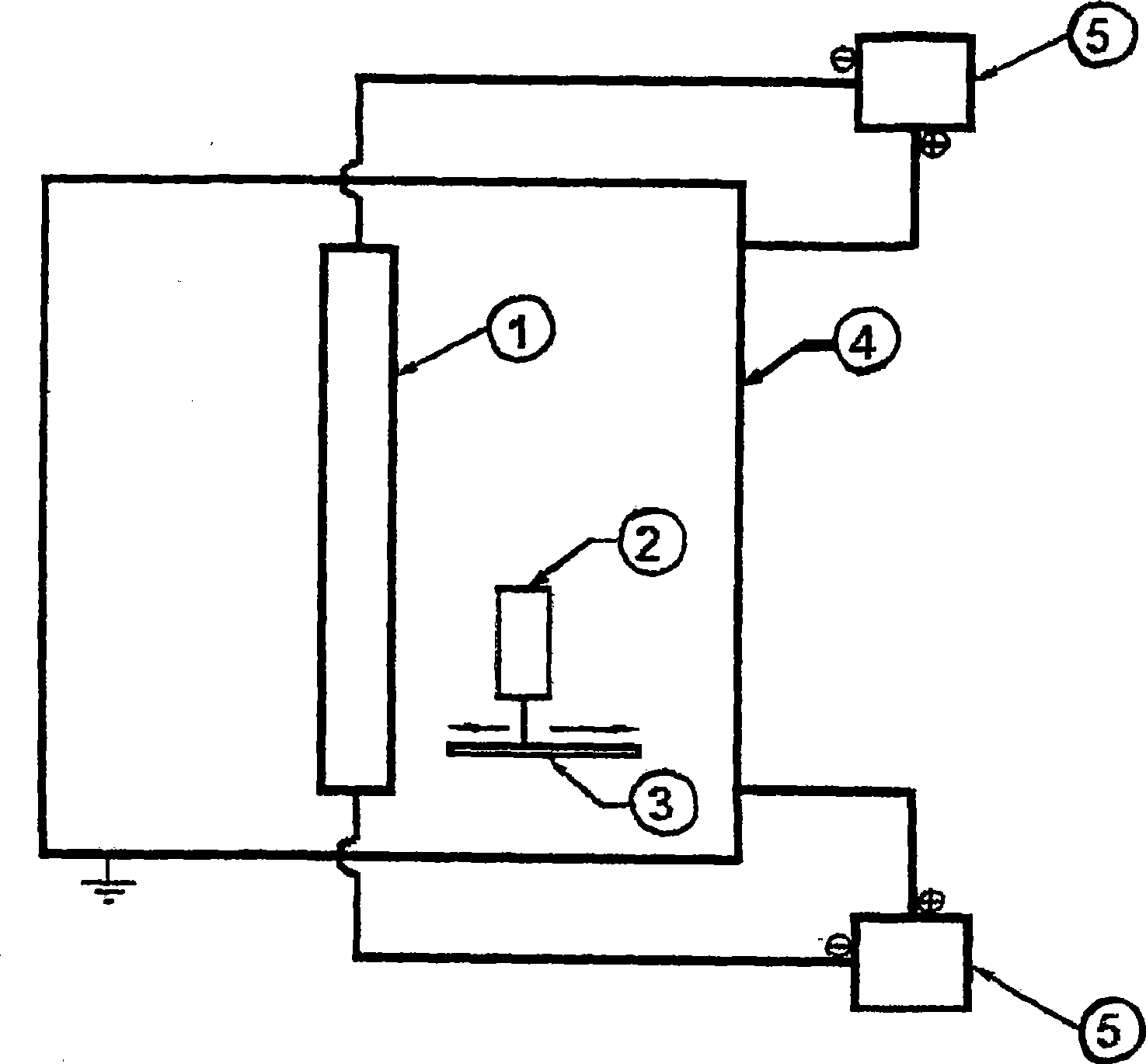
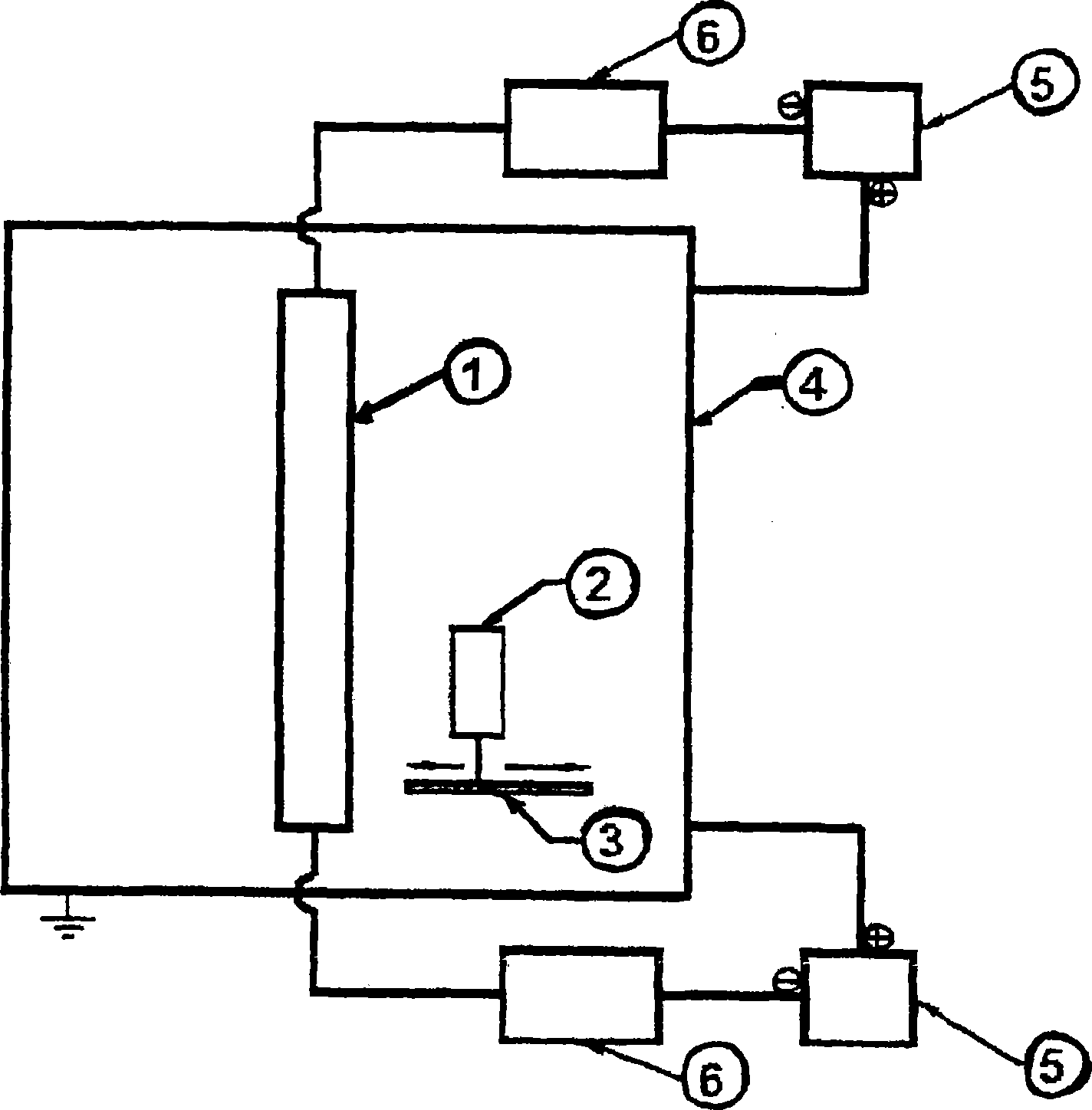
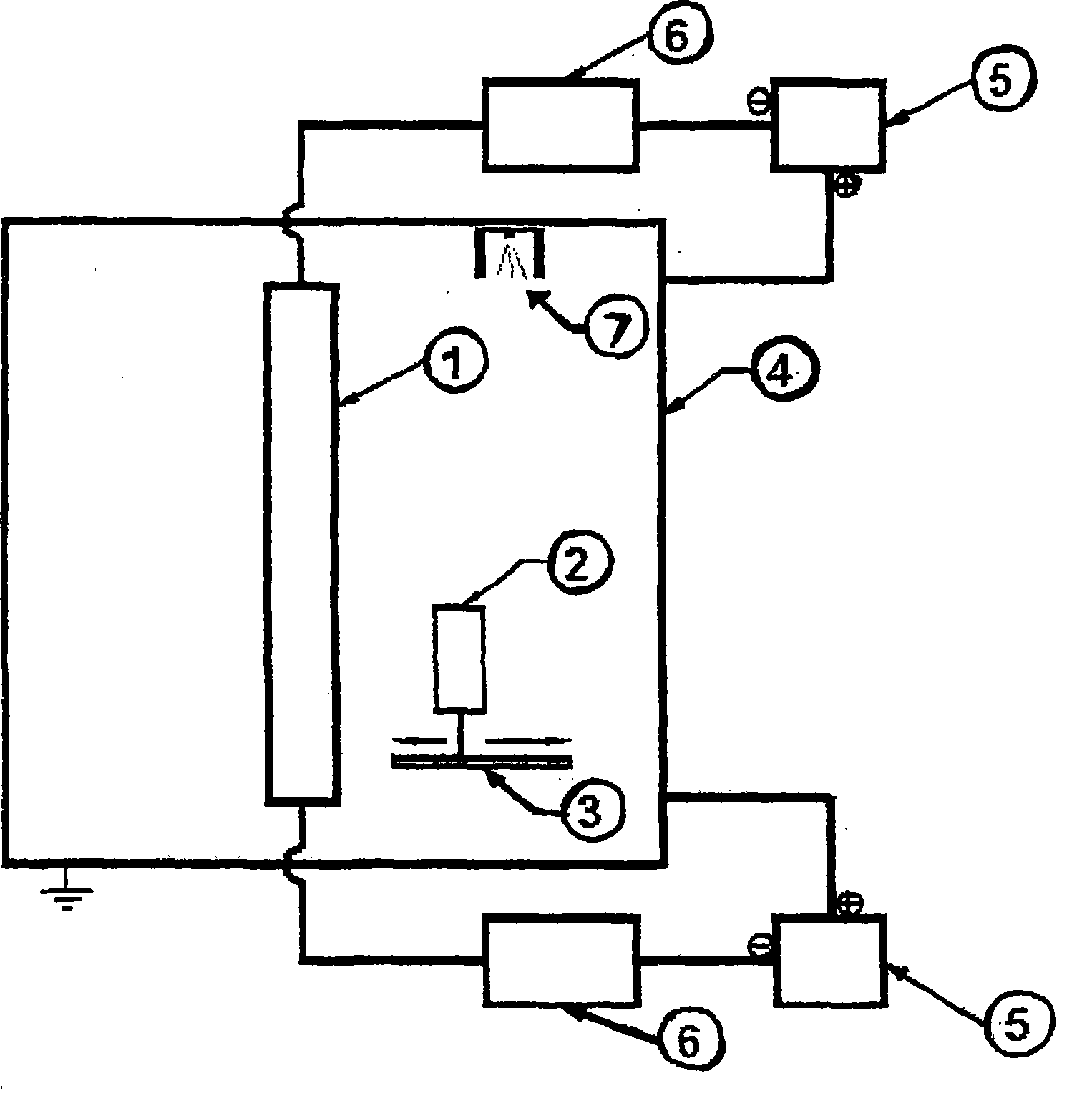
Ultraviolet activated antimicrobial surfaces
An anti-microbial, surface layer technology, applied in the field of light-induced activation, which can solve the problems of low activity, poor substrate adhesion of antibacterial coatings, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1. Antimicrobial Activity of Sputtered Silver Coatings on Rubber
[0076] This example was performed following the coating and detection procedures described in US Patent No. 5,454,886 (the '886 patent). The method and assays were carried out as detailed in Example 6 of the '886 patent.
[0077] Metallic silver was deposited on a 2.5 cm portion of the rubber Foley catheter using a magnetron sputtering facility. The operating conditions are as follows: the deposition rate is 200A° / min; the argon working pressure is 30mTorr; the ratio T / Tm of the substrate temperature to the melting point of the coating