Switching power supply
A technology of switching power supply and high-side switch, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, output power conversion devices, etc., can solve the problems of discontinuous input current waveform, no miniaturization and low energy conduction efficiency, and achieve Effects of reduced driving power, improved parts count, and improved reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
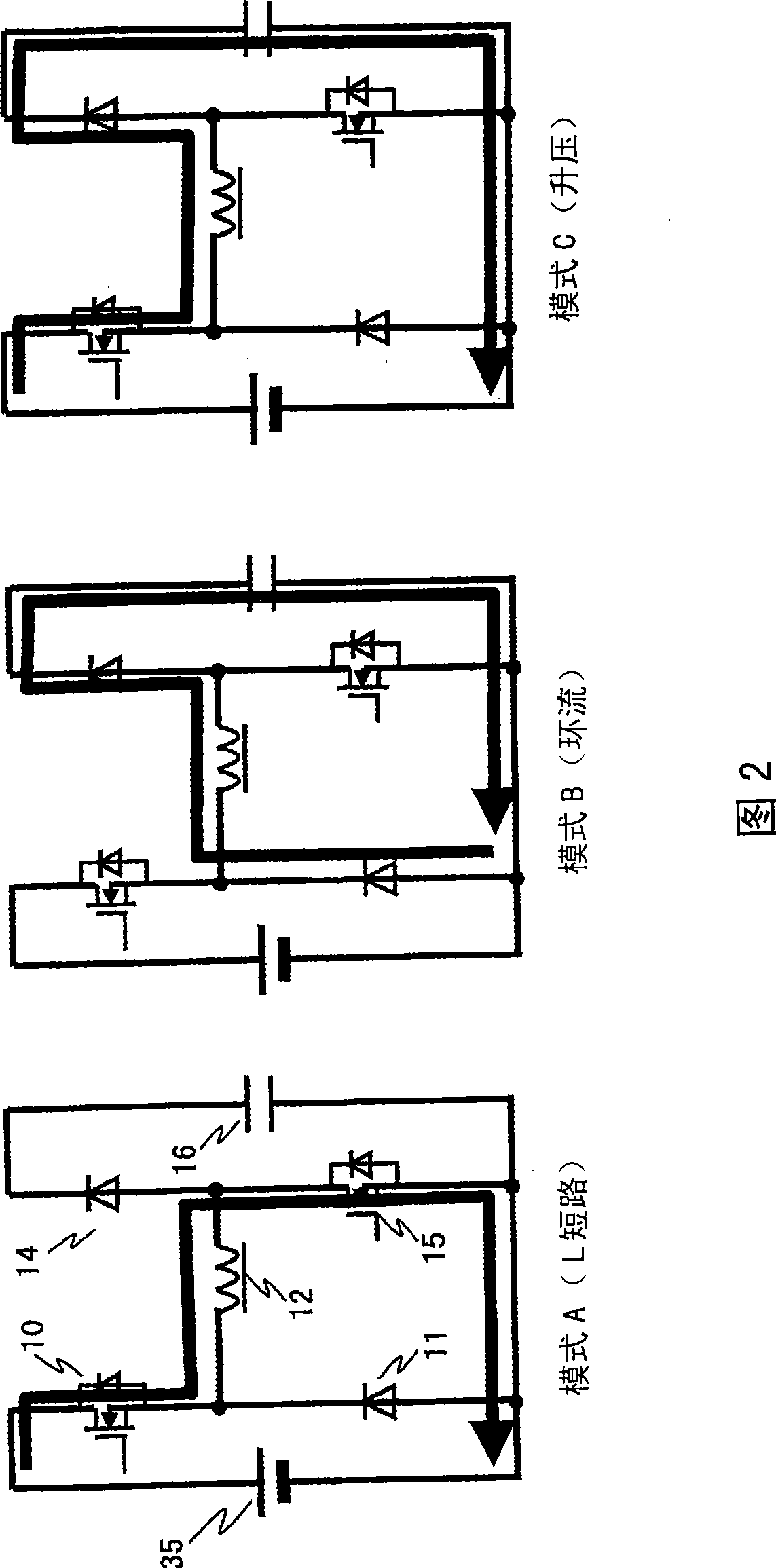
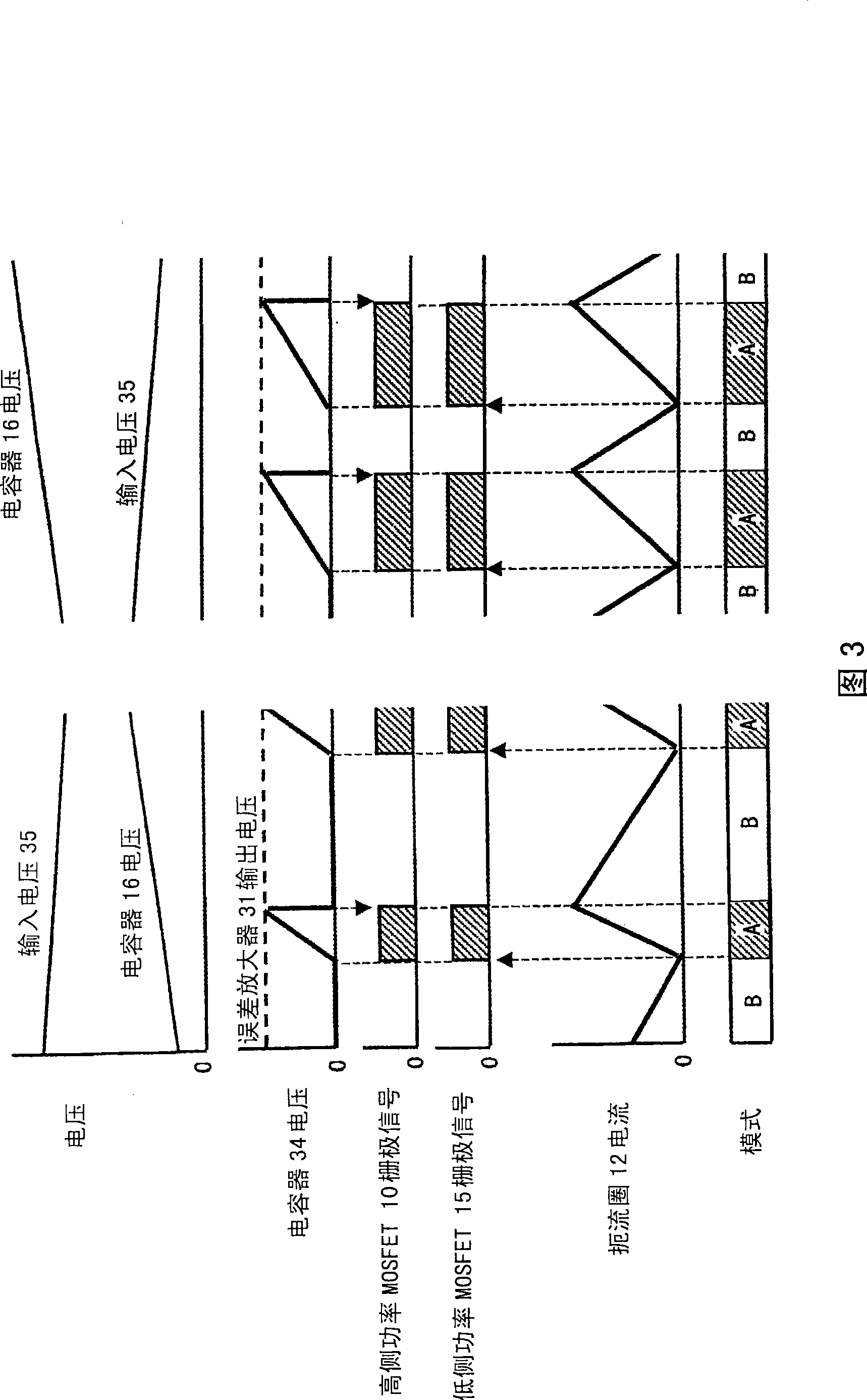
[0035] 1st Embodiment of this invention is demonstrated using FIG.1 and FIG.2, FIG.3, FIG.4, FIG.5.
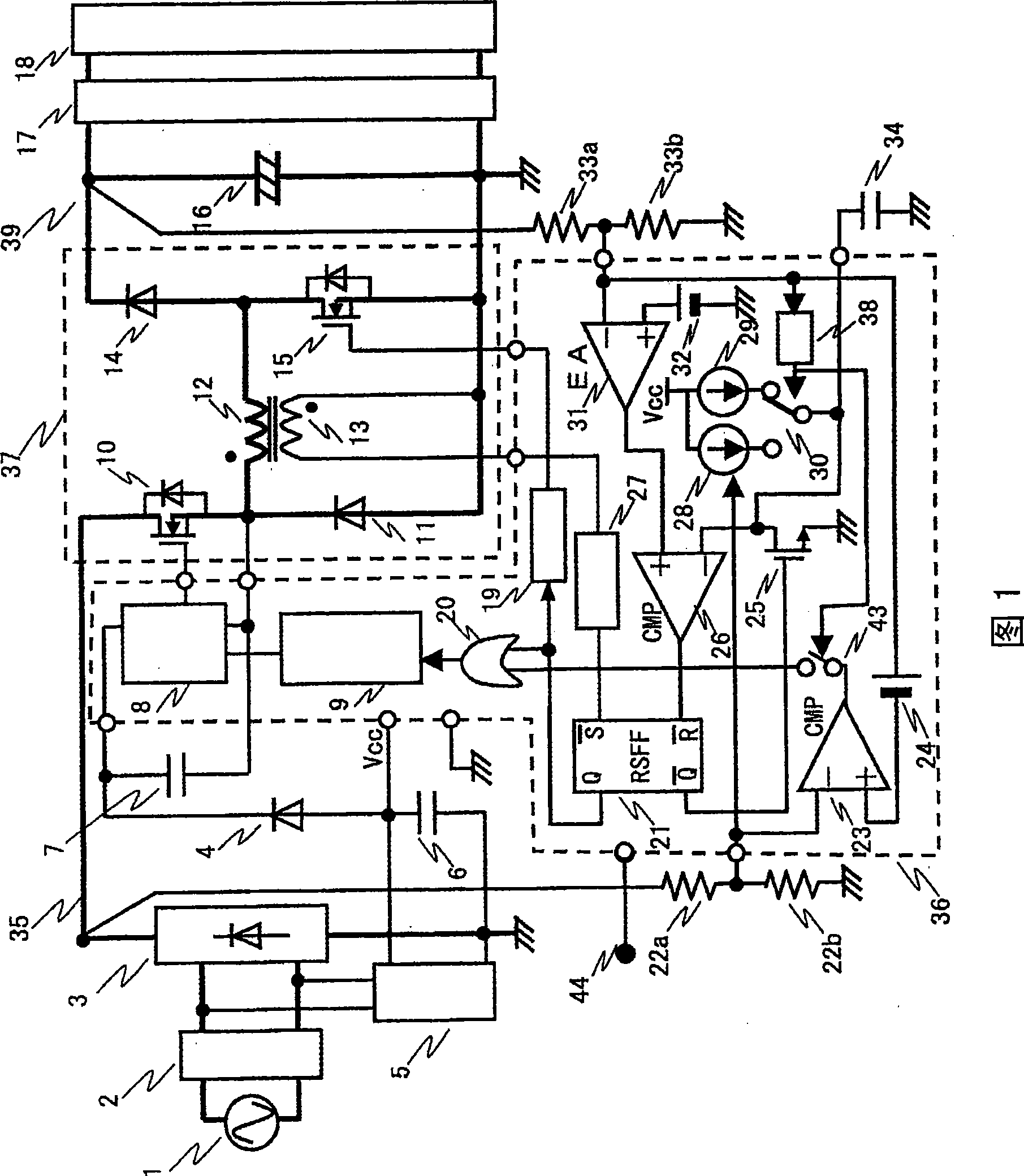
[0036] FIG. 1 is a circuit diagram showing a first embodiment of a buck-boost switching power supply of the present invention. The configuration of Fig. 1 will be described. The AC power supply 1 becomes the input voltage 35 through the input filter 2 and the rectifier 3, and becomes a full-wave rectified waveform. In addition, an auxiliary power supply 5 is connected to the input filter 2 . On the DC output side of the rectifier 3 , the voltage dividing resistors 22 a , 22 b are both connected to the drain of a high-side (side) power