Superhydrophobic surface and method for forming same
A super-hydrophobic and stable technology that can be used in manufacturing tools, liquid chemical plating, transportation and packaging to solve problems such as unsuccessful field tests, low insulator adhesion, and insulator damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
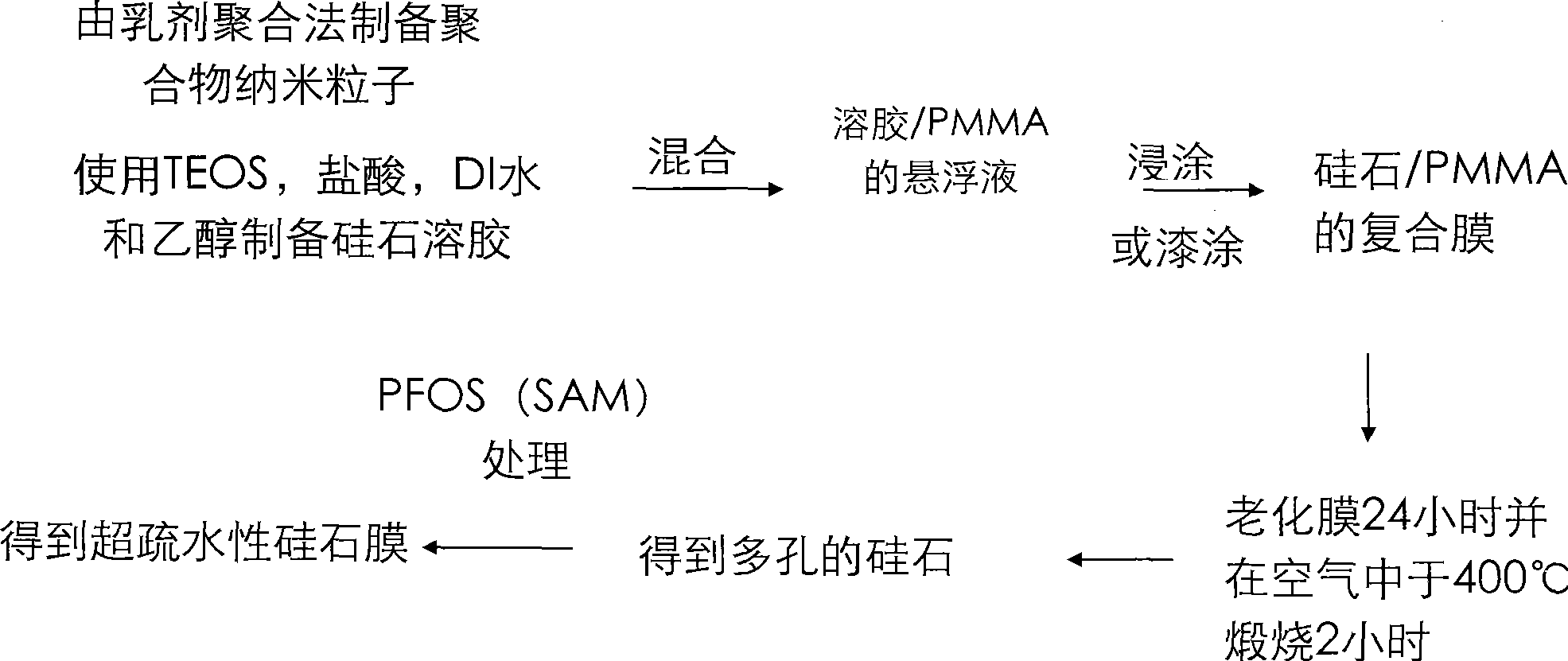
[0150] The preparation of nanoparticles is carried out under controlled conditions, such as substrate, salt, temperature and water. The preparation of core-shell structures can utilize the growth of seeded nanoparticles. The preparation of raspberry structures (multiple species) is achieved by adding different kinds of precursors and controlling the addition time of the second precursor, or by adding cohesive surface functional groups between two different nanoparticles. Additionally, different nanoparticles can be mixed together to form multiple types of nanoparticles. The preferred particle size range is from 30 nm to 20 μm.
