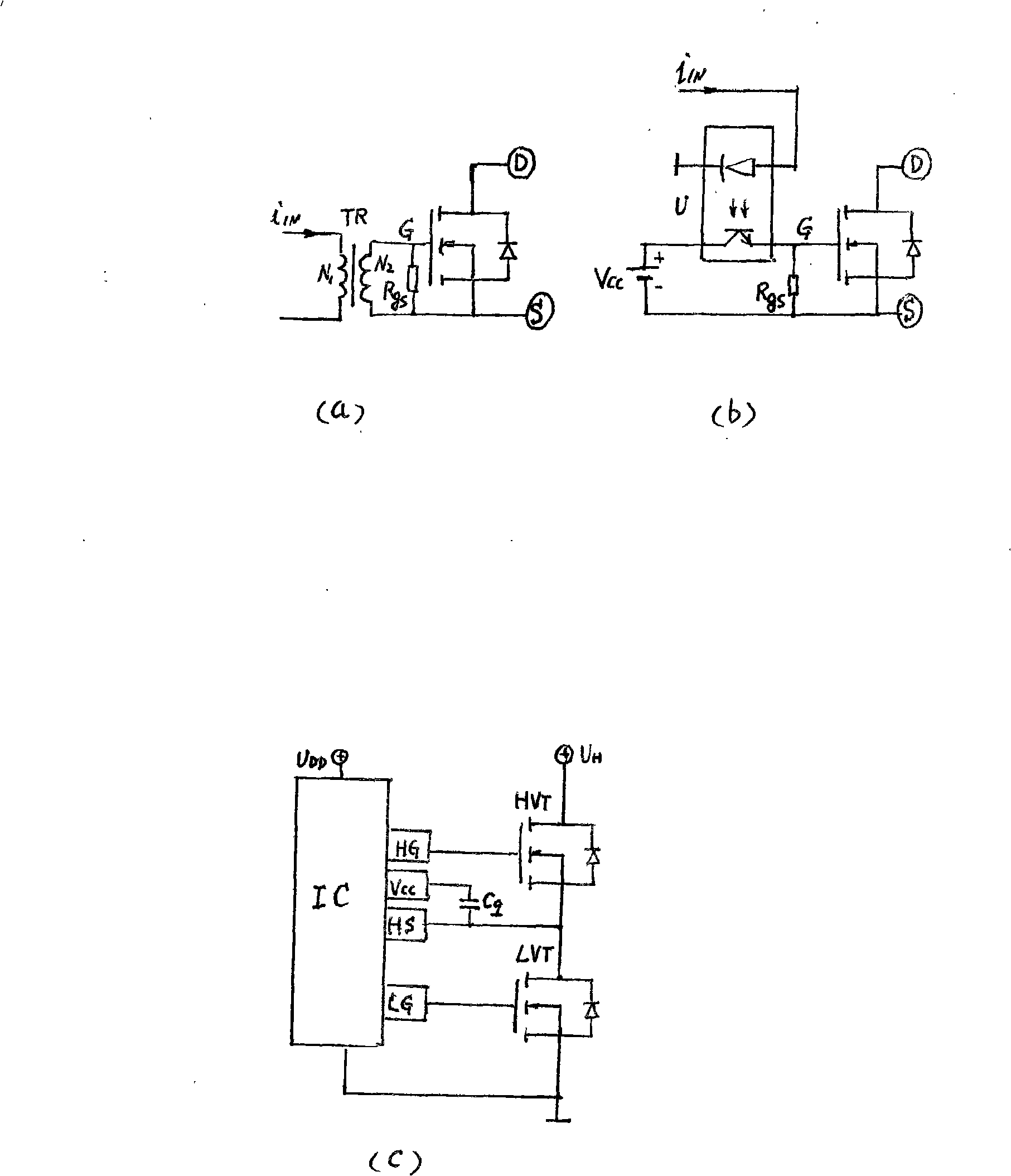
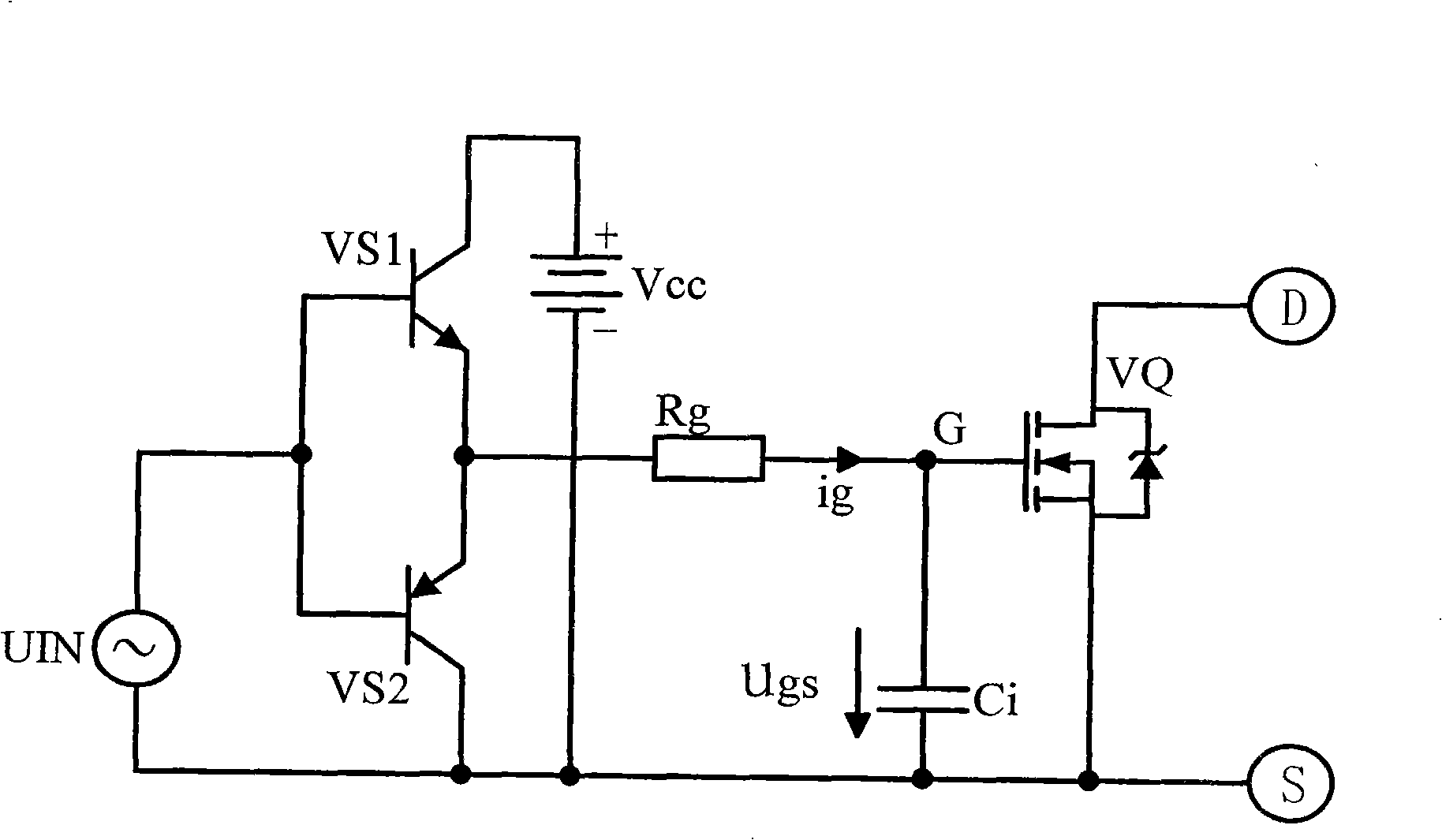
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Miller effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
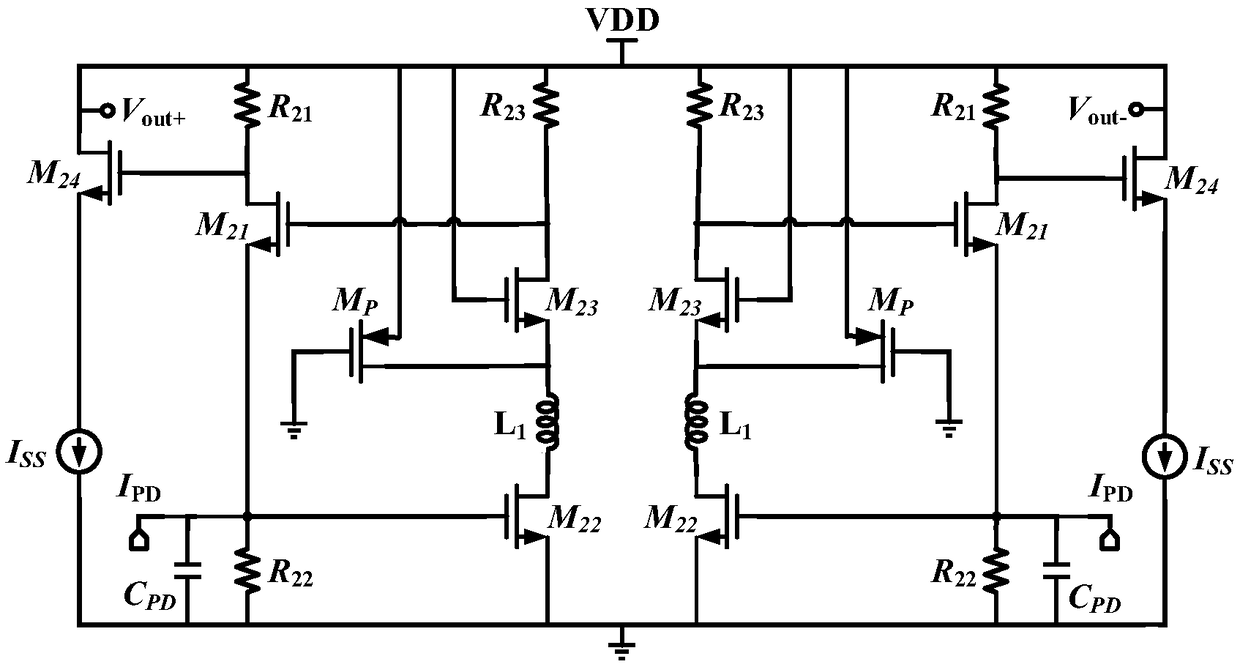
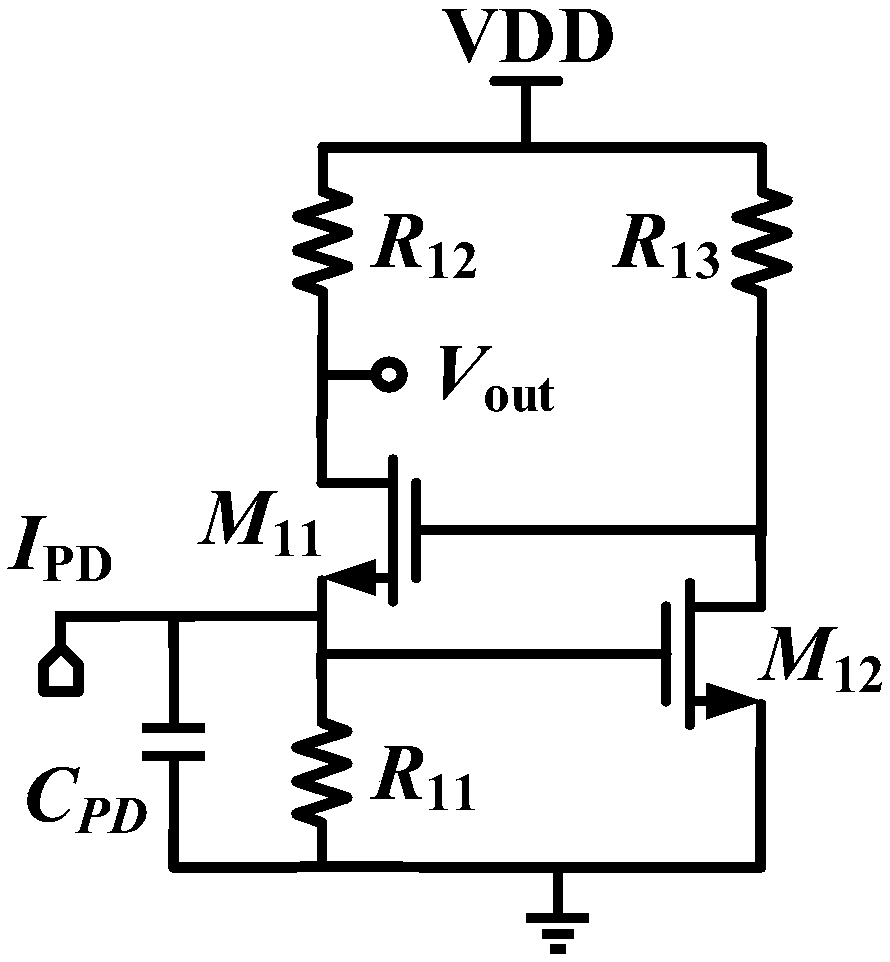
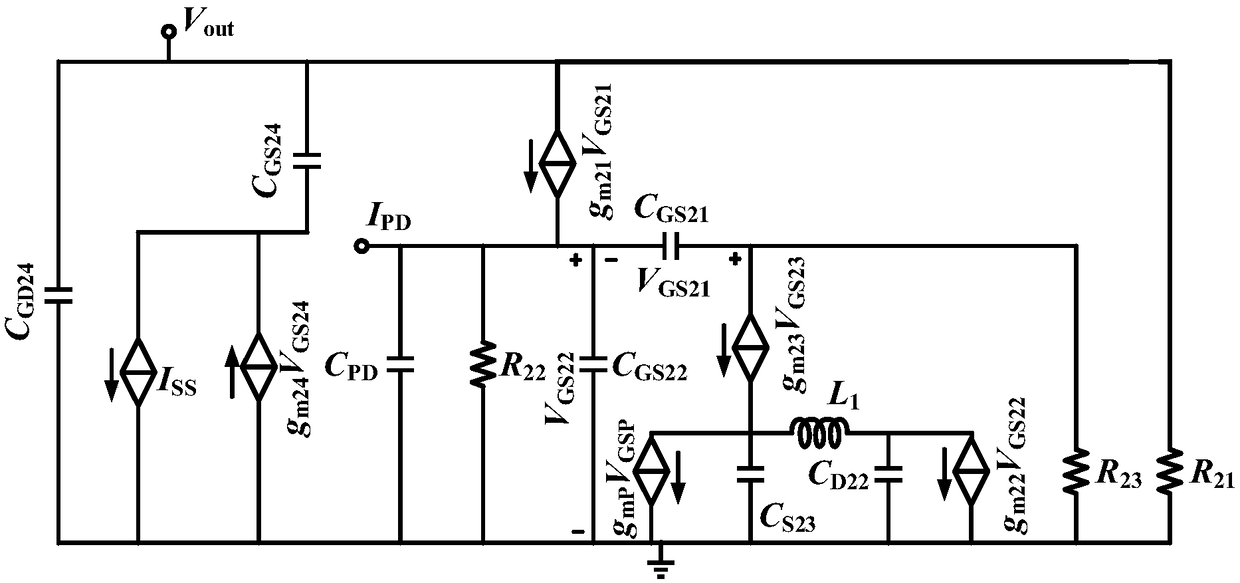
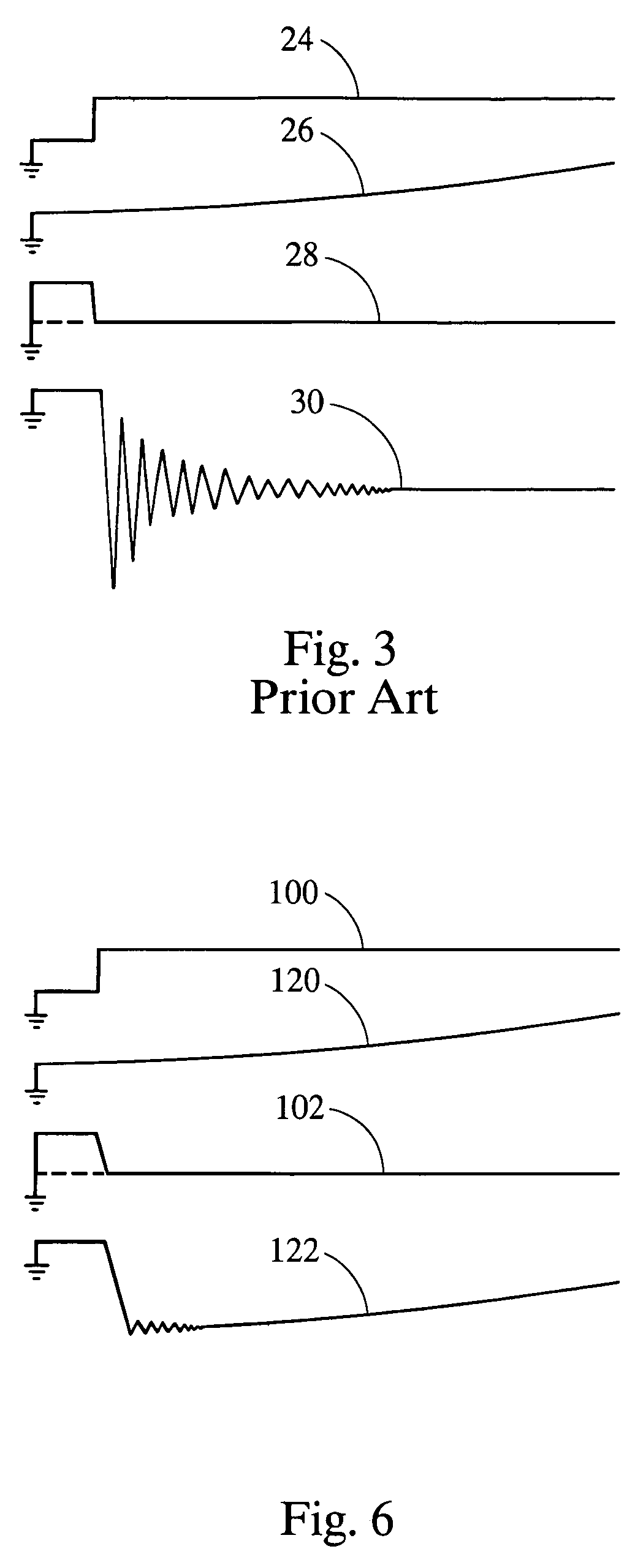
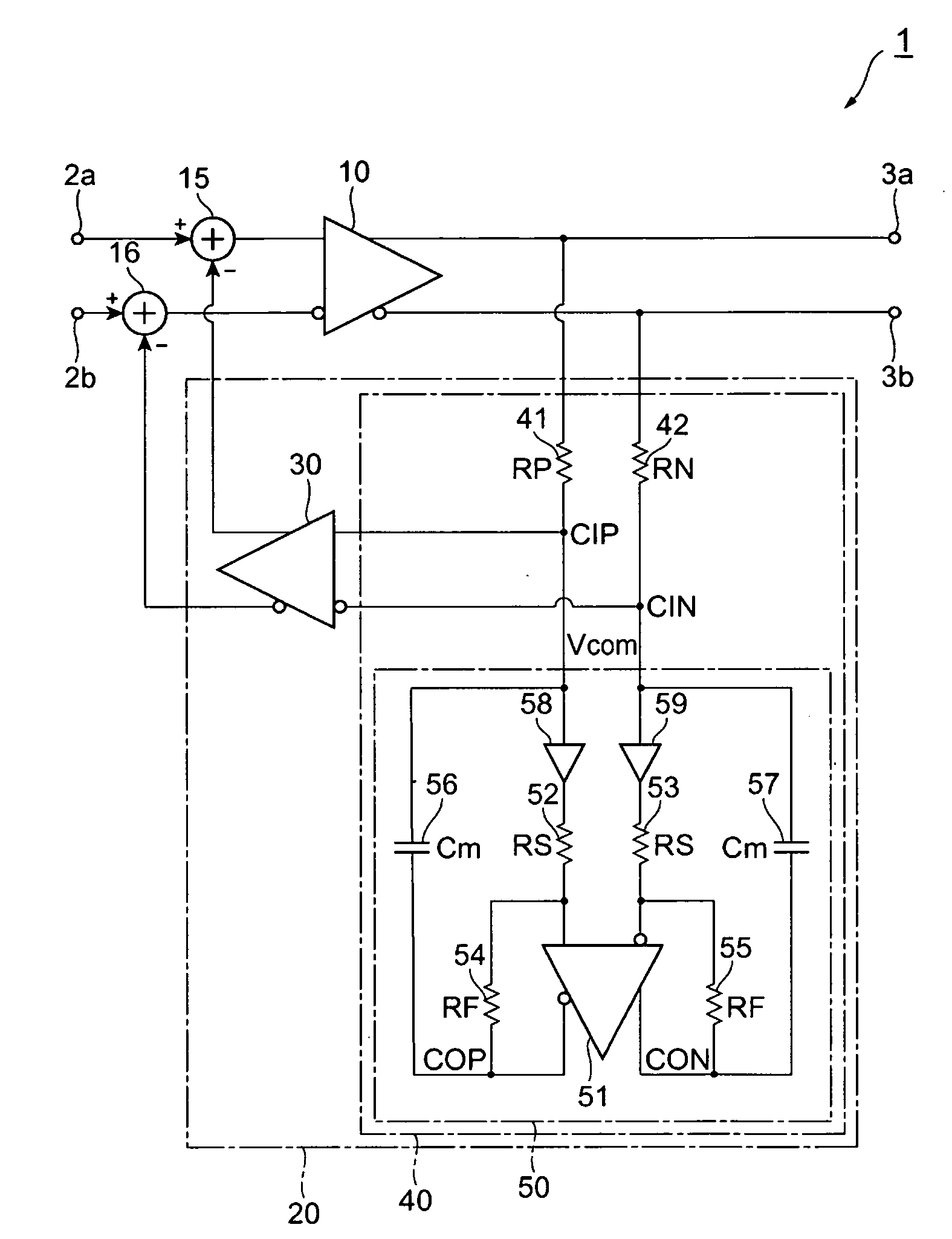
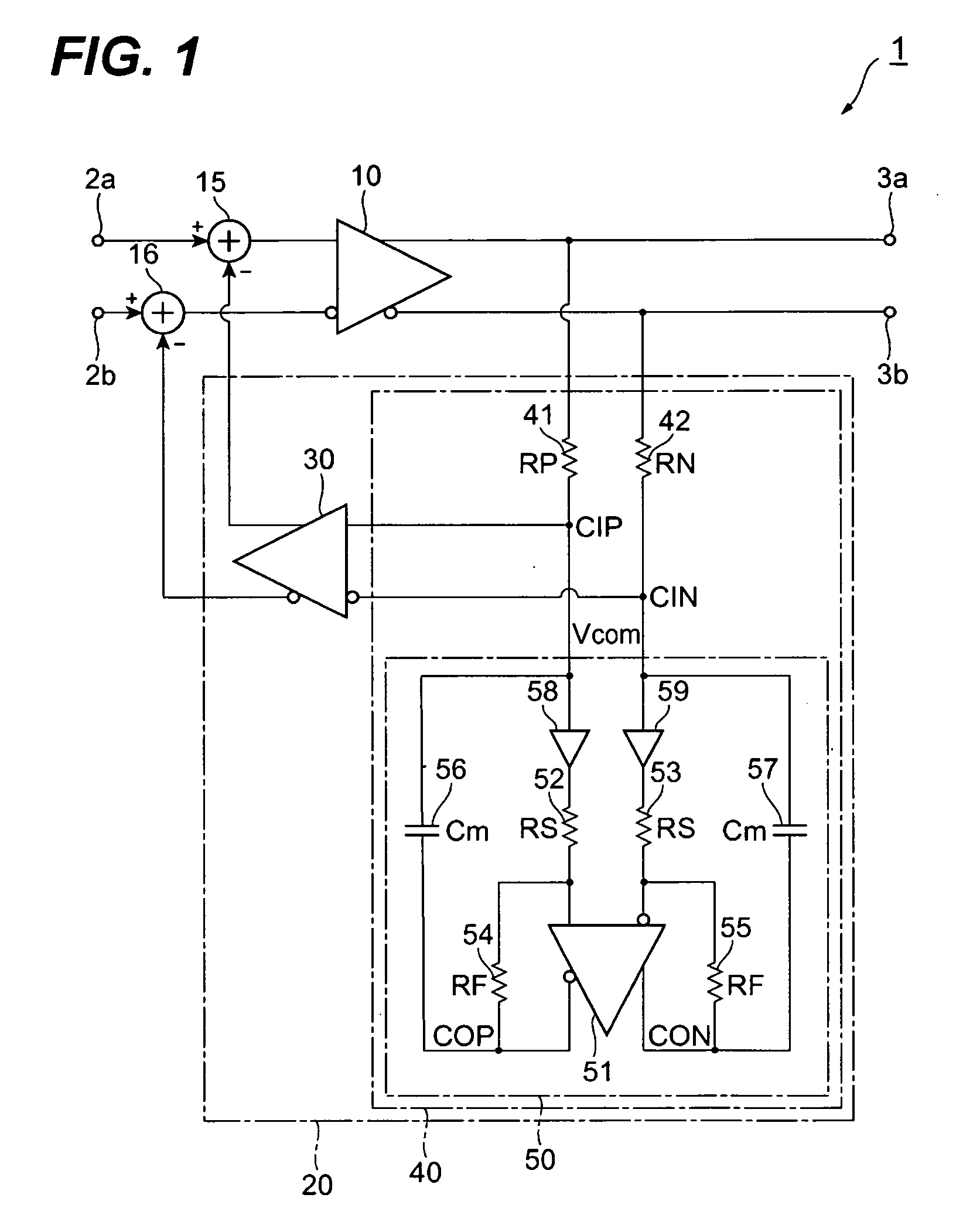
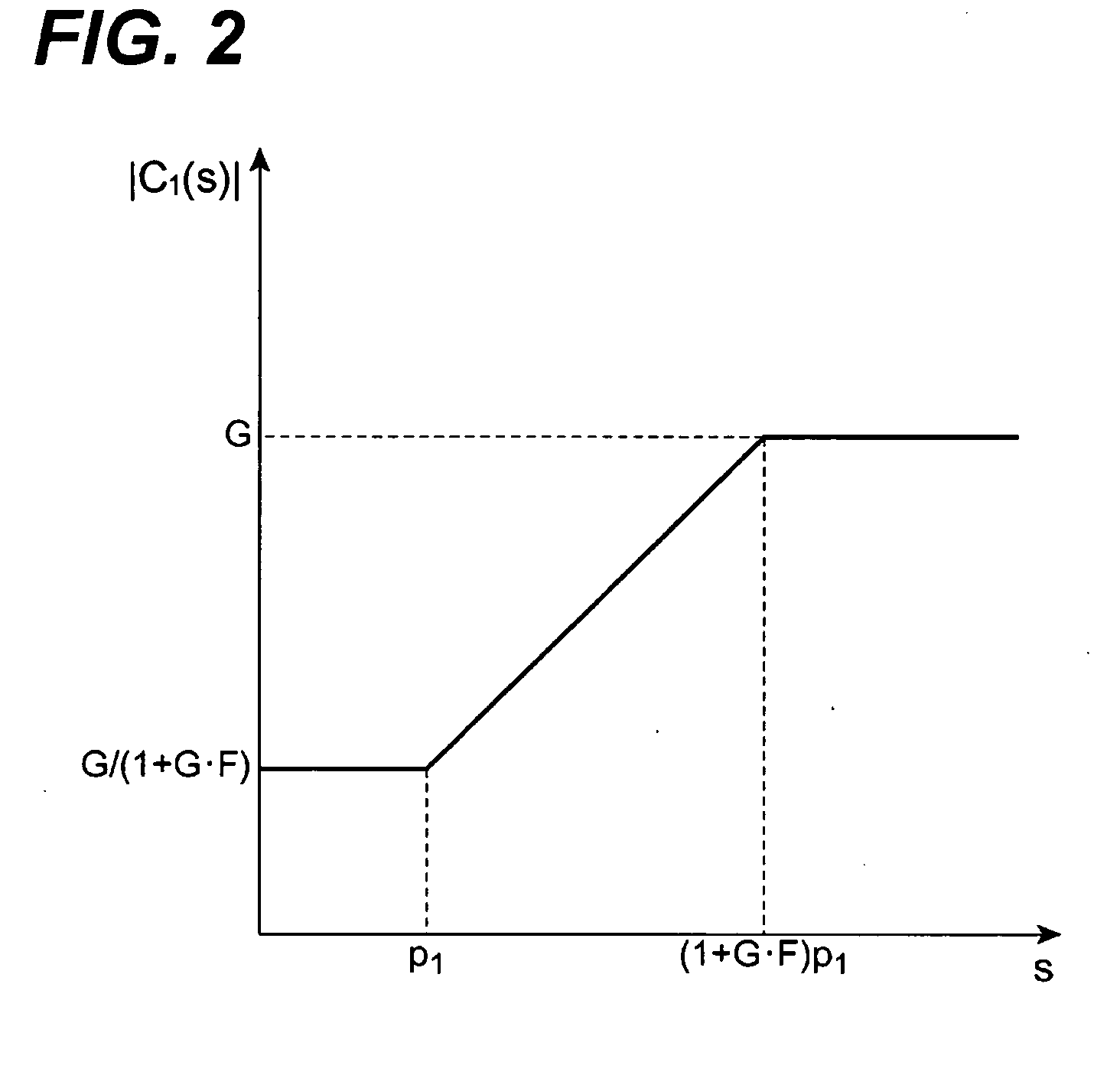
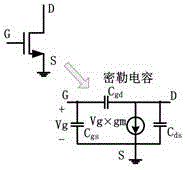
In electronics, the Miller effect accounts for the increase in the equivalent input capacitance of an inverting voltage amplifier due to amplification of the effect of capacitance between the input and output terminals. The virtually increased input capacitance due to the Miller effect is given by CM=C(1+Aᵥ) where -Aᵥ is the voltage gain of the inverting amplifier (Aᵥ positive) and C is the feedback capacitance.
