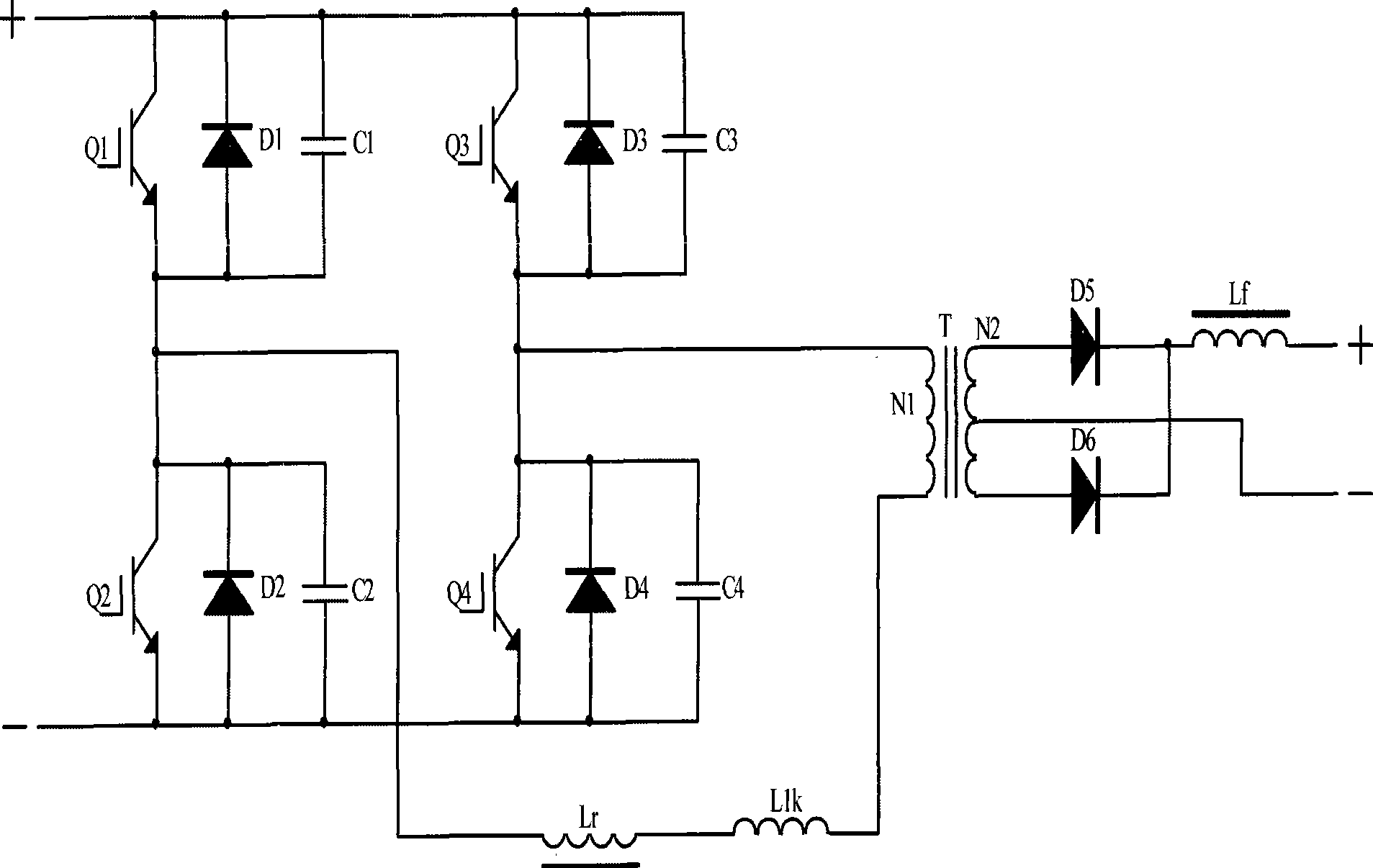
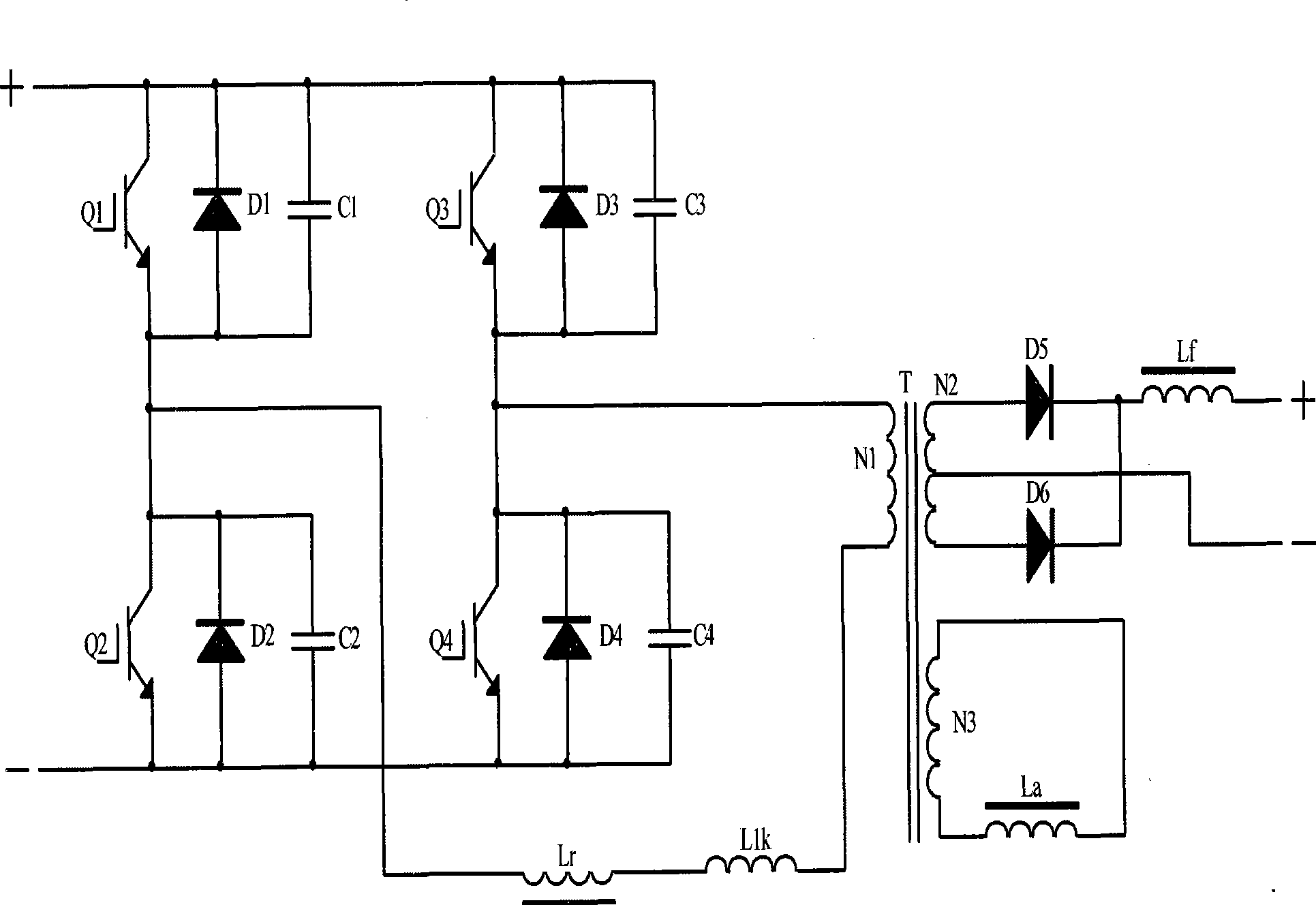
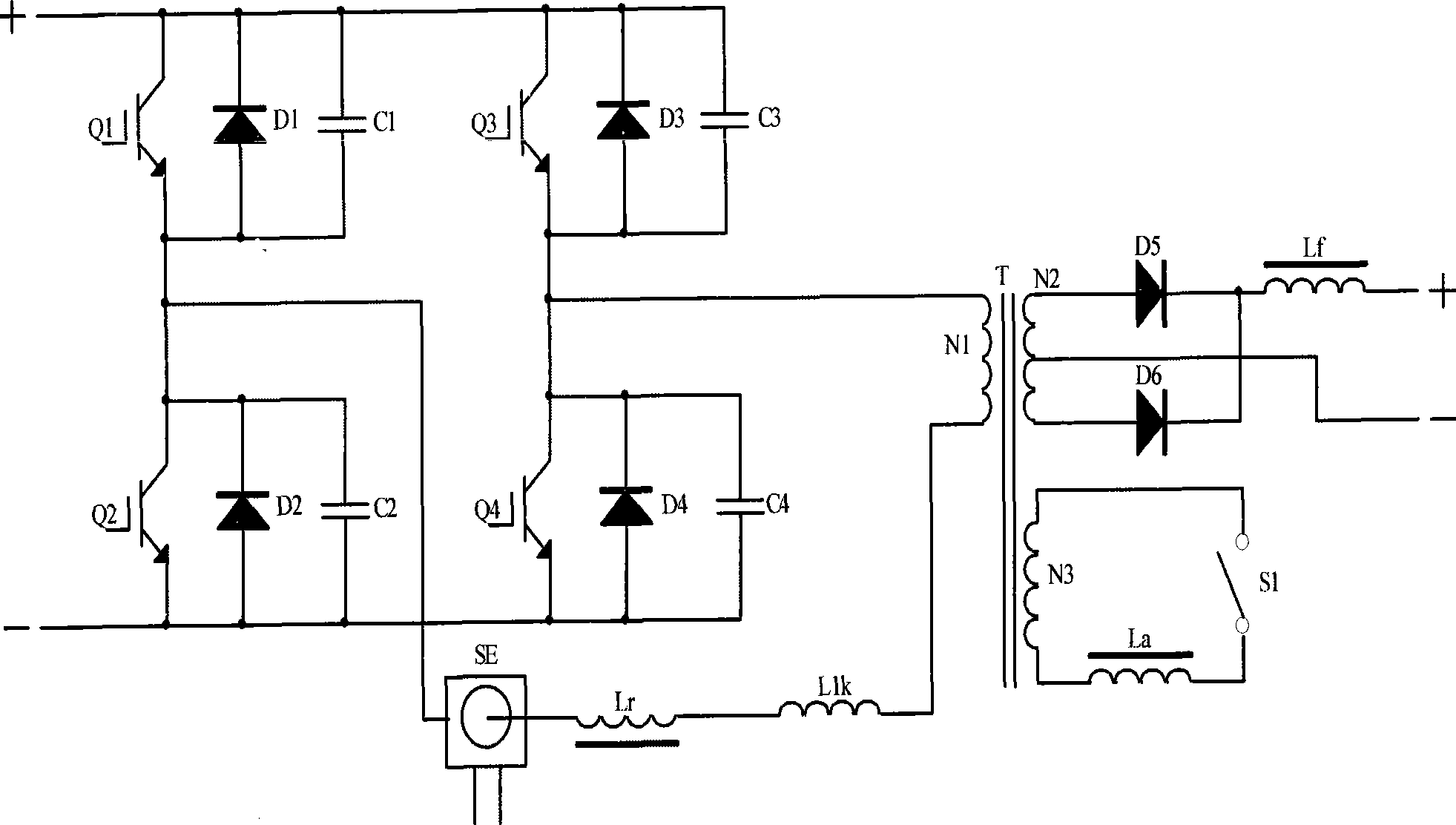
Zero-voltage soft switch topological main circuit of arc welding inverter
A soft-switching and inverter technology, applied in arc welding equipment, adjusting electrical variables, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, etc., can solve problems such as increasing circuit circulation, damage, and reducing power factor.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Such as image 3 As shown, the full-bridge phase-shifting resonant circuit of the present invention is the same as the above-mentioned circuit. An auxiliary coil N3 is connected in parallel on the secondary side of the high-frequency transformer T, the auxiliary coil N3 is connected to the auxiliary inductance La, and the auxiliary inductance La is connected in series with the electronic switch S1, the electronic switch S1 is connected to the control circuit and is sampled by the current sampling coil SE The primary side current of the high-frequency transformer T realizes that the present invention is turned off under heavy load, and turned on under no-load and light-load states.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the full-bridge phase-shifting resonant circuit of the present invention is the same as the above-mentioned circuit. An auxiliary coil N3 is connected in parallel to the primary side of the high-frequency transformer T, the auxiliary coil N3 is connected to the auxiliary inductance La, and the auxiliary inductance La is connected in series with the electronic switch S1, the electronic switch S1 is connected to the control circuit and is sampled by the current sampling coil SE The primary side current of the high-frequency transformer T realizes that the present invention is turned off under heavy load, and turned on under no-load and light-load states.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the full-bridge phase-shifting resonant circuit of the present invention is the same as the above-mentioned circuit. The auxiliary inductor La is directly connected in series with the electronic switch S1 and then connected to the secondary winding N2 of the high frequency transformer T. The electronic switch S1 is connected to the control circuit and samples the primary current of the high-frequency transformer T through the current sampling coil SE, so that the present invention can be turned off under heavy load and turned on under no-load and light-load conditions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com