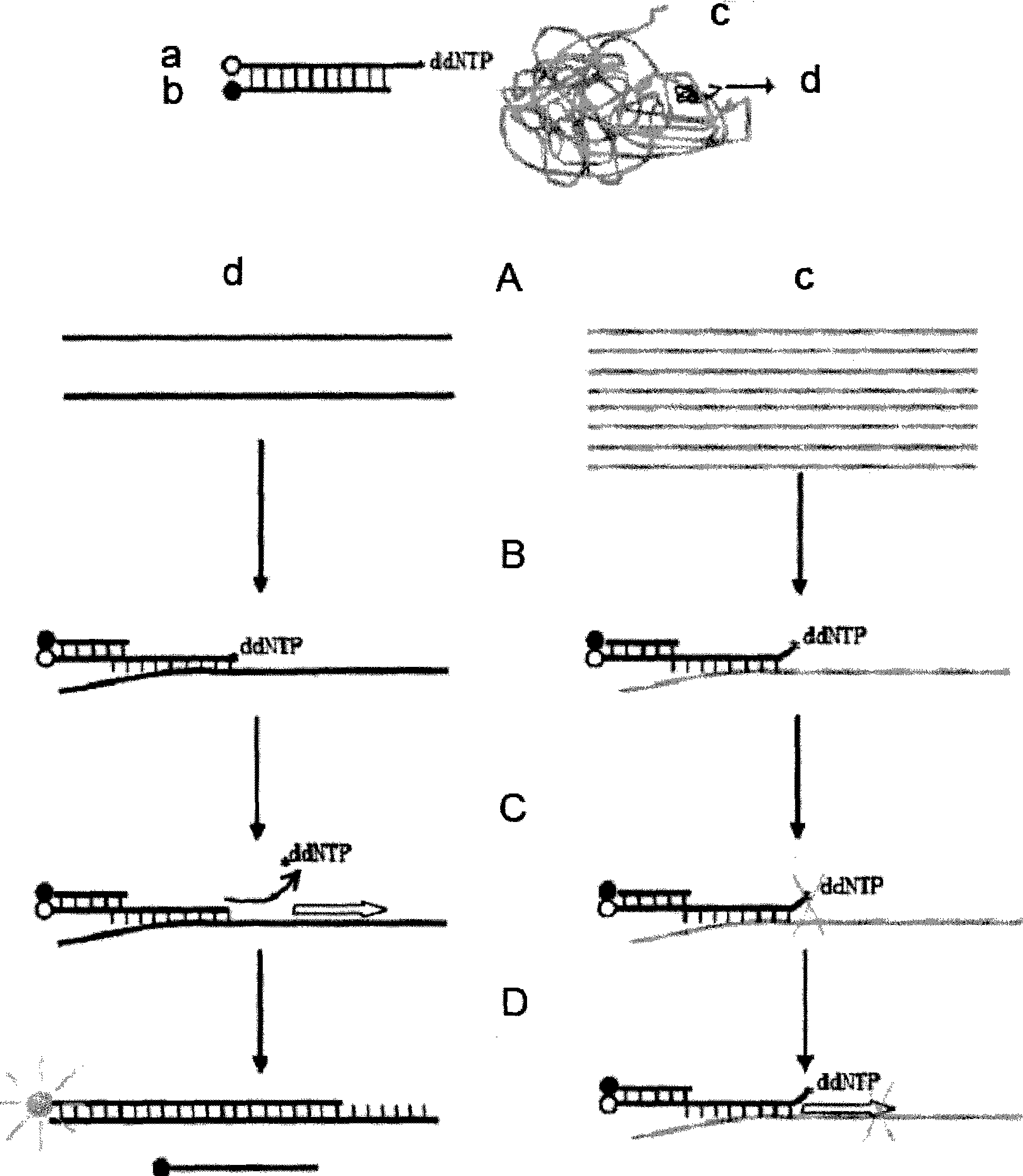
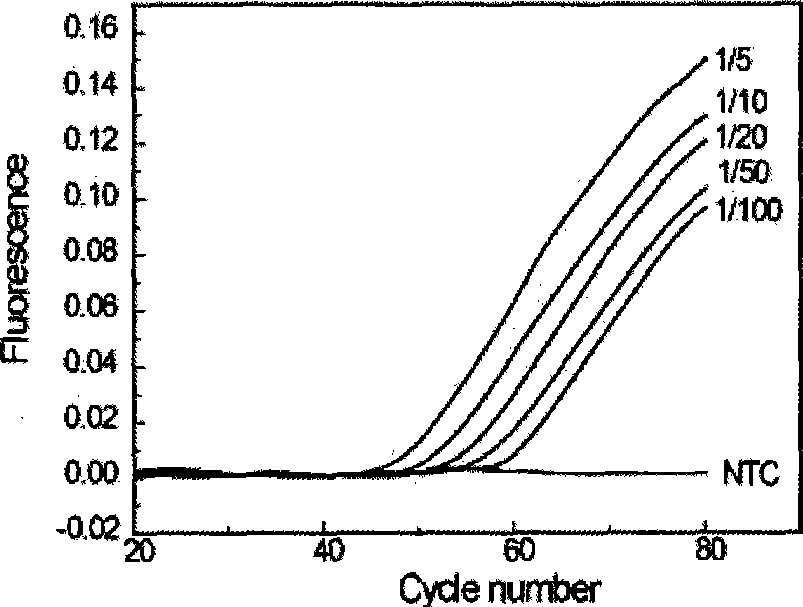
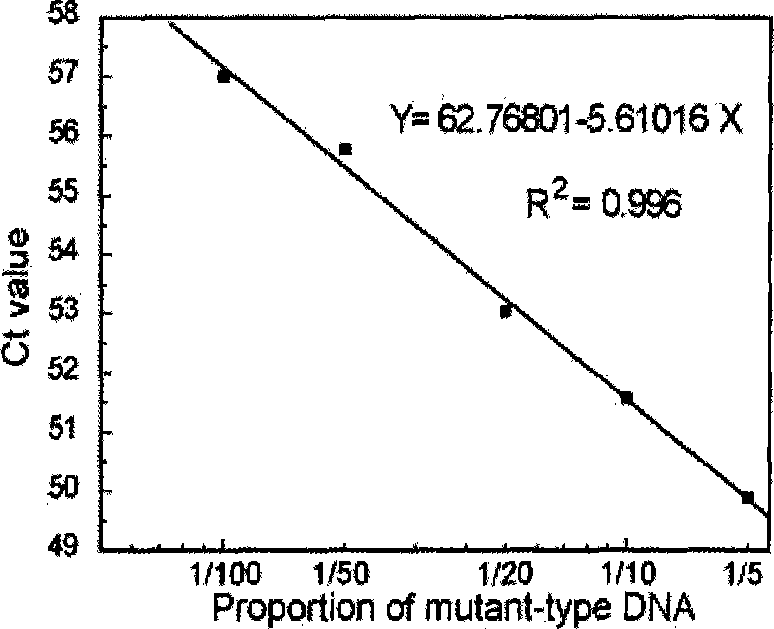
Quantitative detection method of gene rare mutation
A quantitative detection method and rare mutation technology, which is applied in the field of quantitative detection of rare mutations in genes, can solve the problems of low proportion of rare mutation sequences, cross-contamination between samples, and inability to quantify accurately, and achieve the effect of simple quantitative detection of mutations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Example 1 Real-time fluorescent PAP quantitative detection of human K-ras gene mutation
[0065] K-ras gene mutation is a broad-spectrum tumor marker. Currently, K-ras gene mutation detection methods are cumbersome and have poor selectivity. In this example, real-time quantitative PCR with PAP primers was used to detect the second nucleotide mutation in the twelfth codon of the first exon of the human K-ras gene, and the nucleic acid intercalating dye was used to indicate the amplification, to illustrate the effectiveness of the present invention for rare mutations Quantitative ability.
[0066] The mutant genome template was extracted from SW480 cultured cells (containing GGT->GTT mutation of codon 12 of the first exon of K-ras gene), and the wild-type genome template was extracted from 293T cultured cells. Prepare three sets of mixed templates for wild-type and mutant genomes:
[0067] 1. The total amount of template is 1ng / reaction system, and the proportion of mut...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2 Comparison of real-time fluorescent PAP quantitative detection and ARMS quantitative detection of human K-ras gene mutation.