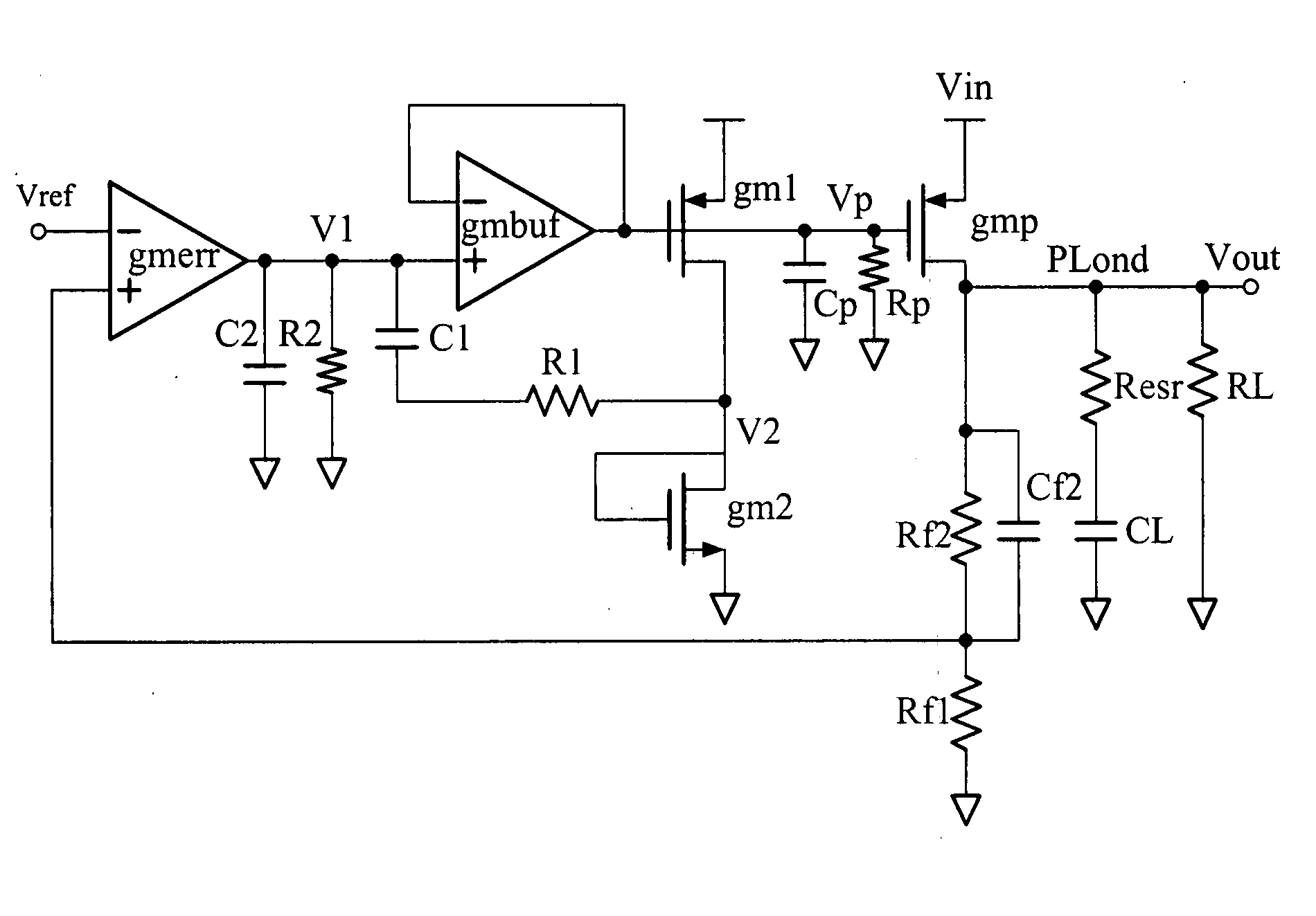
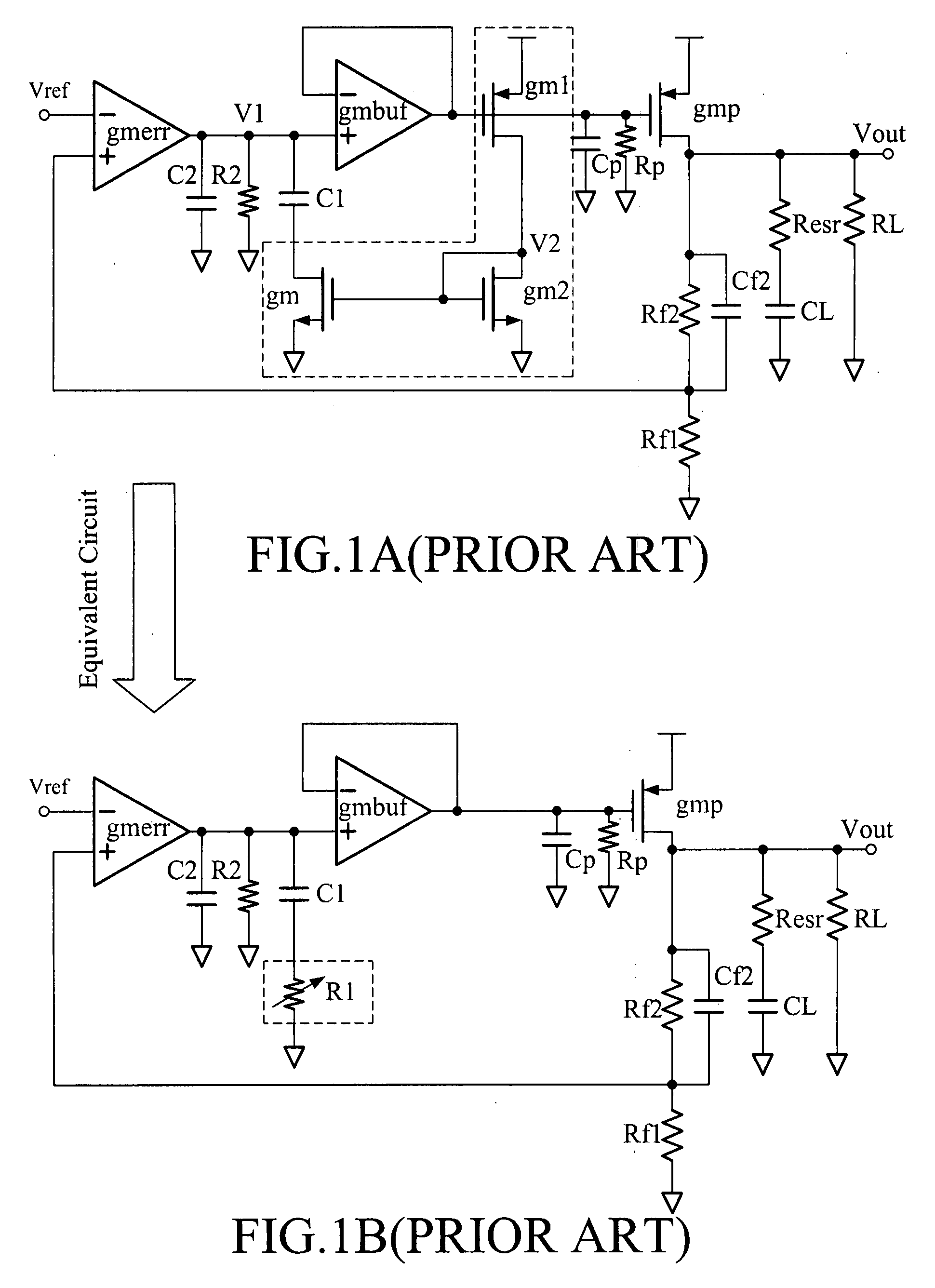
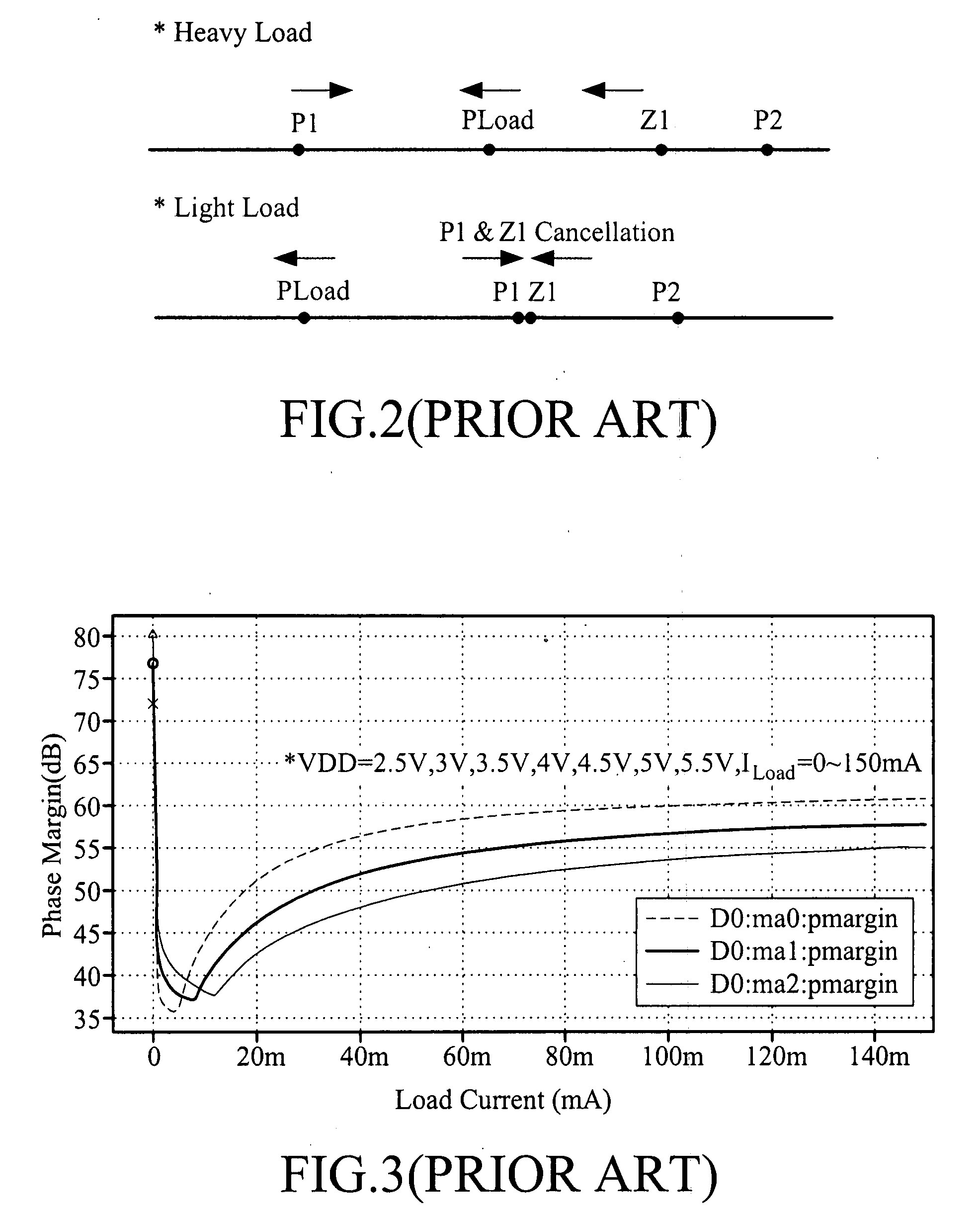
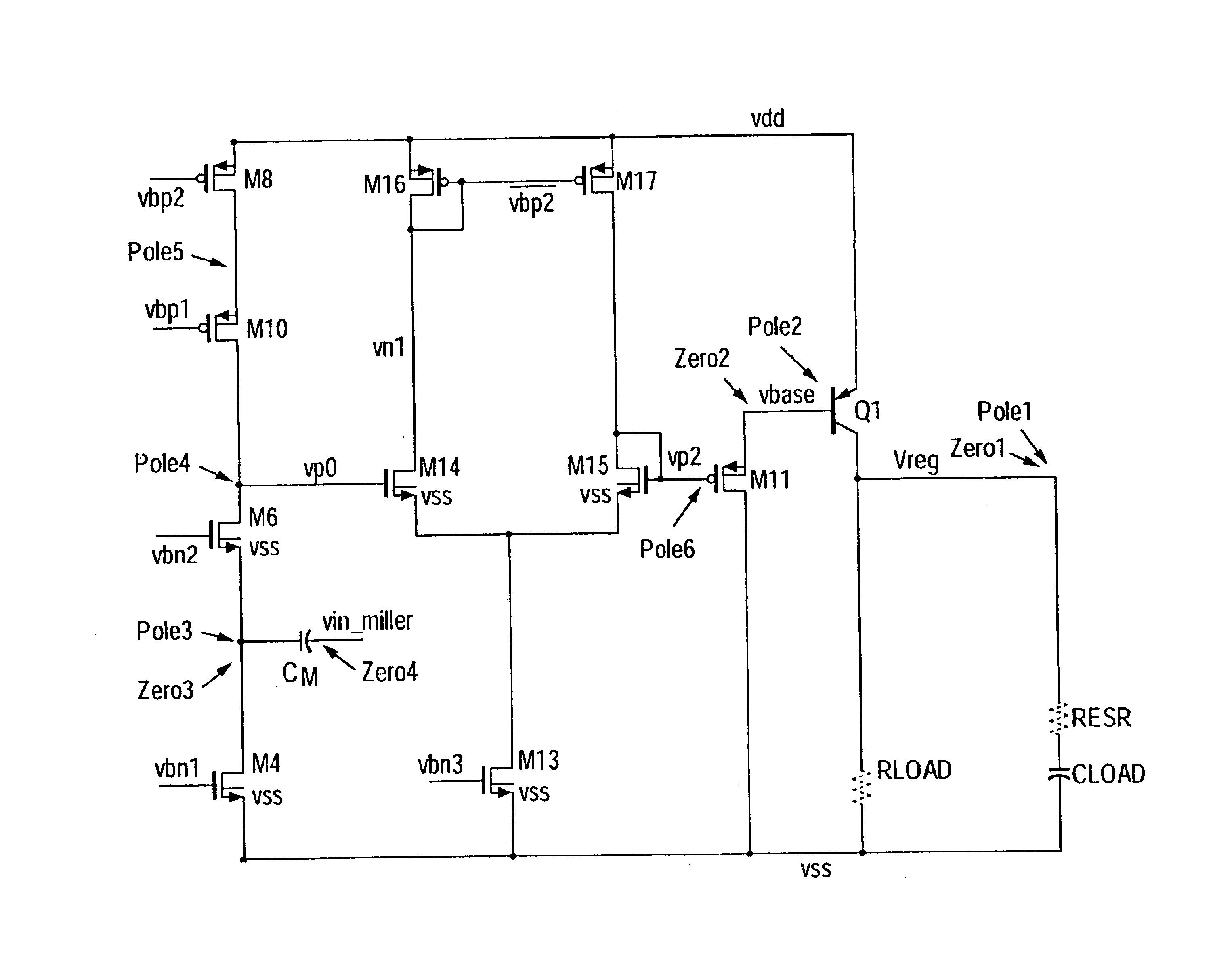
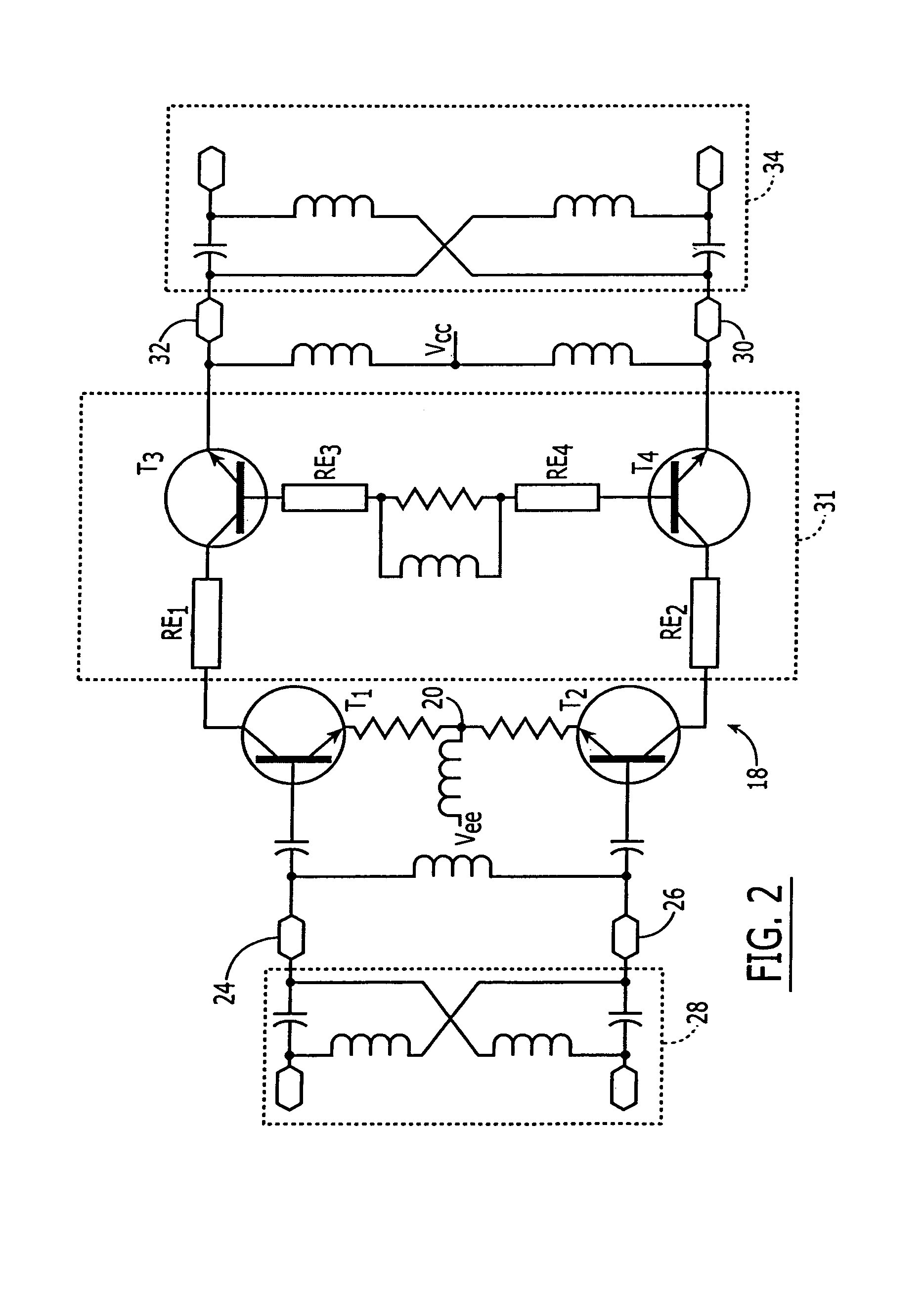
Adaptive pole and zero and pole zero cancellation control low drop-out voltage regulator
InactiveUS20080157735A1Good phase marginBandwidth of loop will become largeElectric variable regulationEngineeringControl theory
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
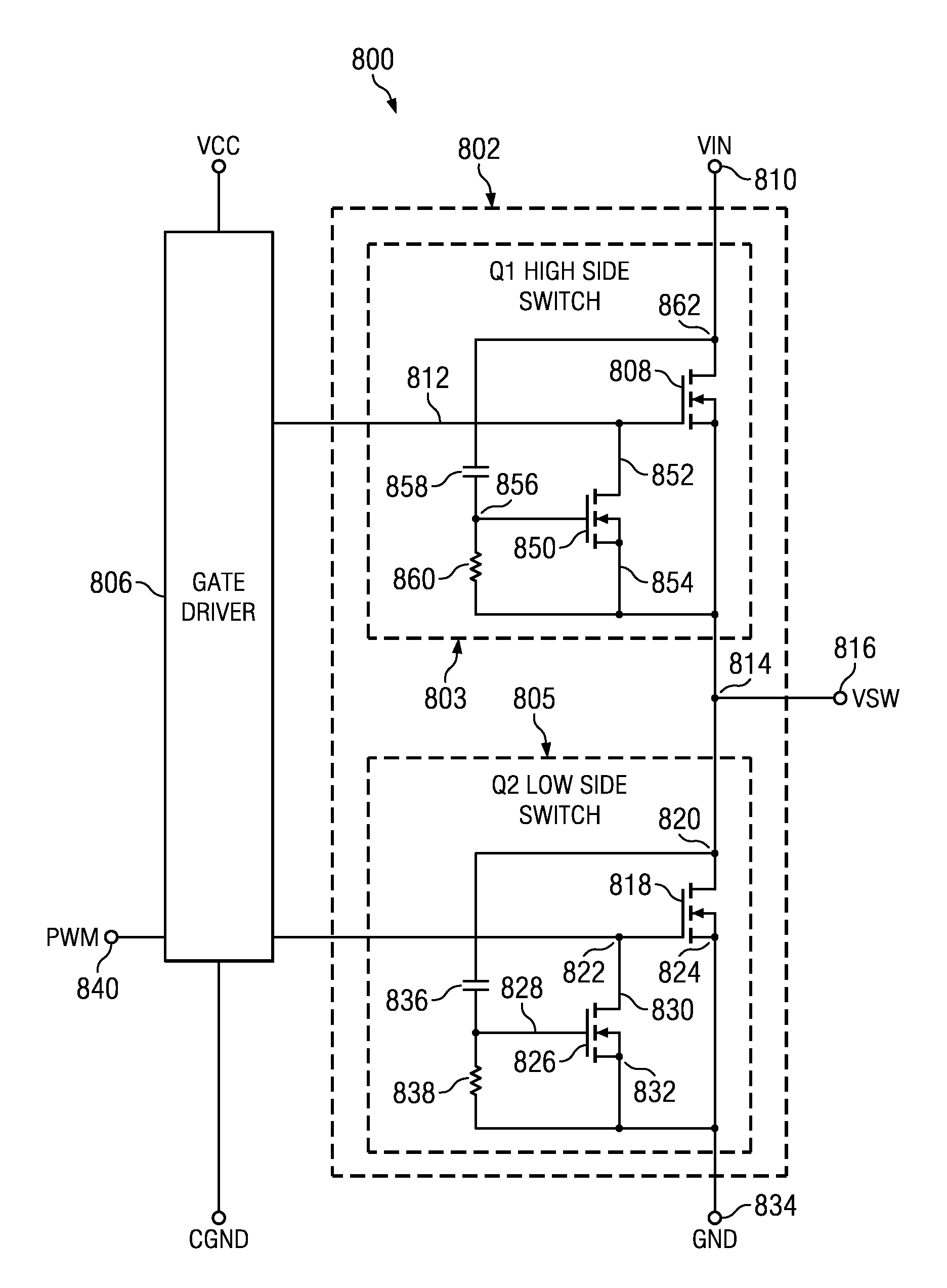
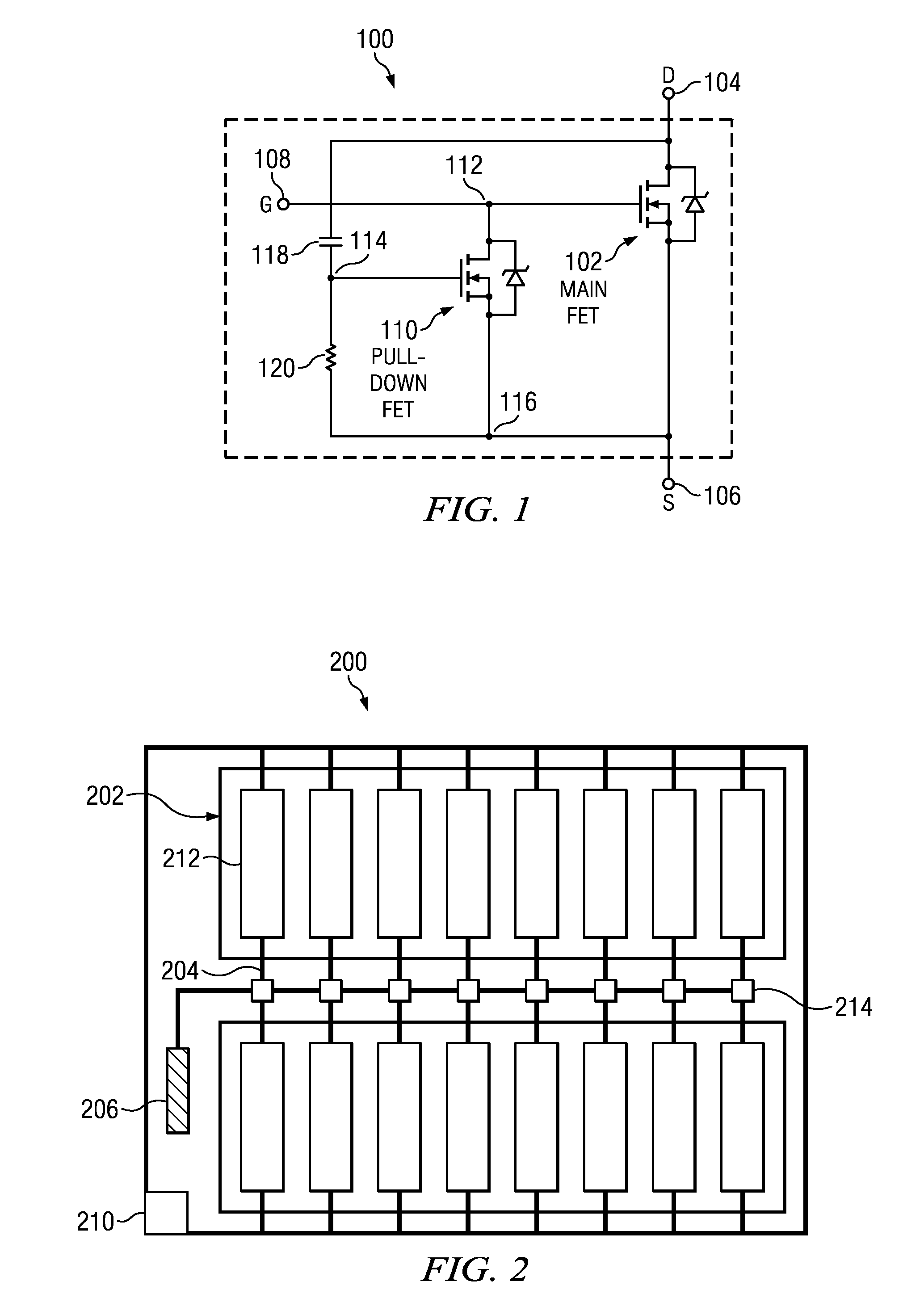
Mosfet with gate pull-down
InactiveUS20110148376A1Reduce switching lossesElectronic switchingElectric variable regulationMOSFETCapacitance
A MOSFET main switch transistor has a pull-down FET coupled between a drain thereof and the gate of the main switch transistor. A gate of the pull-down FET is coupled to the drain of the main switch transistor by a capacitor and is connected to a source thereof by a resistor. The pull-down FET is operated by capacitive coupling to the voltage drop across the main switch and can be used to hold the gate of the main switch transistor at or near its source potential to avoid or reduce unintentional turn-on of the main switch transistor by the Miller effect.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Test structure and probe for differential signals
InactiveUS7403028B2Electrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingDifferential signalingInput impedance
A test structure including a differential gain cell and a differential signal probe include compensation for the Miller effect reducing the frequency dependent variability of the input impedance of the test structure.
