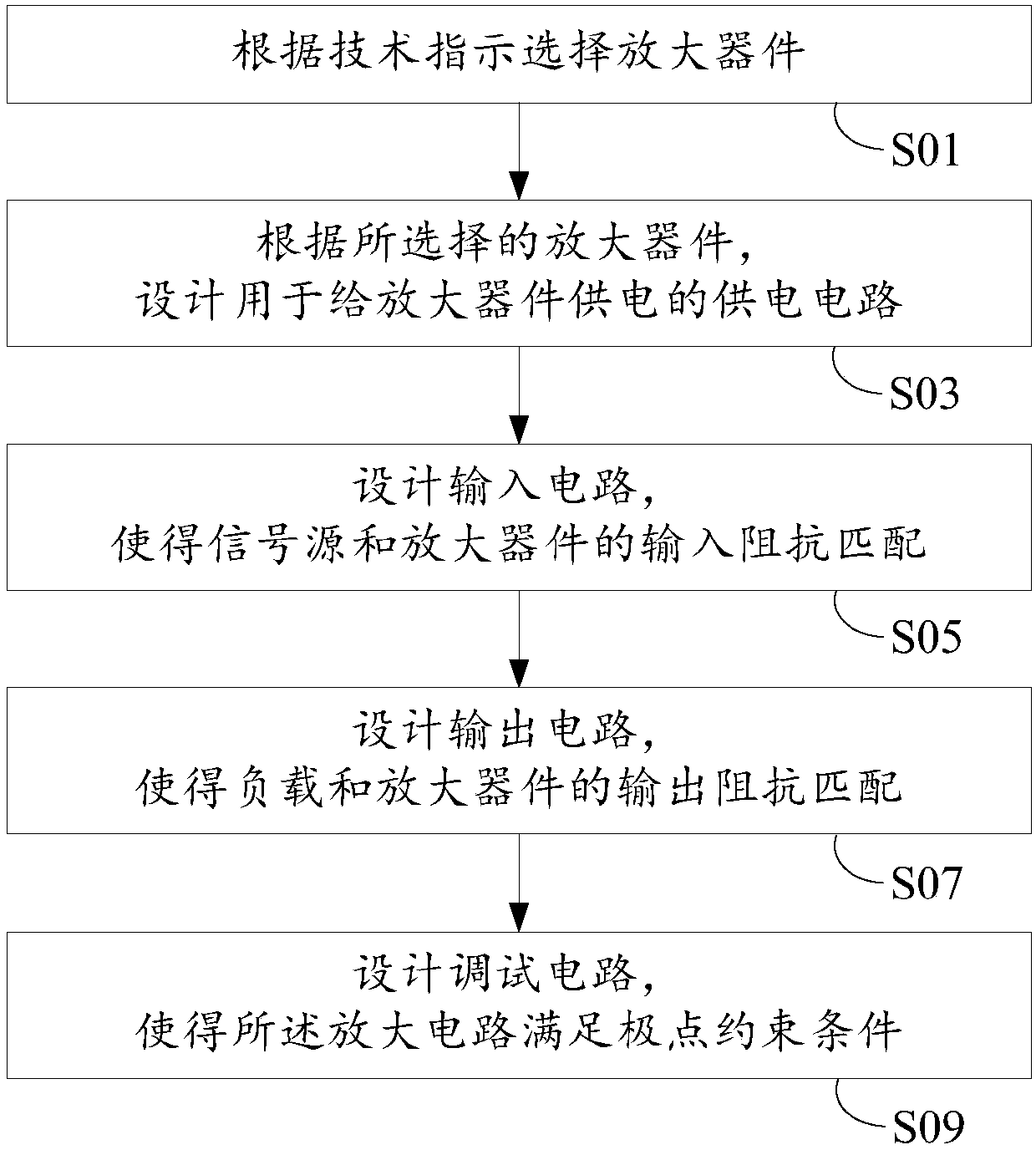
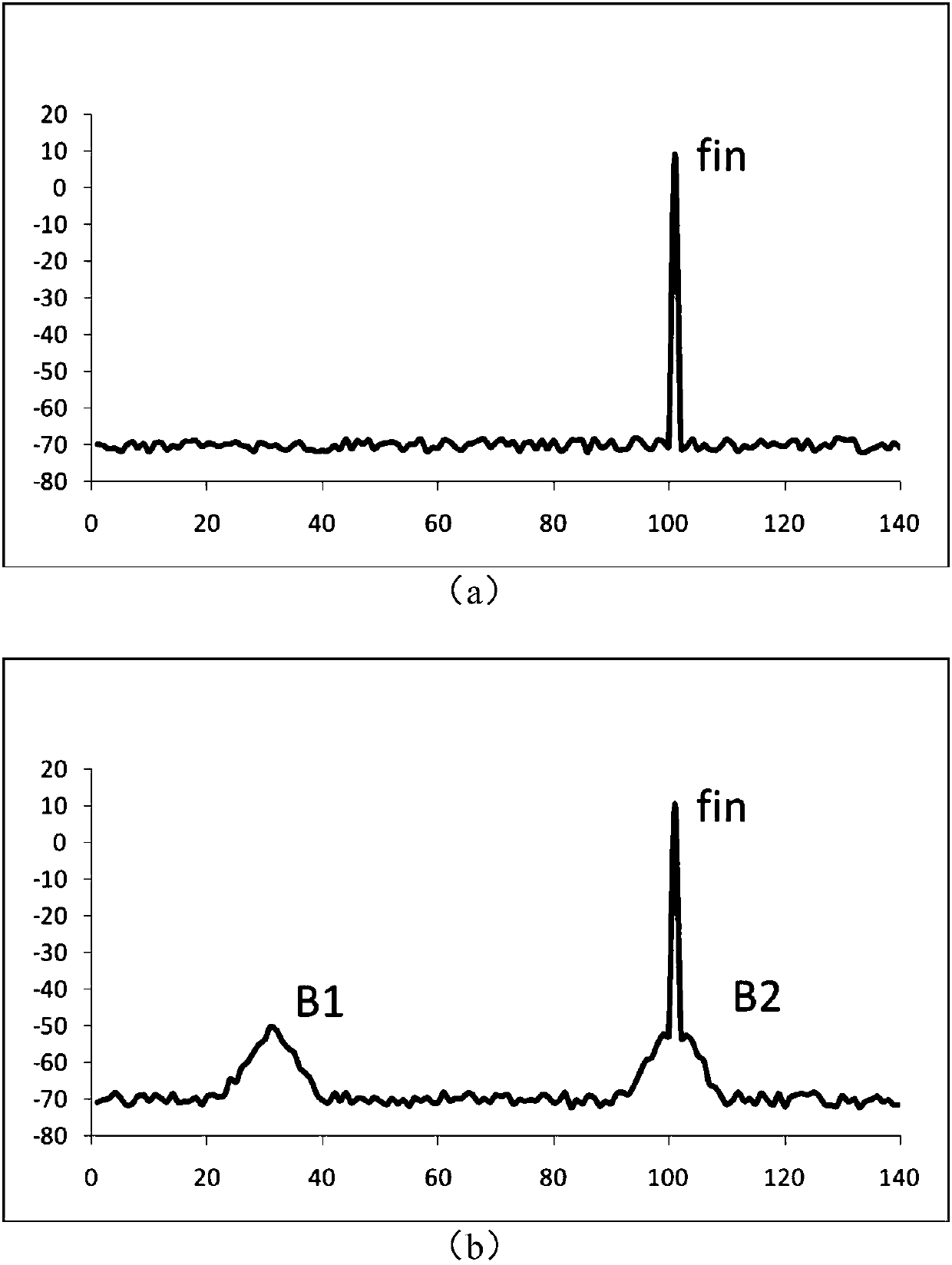
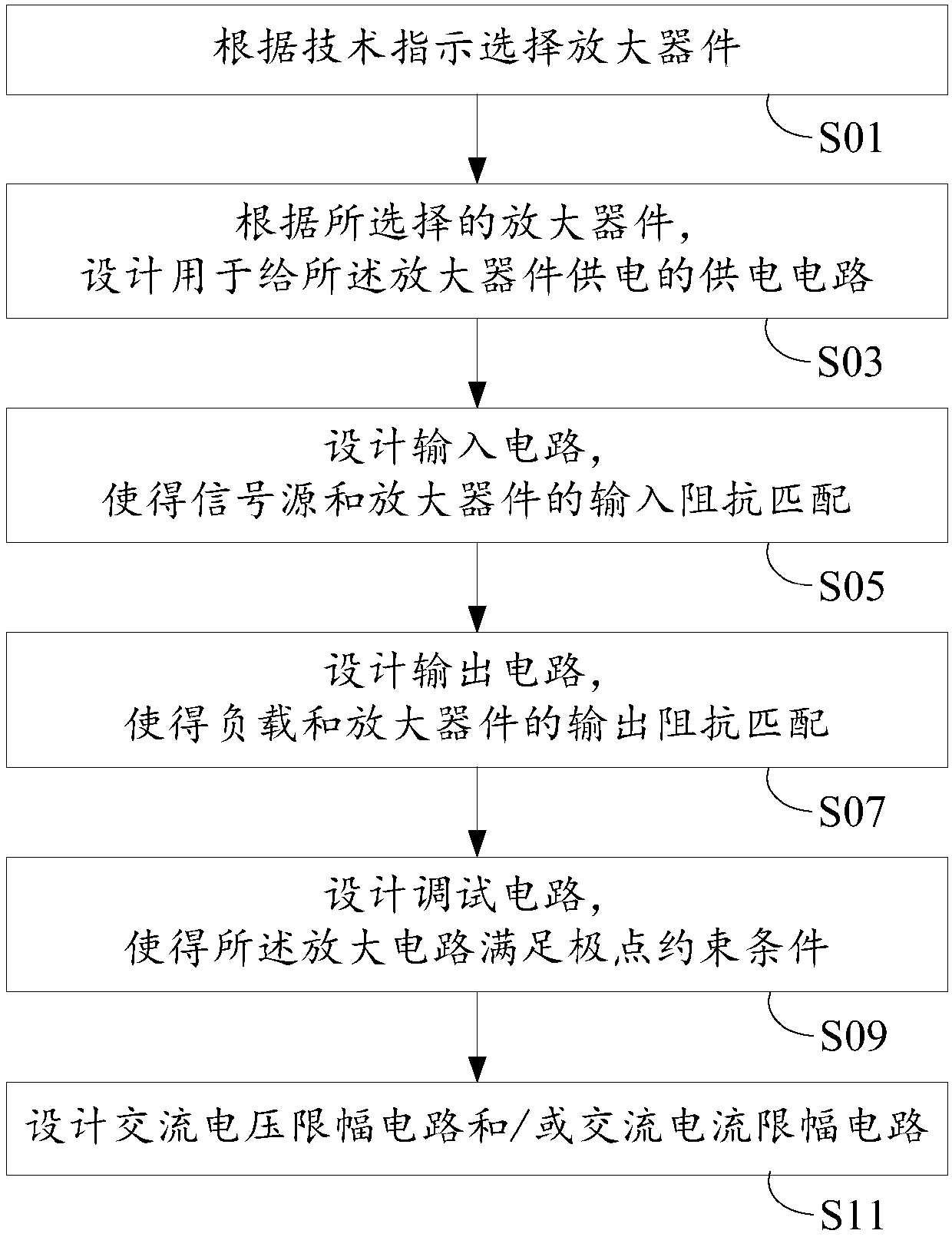
Design method of amplifying circuit and amplifying circuit
The invention discloses a design method of an amplifying circuit and the amplifying circuit. The design method comprises the steps that an amplifying device is selected according to a technical instruction; according to the selected amplifying device, a power supply circuit used for supplying power to the amplifying device is designed; an input circuit is designed, so that a signal source and theamplifying device are matched in input impedance; an output circuit is designed, so that a load and the amplifying device are matched in output impedance; and a debugging circuit is designed, so thatthe amplifying circuit meets a pole constraint condition, wherein the pole constraint condition comprises that at least one pole of the amplifying circuit in a complex plane moves from an initial position to a right half plane, a virtual axis or a position nearby the virtual axis at least along with increase of input signal power and is finally stabilized at the virtual axis, the right half planeor a left half plane. Compared with the prior art, the gain of the amplifying circuit is increased.
