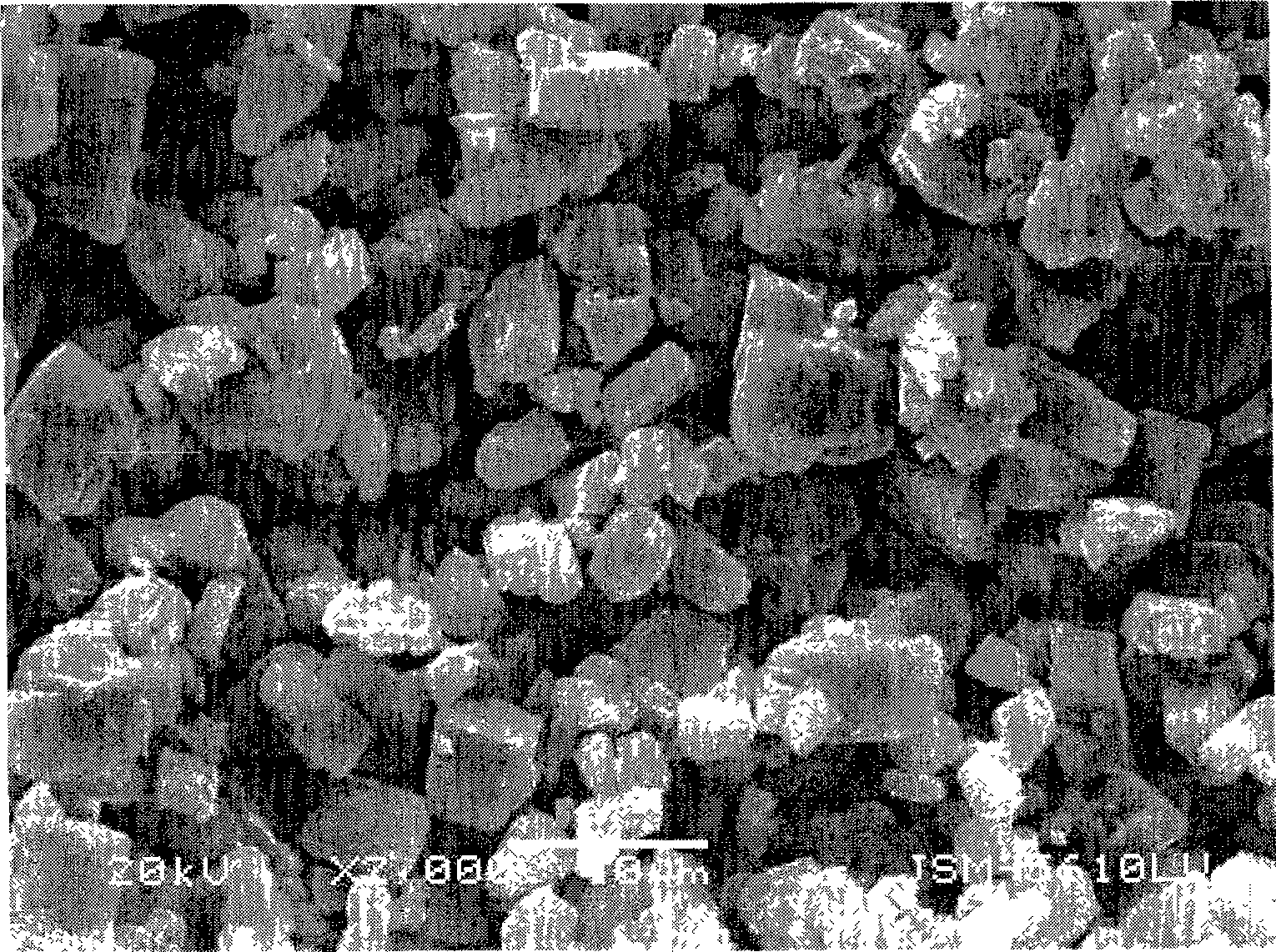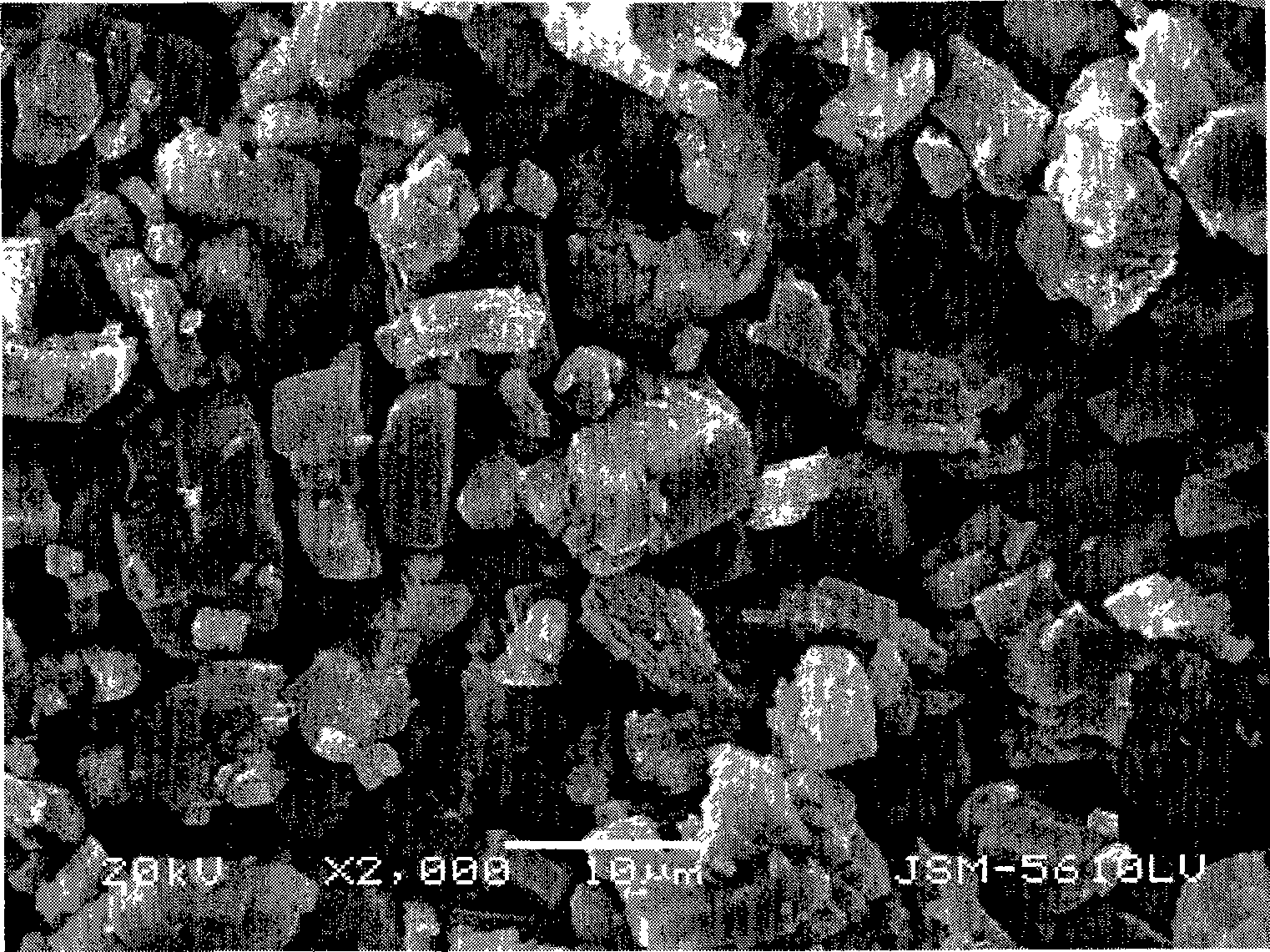Preparation of iron oxalate hydrous salt crystal
A technology of ferrous oxalate and hydrated salt, which is applied in carboxylate preparation, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of large crystal size of ferrous oxalate hydrated salt and easy generation of impurities in ferrous oxalate hydrated salt crystal, and achieve high purity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Under stirring, 20 liters of 2.0 mol / liter ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O) solution, in 1 minute, add to the dihydrate oxalic acid (H 2 C 2 o 4 ·H 2 (0) In the reaction vessel of the solution, after the addition is completed, the temperature of the reaction mixture is 50° C., and ferrous oxalate hydrate crystals are precipitated thereupon, and aged for 30 minutes.
[0034] Next, the ferrous oxalate was recovered by filtration, and the recovered ferrous oxalate was washed three times with 60 liters of deionized water. Next, the washed ferrous oxalate was dried at 80° C. for 12 hours to obtain 5.85 kg of dried product (90.3% yield).