Owner:CASCADE MICROTECH
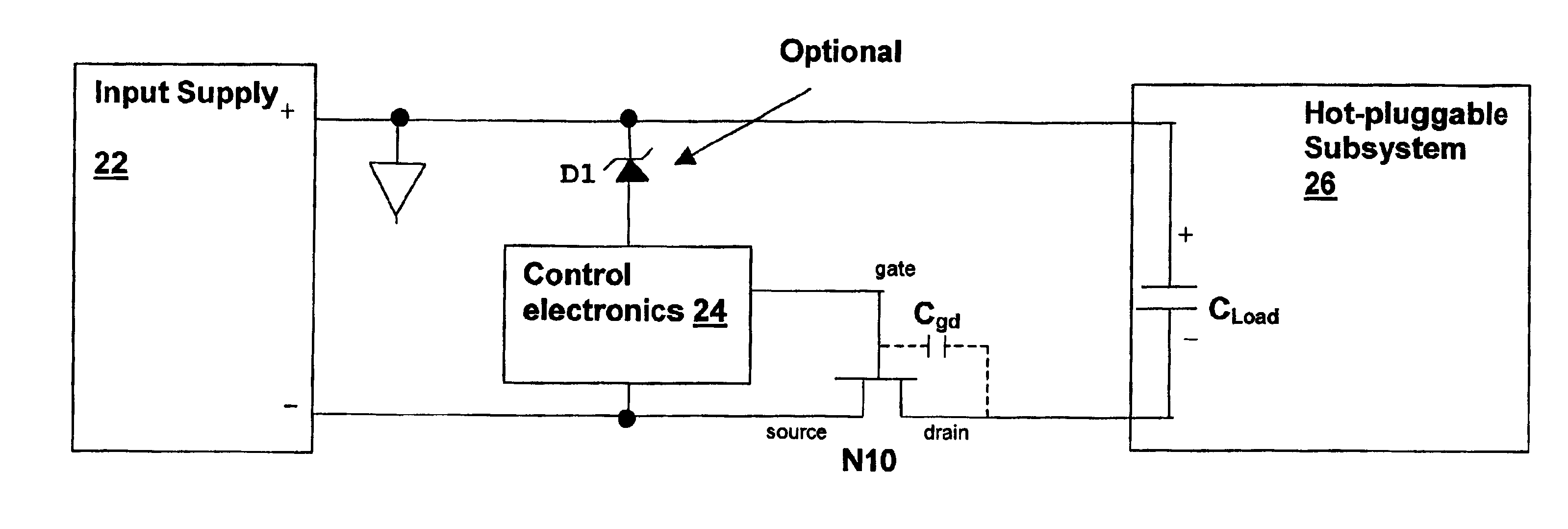
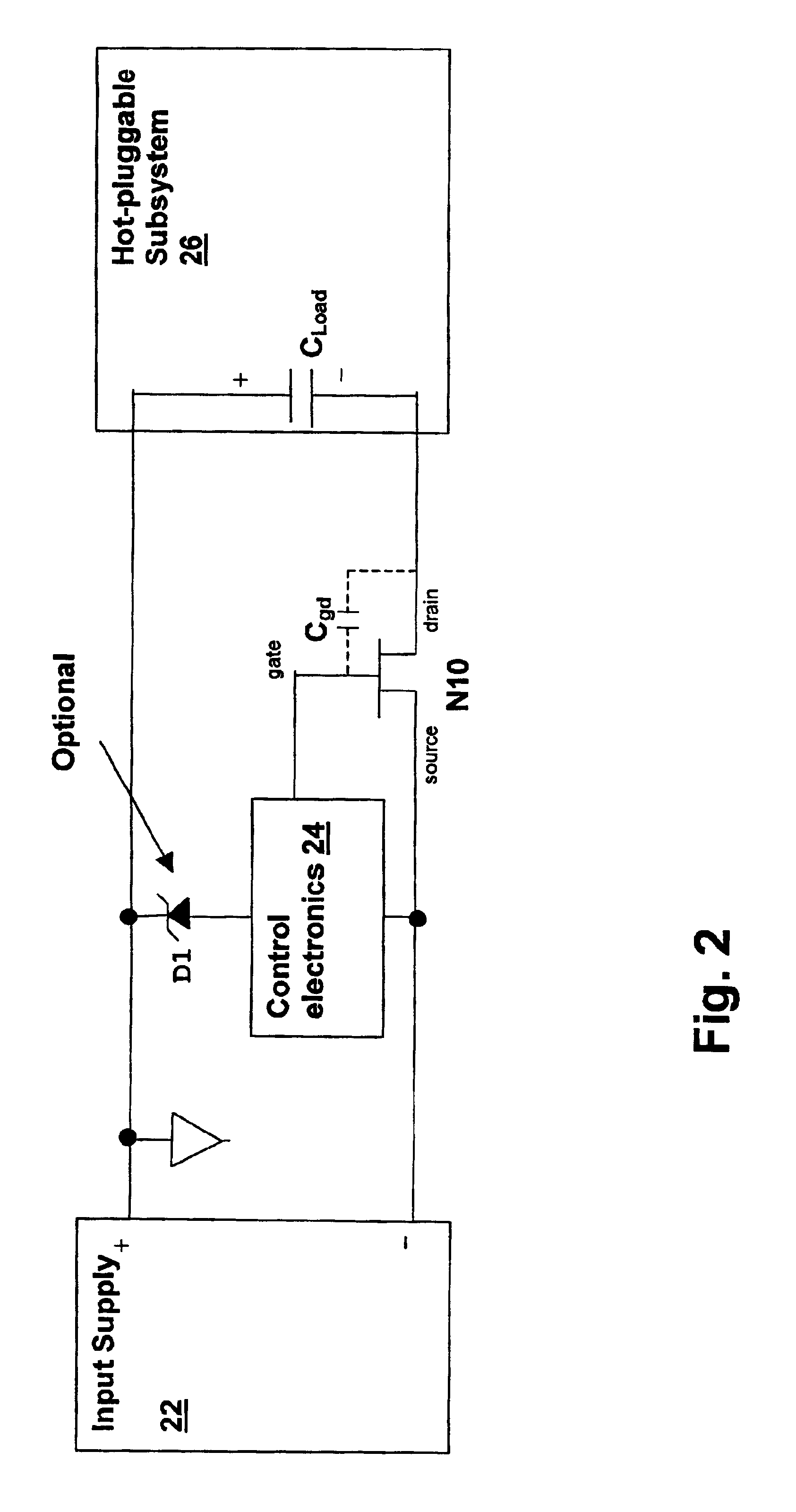
Apparatus and method for adaptively controlling power supplied to a hot-pluggable subsystem
InactiveUS6917504B2Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingPower-on resetCapacitance
An apparatus and method for adaptively controlling power supplied to a hot-pluggable subsystem controls the inrush current of the hot-pluggable subsystem when the subsystem is coupled to another system that supplies power, and optionally other signal connections. The apparatus and method adaptively control a pass device by detecting the voltage at the gate of the pass device during initial charging of the gate. The gate voltage may be sampled and used subsequently to control the operation of the pass device, and short-circuit conditions may be detected by determining that the miller effect does not change the charging of the gate capacitance. Automatic restart circuitry can be included to generate multiple startup attempts, and under-voltage lockout circuitry and power-on-reset timers can be used to provide a robust solution. The apparatus and method can be adapted to provide a three terminal device that does not require a feedback connection from a power supply output. The three terminal device may include the pass device, or may control an external pass device.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
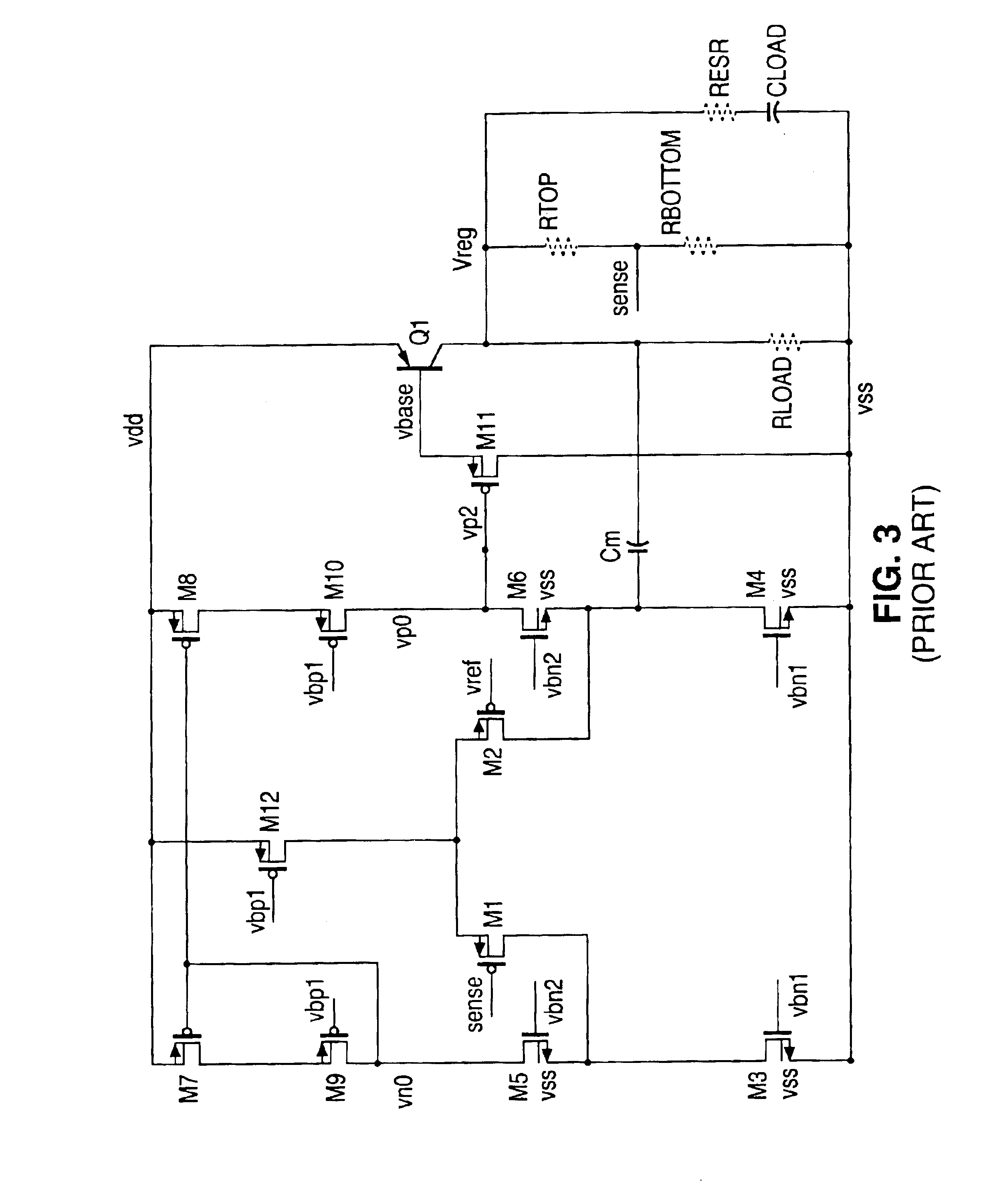
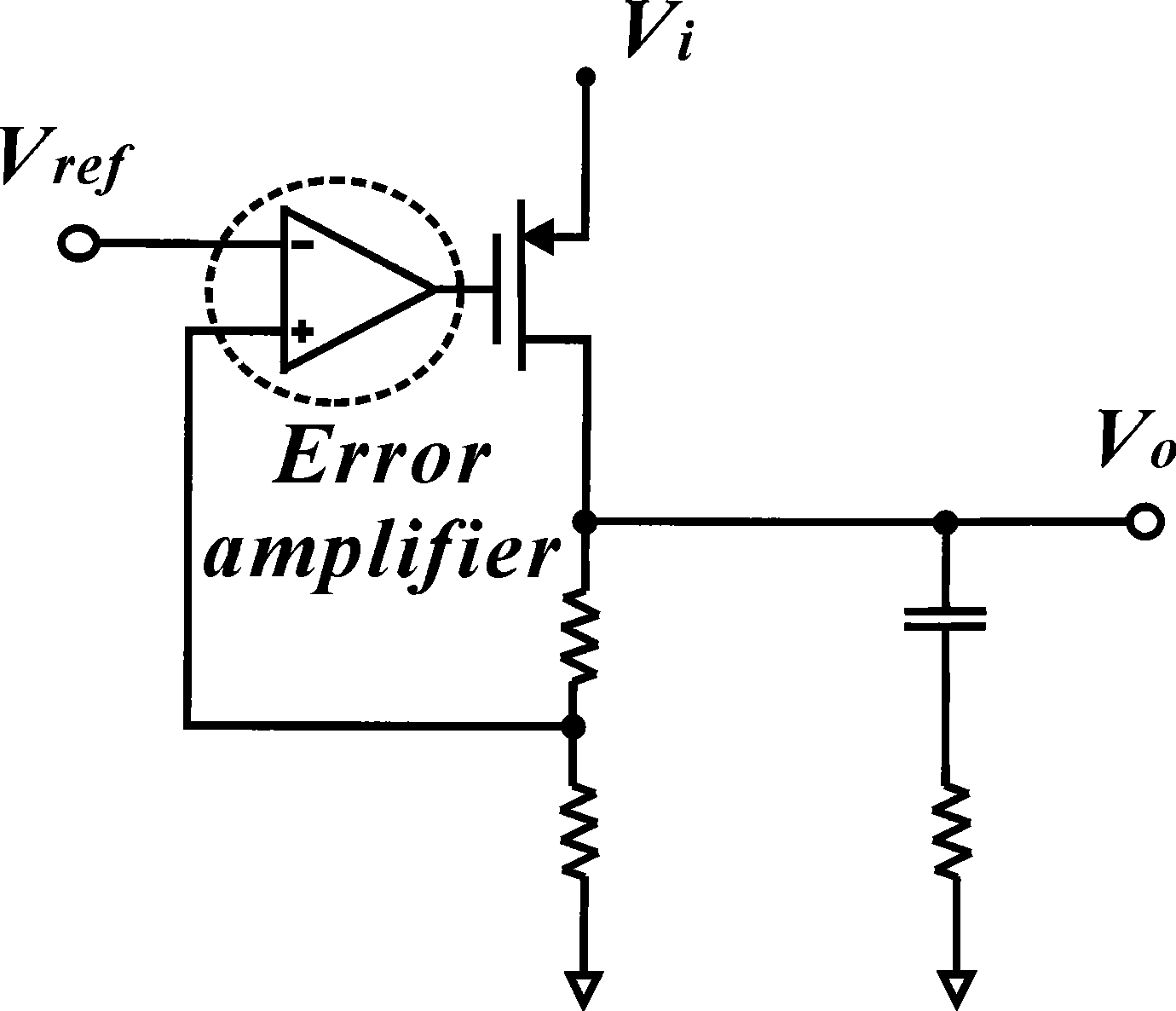
Amplifier with miller-effect compensation for use in closed loop system such as low dropout voltage regulator
InactiveUS6822514B1Amplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceDifferential amplifiersLoad circuitAudio power amplifier
Circuitry including Miller-effect feedback for use as part of a closed loop system such as a low dropout voltage regulator that provides current to a load at a specified voltage close in value to the power supply voltage. Various aspects of the presently claimed invention include using, within the Miller-effect feedback loop: a buffer amplifier to reduce loading effects upon an internal high impedance circuit node, output compensation circuitry to introduce a transfer function pole for substantially canceling a transfer function zero associated with external load circuitry; and Miller-effect compensation circuitry to introduce a transfer function zero for substantially canceling a transfer function pole associated with the Miller-effect feedback.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
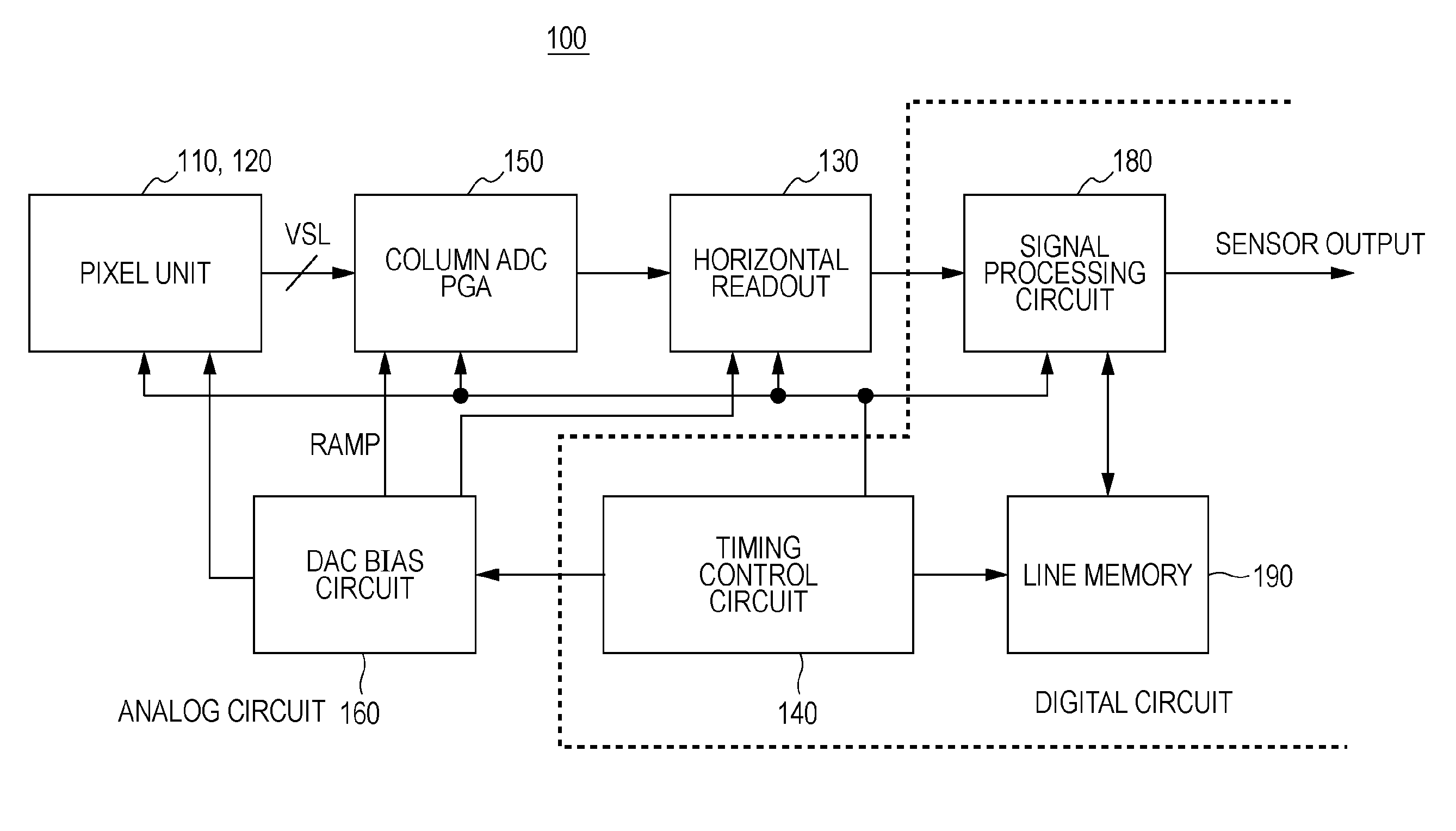
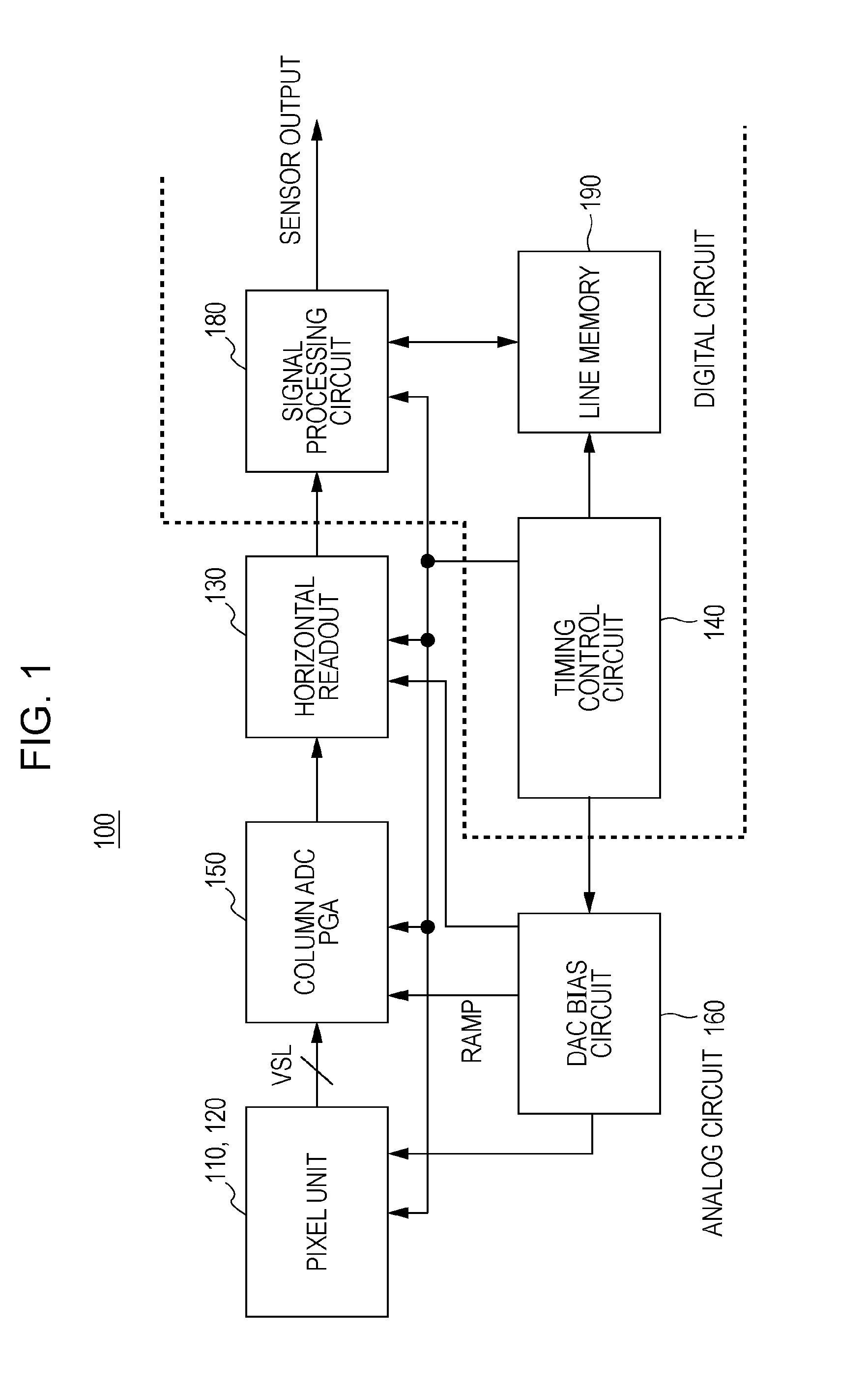
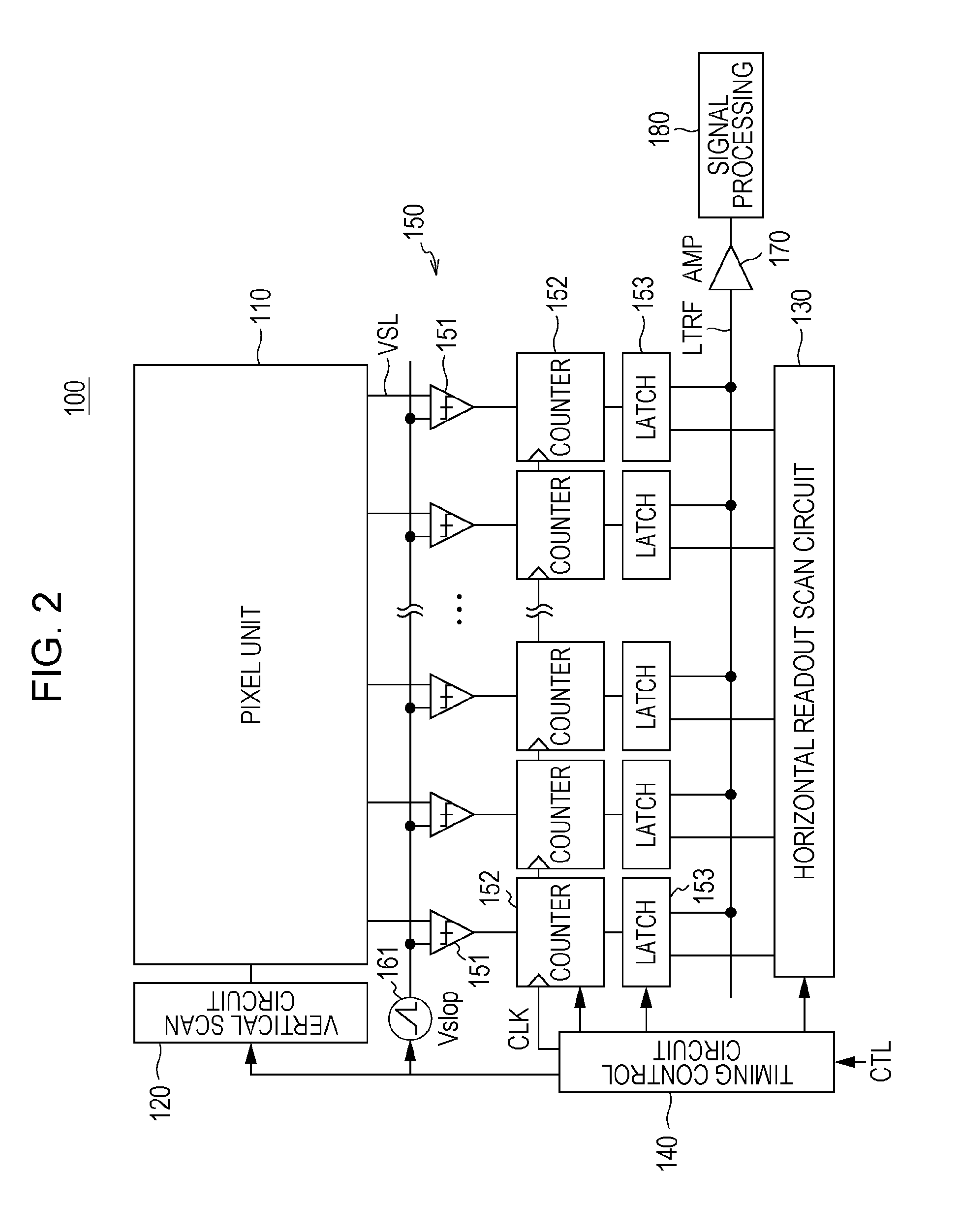
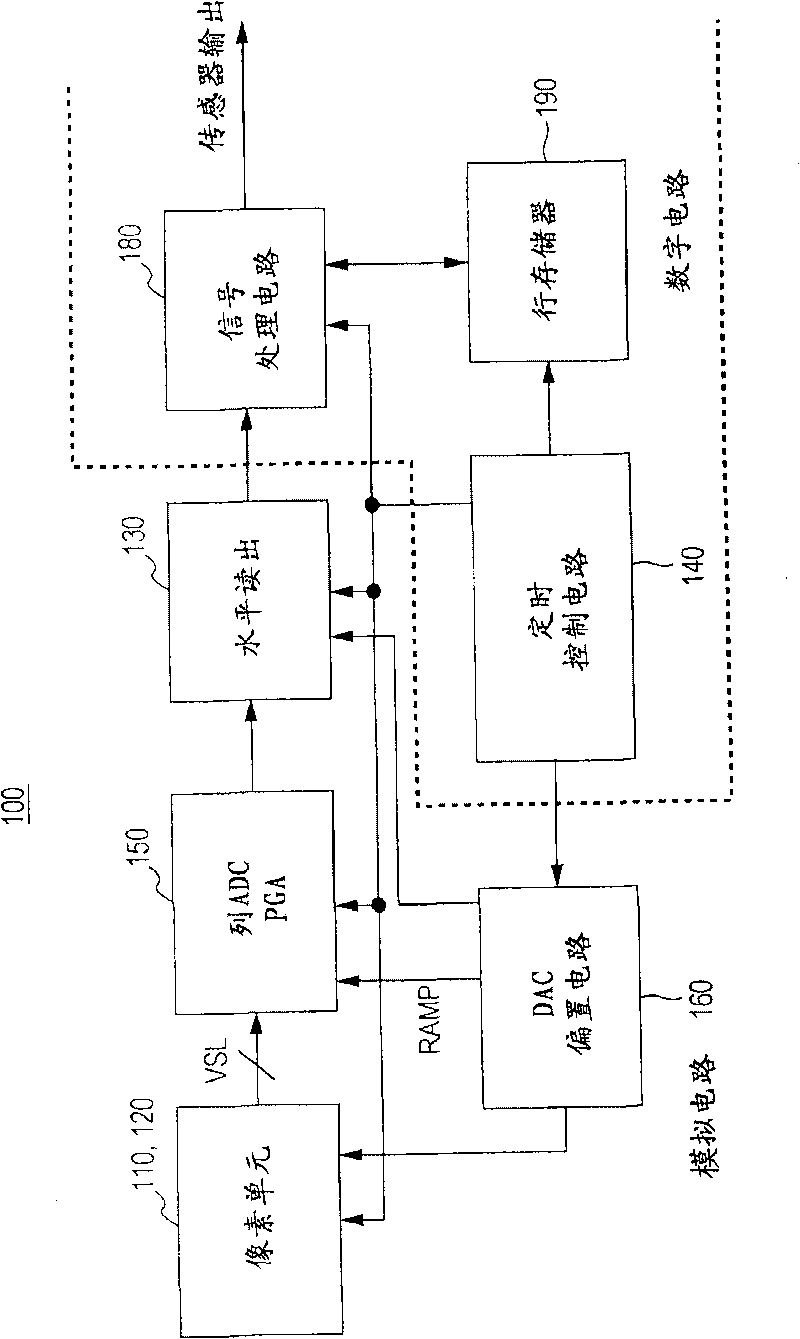
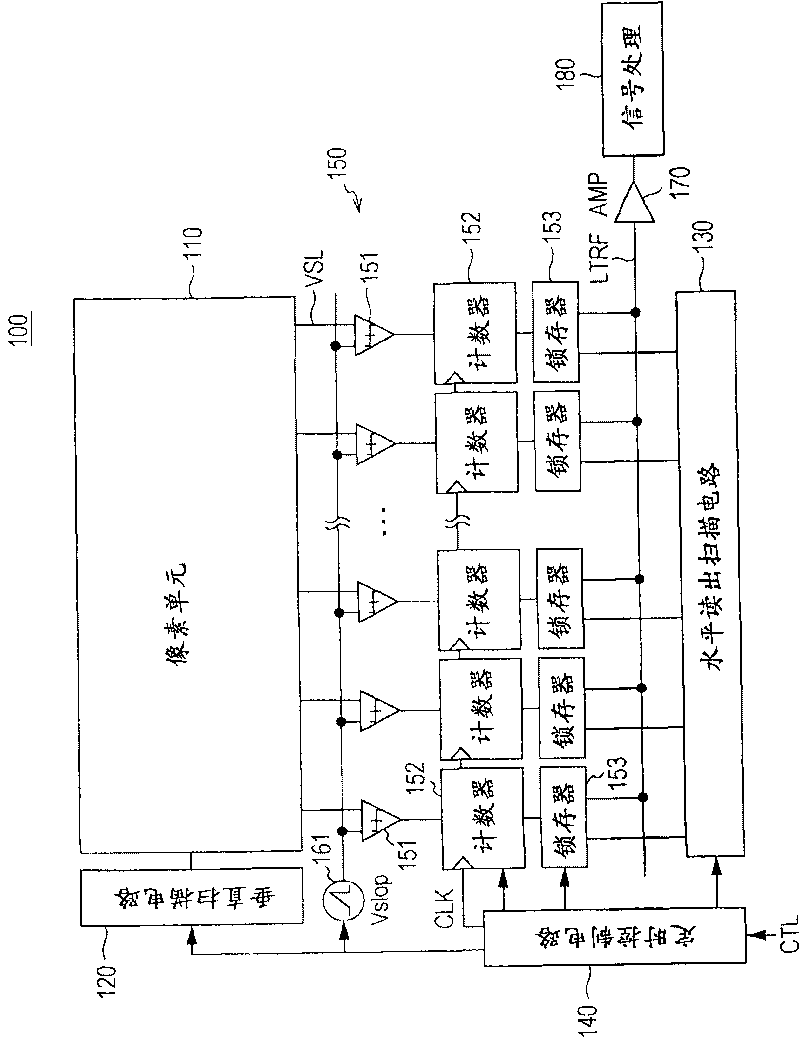
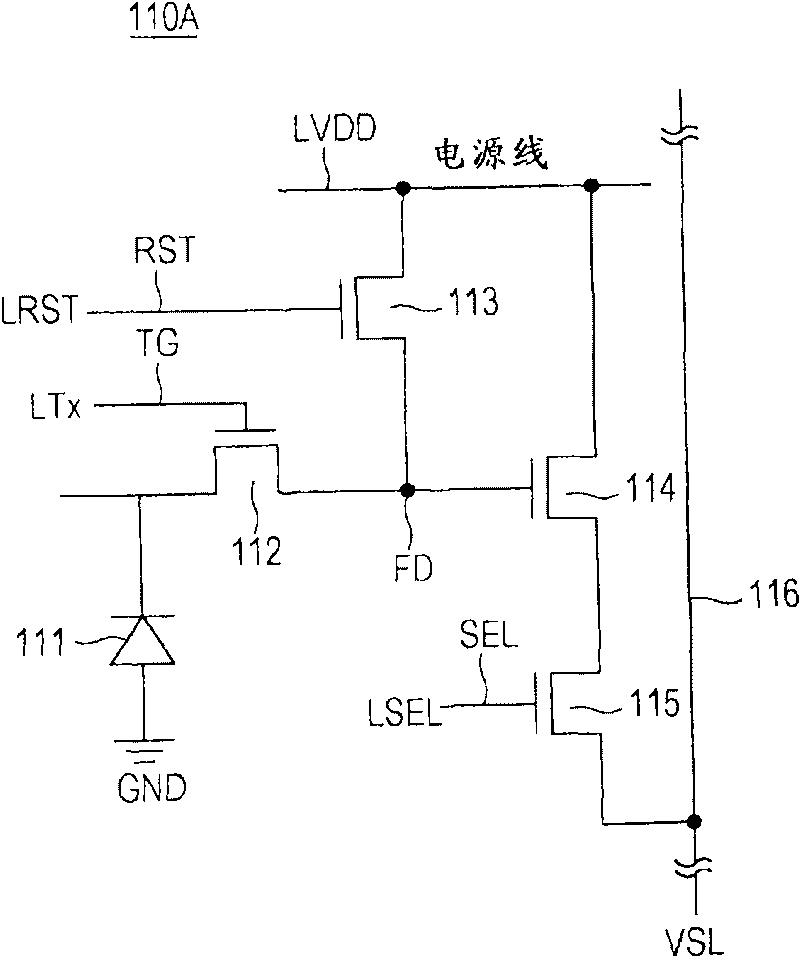
Solid-state image sensor and camera system
InactiveUS20100091167A1Increase frame rateIncreased circuit areaTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierEngineering
A solid state image sensor includes a pixel unit and a readout unit that reads out per-pixel pixel signals from the pixel unit. The readout unit includes: a plurality of column-parallel comparators that compare a readout signal potential to a reference voltage and output a determination signal; and a plurality of counters that count the comparing time of a corresponding comparator. Each comparator includes: a first amp containing a differential amplifier that receives the reference voltage at the gate of a transistor, receives the readout signal at the gate of another transistor, and compares the reference voltage to the readout signal potential; a second amp containing an amplifier that increases the gain of the first amp's output; and a capacitor connected between the input and the output of the amplifier in the second amp in order to exhibit the Miller effect.