Owner:杨娇丽
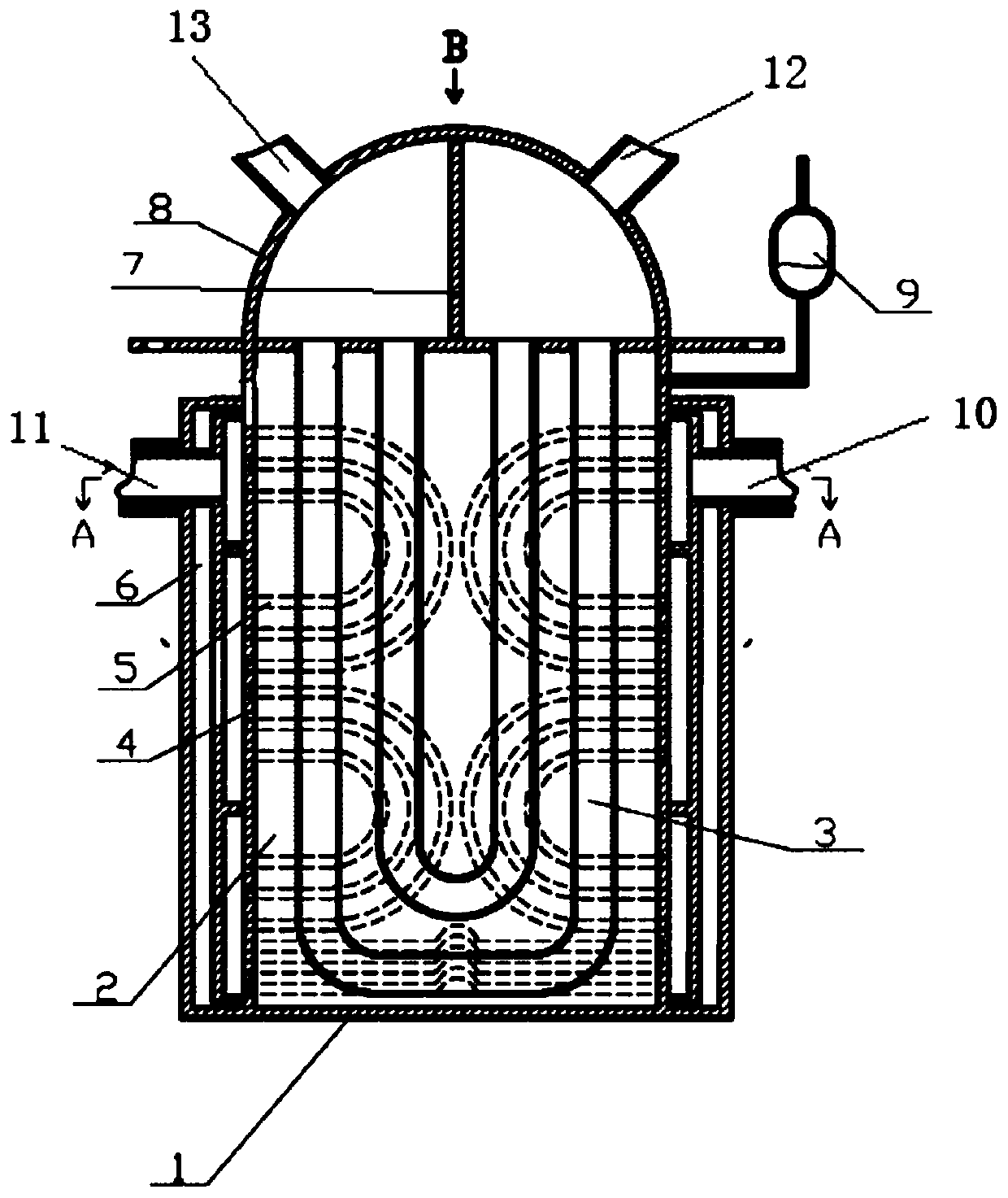
Cuboid sodium-sodium-water integrated steam generator
ActiveCN109737365AReduce the impactAvoid influenceStationary tubular conduit assembliesSteam generation using hot heat carriersRight half-planeHeat transfer efficiency
The invention relates to the technical field of nuclear power plant steam generators and particularly disk a cuboid sodium-sodium-water integrated steam generator. A barrel in the steam generator is of a cuboid shell structure. The upper end of the barrel is provided with an upper tube plate. A plurality of sodium-water heat transfer tubes are arranged in the barrel. The two ends of the sodium-water heat transfer tubes are arranged on a left half plane and a right half plane of the upper tube plate correspondingly. The upper end of the barrel is provided with an upper sealing head. The upper sealing head and the upper tube plate are divided into two independent spaces, namely, a steam chamber and a water supply chamber, through a vertical partition board, and the steam chamber and the water supply chamber communicate with two ports of each sodium-water heat transfer tube. The sodium-water heat transfer tubes are arranged in the barrel. The outer sidewall of the barrel is provided withan encircling plate. One ports of the sodium-water heat transfer tubes on the sidewall of the barrel are enclosed to form primary sodium inlets. The encircling plate encloses the other ports of the sodium-water heat transfer tubes to form primary sodium outlets. The steam generator provided by the invention improves the heat transfer efficiency. The number of sodium circulation processes is reduced to one. The resistance in the technological process is obviously reduced.