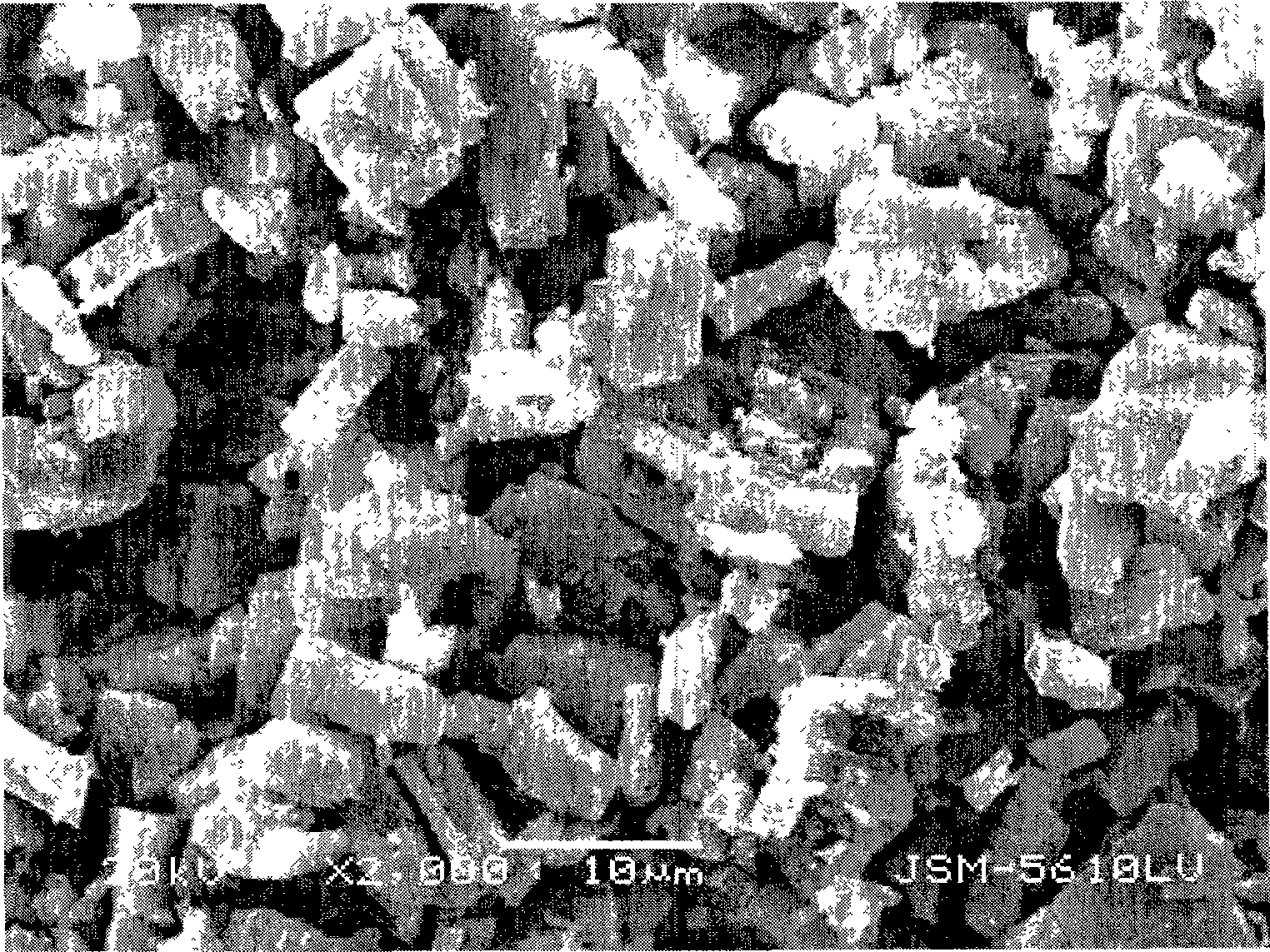
[0035] The SEM image of this ferrous oxalate hydrate crystal measured by the JSM-5610-LV scanning electron microscope of Japan JEOL company is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0036] The XRD diffraction pattern of this lithium ferrous phosphate dry product measured by the D / MAX2200PC type X-ray powder diffractometer of Rigak...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Prepare FeC according to the method identical with embodiment 1 2 o 4 2H 2 O, the difference is that 20 liters of 1.3 mol / liter oxalic acid dihydrate (H 2 C 2 o 4 ·H 2 O) solution was added to 20 liters of 1.5 mol / liter ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O) solution, the addition time is 10 seconds, and the temperature of the reaction mixture is 30°C. After filtering, washing and drying, 4.19 kg of dry product was obtained (yield 89.6%).
[0039] The SEM image of this ferrous oxalate hydrate crystal measured by the JSM-5610-LV scanning electron microscope of Japan JEOL company is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0040] The XRD diffraction pattern of the dried lithium iron phosphate product measured by the D / MAX2200PC X-ray powder diffractometer of Rigaku Corporation is shown in FIG. 7 .
Embodiment 3
[0042] Prepare FeC according to the method identical with embodiment 1 2 o 4 2H 2 O, the difference is that 20 liters of 5 mol / liter ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 (0) Solution is pumped in the reactor at a constant speed of 20 liters / minute, and simultaneously by a metering pump, 20 liters of 5 mol / liter of dihydrate oxalic acid (H 2 C 2 o 4 ·H 2 O) The solution was uniformly pumped into the reactor at a rate of 20 liters / minute, and the temperature of the reaction mixture was 70° C. After filtering, washing and drying, 15.62 kg of dry product was obtained (yield 86.8%).
[0043] The SEM image of this ferrous oxalate hydrate crystal measured by the JSM-5610-LV scanning electron microscope of Japan JEOL company is as follows image 3 shown.
[0044] The XRD diffraction pattern of the dried lithium iron phosphate product measured by the D / MAX2200PC X-ray powder diffractometer of Rigaku Corporation is shown in FIG. 8 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com