Bandwidth extension circuit of cascode trans-impedance amplifier based on CMOS (complementary metal oxide transistor) technology
A technology of transimpedance amplifier and cascode, which is applied in the direction of improving the amplifier to expand the bandwidth, DC-coupled DC amplifier, amplifier, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to meet bandwidth requirements, and achieve extended bandwidth, high gain-bandwidth product, and reduced Effect of Input Impedance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
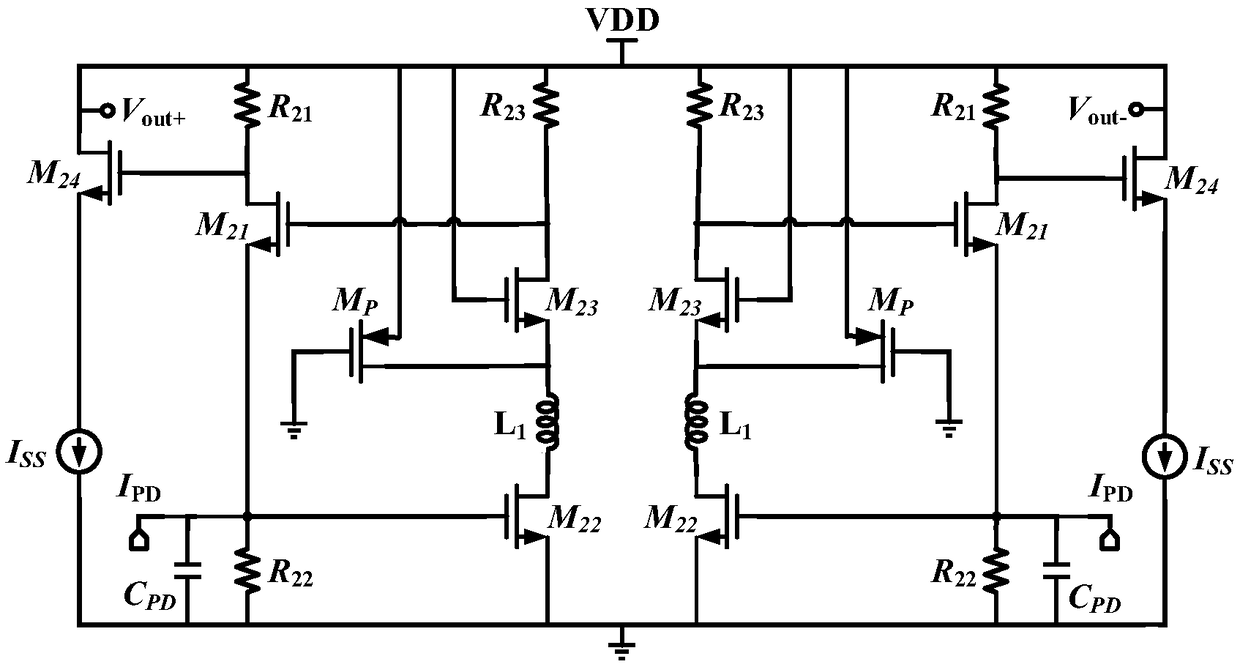
[0024] An embodiment of the present invention provides a bandwidth expansion circuit of a cascode transimpedance amplifier based on a CMOS process, see Figure 1-Figure 3 , the circuit is a completely symmetrical structure;
[0025] Among them, the circuits of the left and right parts include: the traditional main-level cascode amplifier, the new cascode auxiliary amplifier and the end source follower;
[0026] The circuit adopts a novel cascode structure to assist the amplifier to shield the Miller effect; the parallel PMOS structure provides greater transconductance for the common-gate NMOS transistor;
[0027] The circuit shields part of the parasitic capacitance through a π-type matching network, and adds an end source follower to isolate the parasitic capacitance of the rear stage, thereby improving the overall bandwidth of the circuit;
[0028] The circuit adopts the RGC structure to effectively reduce the input impedance and better isolate the input capacitance mainly ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Combine below Figure 1-Figure 3 The scheme in Example 1 is further introduced, see the following description for details:
[0033] figure 1 A novel differential cascode transimpedance amplifier designed for utilizing a series of cascode transimpedance amplifier bandwidth expansion methods proposed in the embodiment of the present invention, the amplifier has a left-right symmetrical structure (that is, a completely symmetrical structure).