Owner:中核龙原科技有限公司 +1
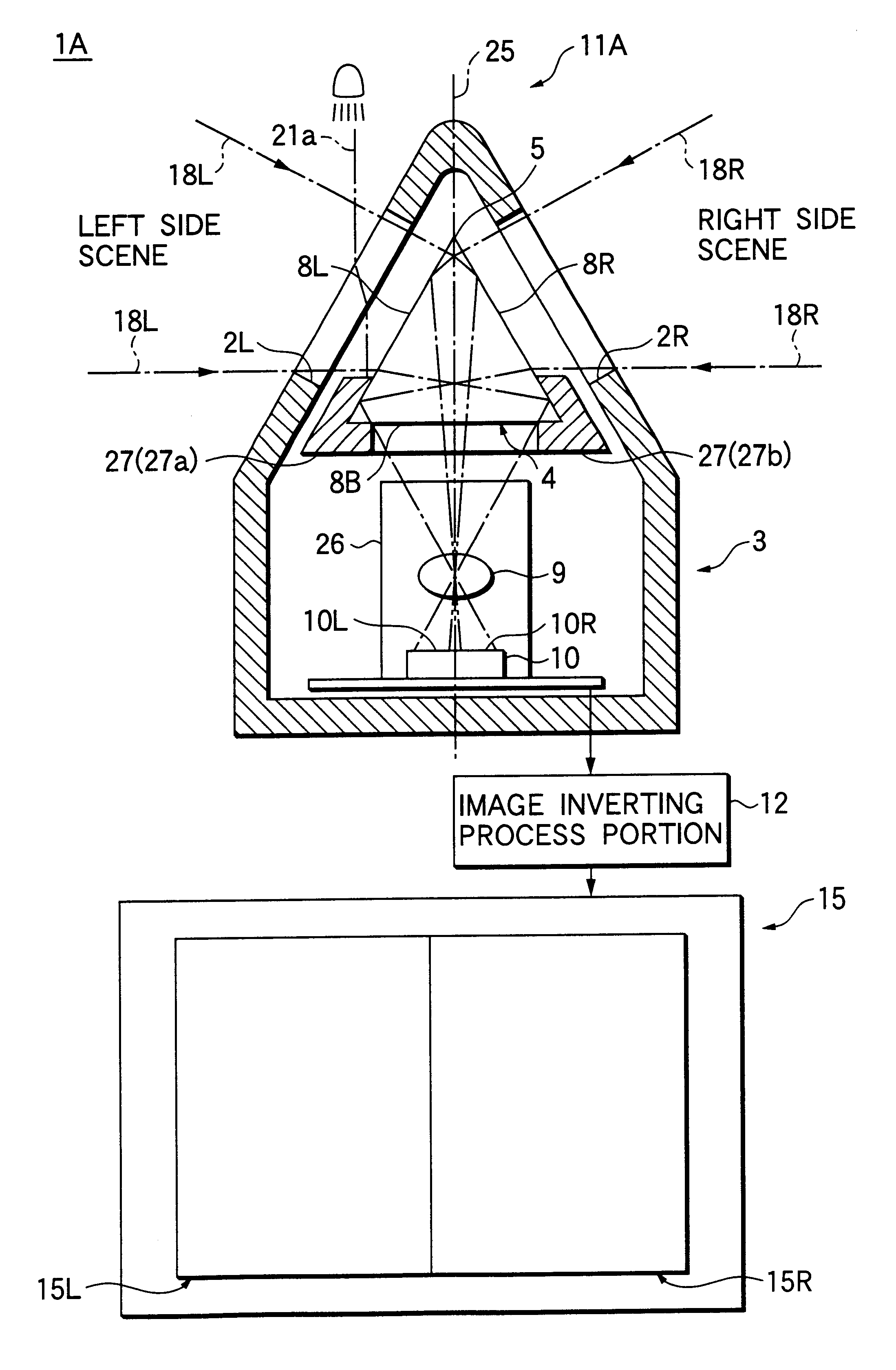
Vehicle surrounding viewing system
InactiveUS20010035904A1Detection of traffic movementColor television detailsRight half-planeOptoelectronics
In the vehicle surrounding viewing system 1A, the light shielding member 27, that is coated on the areas other than the effective area of the surface of the prism 4 provided in the case 3, can transmit only the ray of light 18L, that enters into the transmit window 2L of the case 3, then passes through the prism side surface 8L, and then internally reflects at the prism side surface 8R, and subsequently is focused by the focusing lens 9 to be guided to the left half plane 10L of the image pick-up plane of the image pick-up element 10, and also the ray of light 18R, that enters into the transmit window 2R of the case 3, then passes through the prism side surface 8R, and then internally reflects at the prism side surface 8L, and subsequently is focused by the focusing lens 9 to be guided to the right half plane 10R of the image pick-up plane of the image pick-up element 10.
Owner:AUTONETWORKS TECH LTD +2
Coupling delay synchronization network system and design method thereof
InactiveCN102231664AReduce operating energy consumptionEasy to controlEnergy efficient ICTHigh level techniquesSynchronization networksLeft half plane
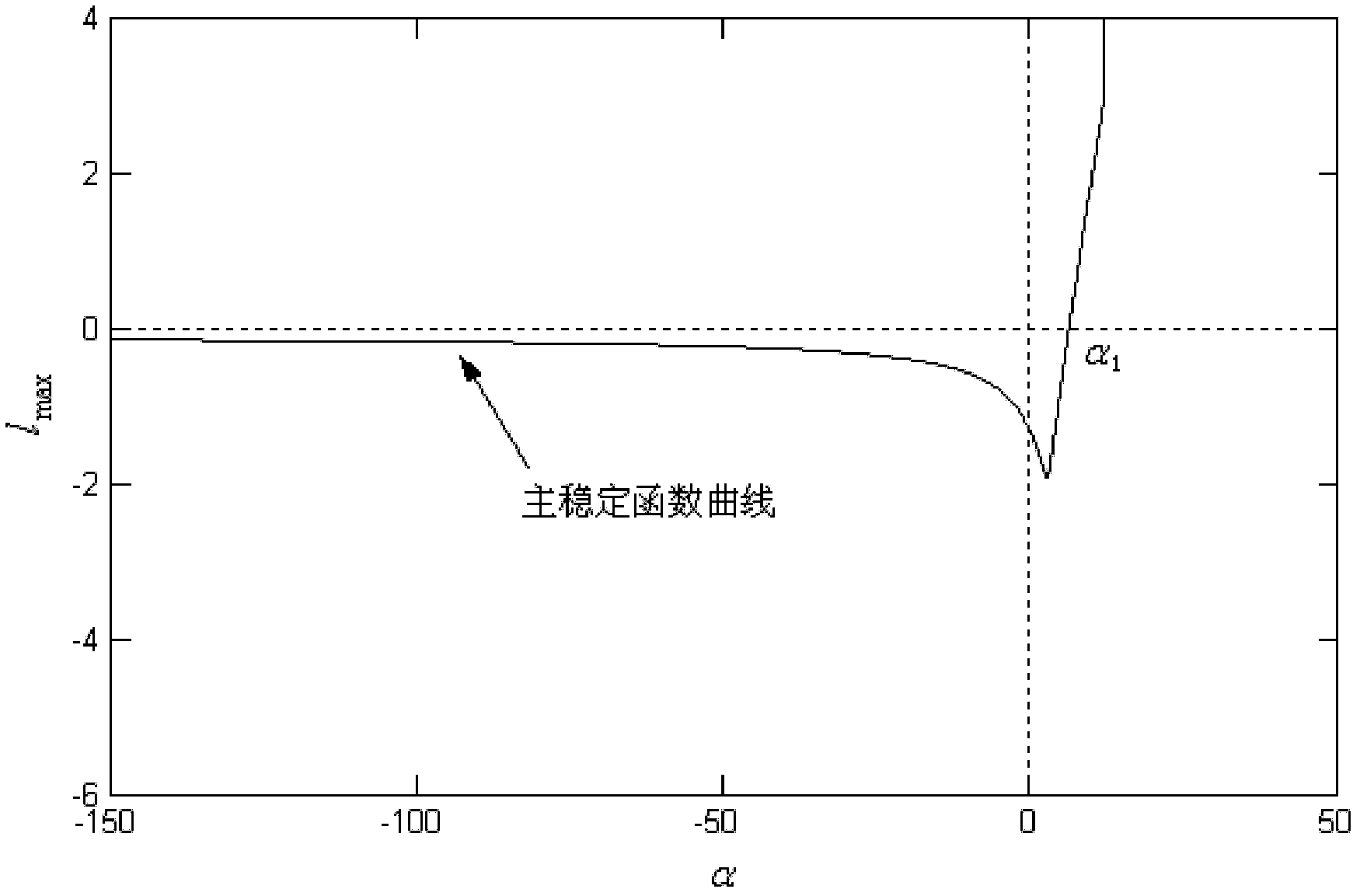
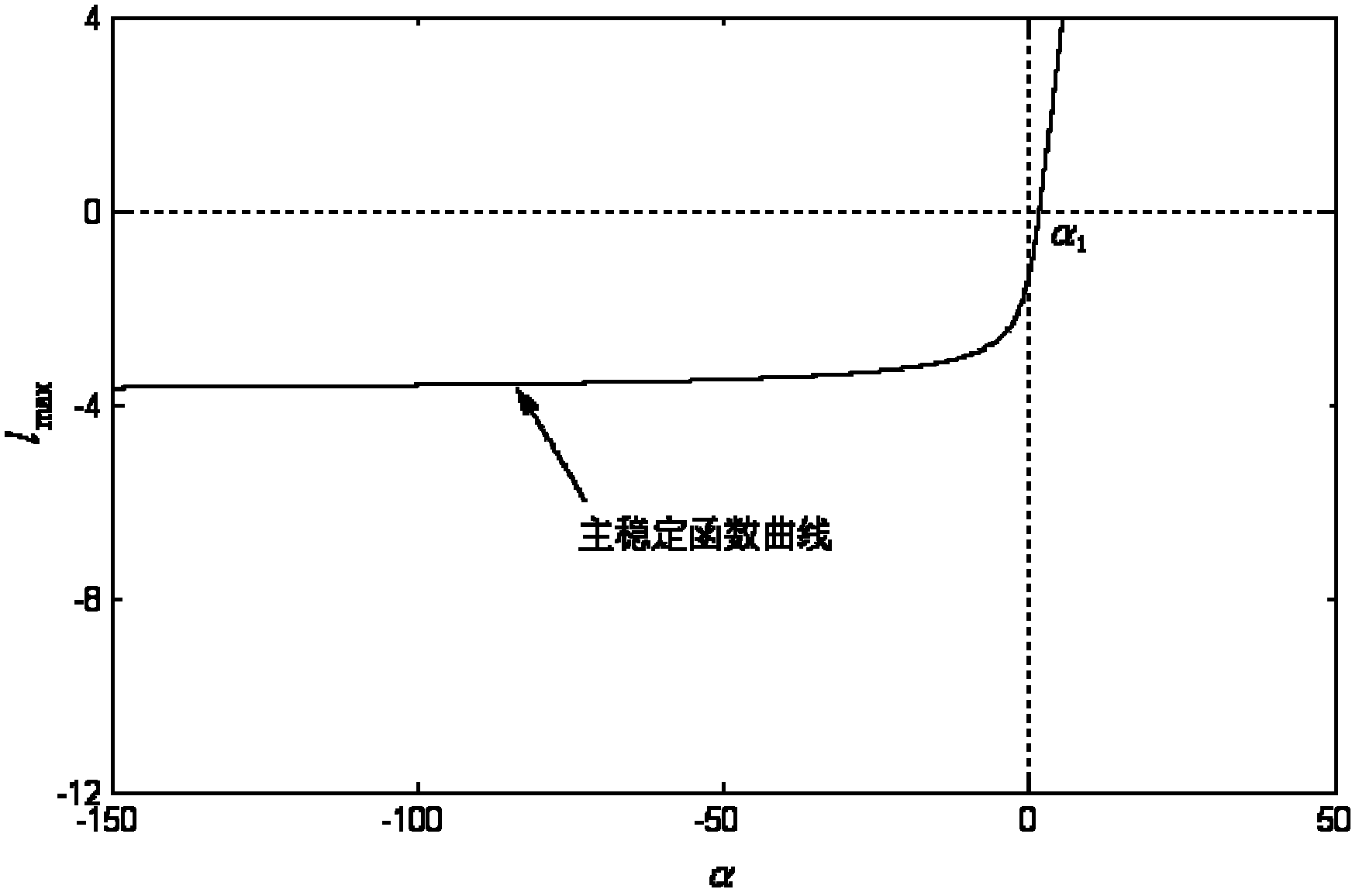
The invention discloses a coupling delay synchronization network system and a design method thereof, wherein the network disclosed by the invention is of a dissipation coupling structure; the infinite synchronization region (minus infinity, alpha 1) of the network covers a minus real axis; and a main stabilization function curve in a left half plane is monotonically decreased, thereby enabling the synchronization speed of the network to be slowed along with the increasing of the coupling intensity. The invention also provides the design method of the coupling delay synchronization network system with the nodes which are two-dimensional and three-dimensional power systems. In the method, the main stable stabilization function curve of the network is ensured to be monotonically decreased in the left half plane under the condition that the synchronization state is a balance point by virtue of computing the coupling matrix in the rank 1, thereby becoming a coupling delay synchronization network. The network disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the synchronization speed is unidirectionally changed along with the coupling intensity, thereby facilitating the regulation and control on the synchronization speed; the network design method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple computation, small parameters to be determined, less transmission signals needed by the network, and low operation energy consumption.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
A high-bandwidth high-gain trans-impedance amplifier applied to a large input capacitor