Owner:SONY CORP
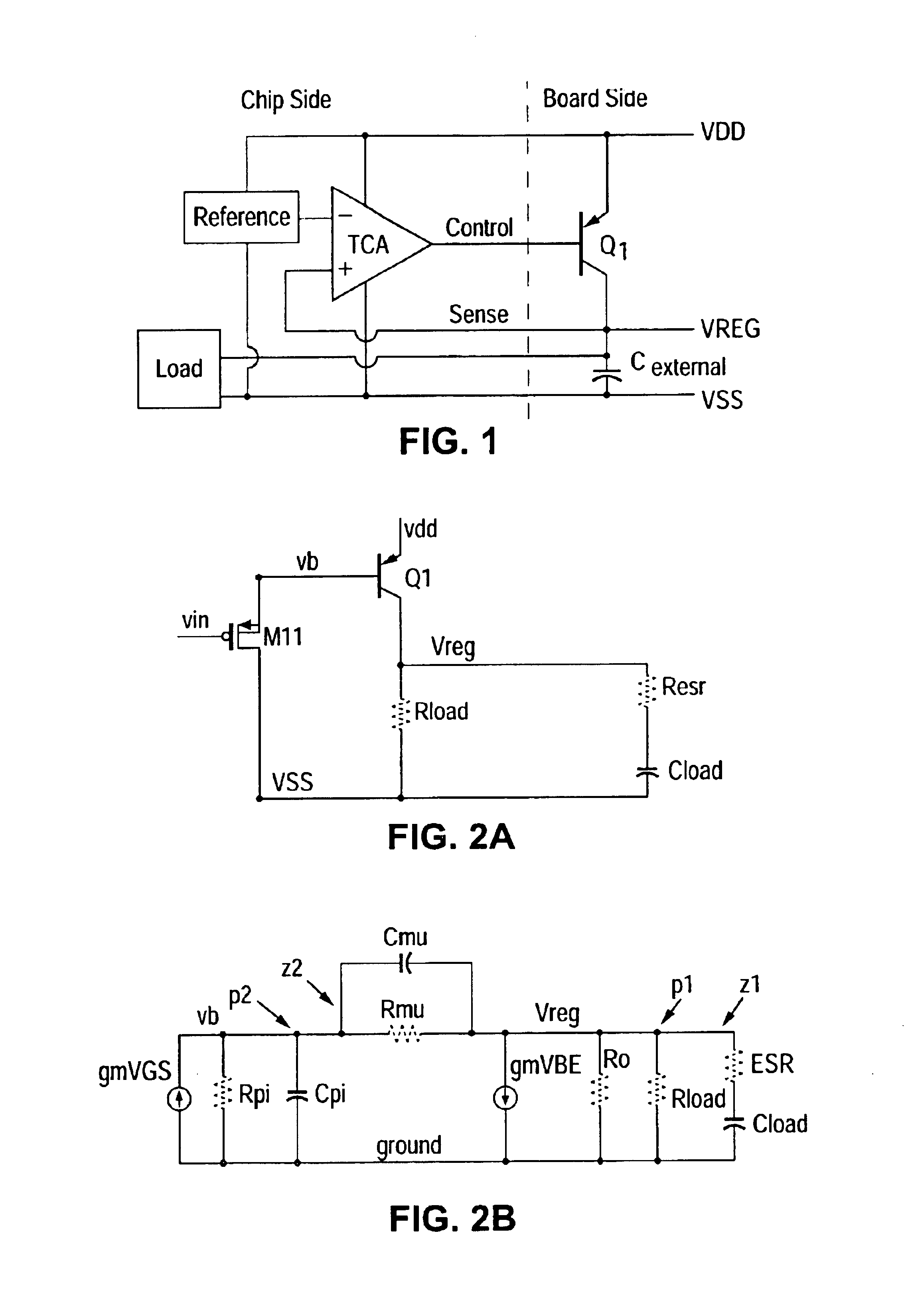
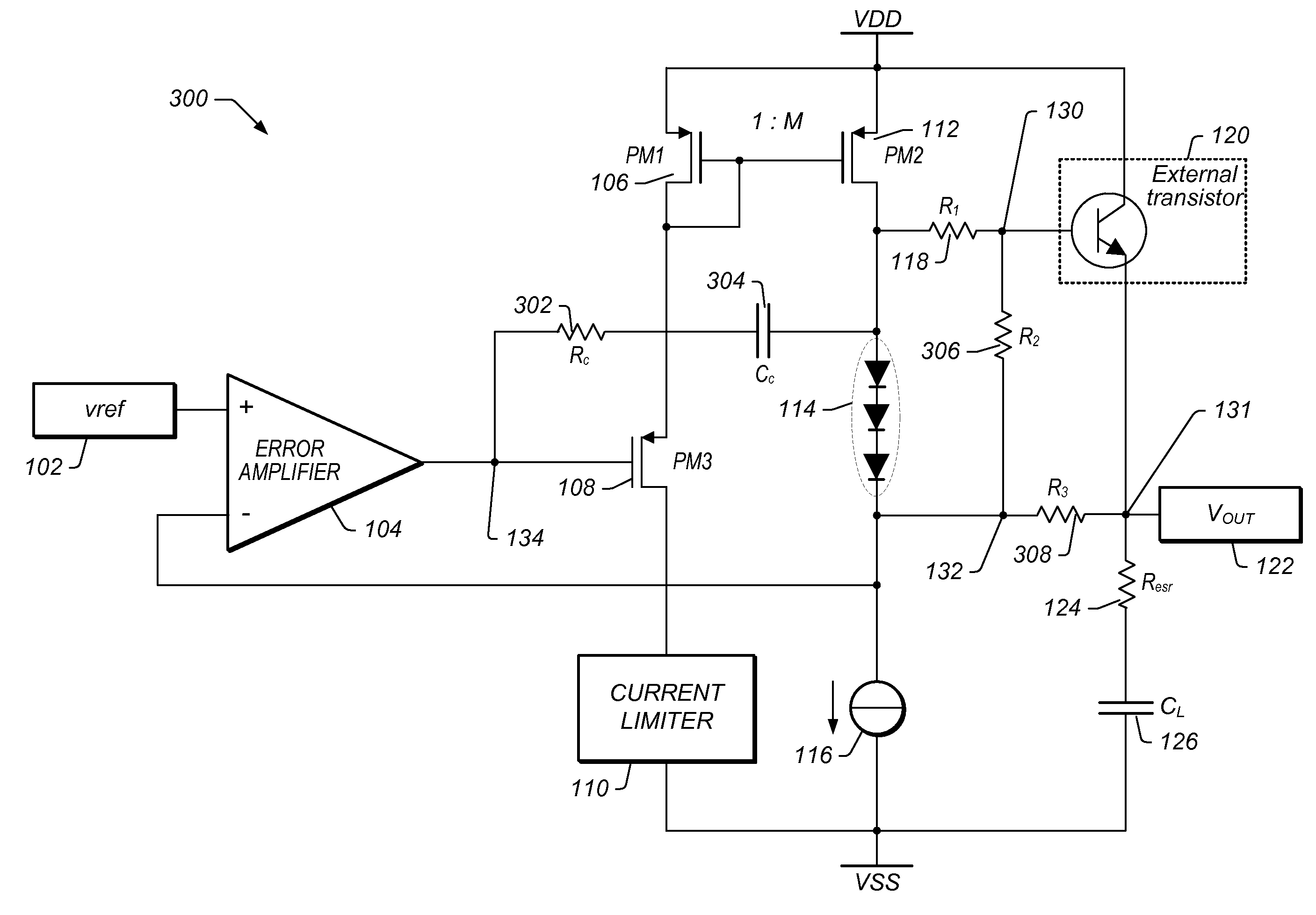
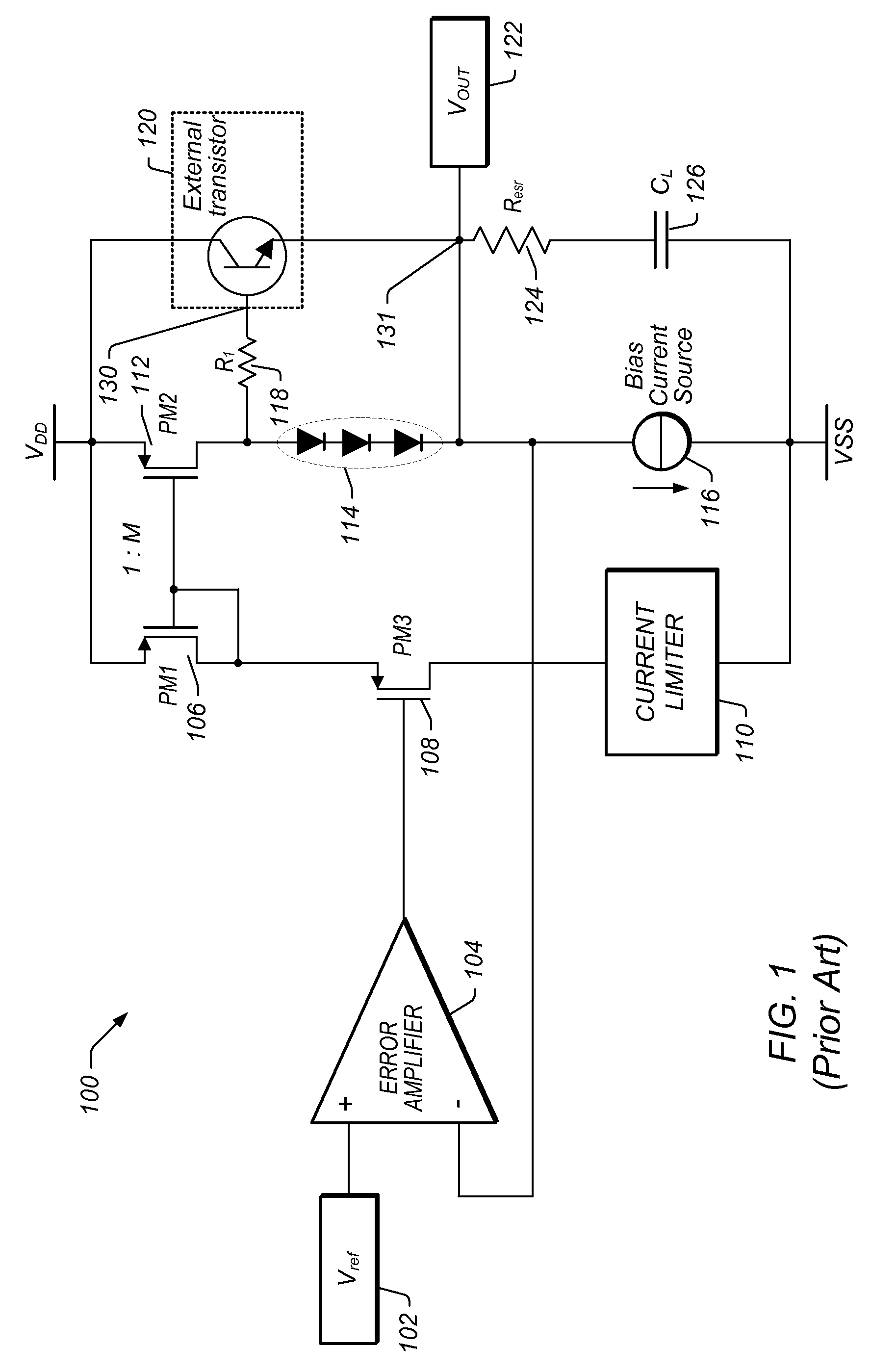
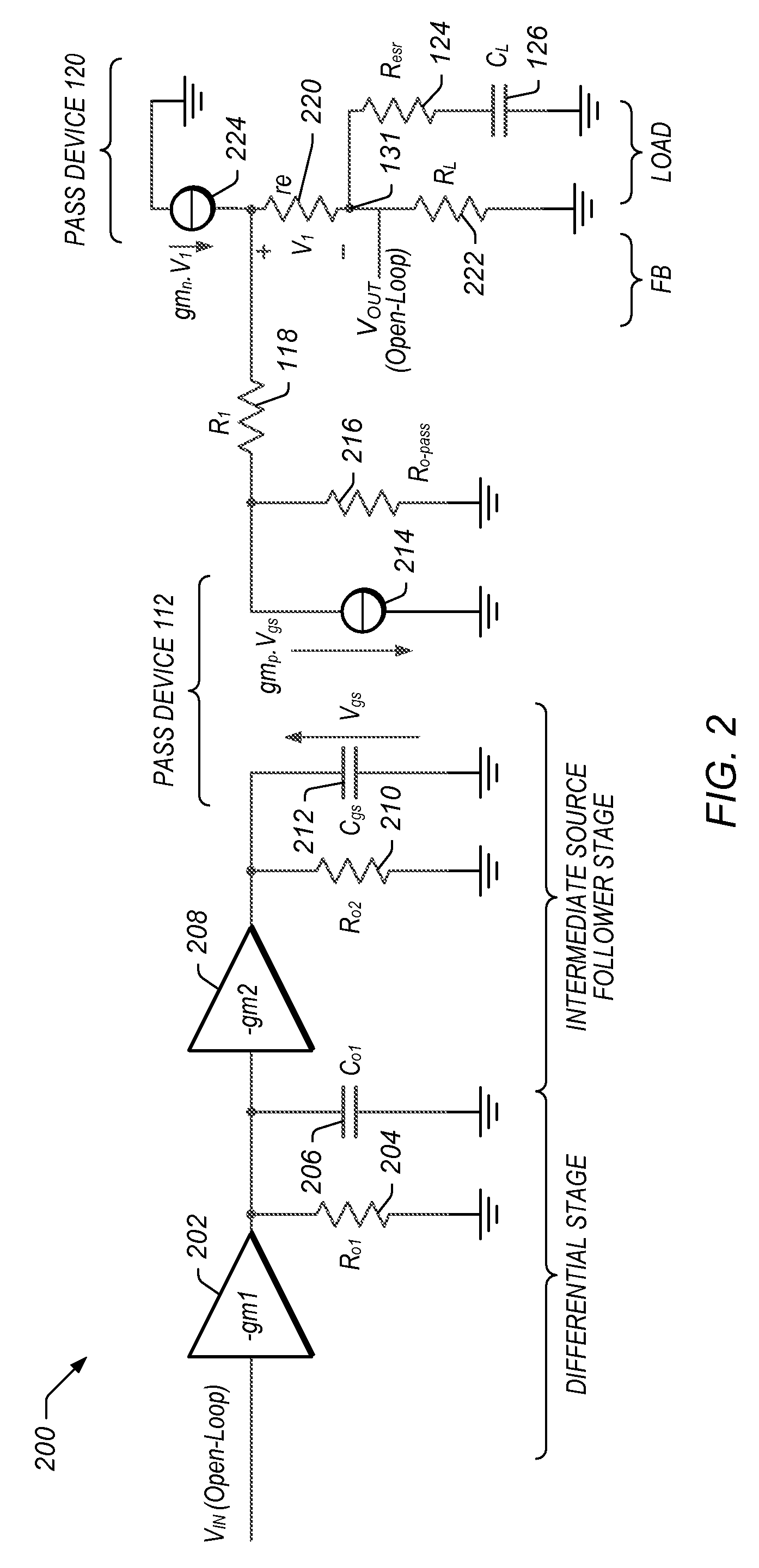
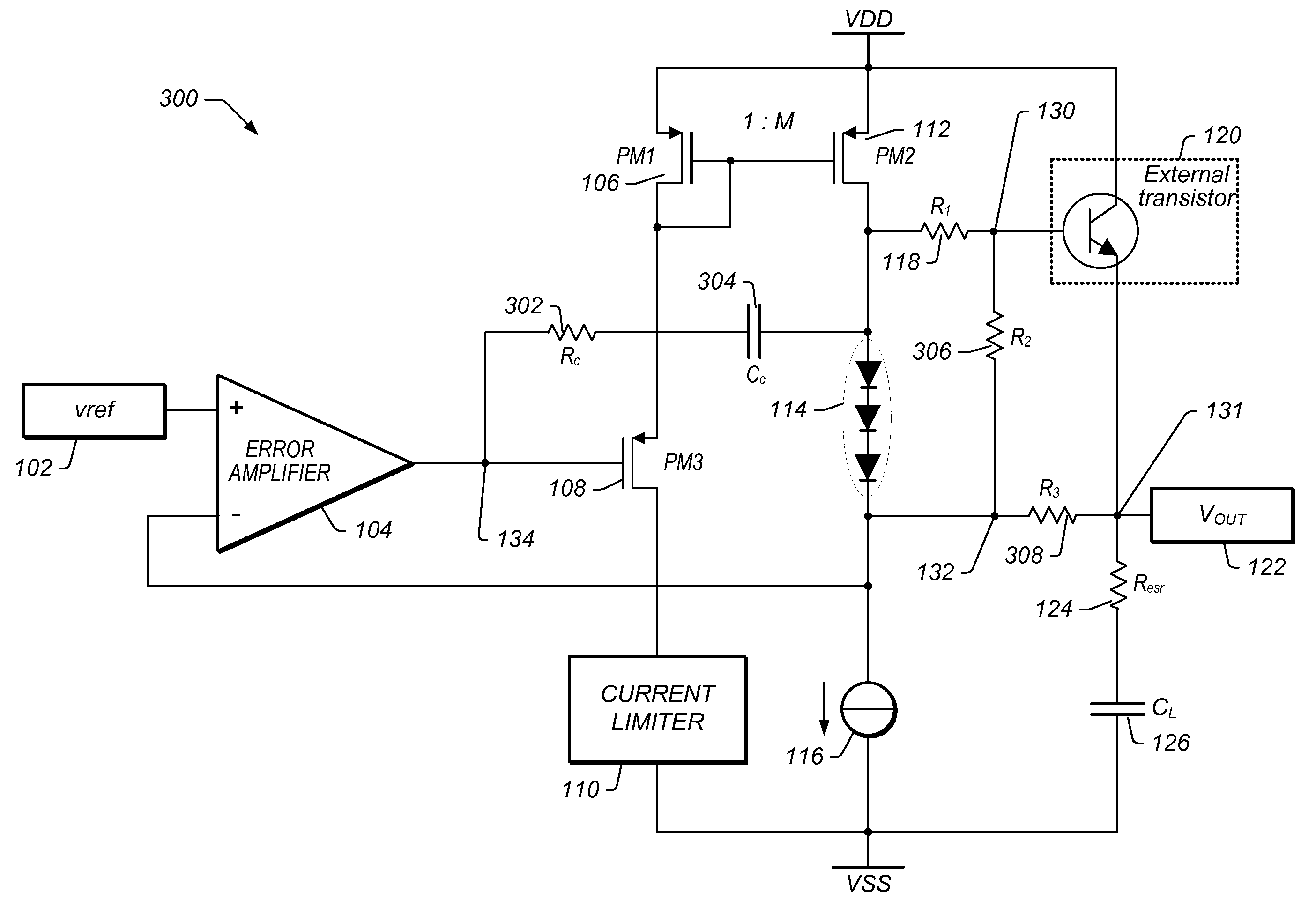
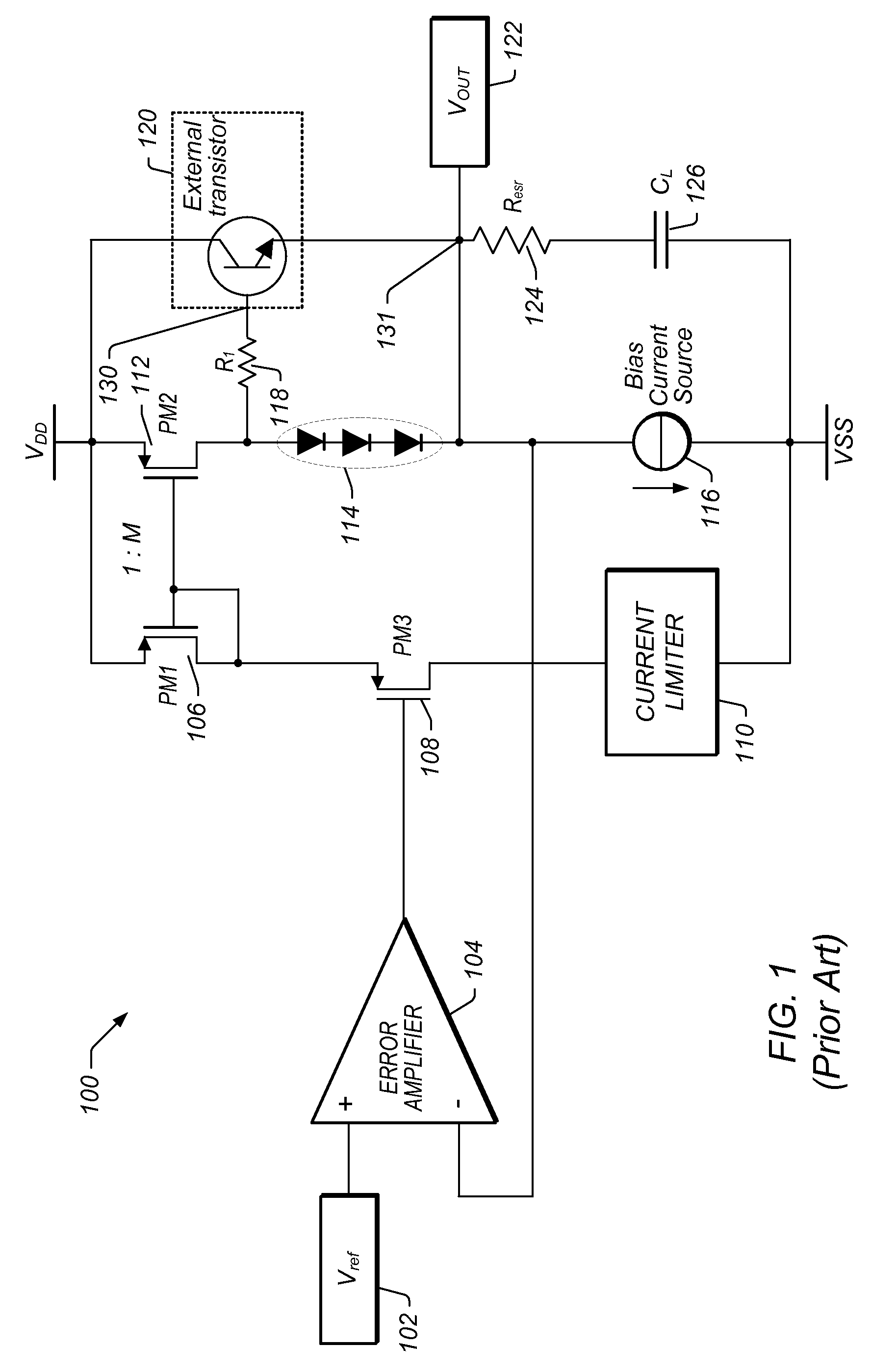
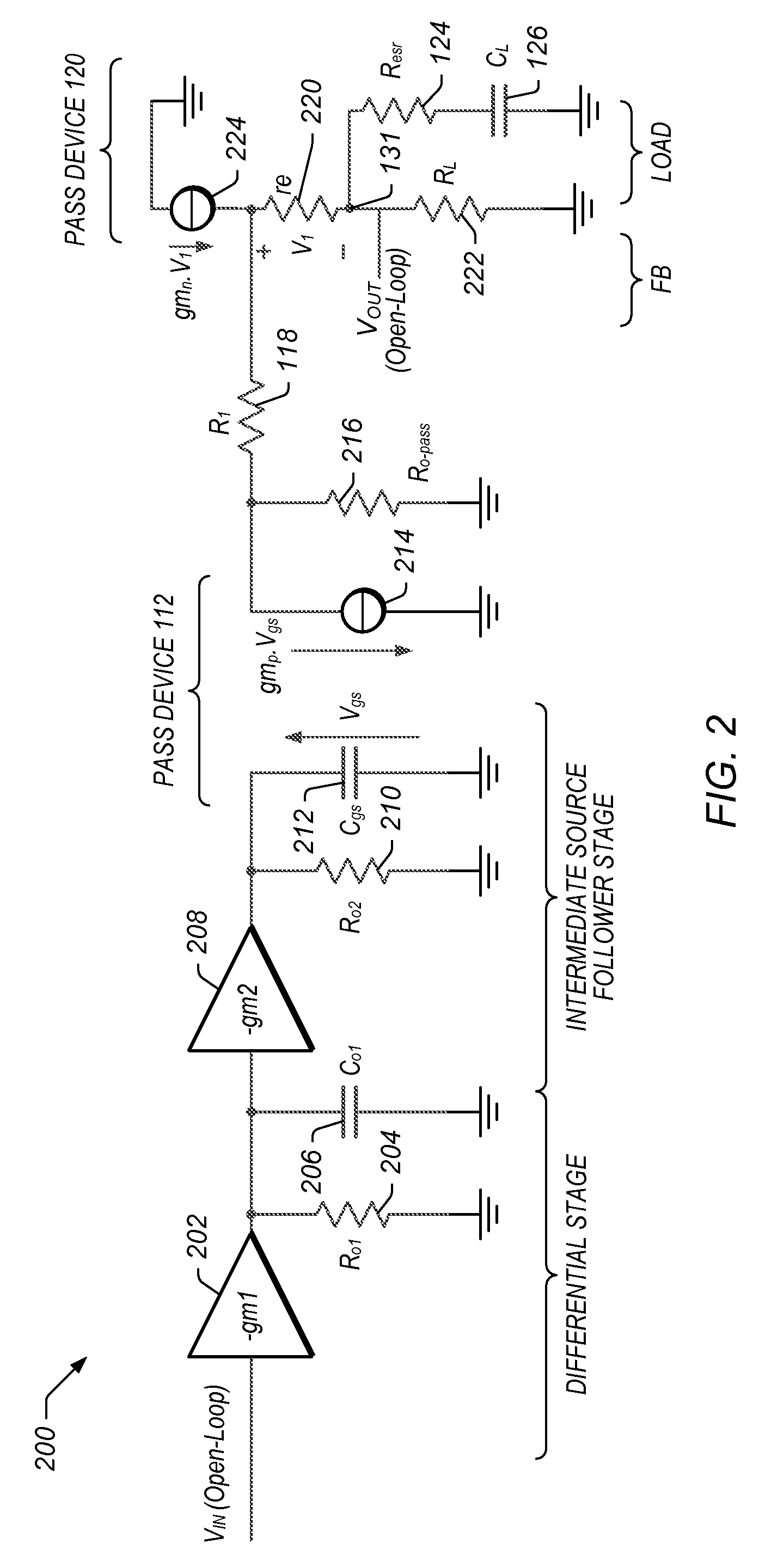
Frequency Compensation Scheme for Stabilizing the LDO Using External NPN in HV Domain
A voltage regulator may comprise a regulator output configured to provide a regulated voltage, which may be controlled by an error amplifier based on the regulated voltage and a reference voltage. The error amplifier may control a source-follower stage to mirror a multiple of the current flowing in the source-follower stage into an internal pass device. A voltage developed by the mirror current may control an external pass device configured to deliver the load current into the regulator output. A first resistor may be configured to decouple a load capacitor coupled between the regulator output and reference ground, when the load current is below a specified value. A second resistor may be configured to create a bias current in the internal pass device even when the external pass device is close to cut-off region. A third resistor may be configured to counter the effects of negative impedance at the control terminal of the external pass device caused by the current-gain of the external pass device. A compensation capacitor and resistor may be coupled in series between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the voltage regulator to provide frequency compensation for the Miller-Effect.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Active surge current control circuit
ActiveCN101505055AEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentMOSFETCapacitance
The invention provides an active surge current control circuit, which consists of an electrification starting circuit, an MOSFET and a gate source voltage Vgs slope control circuit thereof, wherein a drain of the MOSFET is connected to load, and a source is connected to external input; the starting circuit consists of resistors and a Zener diodes series circuit, is spanned at two ends of the input, and sets the minimum input voltage in the working of the whole circuit and the maximum working voltage in the working of the Vgs slope control circuit; the Vgs slope control circuit consists of a resistor, a capacitor spanned between a triode c and a triode b, a diode which is reversely spanned between a triode e and the triode b, and an MOSFET protective resistor between the triode e and the triode c, controls Vgs climbing speed of the MOSFET after a power supply starts supplying power, is combined with the miller effect of Cgd in the MOSFET, and finally controls current amplitude for charging the capacitor of the load input end through the MOSFET so as to ensure that uncontrollable surge current with large amplitude in the electrifying moment can be prevented; the capacitor between the triode c and the triode b in non-electrifying period discharges through the diodes and the triode c and the triode b; and when the spanning of the slope control circuit works normally, the Vgs slope control circuit ensures that the MOSFET is completely conducted and has the minimum power consumption.