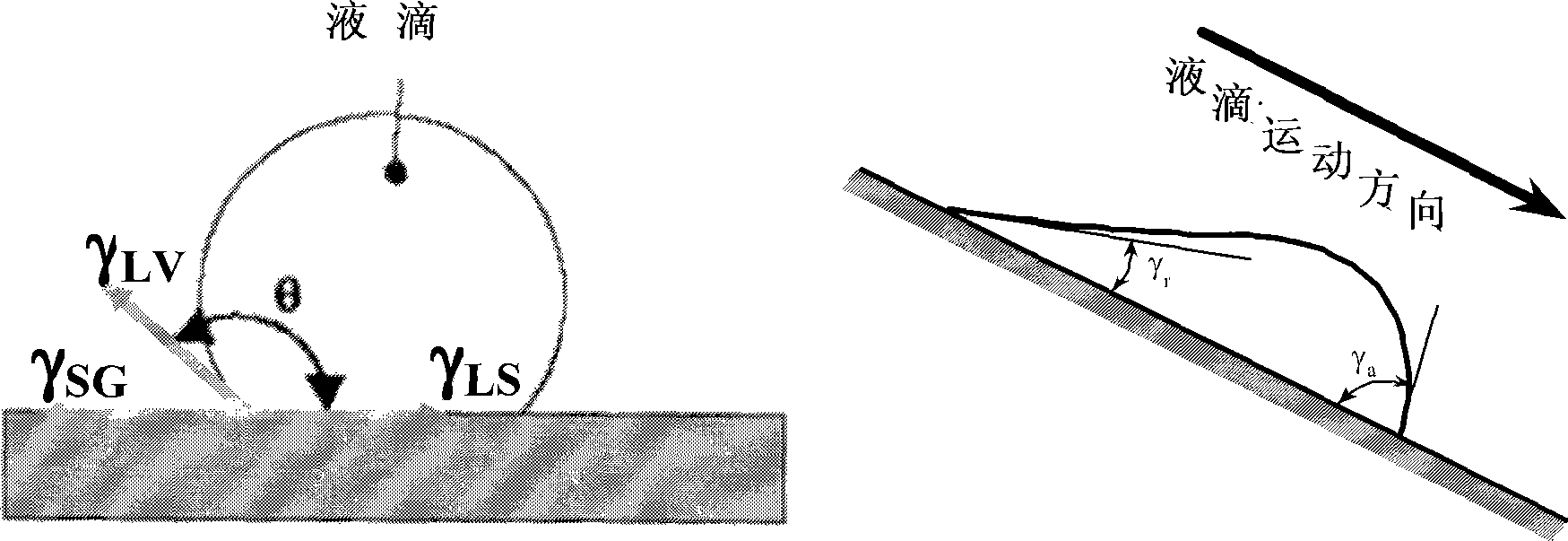
[0151] In another preferred embodiment, the present invention includes surface treatment by applying a coupling agent to the surface at near ambient temperature to increase the contact angle and reduce hysteresis. This embodiment can utilize sol-gel methods and can be monomorphic or polymorphic and single or multispecies. This method involves the us...
Embodiment 1
[0240] First, TMOS (precursor), IBTMOS (co-precursor) and ethanol were mixed in the amounts given in "Material Example I" in Table 6. HCl (0.1M) was then added to adjust the pH of the mixture to about 1.8-2.0. The reaction was initiated by heating to 60°C and then held for five (5) hours. After the reaction is complete, 1.1M NH 3 h 2 O is a base added to the solution to initiate gelation of the polymer.