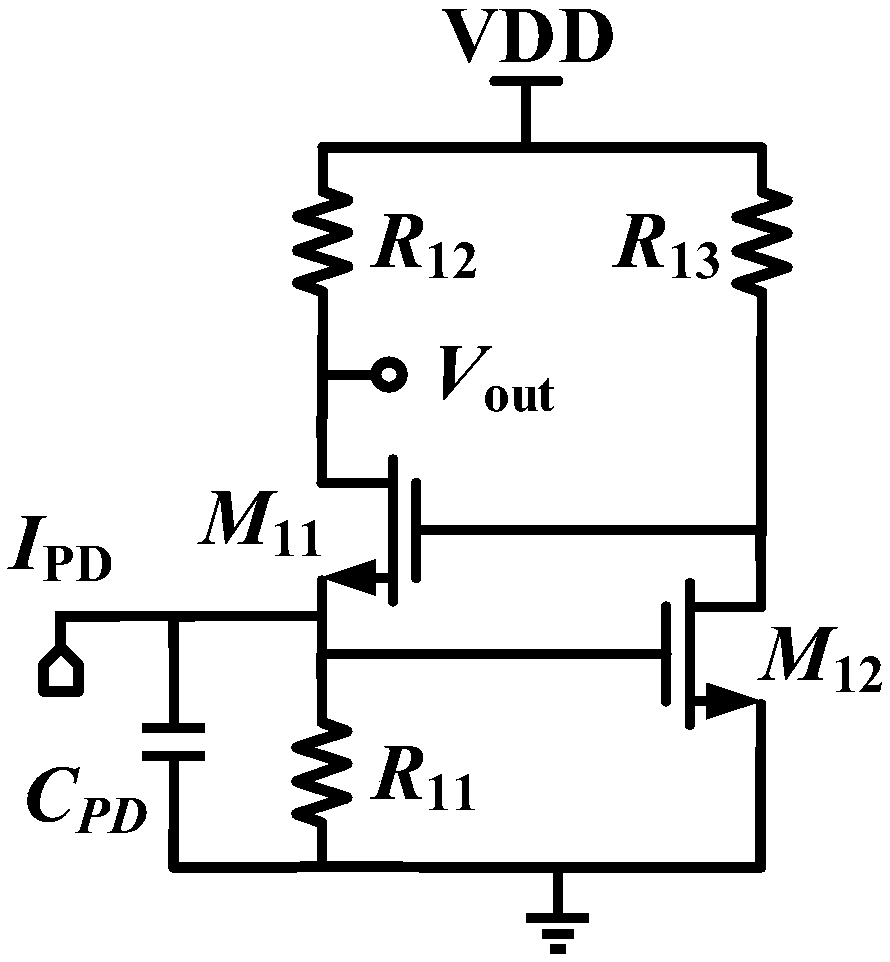
[0034] where the current source I PD and capacitance C PD The parallel structure of is the equivalent circuit model of the photodetector. The new differential cascode transimpedance amplifier is mainly composed of three parts: the traditional primary cascode amplifier, the new cascode auxiliary amplifier and the end source follower.
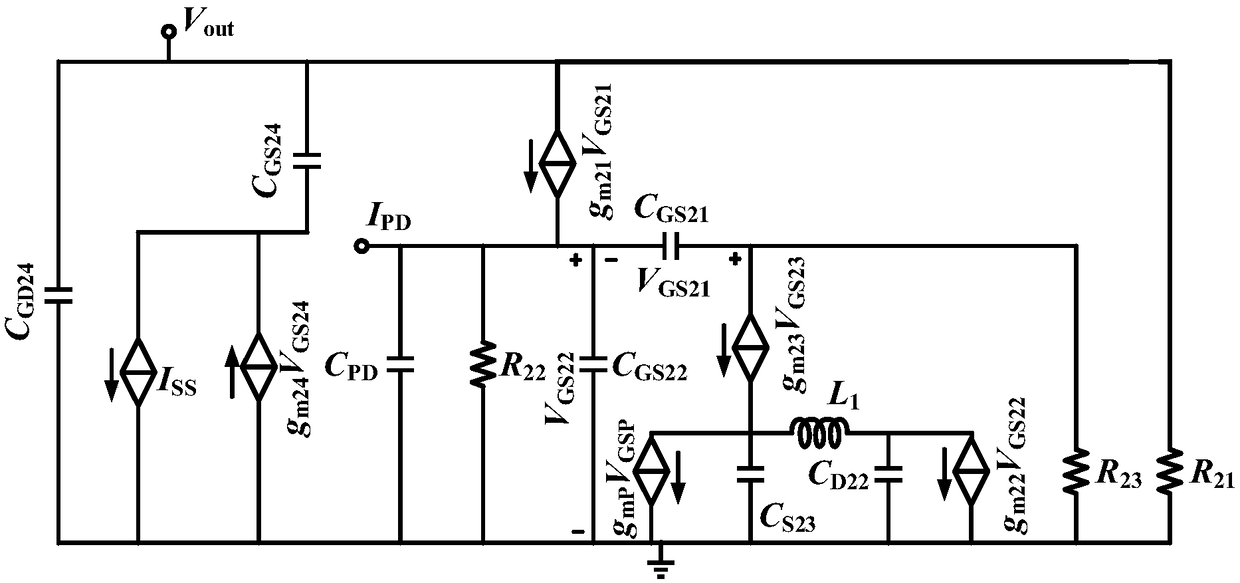
[0035] Among them, the transistor M 21 , resistance R 21 , R 22 Constitute the main common gate amplifier; transistor M 22 , M 23 , M P , resistance R 23 and inductance L 1 form the auxilia...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Combine below Figure 4 and Figure 5 The scheme in embodiment 1 and 2 is carried out feasibility verification, see the following description for details:
[0073] Based on UMC 0.18μm CMOS process, the circuit structure is simulated and parameters are optimized. Figure 4 Shown is a comparison diagram of the frequency response of the new differential cascode transimpedance amplifier and the classic RGC transimpedance amplifier.
[0074] Using the bandwidth expansion method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, the designed new differential cascode transimpedance amplifier has a gain of 61.16dB and a -3dB bandwidth of 8.36GHz. Compared with the classic RGC structure, the gain is slightly improved. Under the premise, the bandwidth has been greatly optimized.
[0075] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the noise current comparison of the new differential cascode transimpedance amplifier and the classic RGC transimpedance amplifier. Compared with the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com