Owner:上海英联电子系统有限公司 +1
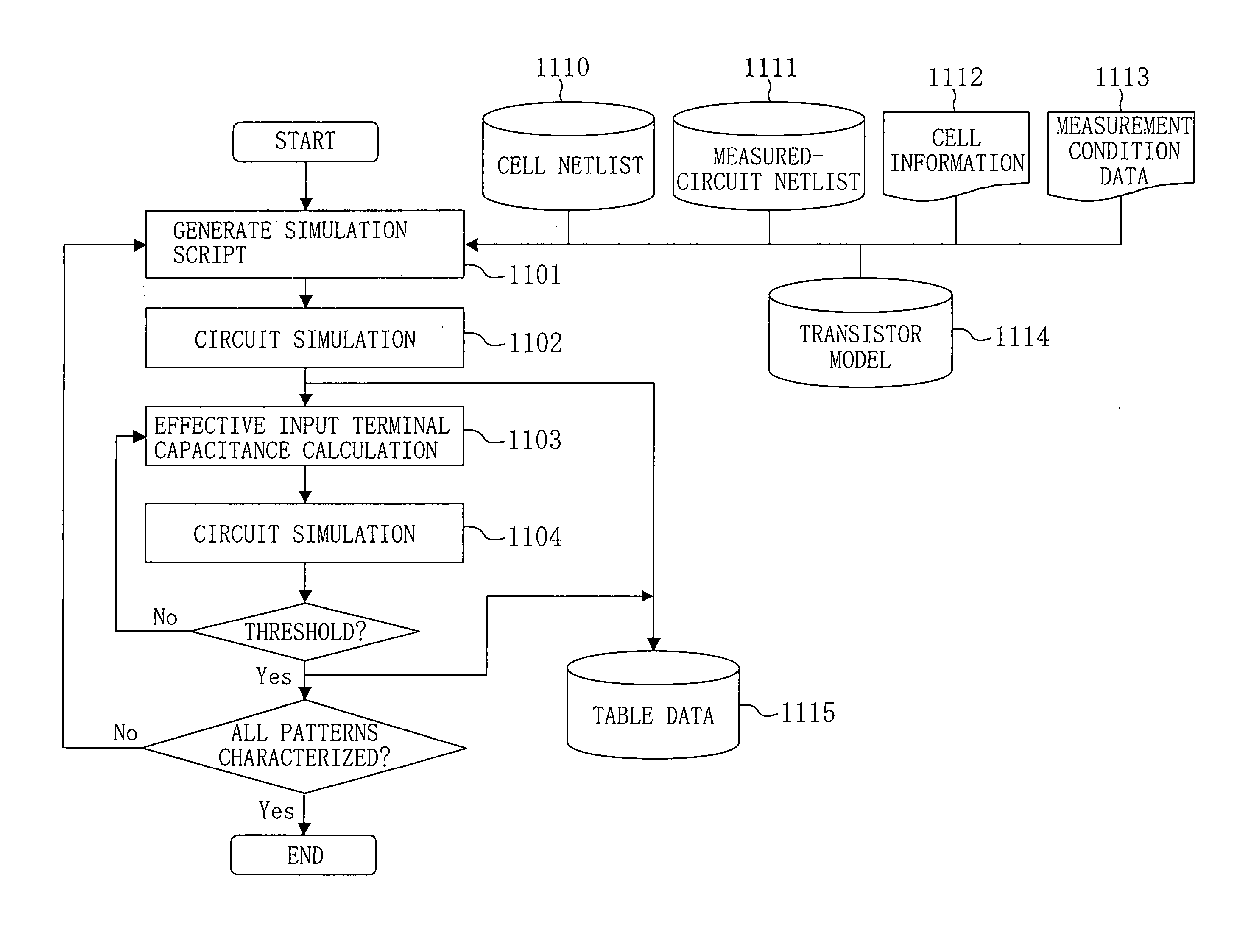
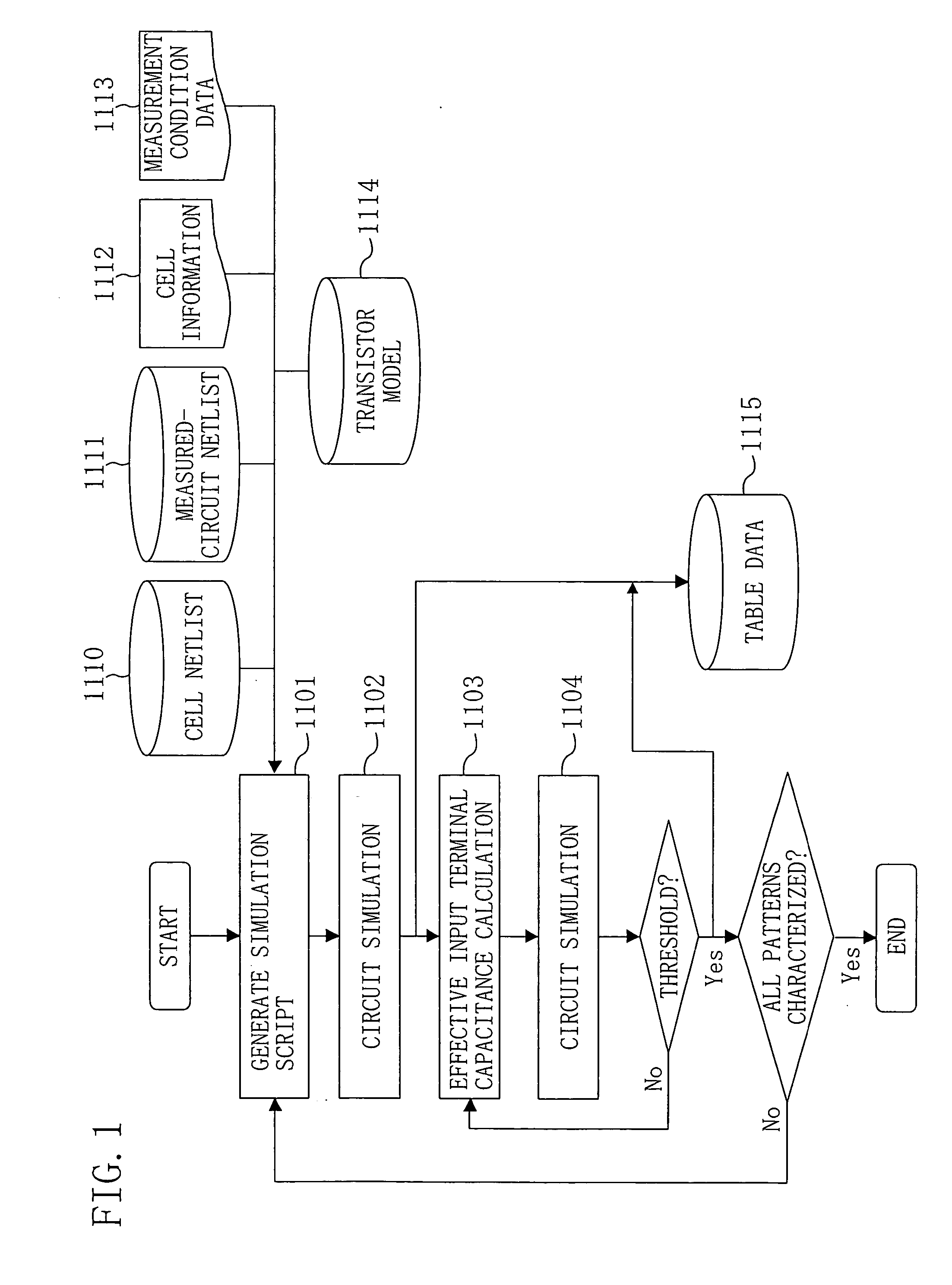
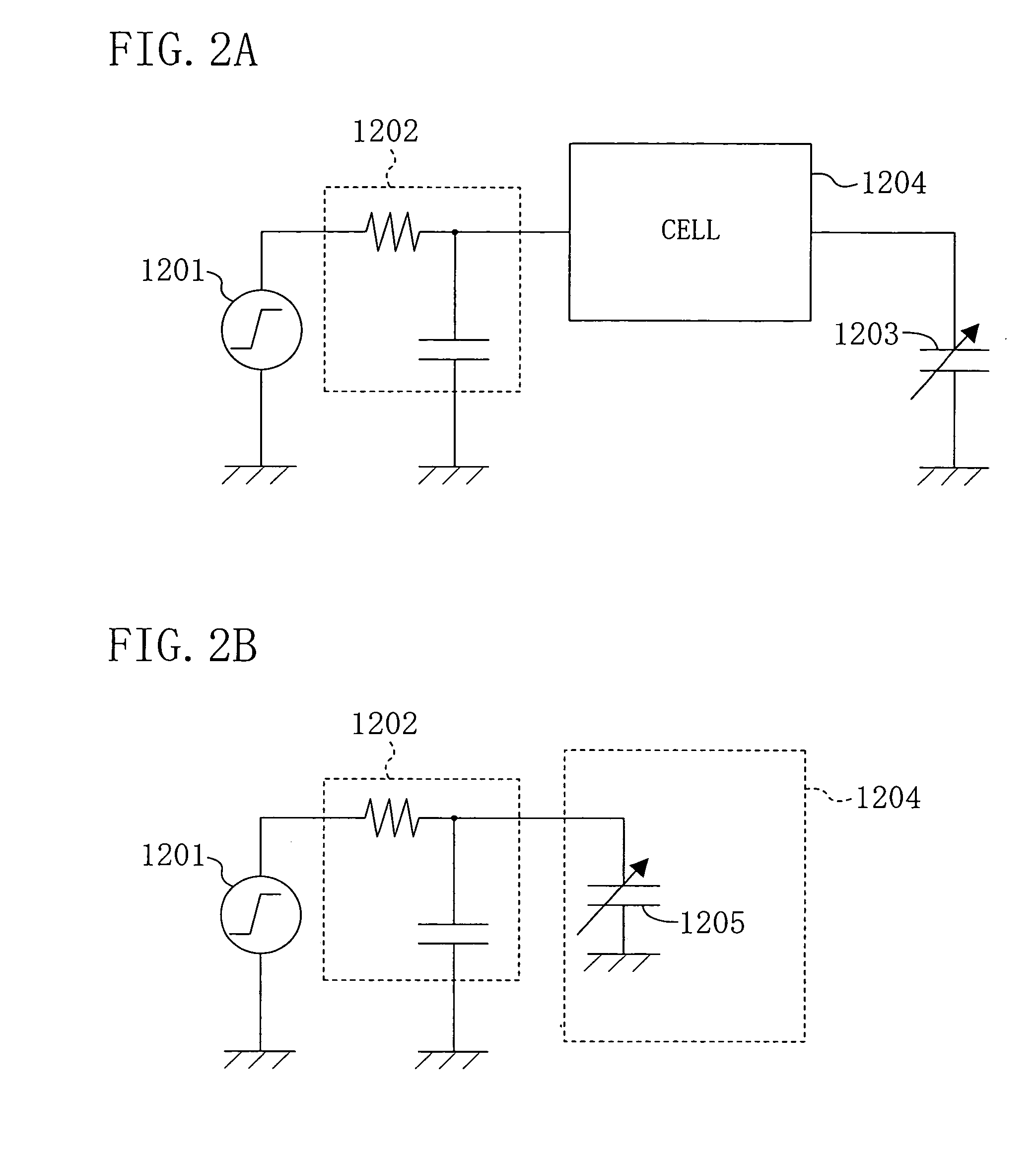
Method for characterizing cells with consideration for bumped waveform and delay time calculation method for semiconductor integrated circuits using the same
An effective input terminal capacitance which is effectively equivalent to a cell in which a waveform distortion is caused due to the Miller effect and a drive load connected to the cell is calculated in advance, and the cell and the drive load are replaced by the calculated effective input terminal capacitance, while considering that the Miller effect is caused according to the size of the drive load driven by a delay time calculation subject circuit, such as a cell, or the like, and a distortion occurs in input and output waveforms of the delay time calculation subject circuit due to the Miller effect. Thereafter, a circuit simulation is carried out using the effective input terminal capacitance. A resultant effective input terminal capacitance value is characterized as a function of an input slope waveform and the drive load and converted to table data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Solid-state image sensor and camera system
ActiveCN101719994AIncrease the areaReduce noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierDifferential amplifier
A solid state image sensor includes a pixel unit and a readout unit that reads out per-pixel pixel signals from the pixel unit. The readout unit includes: a plurality of column-parallel comparators that compare a readout signal potential to a reference voltage and output a determination signal; and a plurality of counters that count the comparing time of a corresponding comparator. Each comparator includes: a first amp containing a differential amplifier that receives the reference voltage at the gate of a transistor, receives the readout signal at the gate of another transistor, and compares the reference voltage to the readout signal potential; a second amp containing an amplifier that increases the gain of the first amp's output; and a capacitor connected between the input and the output of the amplifier in the second amp in order to exhibit the Miller effect.
Owner:SONY CORP
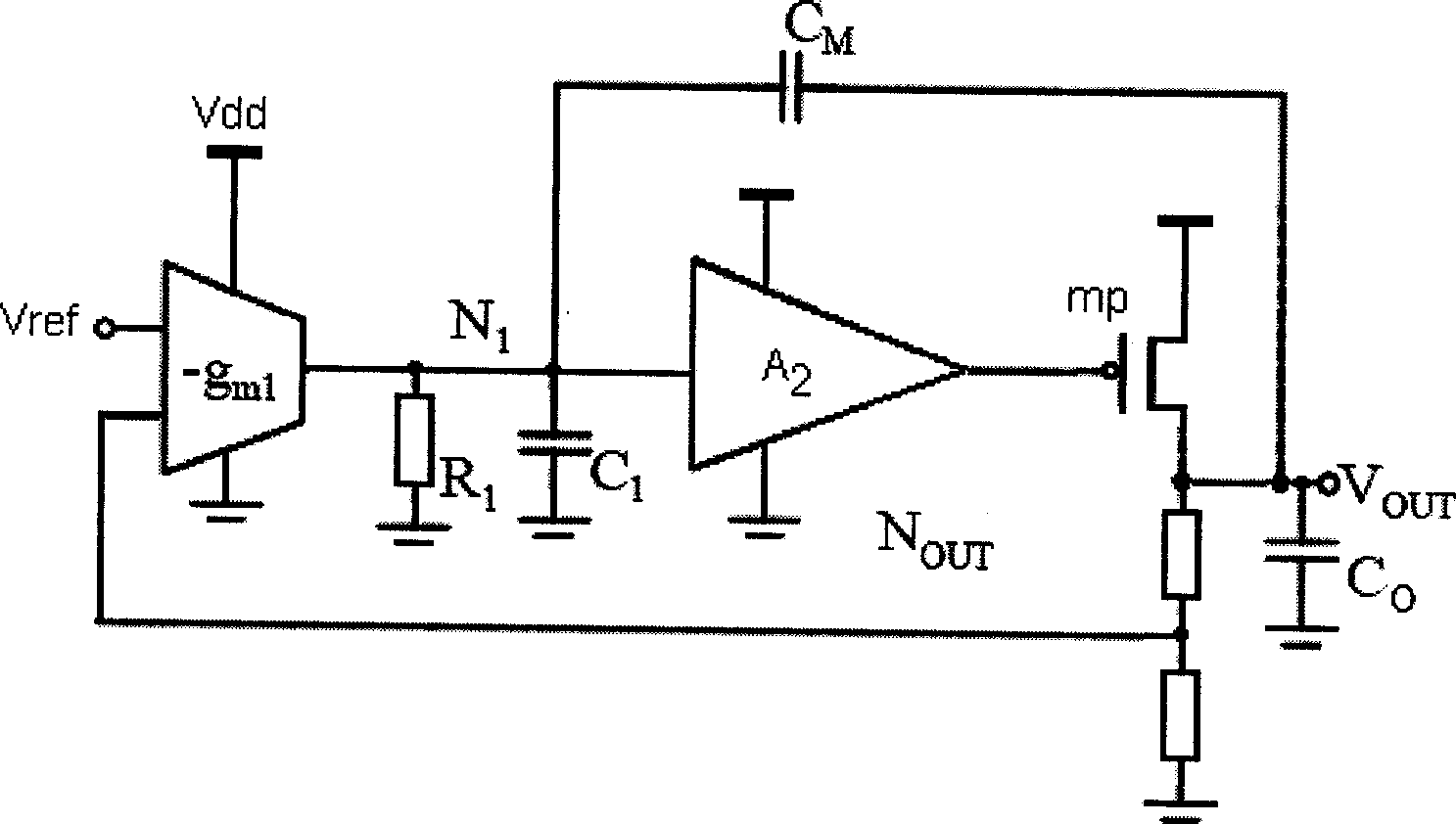
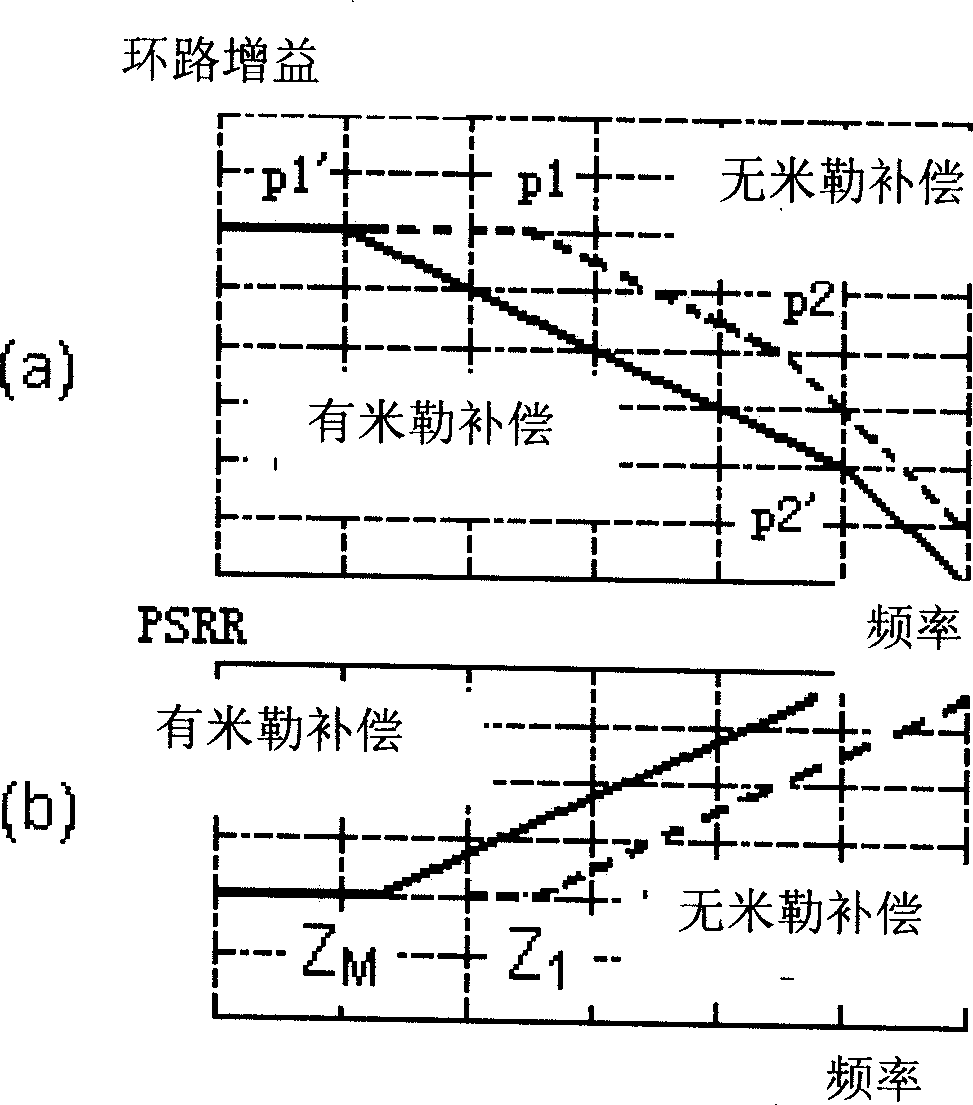
Low-pressure difference linear voltage stabilizer with high power supply rejection ratio
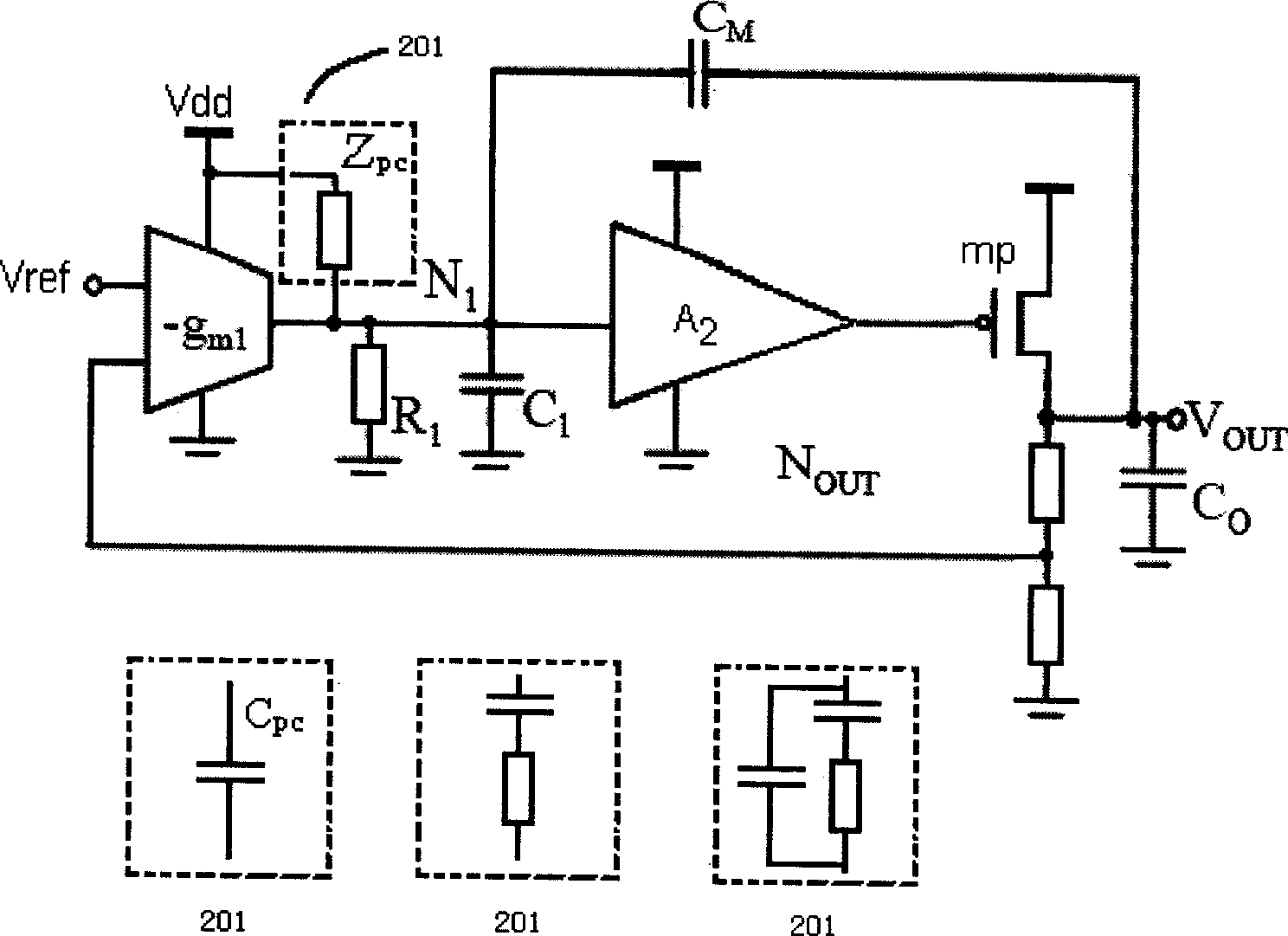
ActiveCN101464699AImprove PSRR characteristicsFix too smallElectric variable regulationCapacitanceLinear regulator
A low dropout linear regulator with high power supply rejection ratio is characterized in that a compensation network (201) with transmission function being Zpc and the ability of reducing equivalent output capacitance of N1 node is arranged between a power supply Vdd and the output end of an error amplifier. With the adoption of the low dropout linear regulator, near-zero points on PSRR curve are effectively pushed away, the stabilization of the LOD can be kept when the PSRR property at high frequency is improved, and the problem that PSRR main zero points are too small, caused by the miller effect, is solved.
Owner:FREMONT MICRO DEVICES SHENZHEN LTD
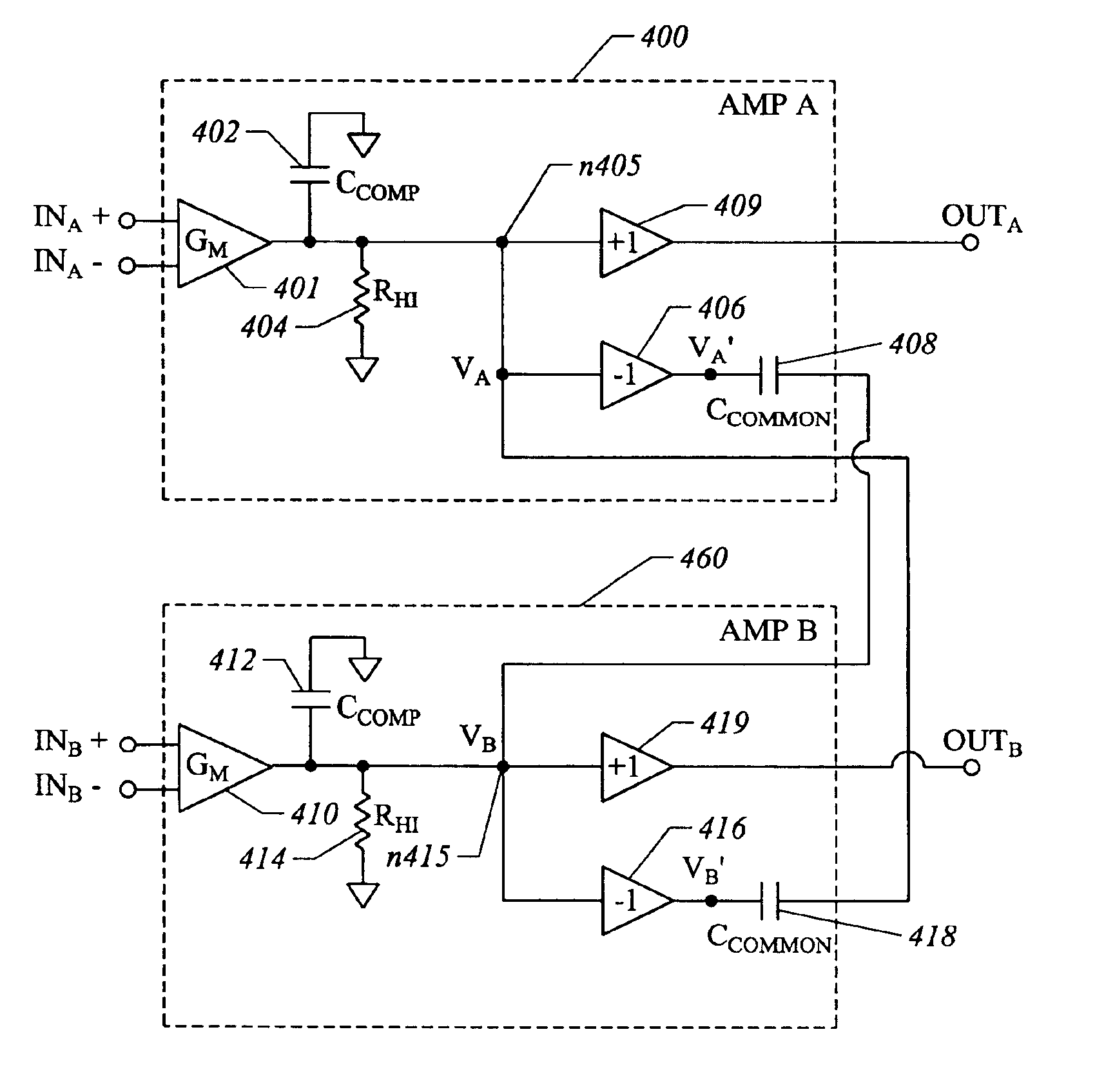
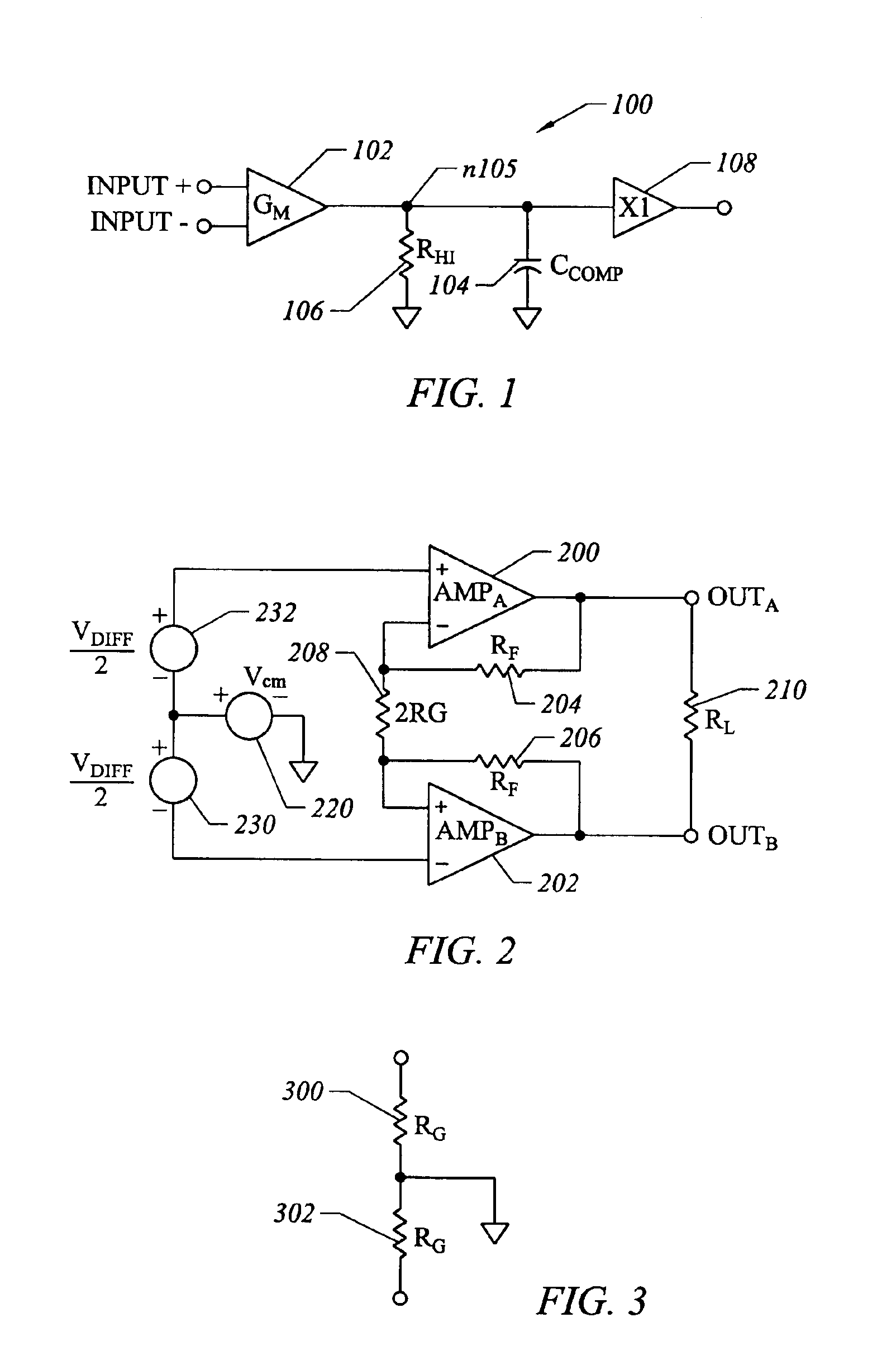
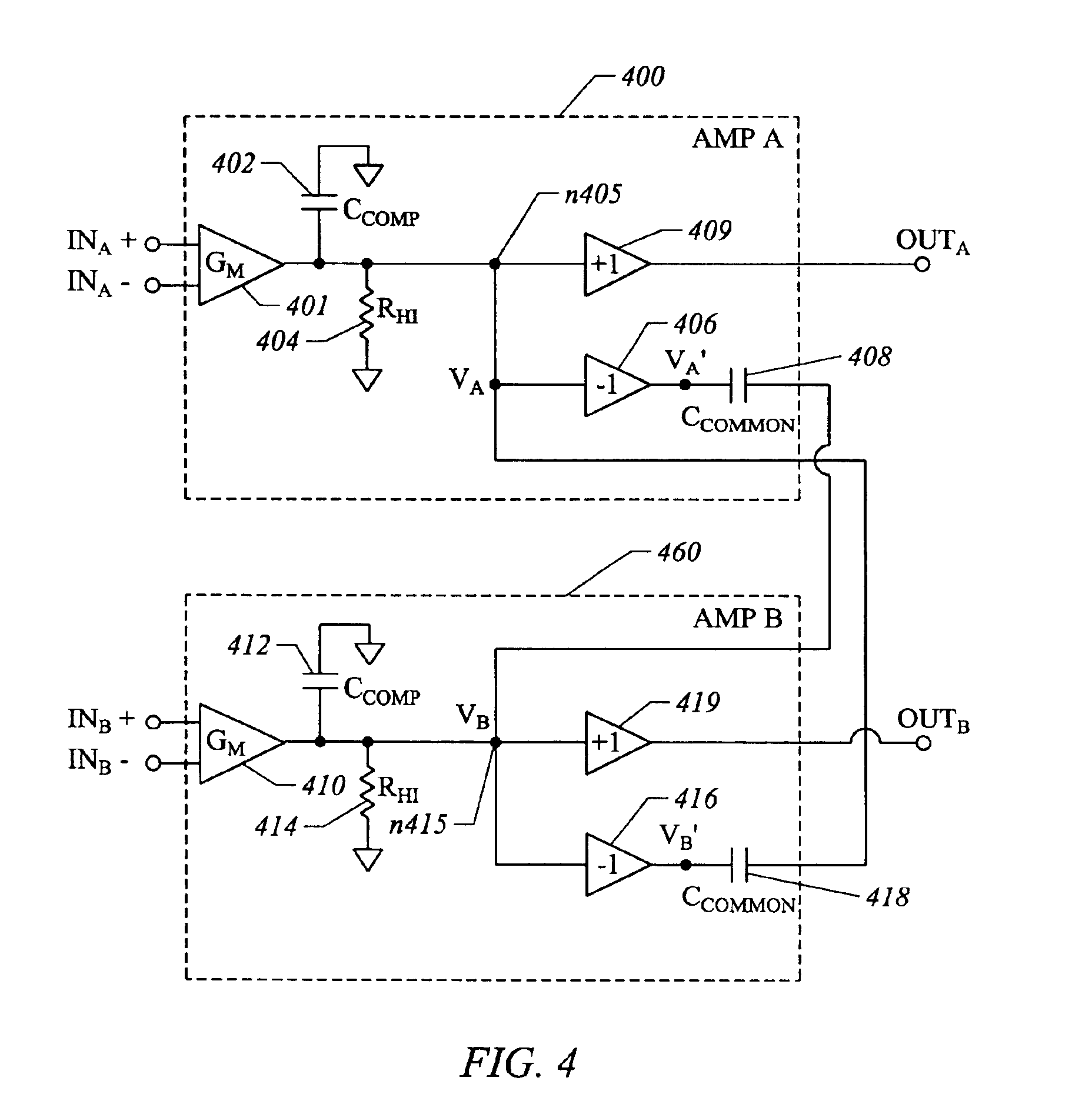
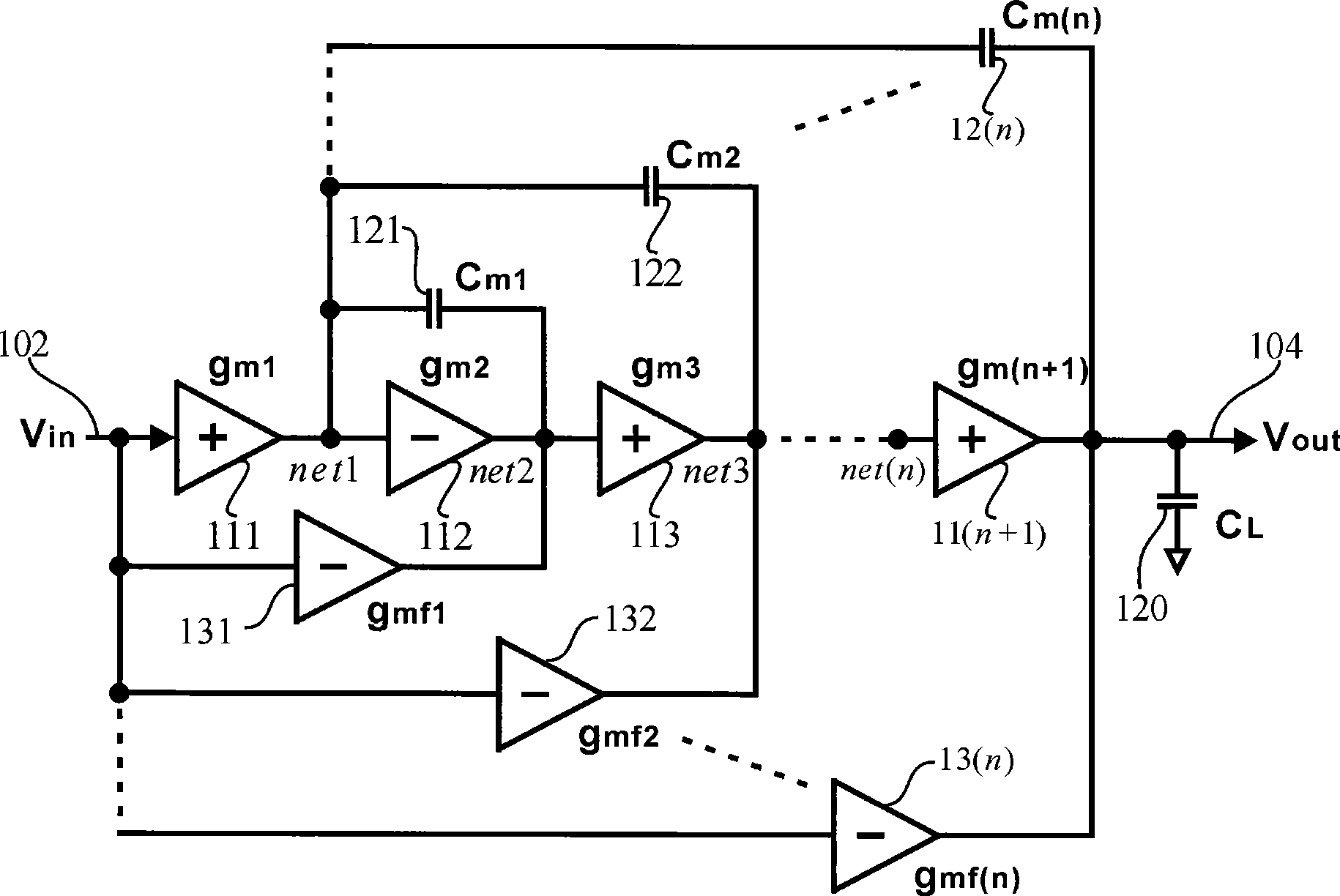
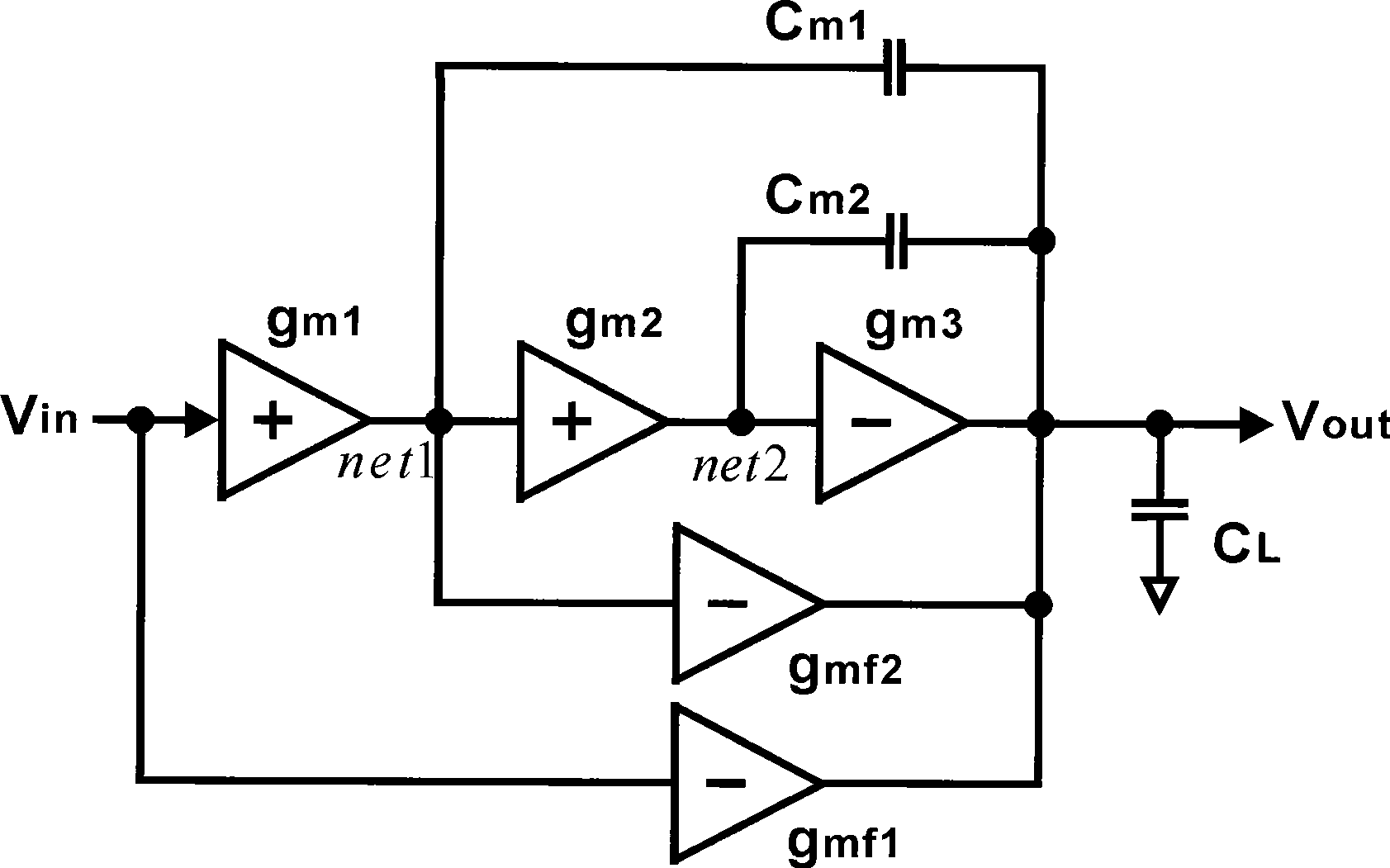
Common-mode and differential-mode compensation for operational amplifier circuits
ActiveUS6867649B2Stabilize differential circuits without compromising performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
An amplifier is configured to provide both common-mode and differential-mode compensation to ensure stability in telecommunications circuits or other circuits where both common mode and differential mode signal paths are provided. The amplifier includes two interconnected operational amplifiers AMPA and AMPB. Common mode compensation is provided by connecting one or more capacitors with a total value CCOMMON connected from a gain node at the input of an inverter in one of the amplifiers AMPA or AMPB to the output of the inverter in the other amplifier. Differential mode compensation can be provided by connecting a capacitor with value CCOMP at the gain node of each of the amplifiers AMPA or AMPB. Alternatively, both differential mode and Miller effect compensation can be provided by connecting one or more capacitors with total value CCOMP from the input to the output of components forming the inverter in each of the amplifiers AMPA and AMPB. As a further alternative, differential mode compensation can is provided independent of common mode compensation by connecting a capacitor with value CDIFF between the outputs of the inverters of the amplifiers AMPA and AMPB.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