ActiveCN109861652AHigh gainHigh bandwidthAmplifier combinationsAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCapacitanceTransimpedance amplifier
The invention discloses a high-bandwidth high-gain trans-impedance amplifier applied to a large input capacitor, and belongs to the field of analog signal processing in laser three-dimensional imaging. The invention can adopt to application conditions of a large input capacitor, and can be especially applied to a large photosensitive surface avalanche diode array read-out circuit. The transimpedance amplifier comprises a slow path and a fast path, the slow path comprises two stages of amplifiers, the first stage of amplifier is a cascode structure formed by a second NMOS transistor and a firstNMOS transistor, the second stage of amplifier is a cascode amplifier formed by a sixth NMOS transistor MN6, and the slow path provides the main gain of the system; The eighth NMOS tube is a common-source amplifier, a fast channel is formed, a feedforward path is provided for the system, and the stability of the system is improved; The fast path and the slow path are connected in parallel in thesystem to generate a left half-plane zero point to replace a compensation capacitor in a traditional transimpedance amplifier, so that the Q value of the system is reduced, the stability of the transimpedance amplifier is realized, and the problem that the bandwidth and the gain of the traditional transimpedance amplifier are limited by the input capacitance of an avalanche diode is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
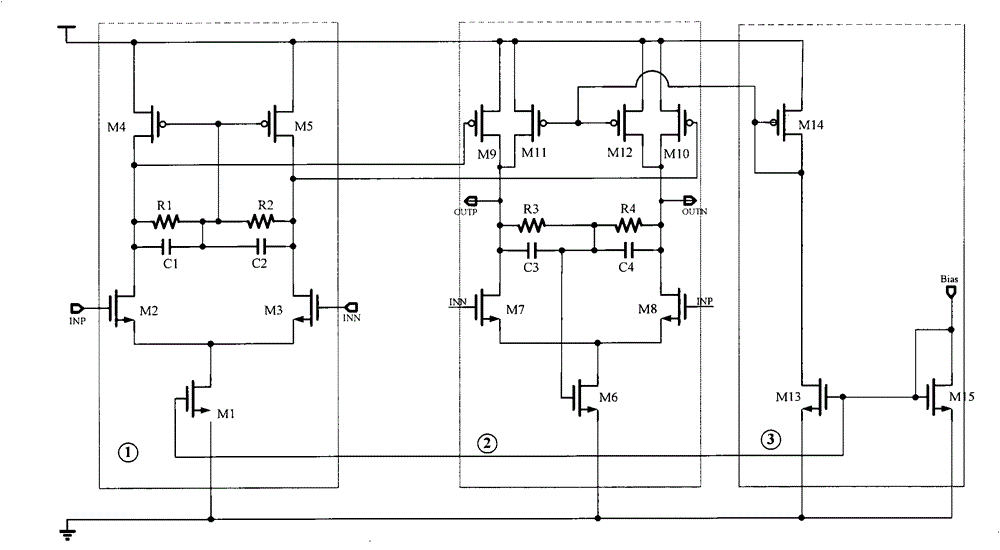
A Low Power Wideband Fully Differential Operational Amplifier
ActiveCN104639076BReduce power consumptionHigh bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCommunications systemHigh bandwidth
The invention relates to a lower-power-consumption broadband fully differential operational amplifier, and belongs to the field of analogue integrated circuits. An operational amplifier circuit is of a feed-forward zero compensation circuit structure. On the basis of an amplifier of a two-stage structure, a feed-forward path from input to output is additionally introduced, and in this way, a left half-plane zero point is formed on the basis of two poles and performs compensation on the phase to achieve stable operational amplification. Because miller compensation is not adopted for the structure, compared with the miller compensation structure, the position of the main pole is higher, and the lower-power-consumption broadband fully differential operational amplifier is more suitable for lower-power-consumption high bandwidth circuit design. The lower-power-consumption broadband fully differential operational amplifier is simple in structure, needs lower power consumption under the condition of meeting the requirement of achieving broadband application, and can meet the requirements of a wireless broadband communication system well.