[0076] In this example, real-time quantitative PCR with PAP primers and classic ARMS method were used to quantitatively detect the mutation of the second nucleotide in the twelfth codon of the first exon of the human K-ras gene, and the nucleic acid intercalating dye was used to indicate the amplification. To illustrate the quantitative ability of the present invention for rare mutations.
[0077] The mutant genome template was extracted from SW480 cultured cells (containing GGT->GTT mutation at position 12 of the first exon of the K-ras gene), and the wild-type genome template was extracted from 293T cultured cells. Two series of mixed templates of wild-type genome and mutant genome were prepared: the first series of mutant-type templates were diluted tenfold with water, as shown in Table 1. In the second series, the wild-type templa...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3 Comparison of real-time fluorescent PAP quantitative detection of rare mutations in clinical samples with other quantitative detection methods.
[0088] In this case, PAP primer real-time quantitative PCR, classical ARMS method and sequencing method were used to quantitatively detect the mutation of the second nucleotide in the twelfth codon of the first exon of the K-ras gene in the tumor tissues of 42 patients with colorectal cancer. The intercalating dye indicates the amplification situation, and the quantitative ability of the present invention for rare mutations in clinical samples is illustrated by comparing the three.
[0089] Primers are:
[0090] 12-2-T*forward:TGACTGAATATAAACTTGTGGTAGTTGGAGCTG-ddT;
[0091] 12-2-T*reverse: GGCACTCTTGCCTACGCCACA-ddA. The original primers were synthesized by Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd. The 3' ends of the primers were blocked by the laboratory itself.
[0092] ARMS forward:ACTTGTGGTAGTTGGAGCTGT
[0093...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com