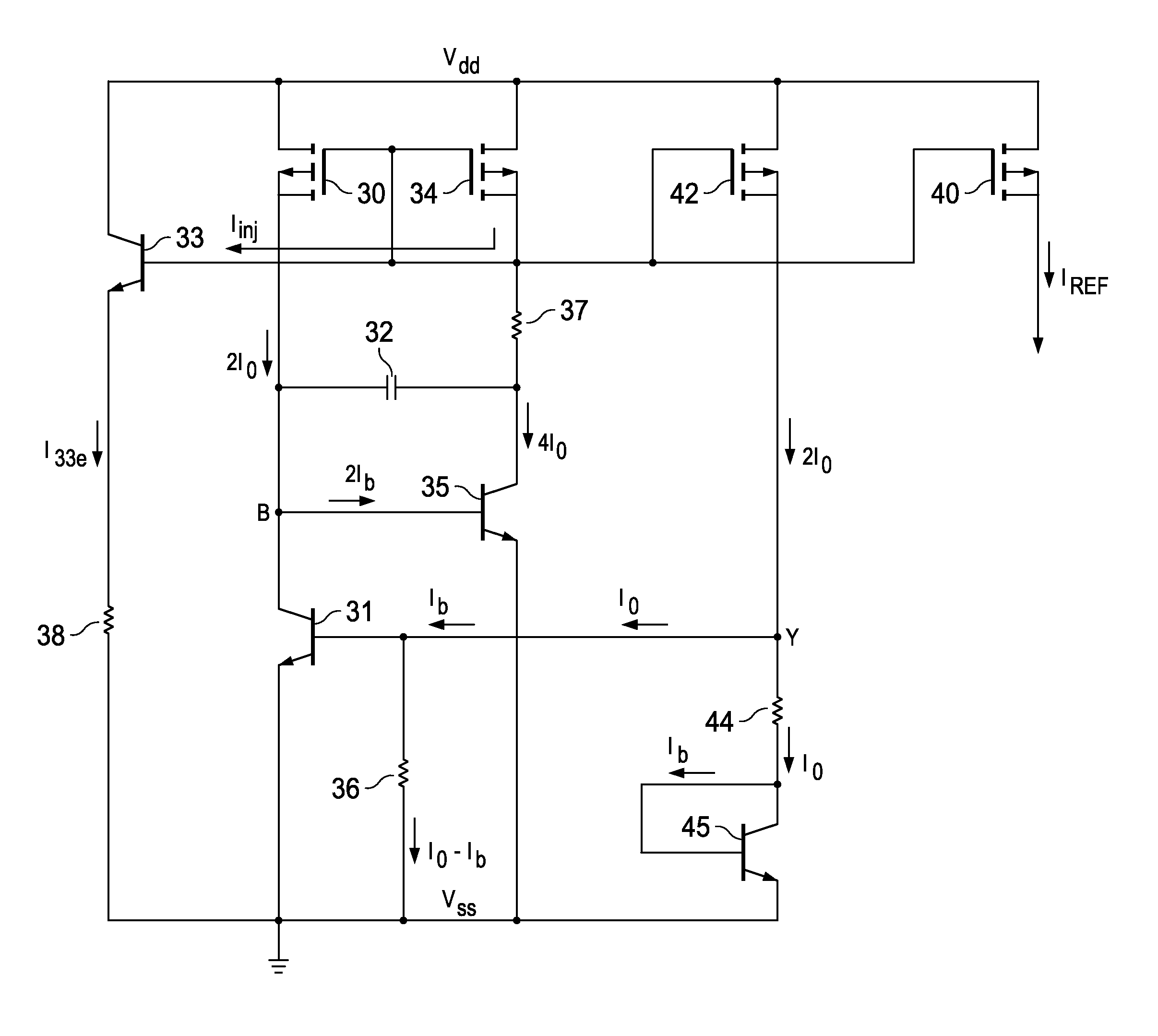
Start-Up Circuit and Method for a Self-Biased Zero-Temperature-Coefficient Current Reference
ActiveUS20090295360A1Efficient implementationEfficiently realizableElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceReference circuit
A current reference circuit is disclosed. A small startup current is defined as the base current into a bipolar transistor with its collector-emitter path connected in series with a resistor between the power supply voltage and ground. This startup current is conducted via a diode-connected MOS transistor in a first leg of a current mirror. Temperature compensation is maintained by a reference leg in the current mirror that includes a bipolar transistor having an emitter area N times larger than that of a bipolar transistor in a second leg of the current mirror, to establish a temperature-compensated current in the reference leg. A compensation capacitor connected between the collector and base of a bipolar transistor in the first leg suppresses oscillation, and can be modest in size due to the Miller effect.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
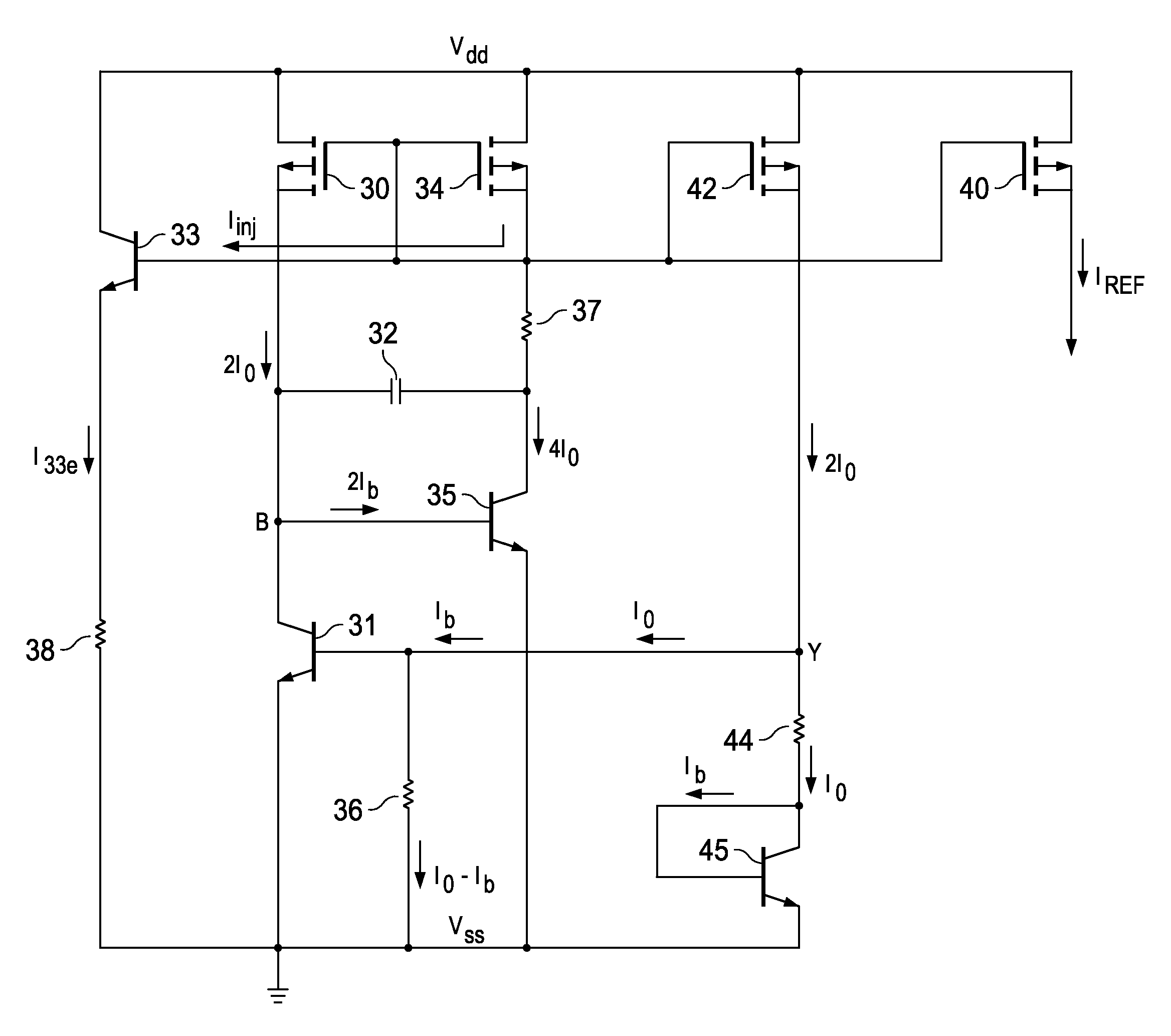
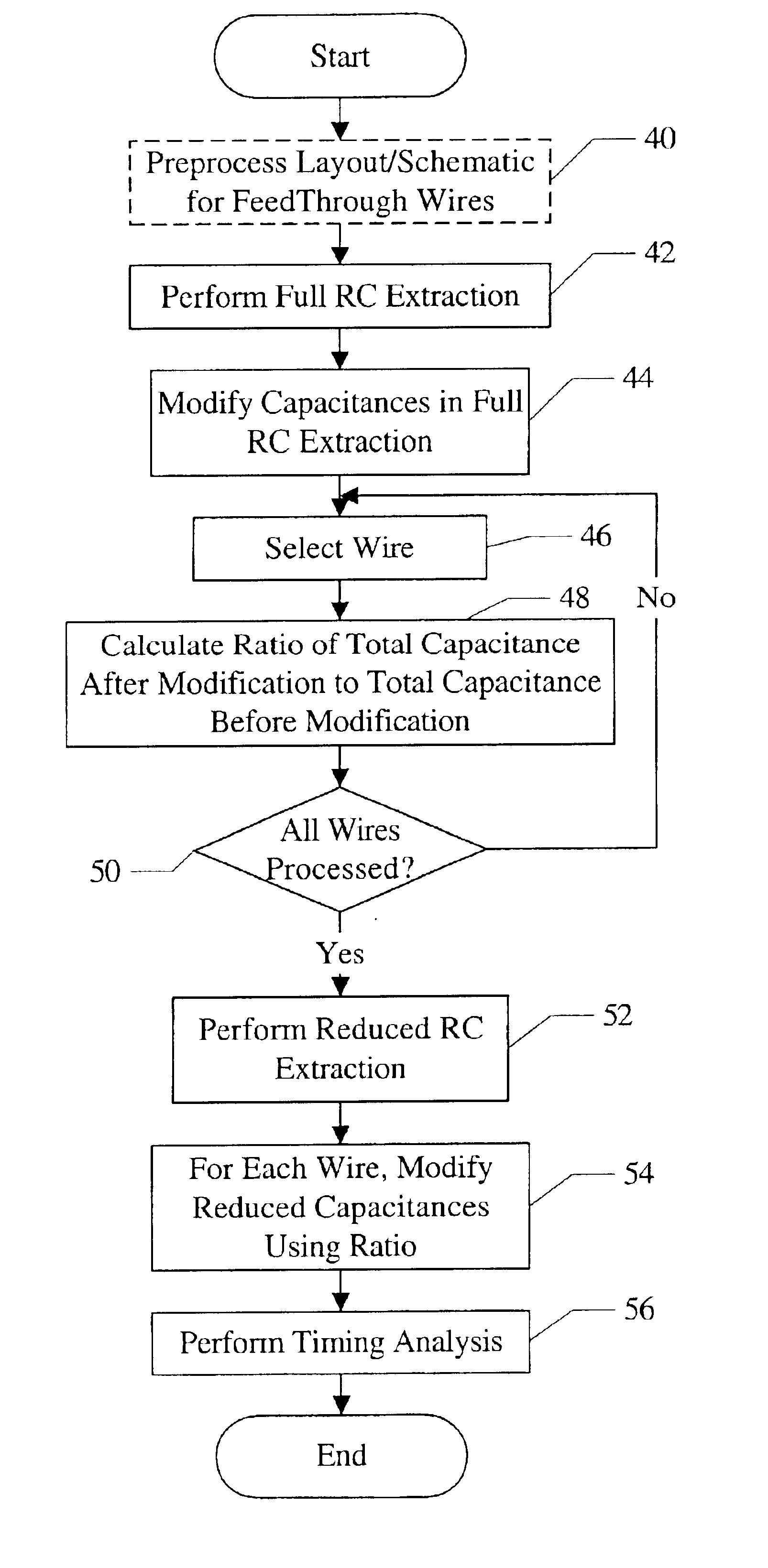
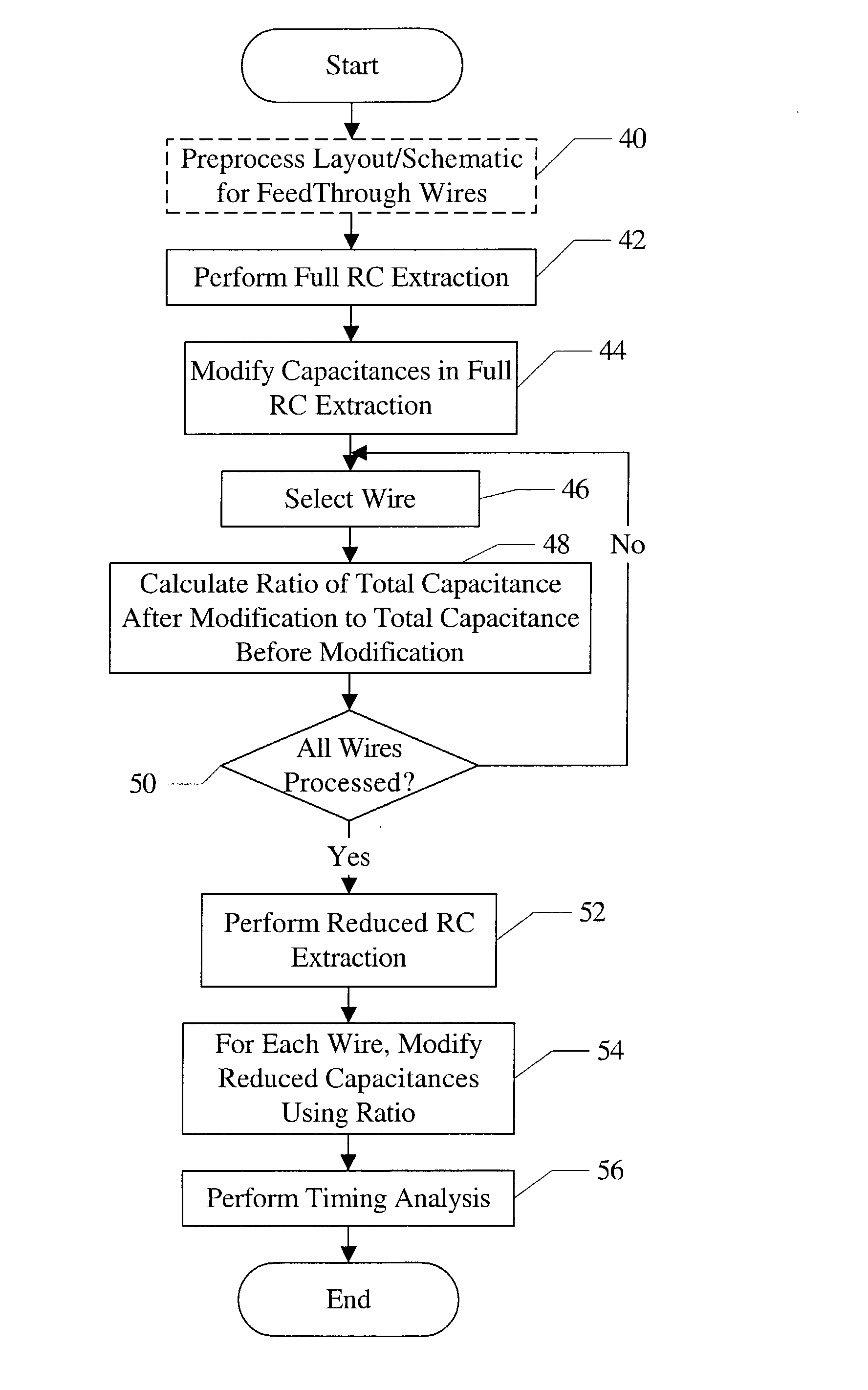
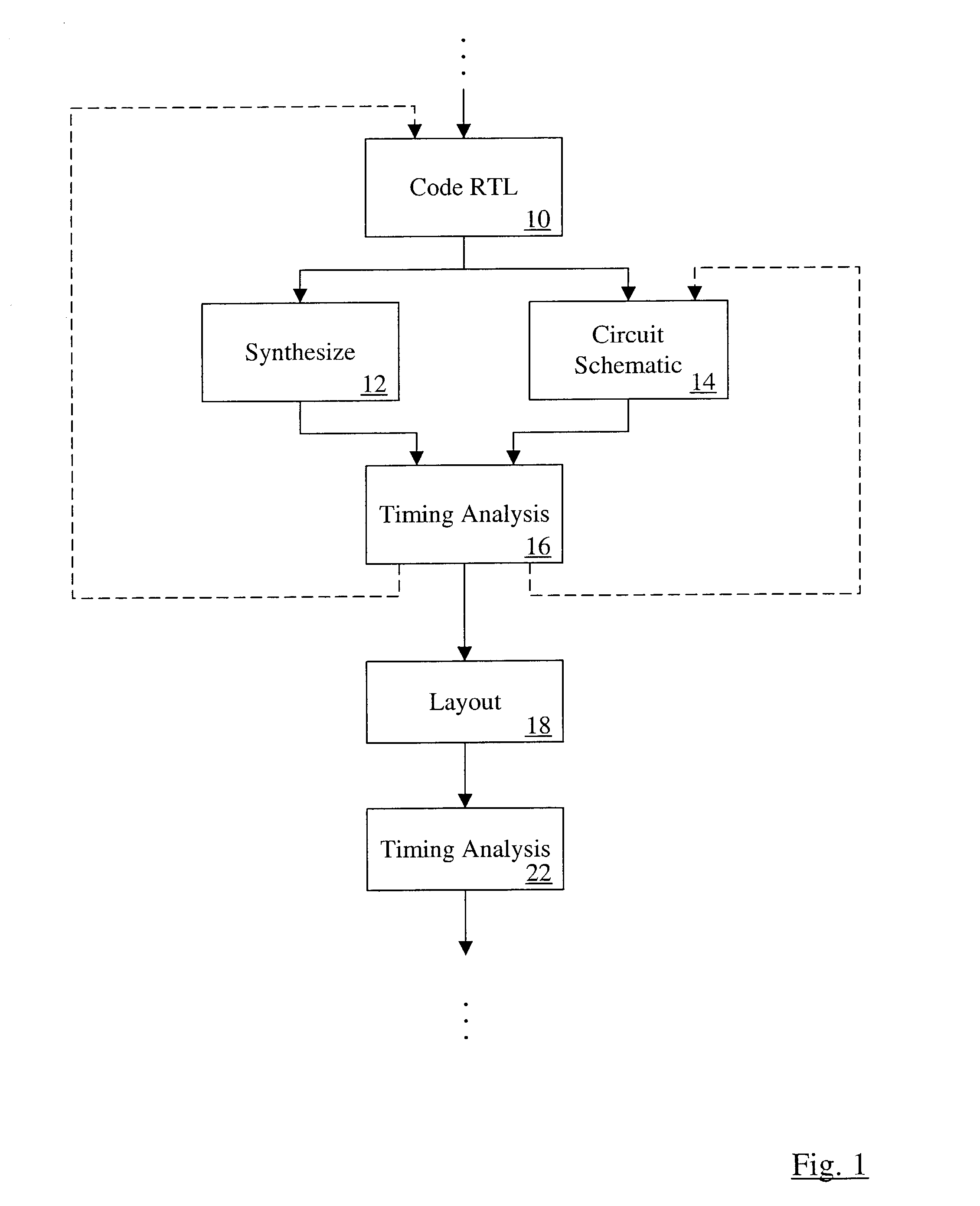
Modeling miller effect in static timing analysis
InactiveUS6791343B2Current/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A method is contemplated. According to the method, capacitances in a first resistance / capacitance (RC) extraction corresponding to a circuit are modified. Each capacitance is modified to estimate Miller effect on that capacitance. A ratio of a total capacitance on a first wire after the modification in the first RC extraction to a total capacitance on the first wire before the modification in the first RC extraction is calculated. Capacitances in a second RC extraction that are coupled to the first wire are modified according to the ratio. The second RC extraction is a reduced extraction as compared to the first RC extraction. A timing analysis is performed for the circuit using the second RC extraction with capacitances modified to estimate Miller effect.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
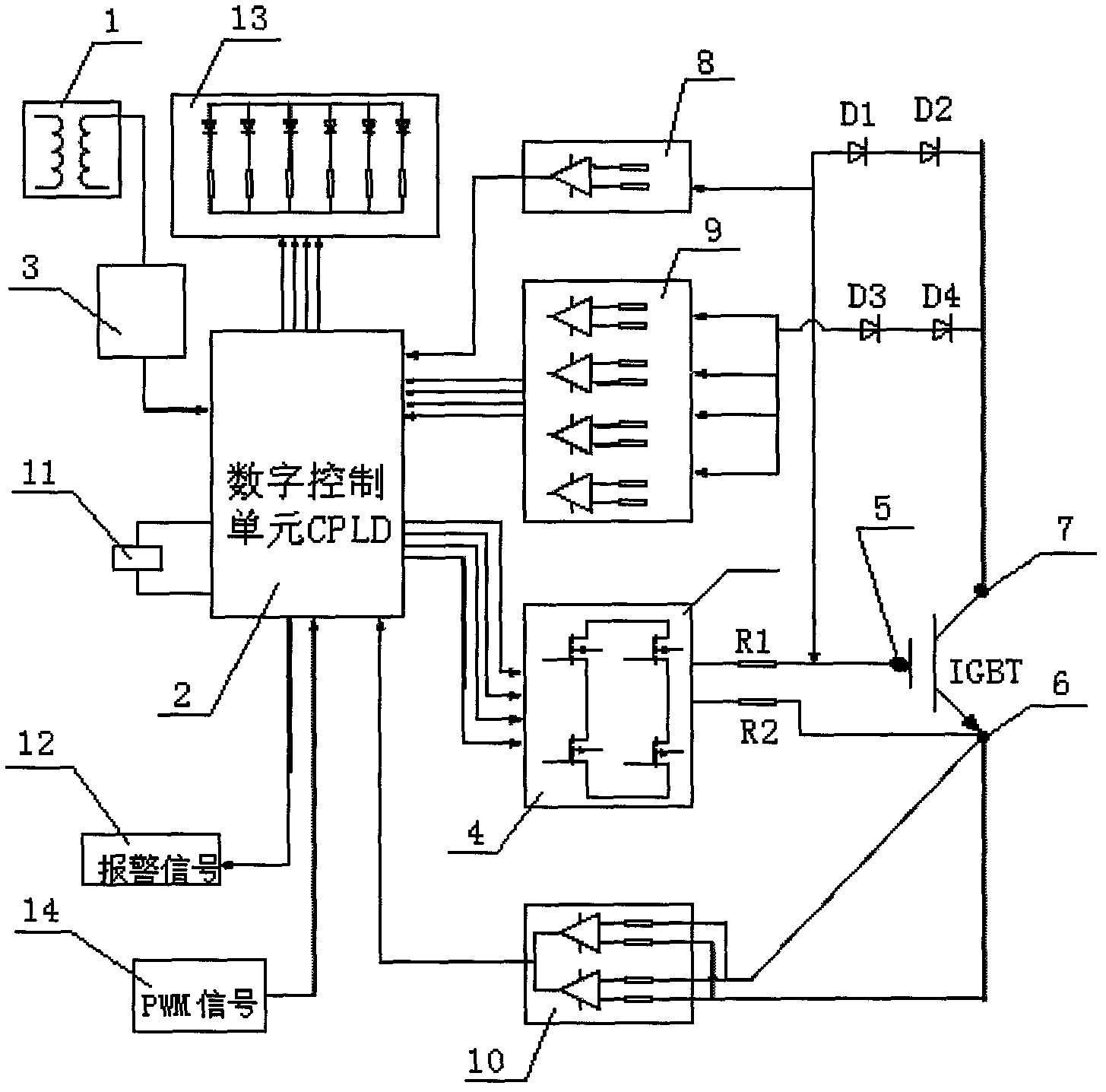
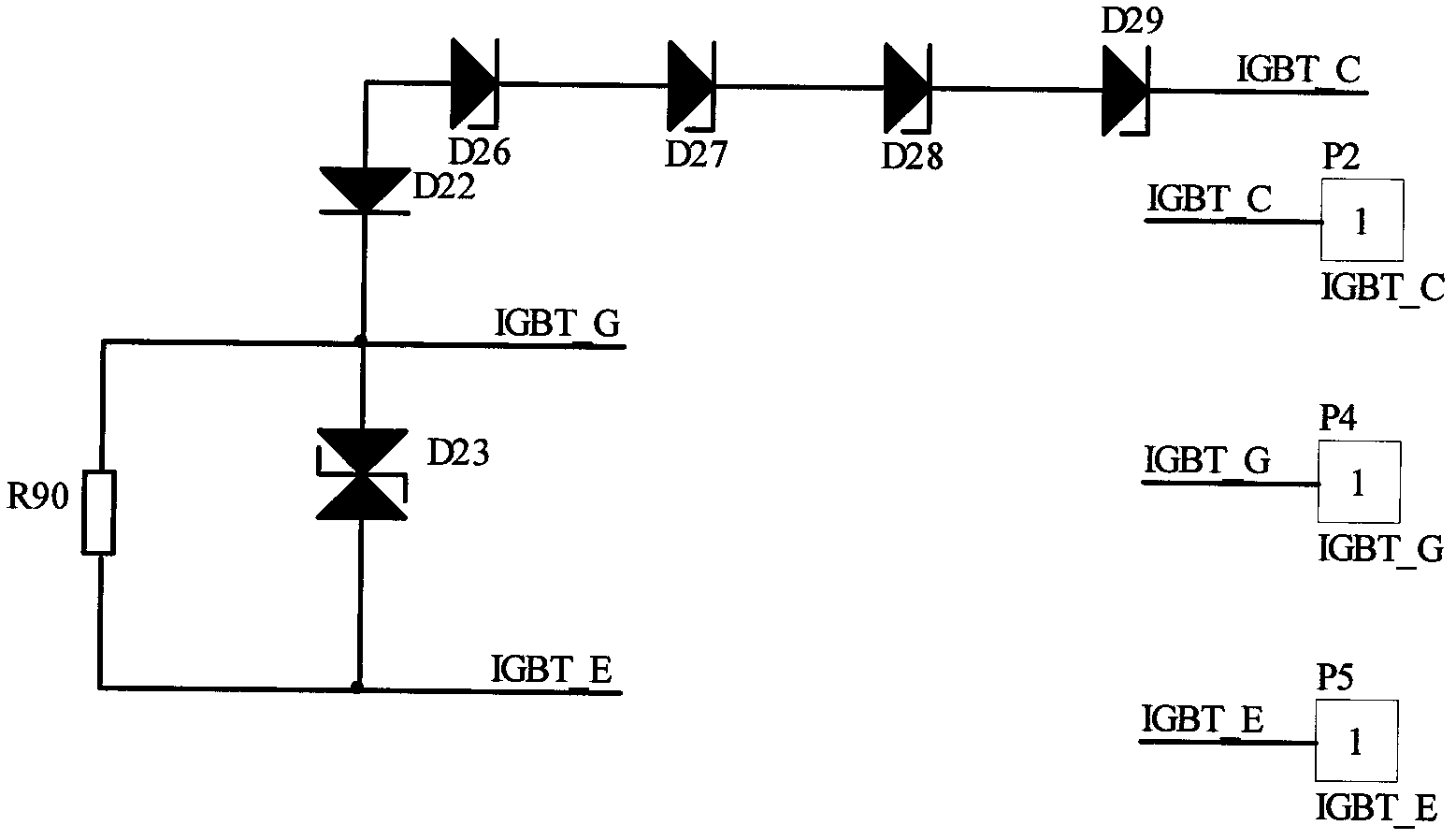
Digital intelligent driving device of high-power IGBT (insulated gate bipolar translator)
ActiveCN102594104ASignificant technological progressIdeal driving stateEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower conversion systemsProgrammable logic deviceComputer module
The invention relates to a digital intelligent driving device of a high-power IGBT (insulated gate bipolar translator). The digital intelligent driving device comprises a DC / DC (direct-current) conversion circuit, a CPLD (complex programmable logic device) logic control module, an active clamping feedback module, a retreating-protection over-current feedback module and a two-stage di / dt detecting module, wherein the output end of the DC / DC conversion circuit is connected with an undervoltage protection module; the output end of the undervoltage protection module is connected with the CPLD logic control module; and the input end of the CPLD logic control module is connected with a PWM (pulse-width modulation) pulse-width modulator, and the output end of the CPLD logic control module is connected with a variable-gate resistance module. The digital intelligent driving device provided by the invention has the advantages that the protection functions such as power isolation, over-current protection, di / dt and active clamping are integrated, the logic control is realized by adopting the programmable logic device CPLD, the ideal driving performance is achieved by real-time variable-gate resistance driving, and soft shut-off is realized by selecting proper shut-off resistance according to the over-current degree, so that the switching loss is effectively reduced and a Miller effect is weakened.