Owner:BEIJING CEC HUADA ELECTRONIC DESIGN CO LTD
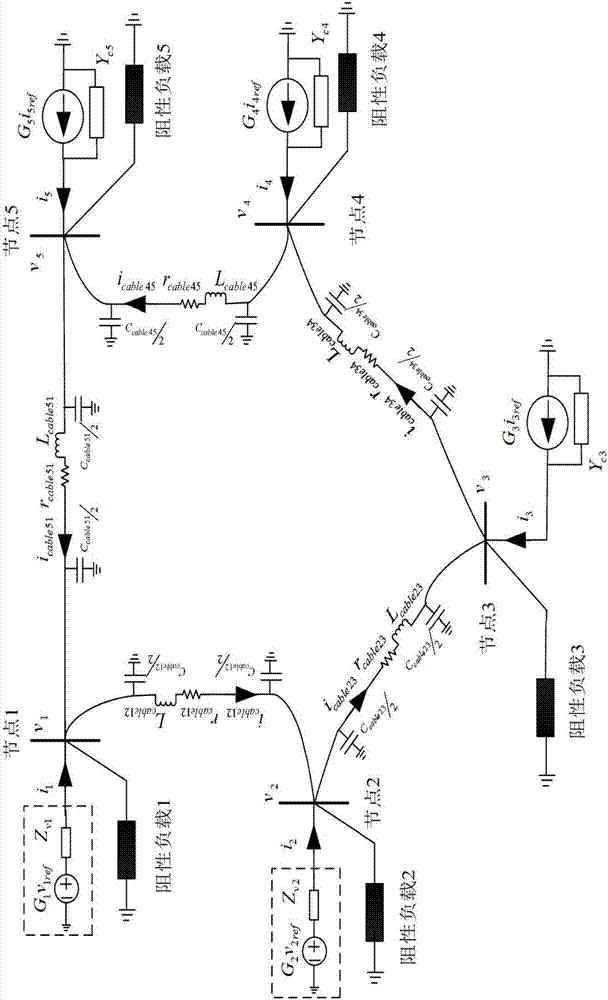
Stability determination method for DC distributed system in peer-to-peer control mode
The invention relates to the stability analysis technology of the DC distributed system and aims to provide a stability determination method for a DC distributed system in a peer-to-peer control mode.The method comprises steps that Thevenin / Norton equivalent is carried out for a power source or a load through utilizing a unit connection method, an impedance matrix or an admittance matrix is constructed according to impedance or admittance of the power source, the load or a system mode; each matrix is inputted to stability criteria to acquire characteristic values of a system, if the characteristic values of the system are all on a left half plane, the system is stable; if characteristic values of a right half plane are contained in the characteristic values of the system, the system isunstable. The method is advantaged in that the stability criteria has no specific requirements for the system structure, the method is suitable for radiation type systems and annular systems, and theapplication scope is wide; the method can be used for effectively analyzing stability of complex DC distributed systems including multi-sagging control type power sources, current control type power sources, constant current loads, constant power loads and system inter-node impedance, and impedance regulation measures are carried out to guarantee stability of the systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Dual-band detector based on indium selenide and gallium nitride and its preparation method
ActiveCN107331718BReduce power consumptionImprove detection efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIndiumRight half-plane
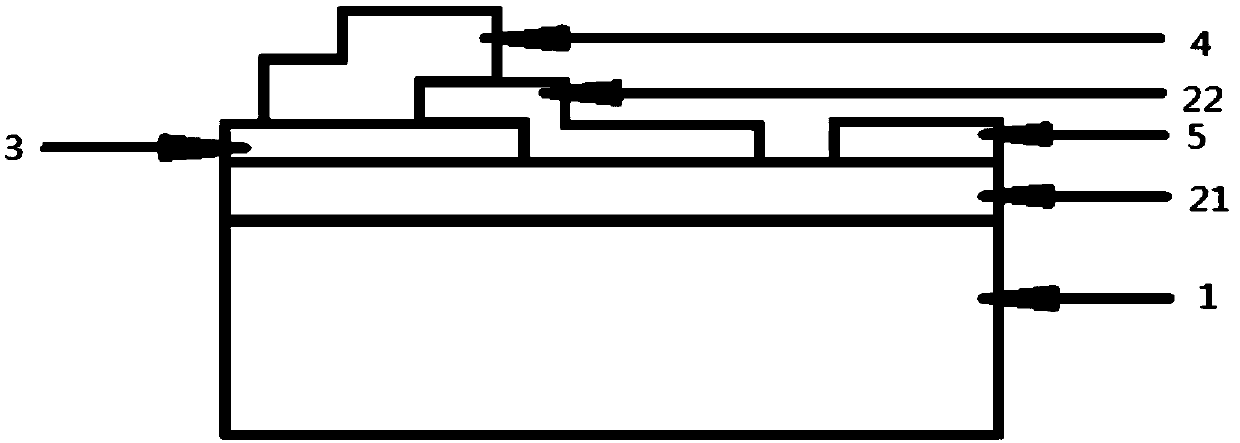
The invention discloses a bi-band detector based on indium selenide and gallium nitride and a preparation method thereof, and mainly solves the problem that simultaneous same-position detection in the prior art is impossible. The bi-band detector comprises a substrate (1), a UV absorption layer (2), an insulating layer (3), an infrared absorption layer (22) and two ohmic electrodes (4, 5), wherein the UV absorption layer is positioned on the substrate, the insulating layer is positioned on the left half plane of the UV absorption layer, a step surface is formed on the right half plane of the UV absorption layer, the left half portion of the infrared absorption layer is positioned on the insulating layer, the right half portion of the infrared absorption layer is positioned on the step surface of the UV absorption layer, the left half portion has a smaller area than the insulating layer, the right half portion has a smaller area than the step surface, a first ohmic electrode is positioned on the infrared absorption layer and has an area greater than the infrared absorption layer and smaller than the insulating layer, and the second ohmic electrode is positioned on the step surface of the UV absorption layer. The bi-band detector allows simultaneous UV and infrared bi-band detection, and improves the performance and detection efficiency of a detection system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Coupling accelerated synchronized network system and design method thereof