metal silver is 0.30. In this embodiment, since the substrate is round and rough, the angle of incidence is variable. That is, the angle of incidence varies around the circumference, on a finer scale, across the sides and vertices of numerous surface features. The antimicrobial effect was detected by a zone of inhibition assay as described in Example 1 of the '8...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2. On rubber Antimicrobial Activity of Sputtered Silver Coatings Over
[0080] This example follows what has been reported for the preparation of a coating coated by DC magnetron sputtering according to Example 7 of U.S. Patent No. 5,454,886. Steps for coating rubber conduit. Antimicrobial testing was performed with Staphylococcus aureus as already described.
[0081] Teflon-coated rubber Foley catheters were coated by DC magnetron sputtering silver with a purity of 99.99% on the surface, the coating conditions were as follows: power 0.5kW, 40mTorrAr / O 2 , an initial substrate temperature of 20° C., a cathode / anode distance of 100 mm, and a final film thickness of 300 nm. The working gas is commercial Ar and 99 / 1wt% Ar / O 2 .
[0082] The antimicrobial effect of the coating was tested by ZOI as described in Example 7 of the '886 patent. Pour the Mueller Hinton agar into Petri dishes. The surface of the agar plate was allowed to dry prior to inoculation w...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3. Sputtered Antimicrobial Silver Coatings
[0085] This example was carried out following the procedure described in Example 11 of the '866 patent. The conditions used in this example include: RF magnetron power 0.5kW, pressure 40mTorr, anode / cathode distance 100mm, 20°C.
[0086] Under the conditions listed above, when the antimicrobial coating was sputtered with argon and 20 wt% oxygen as the working gas, the zone of inhibition varied from 0-2mm, compared with that in Example 11 of the '866 patent The reported ZOI ranges from 6-12mm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com