Owner:WUHAN ZHENGYUAN ELECTRIC
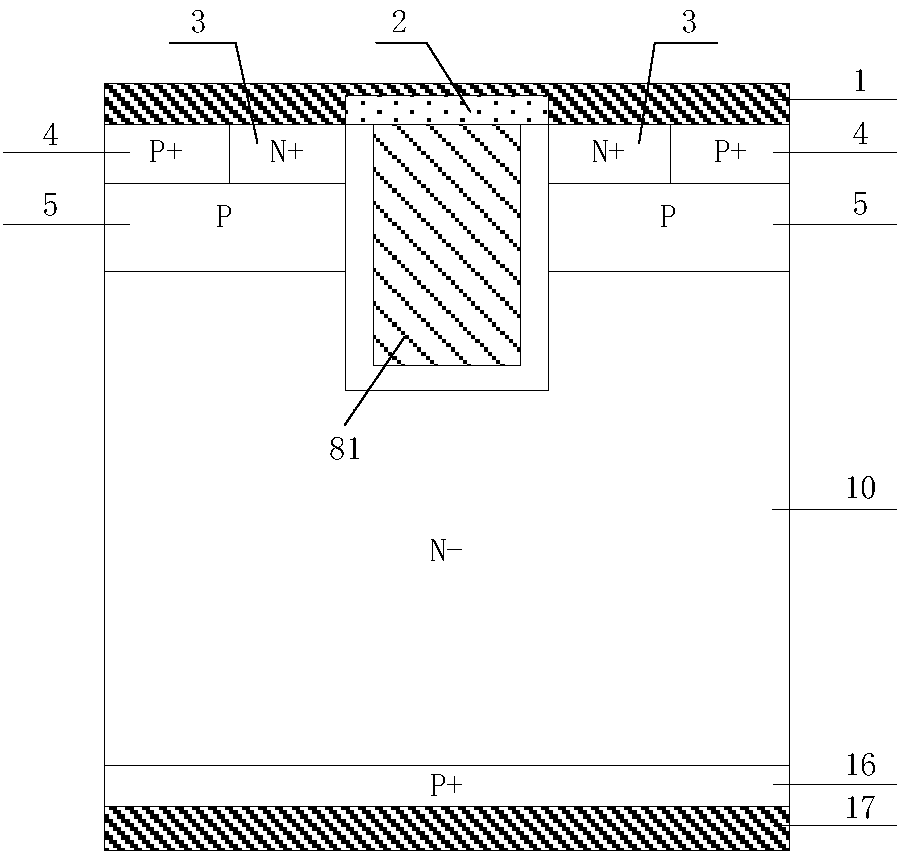
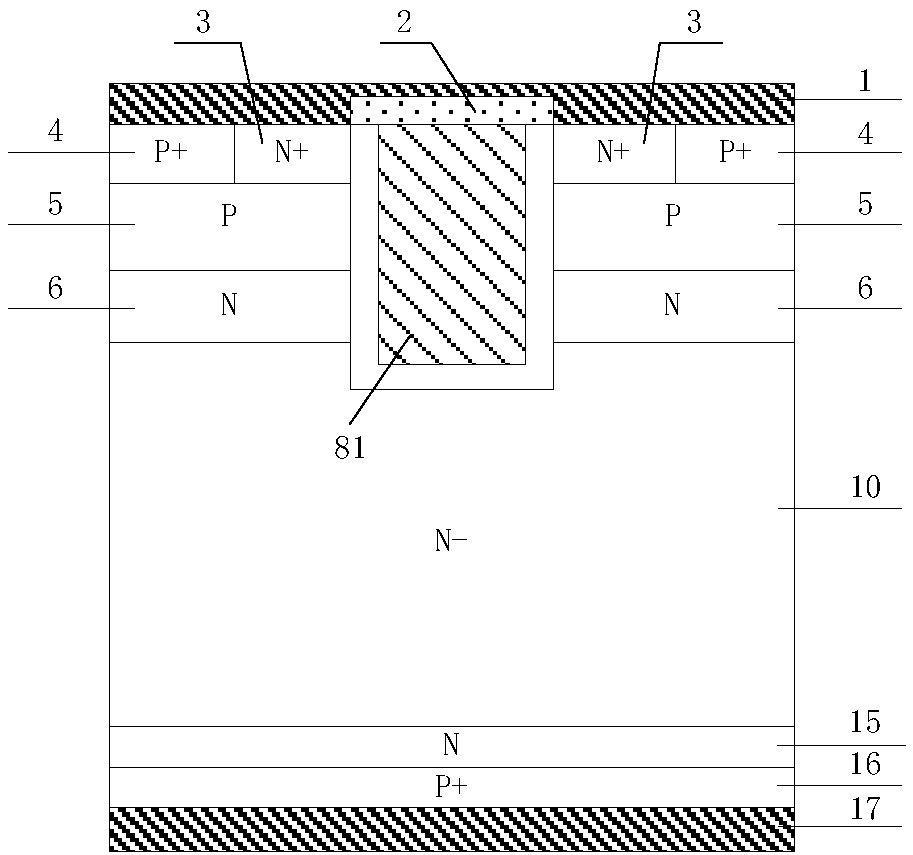
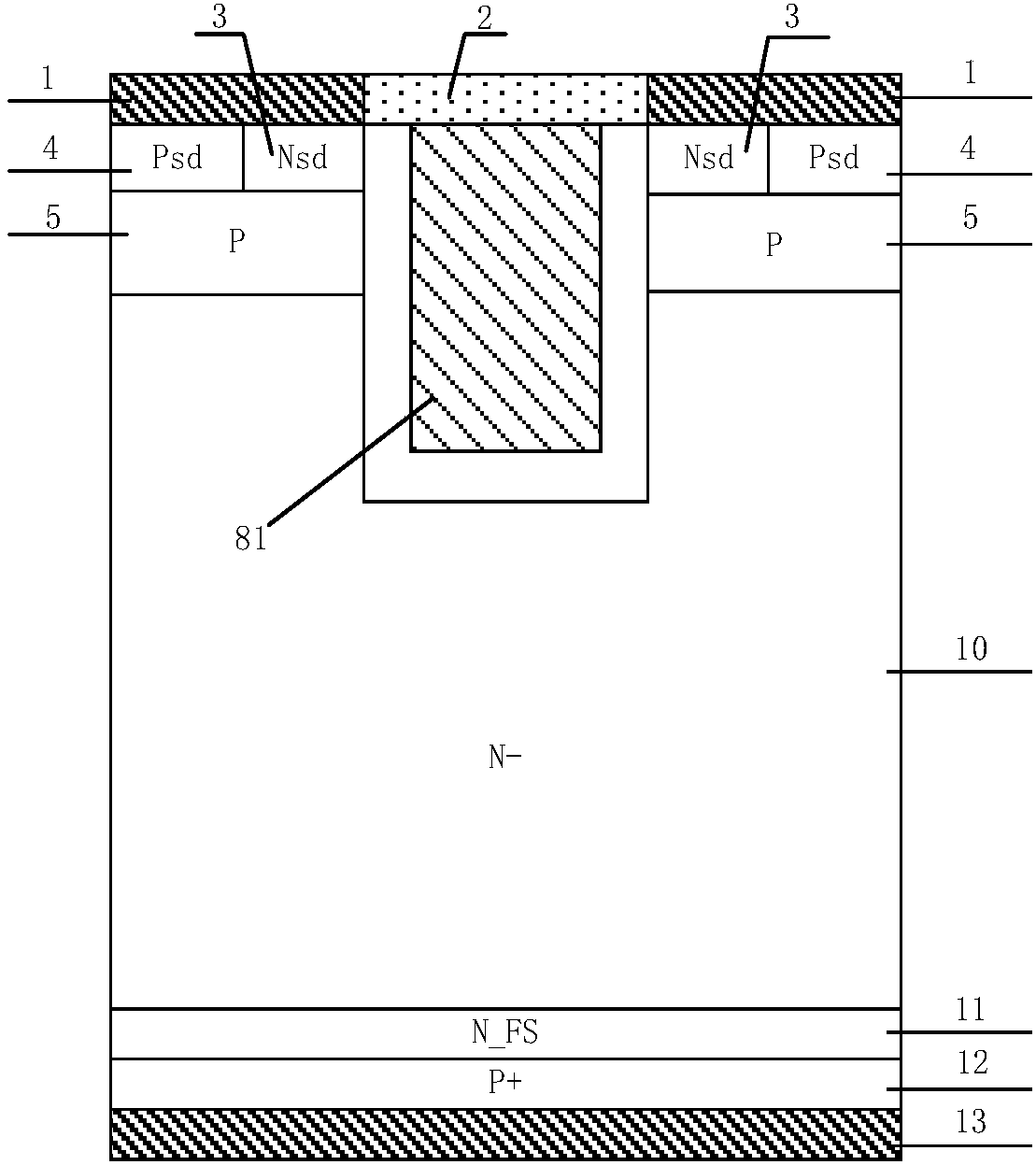
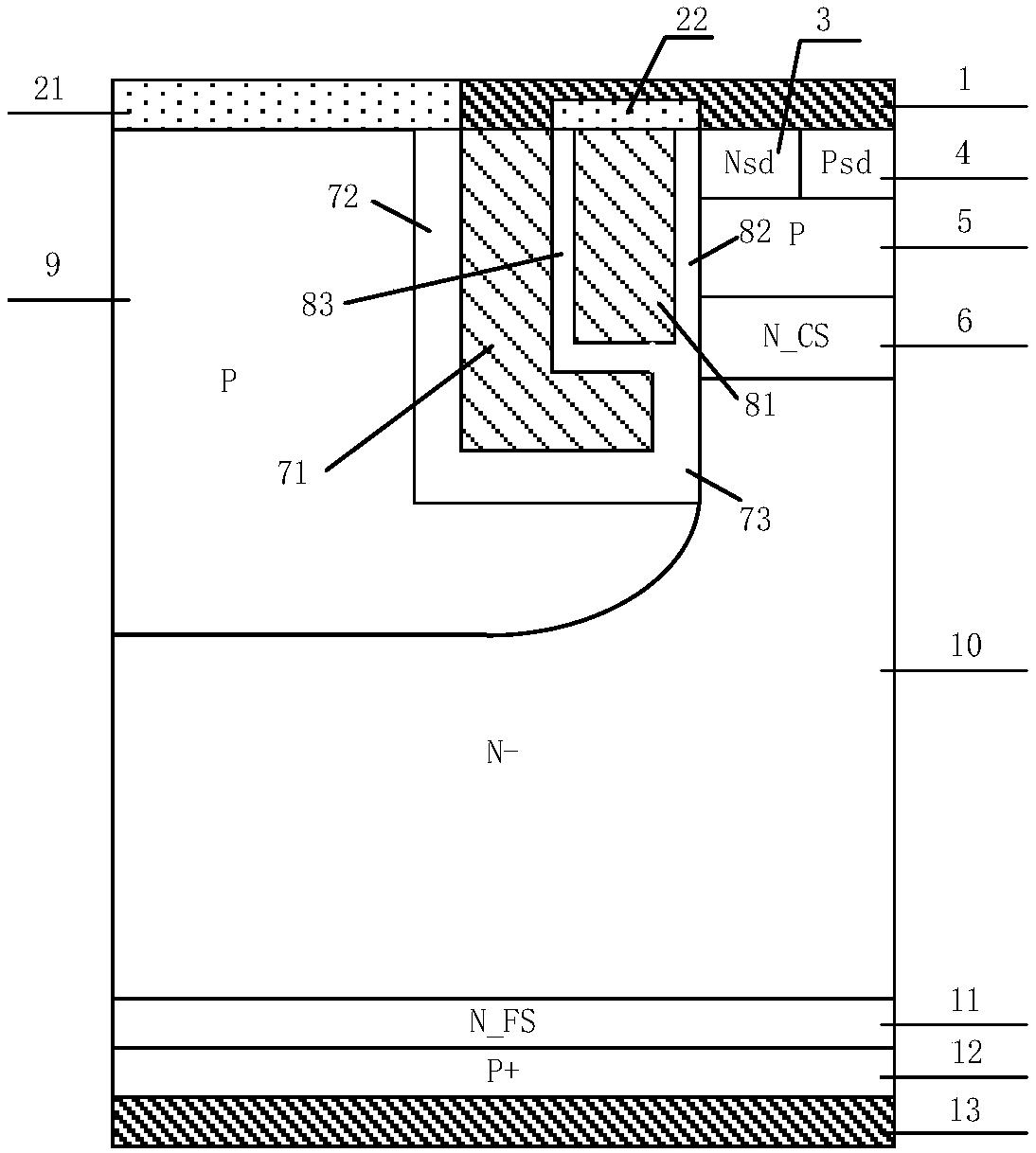
Reverse blocking type IGBT and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveCN107799587AImprove reverse breakdown voltageGood positive characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitancePower semiconductor device
The invention discloses a reverse blocking type IGBT and a manufacturing method therefor, and belongs to the technical field of a power semiconductor device. By introducing a floating P type body region on one side of a trench gate and introducing a trench collector structure in a collector region and a field stop layer, the positive breakdown voltage of a device is improved without influencing the threshold voltage and switch-on of an IGBT device; the gate-collector capacitance is lowered, and adverse influence caused by a Miller effect can be relieved; the overall gate capacitance is lowered, the switching speed of the device is improved, the switching loss of the device is lowered, and the compromising relation between forward switch-on voltage drop and switch-off loss of the conventional CSTBT device is improved; the problems of current, voltage oscillation and EMI in the device starting dynamic process can be avoided, and device reliability is improved; the current carrier enhancement effect at the emitter end of the device is improved, the current carrier concentration distribution in a drift region can be improved, and compromising between forward switch-on voltage drop andswitch-off loss can be further improved; and the reverse breakdown voltage of the device is improved, and high forward characteristic of the device is ensured while excellent reverse blocking performance is obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
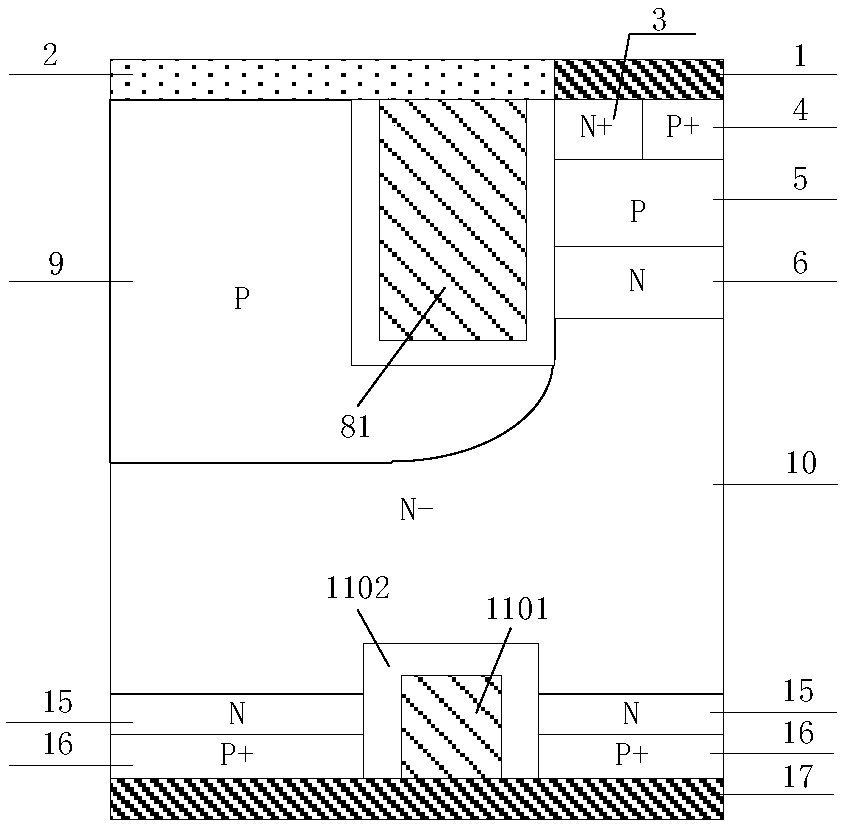
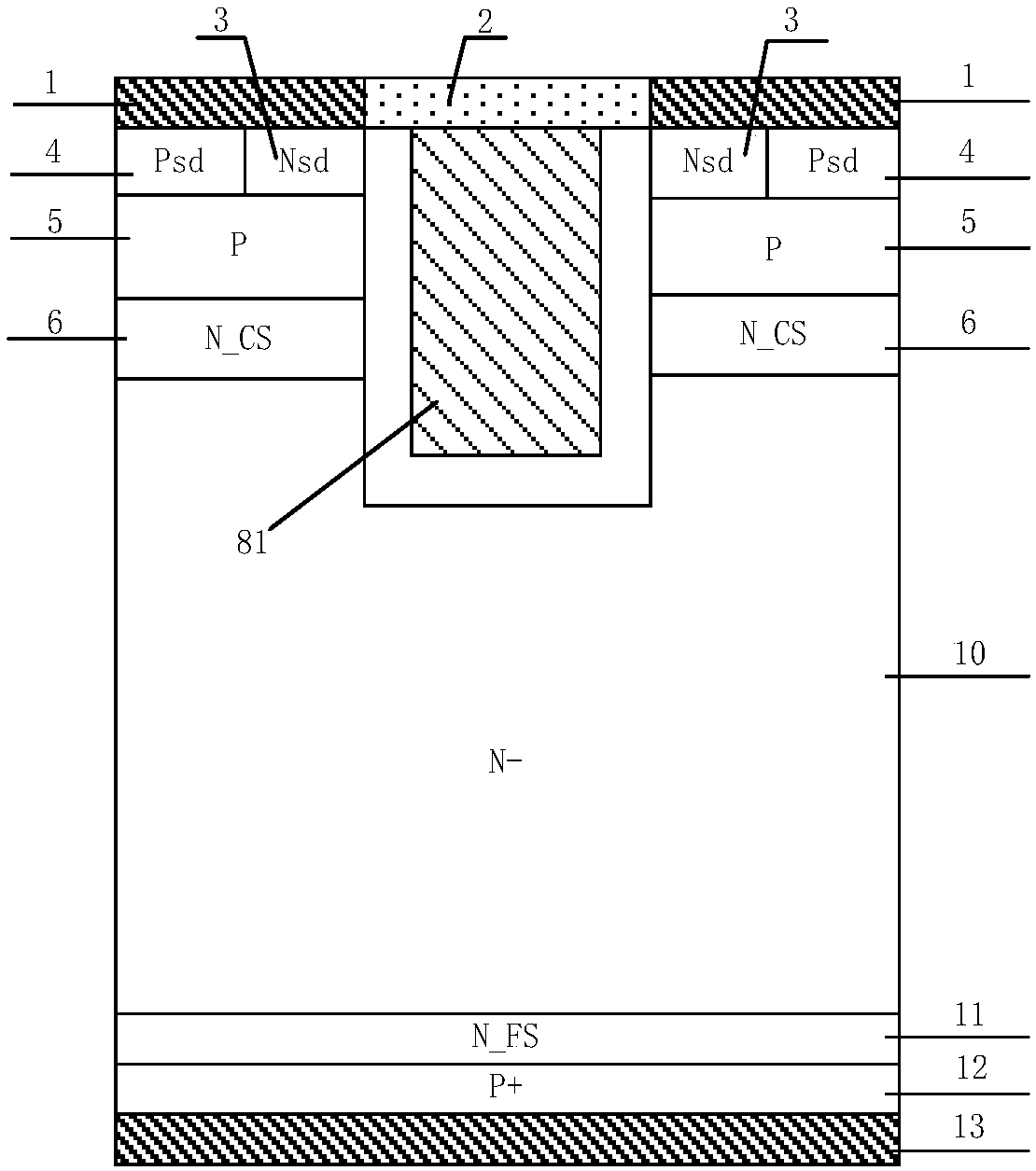
Trench gate charge storage-type IGBT and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN107731897AFast switching speedReduce gate capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceBreakdown voltage
The invention discloses a trench gate charge storage-type IGBT and a manufacturing method thereof, which belong to the technical field of power semiconductor devices. Through reasonably introducing asplit trench gate structure and an air floating P-type region, in a condition of not influencing the threshold voltage of the IGBT and conduction, Miller capacitance is reduced, and bad influences brought by Miller effects are improved; the overall gate capacitance is reduced, the device switching speed is improved, the switching losses of the device are reduced, and the compromise between forwardconduction voltage drop and turn-off losses of the traditional CSTBT structure is improved; current and voltage oscillations and EMI problems in the device dynamic starting process are avoided, and the device reliability is improved; electric field concentration effects at the bottom part of the trench are improved, and the breakdown voltage of the device is improved; carrier enhancement effectsat an emitter end of the device are improved, the carrier concentration distribution in a drift region is improved, and the compromise between forward condition voltage drop and turn-off losses is further improved; and besides, the manufacturing method disclosed in the invention has the advantages of low realization difficulty, high product rate and low cost.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
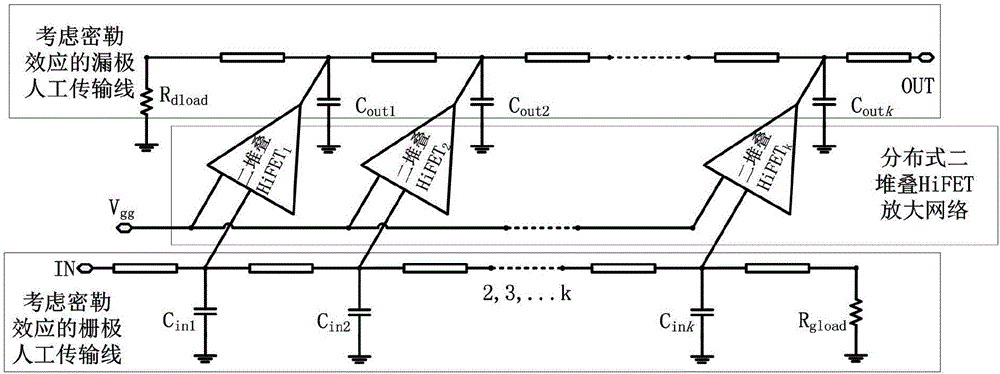
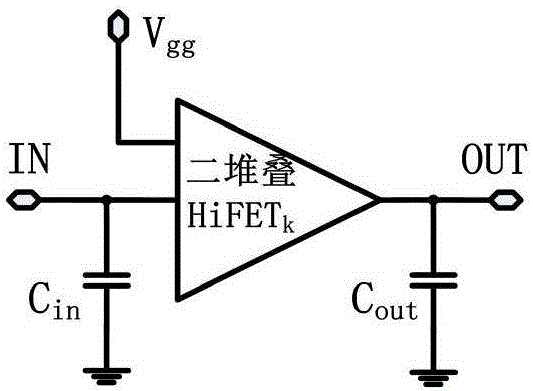
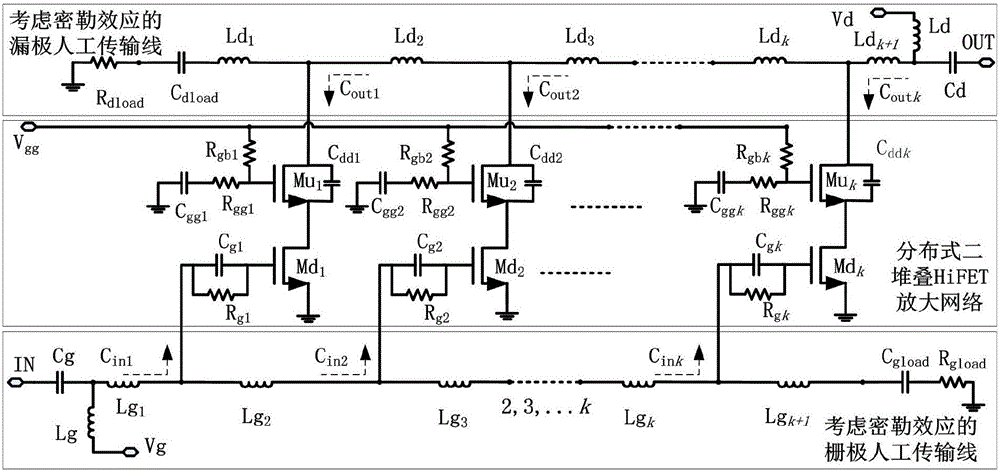
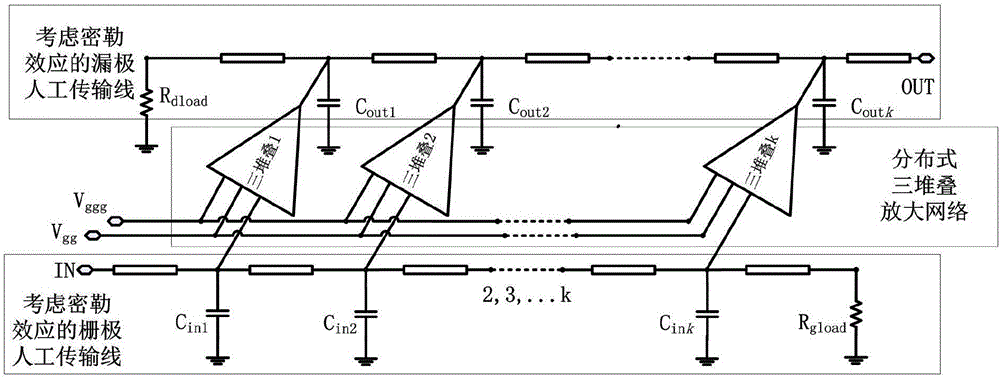
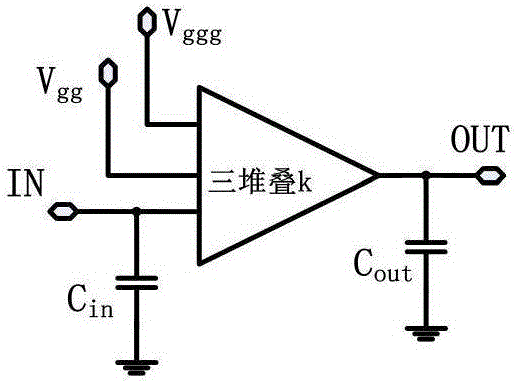
Power amplifier of distributed two-stack structure considering miller effect
ActiveCN106411268APlay a role in stabilizing the circuitReduce difficultyPower amplifiersRF amplifierArtificial transmission lineEngineering
The invention discloses a power amplifier of a distributed two-stack structure considering a miller effect. The power amplifier comprises a distributed two-stack HiFET (High-Impedance, High-Voltage field-effect transistor) amplification network, bias voltage, a grid electrode artificial transmission line considering the miller effect, and a drain electrode artificial transmission line considering the miller effect. According to the power amplifier provided by the invention, a core framework adopts the distributed two-stack HiFET amplification network, which is formed by at least three two-stack HiFET structures; meanwhile, the influence of the miller effect of a two-transistor stack structure on equivalent capacitance of the artificial transmission lines is considered, the accuracy of a circuit design is improved, and the difficulty in later debugging of the circuit is reduced, so that the whole power amplifier acquires a favorable broadband power output capability and a power gain capability, a low breakdown voltage characteristic of an integrated circuit process is avoided, and the stability and the reliability of the circuit are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU GANIDE TECH
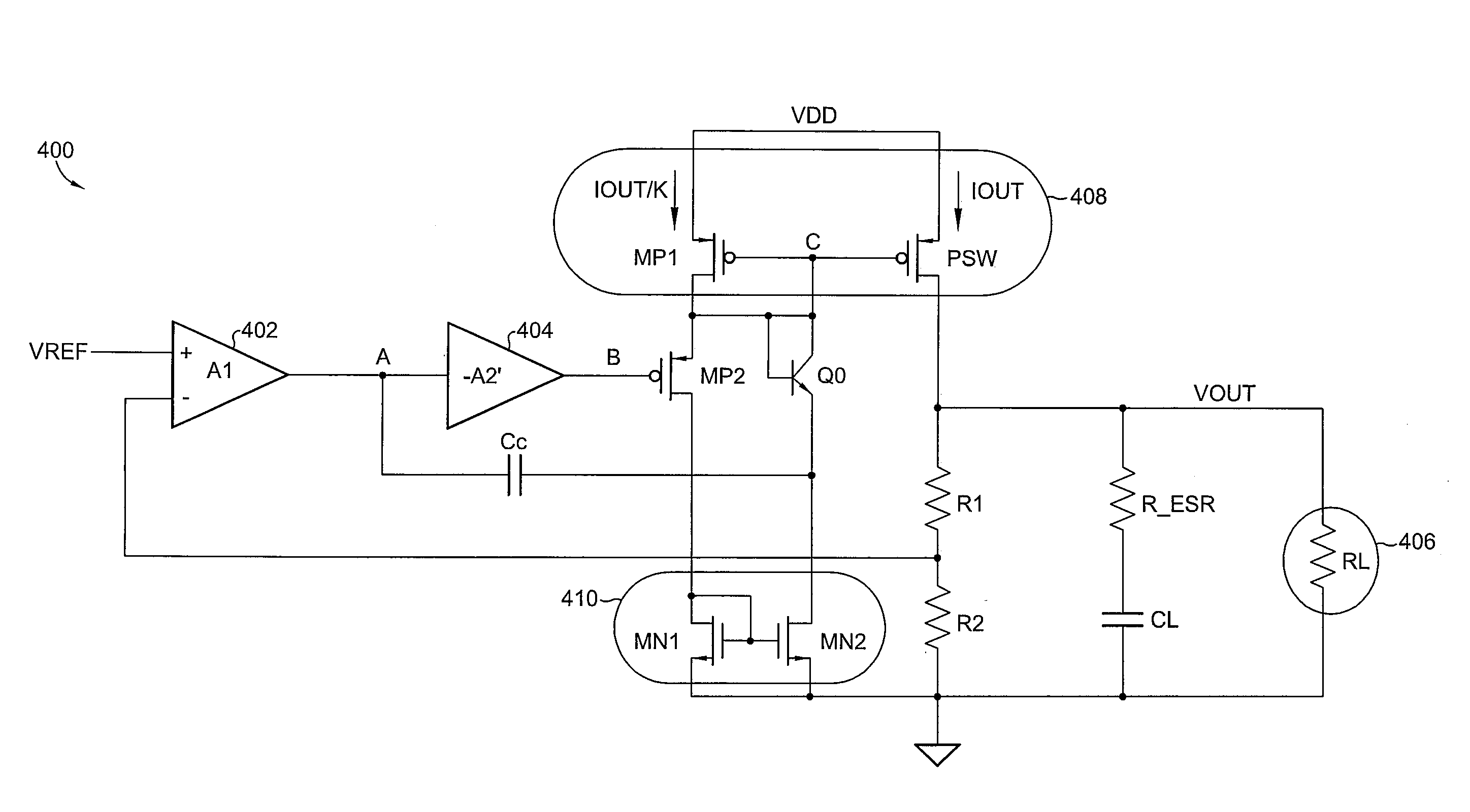
Frequency compensation scheme for stabilizing the LDO using external NPN in HV domain
A voltage regulator may comprise a regulator output configured to provide a regulated voltage, which may be controlled by an error amplifier based on the regulated voltage and a reference voltage. The error amplifier may control a source-follower stage to mirror a multiple of the current flowing in the source-follower stage into an internal pass device. A voltage developed by the mirror current may control an external pass device configured to deliver the load current into the regulator output. A first resistor may be configured to decouple a load capacitor coupled between the regulator output and reference ground, when the load current is below a specified value. A second resistor may be configured to create a bias current in the internal pass device even when the external pass device is close to cut-off region. A third resistor may be configured to counter the effects of negative impedance at the control terminal of the external pass device caused by the current-gain of the external pass device. A compensation capacitor and resistor may be coupled in series between the output of the error amplifier and the output of the voltage regulator to provide frequency compensation for the Miller-Effect.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Adaptive miller compensated voltage regulator
ActiveUS20110018510A1Maintain stabilityHigh PSRRElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorFrequency compensation
A linear voltage regulator includes a Miller frequency compensation having a movable zero, which tracks the frequency of the load pole as the load condition changes. The compensated voltage regulator maintains stability under variable load conditions. Because of the Miller effect, DC open-loop gain and bandwidth are not sacrificed for stability. The compensated voltage regulator can therefore maintain high power supply rejection ratio (PSRR).