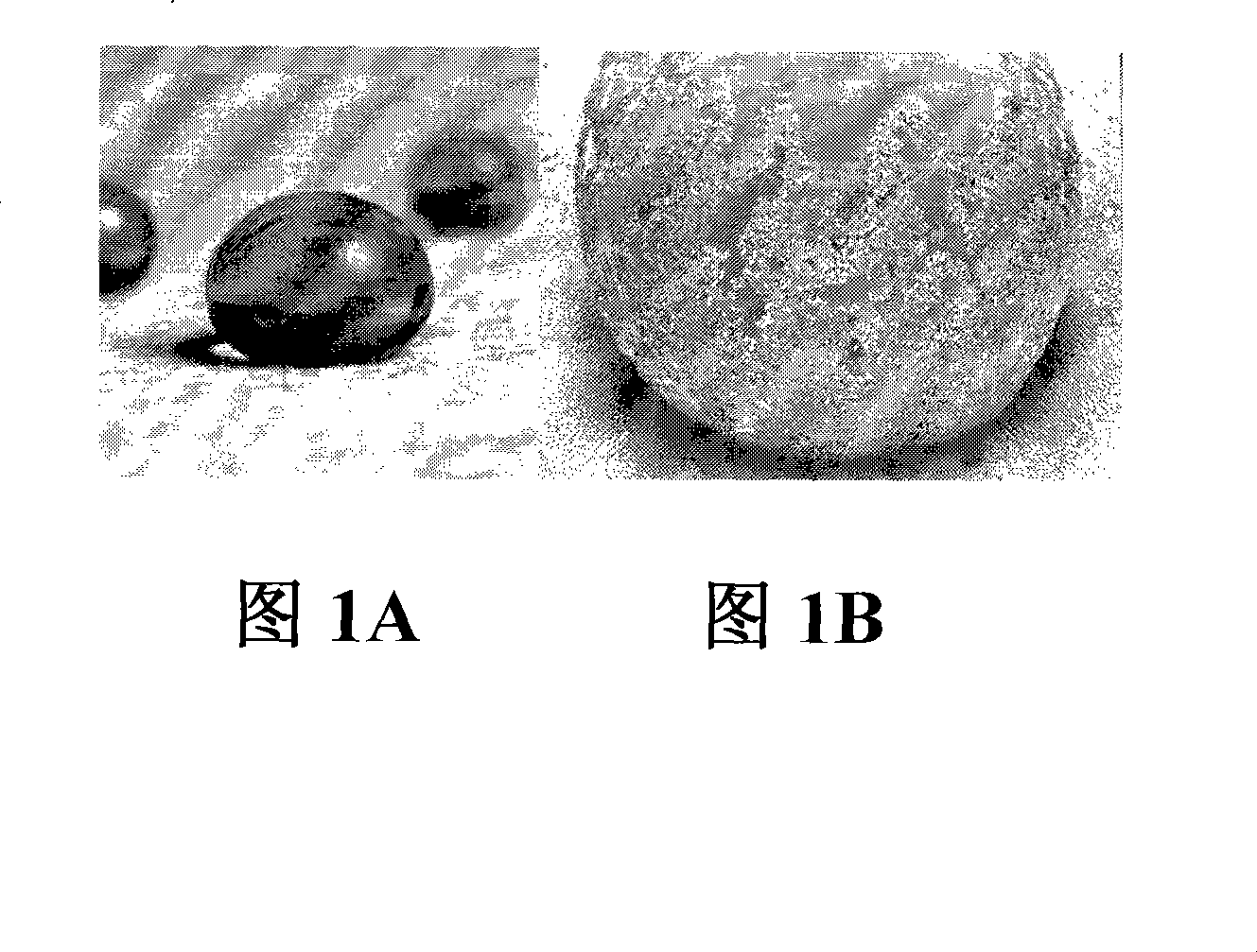
[0241] Before gelation is complete, the solution is cast on a suitable substrate (microscope slide, elastomer, etc.) to form a thin layer. Cover the surface to allow slow evaporation of ethanol and ammonia. After two (2) days, the film had completely gelled and the ethanol had evaporated completely. A thin silica layer is thus formed on the surface of the substrate. Execution of the above method on a microscope glass slide shows that the surface directly after coating is hydrophobic, which is due to the presence of hydrophobic side chains in the IBTMOS co-precursor ( ...
Embodiment II
[0250] TEOS (precursor), TFPS (co-precursor) and ethanol were first mixed in the amounts given in "Material Example II" in Table 6. HCl (1M) was then added to adjust the pH to about 1.8-2.0. The reaction was initiated by heating to 60°C and then held for five (5) hours. After the reaction, 0.1 g of ammonium hydroxide (29% by weight) (1.1 M) was added to 2 g of the solution to perform gelation of the polymer.
[0251]Before gelation is complete, the solution is cast on a suitable substrate to form a thin layer. Cover the surface to allow slow evaporation of ethanol and ammonia. After two (2) days, the film had gelled and the ethanol had evaporated completely. A suitable example for forming a thin silica layer on a substrate is a glass microscope slide.
[0252] The reason why the surface is hydrophobic is due to the presence of hydrophobic side chains in the TFPS co-precursor ( Figure 20-21 ). Figure 21 Including different reagent ratios (respectively Figure 21 A 1:3,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com