Method for mediated gene transfection
A gene transfection and mediation technology, which is applied in the fields of biomedicine and bioengineering, can solve the problems of transient transfection effect and low transfection efficiency, so as to reduce virus dosage, improve transfection efficiency, and increase targeting sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1 Determining the implementation of UTMD combined with AAV-mediated gene transfection method
[0030] 1) UTMD pre-irradiated rAAV2
[0031] The mechanism of UTMD-mediated gene transfection is mainly related to the instantaneous cavitation effect, that is, under the irradiation of high ultrasonic sound pressure, the microbubbles rapidly expand and contract, and even collapse, and then generate strong shock waves and acoustic waves around the microbubbles. Jet flow and a large number of free radicals, etc. These effects can be increased to a certain extent to affect the performance of proteins and genes.
[0032] In this example, rAAV2-EGFP was administered with a certain dose of UTMD before being added to the cell well: ultrasonic intensity 2 , irradiation time<120seconds and microbubble<60μl, frequency 1MHz, duty cycle 50%, pulse repetition frequency 100Hz, pre-irradiation, the results showed that the efficiency of infecting human renal cancer cells (786-0) was...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2 Optimizing the effect of UTMD combined with AAV-mediated gene transfection method
[0038] A. Irradiation with different sound intensities
[0039] Since the cavitation effect caused by UTMD is positively correlated with the cell transfection rate, but negatively correlated with the cell viability, it is necessary to optimize its influencing factors in the in vivo and in vitro experiments to achieve the highest transfection efficiency while ensuring the cell survival rate. Minimal damage. The main factors of UTMD-mediated gene transfection include ultrasonic irradiation conditions and microbubble dosage. The magnitude of the ultrasonic alternating sound pressure is proportional to the amplitude of the microbubble vibration, that is, when the irradiation sound intensity increases, the nonlinear vibration of the microbubble intensifies, so that the microbubble is more likely to rupture, resulting in stronger shock waves, microjet flow and shear stress, etc., in...
Embodiment 3
[0049] In vivo and in vitro research application of UTMD combined with AAV-mediated gene transfection method
[0050] A. In vitro experiments
[0051] A). Human kidney cancer cells
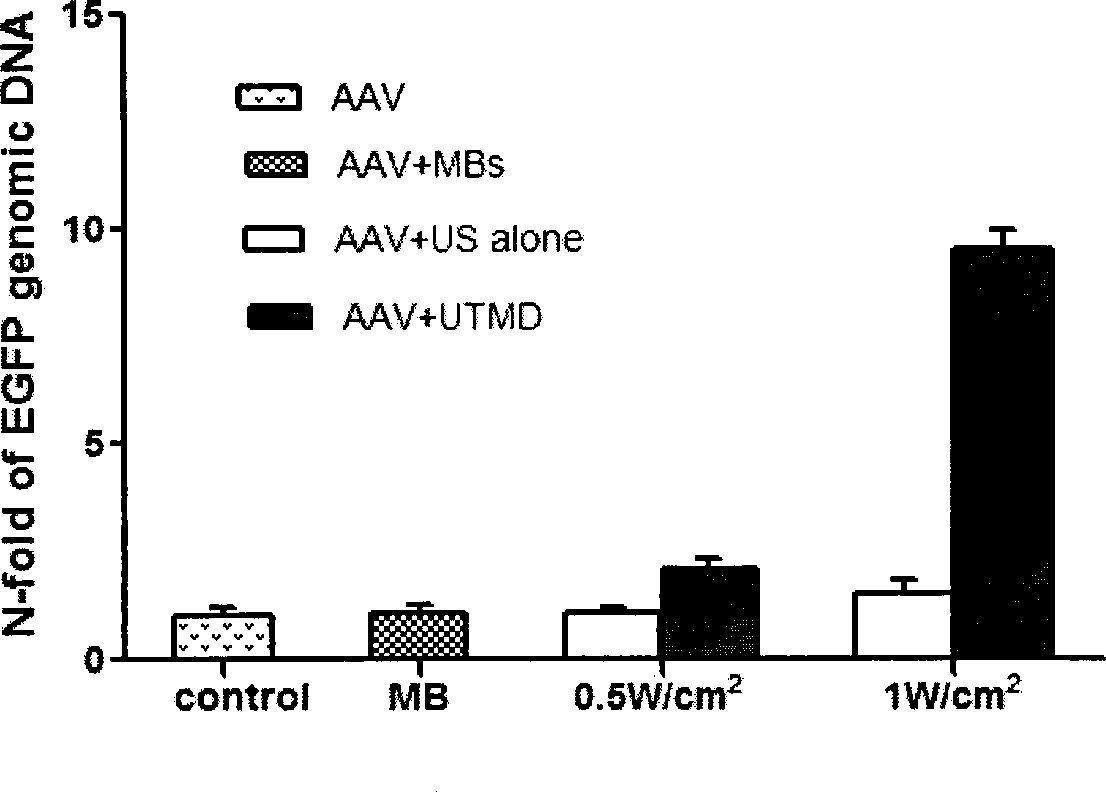
[0052] Renal cancer cells are rAAV2 non-tropic cells. Human kidney cancer cells were purchased from the Cell Resource Center, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. In the present invention, rAAV2 (1×10 4 ~5×10 6 MOI) was used to infect human renal carcinoma (786-0) cells, and the transfection rate of EGFP was detected after 48 hours. The results showed that the infection efficiency of rAAV2 to 786-0 cells was low, with an average of (14.31±2.50)%. With the optimal UTMD irradiation conditions (sound intensity 1W / cm 2 , microbubble 30μl, irradiation time 60s, frequency 1MHz, duty cycle 50%, pulse repetition frequency 100Hz) combined with rAAV2, the infection efficiency increased by 200%-300% on average.
[0053] B). Human liver cancer cells
[0054] Human l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com