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SHANGHAI R&D
Ignition coil driver device with slew-rate limited dwell turn-on
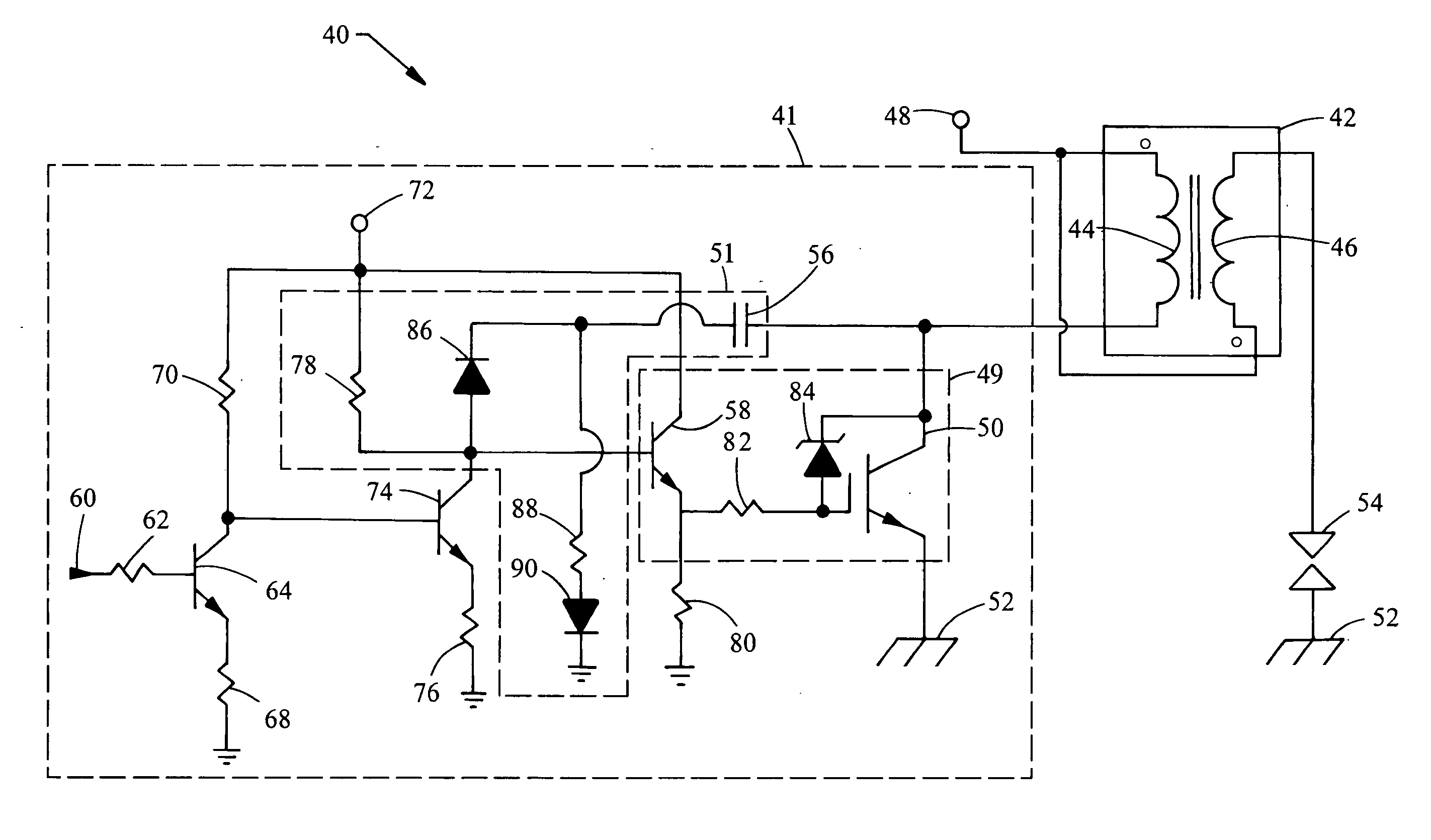
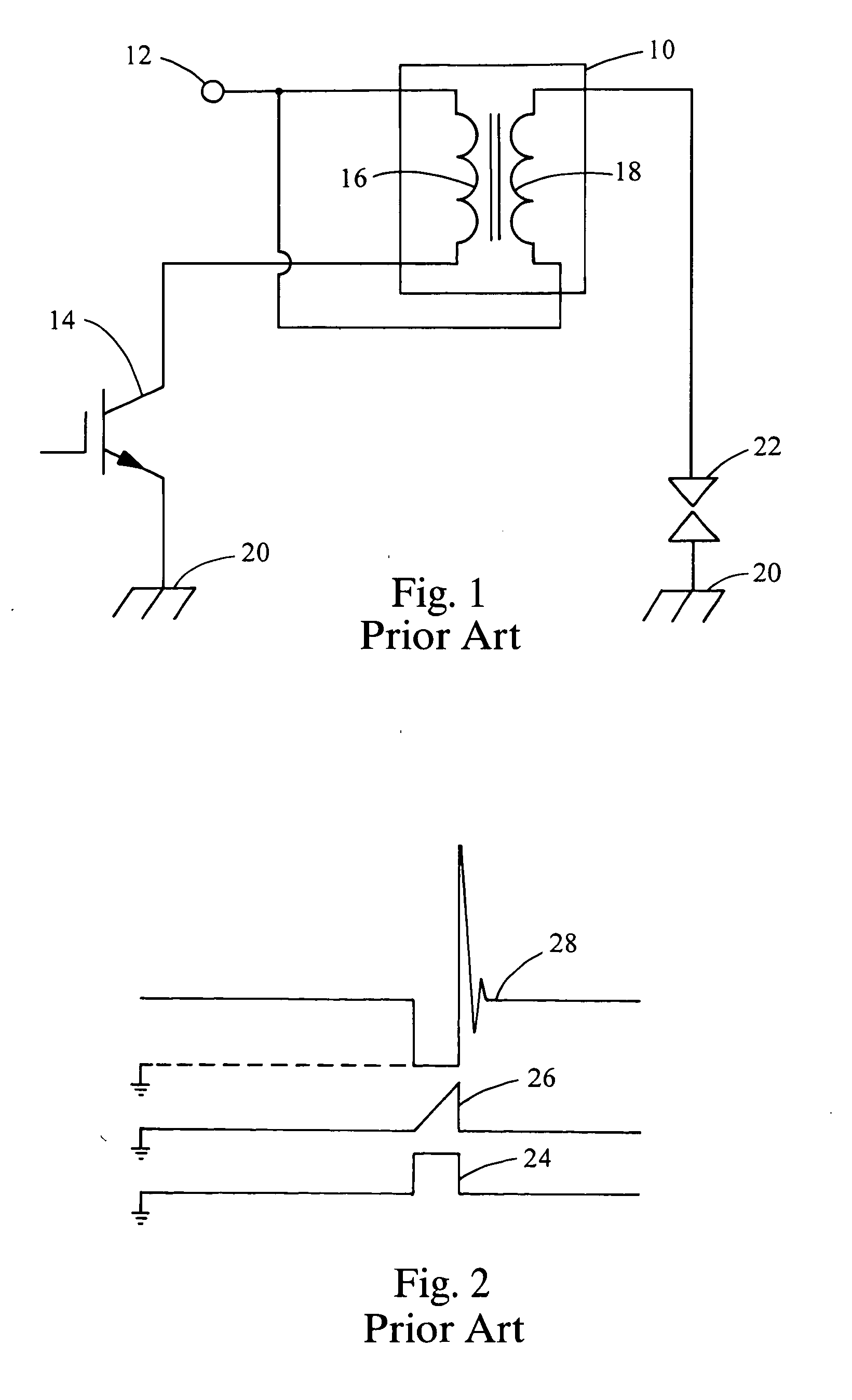
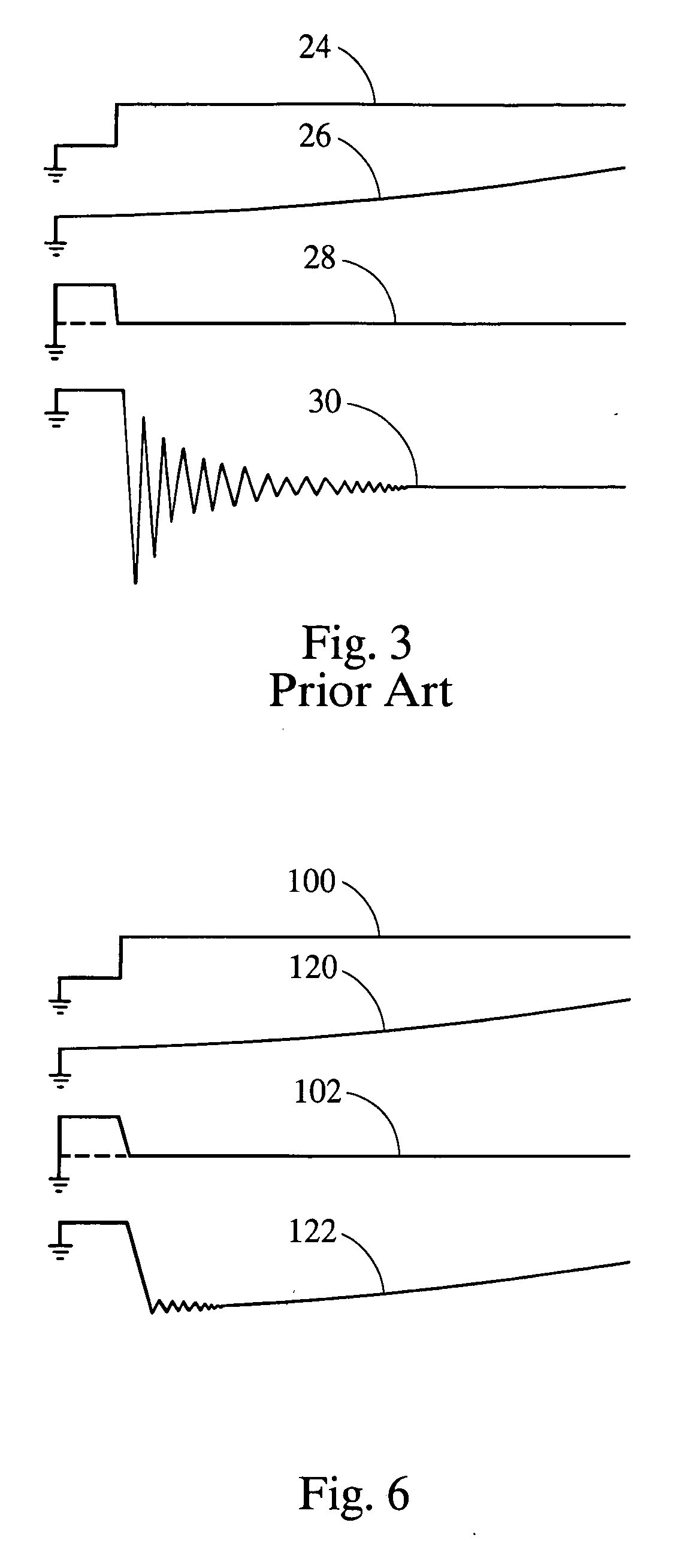
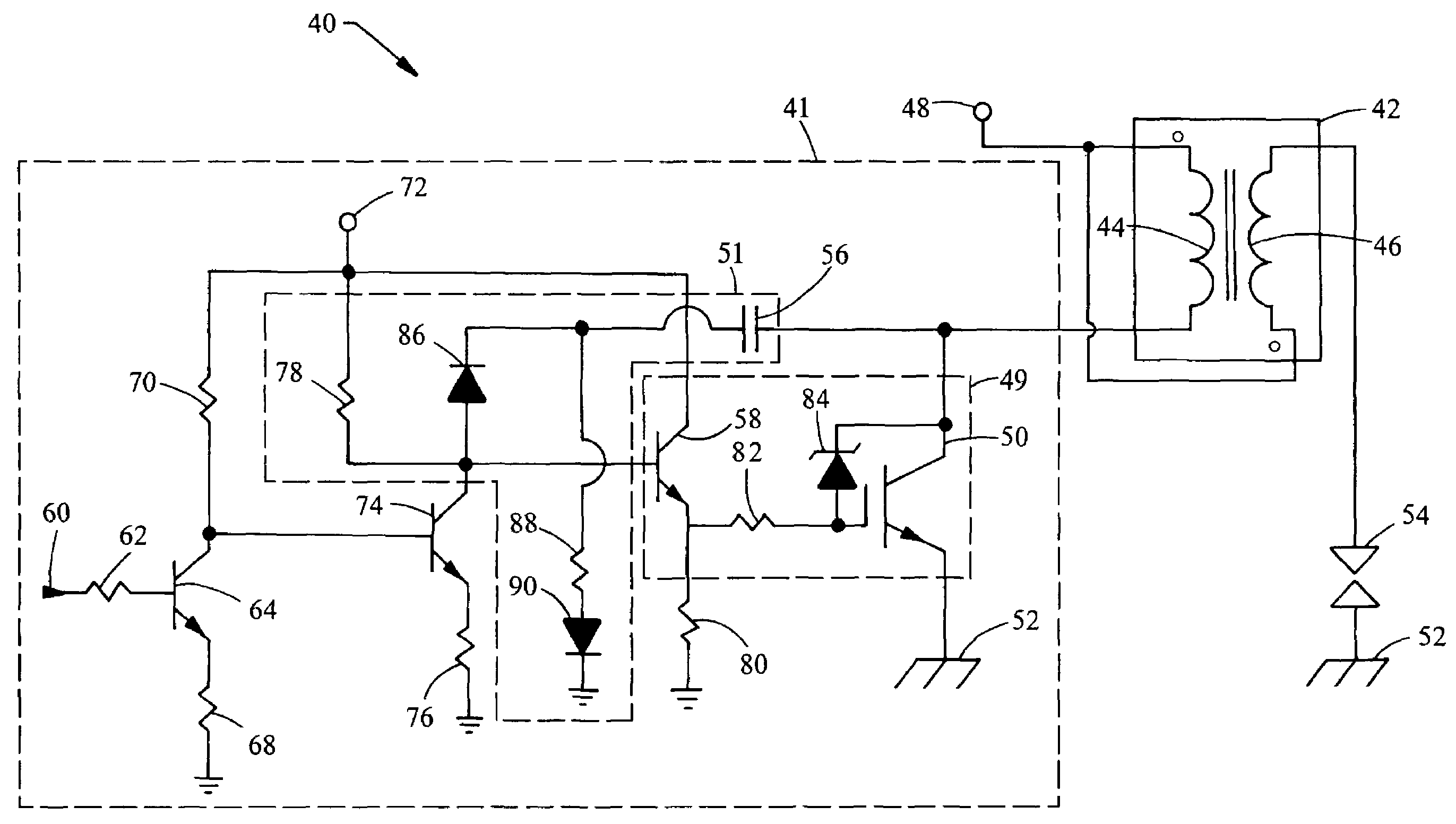
InactiveUS20060213489A1Reduce probabilityReduce rateElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesIgnition coilCharge rate
A device to control the charging rate of an ignition coil for an internal combustion spark ignition engine. The device controls the turn-on rate of the primary coil by slew-rate limiting using switching devices and a Miller-effect capacitor in order to reduce secondary oscillation magnitudes originated by a sharp transition of the controlling switch.
Owner:MICHIGAN MOTOR TECH LLC
Transconductance-capacitor compensation circuit for rolling over network
ActiveCN101425785ASimple in-phase transconductanceSimple structureDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCapacitanceCMOS
The invention relates to a turning network transconductor, namely a capacitance compensating circuit which comprises a main signal transconductor, a feedforward compensating transconductor, a compensating capacitor and a loading capacitor, wherein the main signal transconductor comprises N+1 main signal transconductance units which are in step linkage to form a main signal path, the feedforward compensating conductance comprises N feedforward compensating conductance units which are used for forming a left half-plane zero point and improving the phase margin, the compensating capacitor comprises N capacitors used for improving the stability of a high-conductance amplifier because the Miller effect enables main poles are separated from non-main poles, and the loading capacitor comprises a capacitor forming the pole of a conductance amplifier with a loading resistor. An RNGCC circuit provided by the invention effectively improves the phase margin, has simple structure and is suitable for the necessary low power supply voltage of the future CMOS technology, and the applying prospect is wide.
Owner:灿芯创智微电子技术(北京)有限公司
SiGe differential cascode amplifier with miller effect resonator
InactiveUS7205836B2Total current dropAmplifier combinationsDifferential amplifiersHemt circuitsBreakdown voltage
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
Start-up circuit and method for a self-biased zero-temperature-coefficient current reference
ActiveUS7915882B2Efficient implementationEfficiently realizableElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceReference circuit
A current reference circuit is disclosed. A small startup current is defined as the base current into a bipolar transistor with its collector-emitter path connected in series with a resistor between the power supply voltage and ground. This startup current is conducted via a diode-connected MOS transistor in a first leg of a current mirror. Temperature compensation is maintained by a reference leg in the current mirror that includes a bipolar transistor having an emitter area N times larger than that of a bipolar transistor in a second leg of the current mirror, to establish a temperature-compensated current in the reference leg. A compensation capacitor connected between the collector and base of a bipolar transistor in the first leg suppresses oscillation, and can be modest in size due to the Miller effect.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Bandwidth extension circuit of cascode trans-impedance amplifier based on CMOS (complementary metal oxide transistor) technology
InactiveCN108923753AImprove isolationLower input impedanceDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCascodeEngineering
The invention discloses a bandwidth extension circuit of a cascode trans-impedance amplifier based on CMOS (complementary metal oxide transistor) technology. The bandwidth extension circuit is of completely bilaterally symmetric structure; each of the left and right parts of the bandwidth extension circuit includes a traditional primary cathode-input amplifier, a novel cascode auxiliary amplifierand a terminal source follower; the novel cascode structure is used herein to assist the amplifiers in shielding Miller effect; the concurrent PMOS (P-channel metal oxide semiconductor) structure provides greater transconductance for the cathode-input NMOS (N-channel metal oxide semiconductor); stray capacitance is partially shielded with a Pi-shaped matching network shielding portion; the terminal source follower is added to isolate stray post-capacitance, and total bandwidth of the circuit herein is increased; the circuit herein helps effectively reduce input impedance via RGC structure, andinput capacitance that is mainly of photoelectric detector junction capacitance is better isolated; the circuit herein gains adjustment and optimization for component parameters; differential structure is utilized so that working bandwidth of the circuit herein is greatly widened.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Modeling miller effect in static timing analysis
InactiveUS20040100286A1Current/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceStatic timing analysis
A method is contemplated. According to the method, capacitances in a first resistance / capacitance (RC) extraction corresponding to a circuit are modified. Each capacitance is modified to estimate Miller effect on that capacitance. A ratio of a total capacitance on a first wire after the modification in the first RC extraction to a total capacitance on the first wire before the modification in the first RC extraction is calculated. Capacitances in a second RC extraction that are coupled to the first wire are modified according to the ratio. The second RC extraction is a reduced extraction as compared to the first RC extraction. A timing analysis is performed for the circuit using the second RC extraction with capacitances modified to estimate Miller effect.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Ignition coil driver device with slew-rate limited dwell turn-on
InactiveUS7293554B2Reduce probabilityReduce rateElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesIgnition coilCharge rate
A device to control the charging rate of an ignition coil for an internal combustion spark ignition engine. The device controls the turn-on rate of the primary coil by slew-rate limiting using switching devices and a Miller-effect capacitor in order to reduce secondary oscillation magnitudes originated by a sharp transition of the controlling switch.
Owner:MICHIGAN MOTOR TECH LLC
Differential circuit providing a function to cancel input offset voltage
ActiveUS20090079502A1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceOffset cancellation
A new offset canceling circuit for a differential circuit is disclosed whose input offset voltage may be cancelled independent of the variation of the input level, accordingly, enables the cut-off frequency of the canceling circuit unchanged. The offset canceller of the invention provides a buffer amplifier and a filter. The filter includes a capacitance multiplier including an operational amplifier (Op-Amp) operating in the inverting mode and a capacitor connected between the input and output of the Op-Amp. The Op-Amp operating in the inverting mode whose closed loop gain is solely determined by resistors, and the capacitance of the capacitor is multiplied by the closed loop gain of the Op-Amp by the Miller effect.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Power amplifier having distributed three stacking structure and considering miller effect
ActiveCN106487338AHigh precisionReduce difficultyPower amplifiersRF amplifierArtificial transmission lineAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a power amplifier having a distributed three stacking structure and considering miller effect. The power amplifier comprises a distributed three stacking amplification network, a grid artificial transmission line considering the miller effect, a drain artificial transmission line considering the miller effect, a first bias voltage and a second bias voltage. The core architecture of the power amplifier adopts the distributed three stacking amplification network, the distributed three stacking amplification network is composed of at least three transistor stacking structures; meanwhile, influence of the miller effect of the three transistor stacking structures on equivalent capacitance of the artificial transmission lines is considered, circuit design accuracy is improved, and difficulty in later-stage circuit debugging is reduced, so that the whole power amplifier obtains good broadband power output capability and power gain capability, the low breakdown voltage characteristic of an integrated circuit technology is avoided, and circuit stability and reliability are improved.
Owner:CHENGDU GANIDE TECH
Resonance drive modular control method with dynamic power supply
InactiveCN101325363AOvercoming the "Miller Effect"Degradation hazardEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsCapacitanceFull bridge
The invention provides a resonance drive module control method with a dynamic power, adopting the technical scheme: the traditional hard switch drive is improved to the resonance soft switch drive, the dynamic power +Von capacitance pump lower than Ugs is used to supply power to drive the voltage Ugs, in the non-driving period, the grid voltage Ugs is -Voff negative bias, which effectively overcomes Ci 'the Miller effect', reduces the feedtrhough harm of the half bridge or the full bridge; the capacitance pump of the power Von in the driving period and the capacitance pump of the -Voff in the non-driving period are all supplied with power by a secondary winding of an isolating transformer, namely the transformer transmits the driving frequency f, also transmits the two dynamic capacitance pump power +Von and -Voff. The invention has the advantages of strong interference killing feature, higher reliability of the negative bias drive of the combination module, little loss, high efficiency and excellent performance price ratio.
Owner:深圳市美吉星集成科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com