InactiveCN102427403ASynchronization speed is fastReduce operating energy consumptionSynchronising arrangementOperating energyNetwork on
The invention discloses a coupling accelerated synchronized network system and a design method thereof. A network provided by the invention has a dissipative coupling structure. A unique synchronization area of the network on the negative real axis is a synchronization area in the shape of (-infinity, alpha 1). The main stability function curve at the interval of (-infinity, alpha 1) shows monotone increasing so that the network synchronizing speed is accelerated with the increase of the coupling strength. The invention further provides a design method of the coupling accelerated synchronized network with nodes of two-dimensional and three-dimensional dynamic systems. The method ensures that the main stability function curve is in monotone increasing on the left half plane under the condition that the synchronization state of the network is at an equilibrium point through calculations over a coupled matrix in a rank 1, thereby a coupling accelerated synchronized network is formed. The network provided by the invention has the advantage that synchronization speed changes with the coupling strength in a monotone way, thus the synchronization speed is conveniently regulated and controlled. The network design method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple calculation, less parameters to be determined, less transmission signals needed by the network and low consumption of operating energy.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for controlling output ripple of DC-DC converters with leading edge modulation control using current injection
In a preferred embodiment, a voltage converter comprises a voltage converter circuit, an output adjuster and a controller. The controller provides a control signal at a duty ratio determined dynamically by a set of input signals. The dynamic output adjuster determines the set of input signals by adjusting the ac component of an output voltage based on a gain Q. The dynamic output adjuster alleviates dependence on the value of Rc under leading edge modulation in either analog or digital converter systems. In addition to delivering the desired left half plane zero effects, dynamic output adjustment reduces the value of the output ripple. As a result, modern control methods such as input-output linearization can be used to design both boost and buck-boost PWM converters if only left half plane zero effects are present.