MOSFET 10 . One end of a choke coil (choke coil) 12 (start of winding) and a cathode of a freewheel diode 11 are connected to the source of the high-side power MOSFET 10 . The anode of the freewheeling diode 11 is connected to the ground of the rectifier 3 . Also, the drain of the low-side power MOSFET 15 and the anode of the boost diode 14 a...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 6 , 7 , 8 , and 9 . FIG. 6 shows the main circuit portion of the buck-boost switching power supply, and FIG. 7 shows its control circuit. In FIGS. 6 and 7 , the same reference numerals are assigned to the same components as in FIG. 1 . The difference between the main circuit section in FIG. 6 and FIG. 1 is that two sets of main circuits, ie, H-bridge circuits, are prepared and connected in parallel. That is, the connection form of the high-side power MOSFET 10a, the freewheeling diode 11a, the choke coil 12a, the low-side power MOSFET 15a, and the boost diode 14a constituting the H-bridge circuit 37 is the same as that of the main circuit of FIG. 1 . In addition, in FIG. 6 , there are high-side power MOSFET 10b, freewheel diode 11b, choke coil 12b, low-side power MOSFET 15b, and boost diode 14b, and these are also connected in the same manner. In addition, the drains of the hi...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Next, other embodiments of the present invention will be described using FIG. 10 and FIG. 11 .
[0092] Fig. 10 is the main circuit of the buck-boost switching power supply of the present invention similar to Fig. 6 and Fig. 1 . In FIG. 10 , the same reference numerals are assigned to the same components as those in FIG. 6 or FIG. 1 . Here, points different from those in FIG. 6 will be described. In FIG. 10 , the high-side power MOSFET 10 , the circulating diode 11 , the choke coil 12 a, the low-side power MOSFET 15 a, and the boost diode 14 a constituting the H-bridge circuit 37 are connected in the same way as the main circuit in FIG. 1 or FIG. 6 . In FIG. 10 , a choke coil 12 b and a choke coil 12 a are connected in parallel, and these two choke coils are connected to the source of the high-side power MOSFET 10 from FIG. 6 . In other words, the high-side power MOSFET 10b and its drive circuit system described in FIG. 6 are omitted.
[0093] Next, Fig. 11 will be d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com