Nitration of aromatic compounds
A technology of aromatic compounds and nitrating agents, applied in the field of nitration of aromatic compounds, can solve problems such as not easy to contain, easy to explode, and harmful to the environment, and achieve the effects of easy packing, high yield and selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Example 1 Nitration of Benzene in Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonamide)trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium
[0054] Put 2.0g of bis(trifluoromethanesulfonamide)trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium and 1.56g of benzene into a 50ml round bottom flask, then slowly add 1.50g of 100% nitric acid for more than 5 minutes. The contents of the flask were then heated at 80°C for 2 hours.
[0055] After 2 hours of reaction at 80°C, the contents of the flask were worked up in the usual manner. Then by weighing, gas chromatography and nuclear magnetic resonance analysis, it is known that quantitative nitrobenzene is basically generated.
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 Nitration of various aromatic compounds in bis(trifluoromethanesulfonate)trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium at a temperature of 80°C
[0057] The following aromatic compounds were nitrated essentially as described in Example 2: benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene and naphthalene. The aromatic compound to be nitrated is dissolved in trihexyl(tetradecyl)phosphonium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonate), and fuming nitric acid is added. The equivalent ratio of aromatic compounds to nitric acid is 1:1.2. The contents of the flask are then heated at 80°C for up to 6 hours.
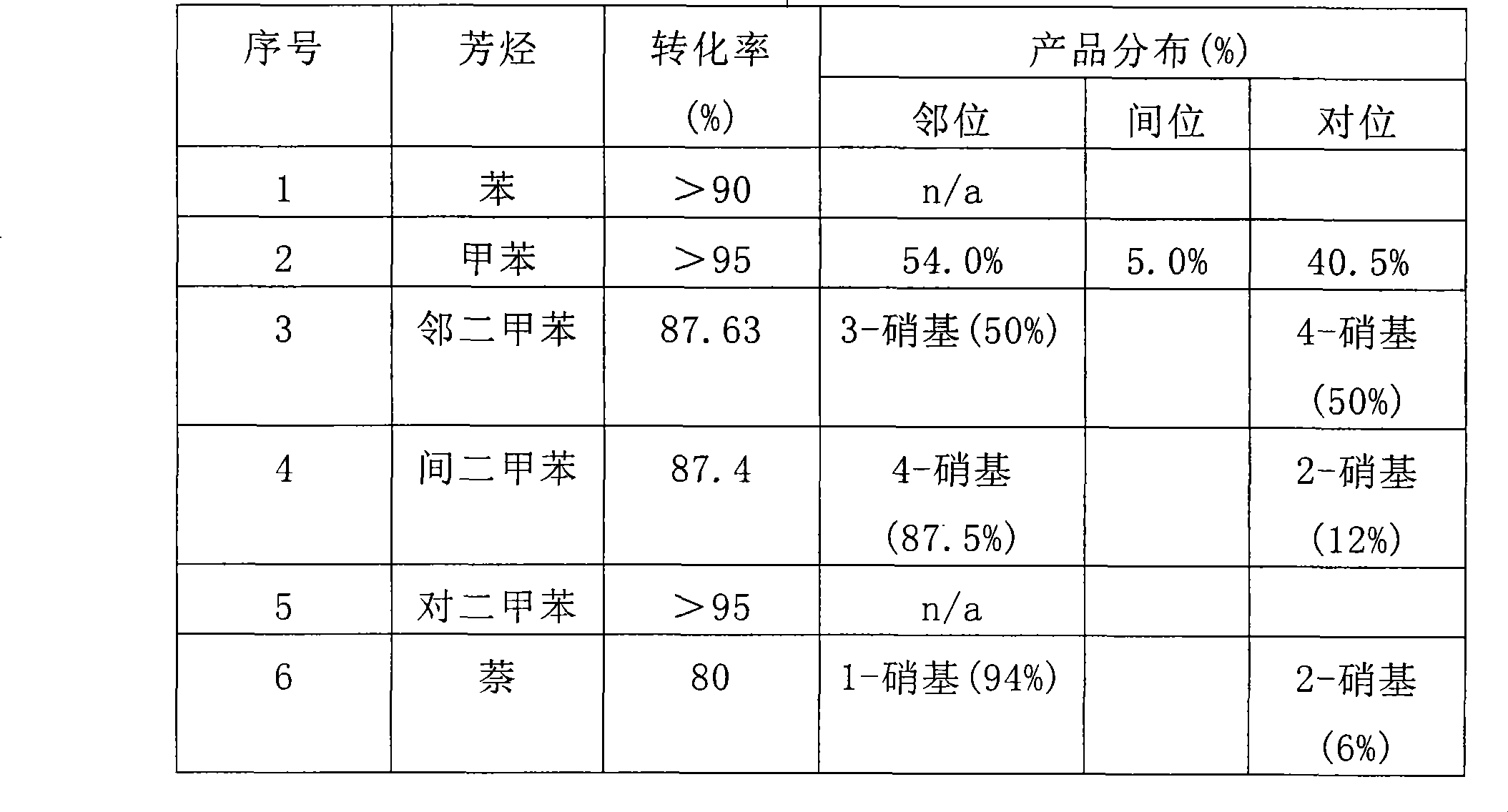
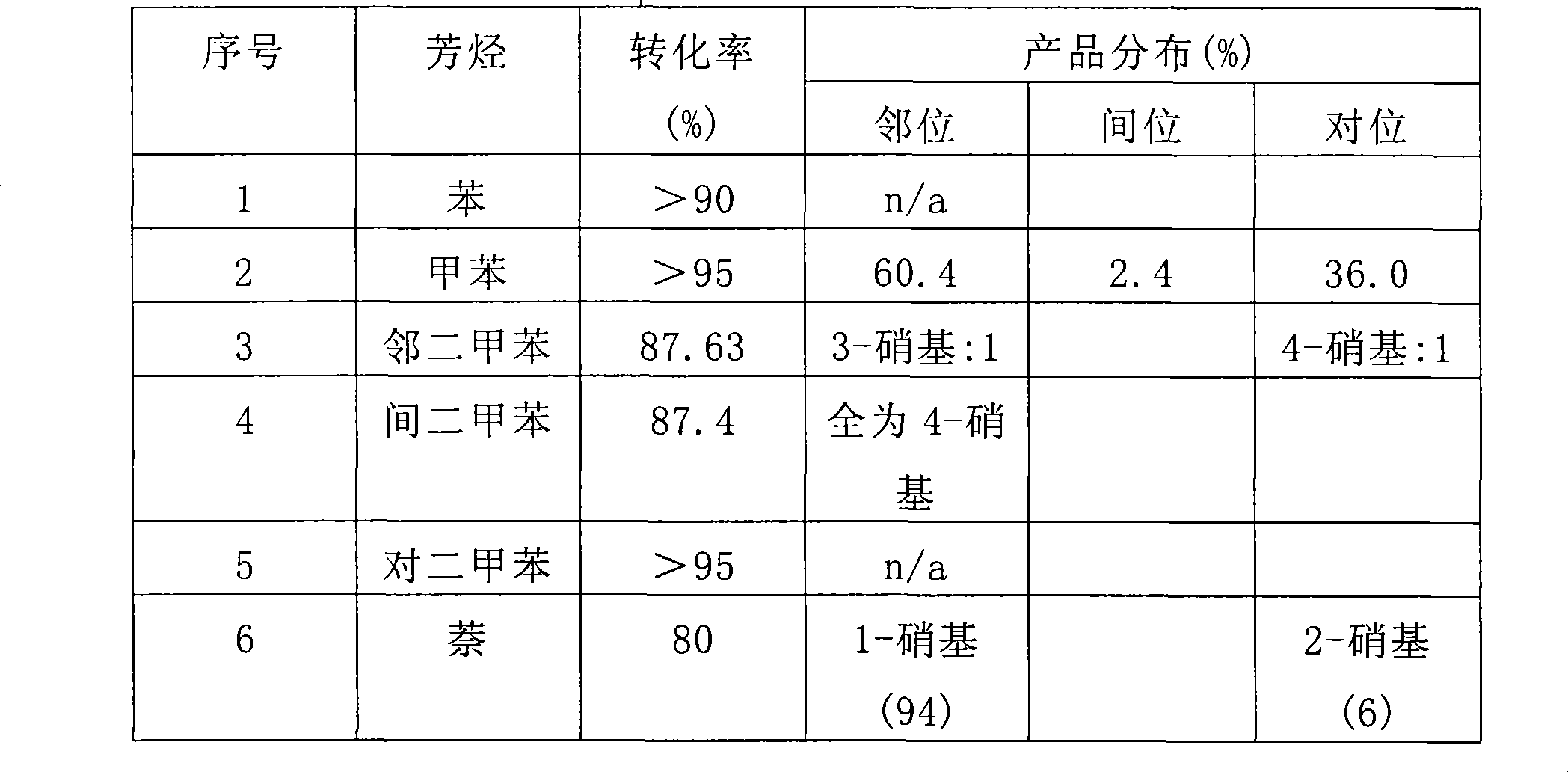
[0058] After 6 hours of reaction, the contents of each flask were processed and the product analyzed for conversion and product distribution. Product distribution was obtained by gas chromatography and NMR methods. See Table 1 for the analysis results. No polynitroaromatic compounds were detected in the reaction product.
[0059] Table 1
[0060]
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3: (used as contrast)
[0062] In this comparative example without the use of the phosphorus ionic liquid solvent, nitric acid and toluene were reacted at a temperature of 80°C for one day. The results showed that the conversion of mononitrotoluene was only 48%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com