Owner:CIRASYS +1
A three-stage transconductance amplifier
ActiveCN105897206BDoes not lower the dominant poleAchieve mutual cancellationDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a three-stage transconductance amplifier design. The three-stage transconductance amplifier is characterized in that NMOS (N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tubes M3 / M4 / M5 / M6, PMOS (P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tubes M1 / M2 / M7 / M8 and a tail current source Iss form a folding input structure and a first stage; NMOS tubes M9 / M10 / M11 / M12 and PMOS tubes M13 / M14 form a second stage; an NMOS tube M15 and a PMOS tube M16 form a third stage; NMOS tubes M17 / M18, PMOS tubes M19 / M20 and a capacitor Cc form a compensation structure; the input end of the compensation structure is connected to the output end of the second stage of the transconductance amplifier; and the output end of the compensation structure is connected to the output end of the transconductance amplifier. A power supply of the transconductance amplifier is vdd1, a power supply of the compensation structure is vdd2 and a capacitor CL represents a load capacitor of the transconductance amplifier. According to the three-stage transconductance amplifier, a left half plane zero is introduced into a product of a gain A of a gain stage and the capacitor Cc, so that a dominant pole of a transmission function of the three-stage transconductance amplifier is not reduced, and the transconductance amplifier is guaranteed to have relatively large -3dB bandwidth and unity-gain bandwidth.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
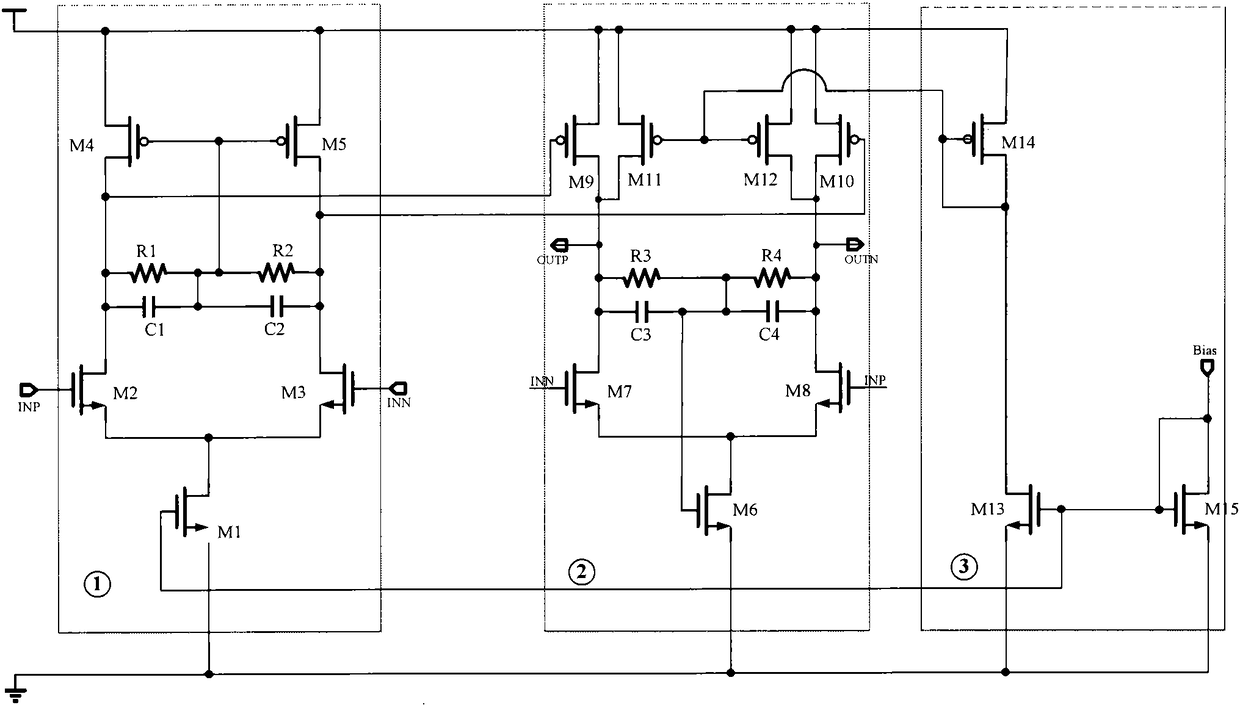
Operational Amplifier
ActiveCN106160683BImprove stabilityNo power consumptionDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Lower-power-consumption broadband fully differential operational amplifier
ActiveCN104639076AHigh bandwidthDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthHigh bandwidthAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a lower-power-consumption broadband fully differential operational amplifier, and belongs to the field of analogue integrated circuits. An operational amplifier circuit is of a feed-forward zero compensation circuit structure. On the basis of an amplifier of a two-stage structure, a feed-forward path from input to output is additionally introduced, and in this way, a left half-plane zero point is formed on the basis of two poles and performs compensation on the phase to achieve stable operational amplification. Because miller compensation is not adopted for the structure, compared with the miller compensation structure, the position of the main pole is higher, and the lower-power-consumption broadband fully differential operational amplifier is more suitable for lower-power-consumption high bandwidth circuit design. The lower-power-consumption broadband fully differential operational amplifier is simple in structure, needs lower power consumption under the condition of meeting the requirement of achieving broadband application, and can meet the requirements of a wireless broadband communication system well.
Owner:BEIJING CEC HUADA ELECTRONIC DESIGN CO LTD
Resistance-capacitance type ring oscillator
InactiveCN101174815BLow costSimple structureOscillations generatorsResistance capacitanceRight half-plane
The present invention discloses a resistor-capacitor type ring oscillator, including two current paths and two gained phase modulation branches. The first current path including an NMOS transistor M1and a PMOS transistor M2, the second current path consist of a PMOS transistor M3 and a current source Iss in tandem connection, the first gained phase modulation branch includes a capacitor C1, a resistor R1, a PMOS transistor M5 and a PMOS transistor M6, the second gained phase modulation branch consist of a fourth PMOS transistor and a fourth NMOS transistor in tandem connection. The present invention is characterized in that the transfer function of a first loop generates a low frequency left half-plane zero point at the first gained phase modulation branch and couples with a right half-plane zero point at the second current path through the second modulation branch, thereby satisfying the Barkhausen rule and achieving an oscillation. The oscillator has a simple structure, a low implementation cost and generates the oscillation with the frequency of 1.544 M in the working range of 2.7 to 5V with the stability as high as 407 ppm.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for compensating common mode feedback circuit frequency of two-stage amplifier
InactiveCN101373956BImprove phase marginImprove stabilityDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesDual stageControl signal
The invention discloses a common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method of a dual-stage amplifier, which belongs to the analog integrated circuit design field. One common-mode feedback circuit is adopted in the dual-stage amplifier to reduce the area and the power consumption of the feedback circuit; the dual-stage amplifier adopts a fully-differential input / output structure; a differential output terminal is used for sampling the common-mode output level; a first-stage amplifying circuit thereof comprises a controllable biasing circuit; a common-mode feedback control signal controls the first-stage common-mode output level and the second-stage common-mode output level of the amplifier at the same time through the controllable biasing circuit; a feedback amplifier is realizedby adopting a dual-stage operational amplifier with miller compensation. The left half plane zero point generated by the feedback amplifier in a loop circuit counteracts a certain left half plane pole in a prime amplifier, thereby forming a stable compensation loop circuit. The common-mode feedback circuit frequency compensation method has the advantages of less feedback circuit elements, lower feedback circuit power consumption, high low-frequency loop gain and better compensation phase margin.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com