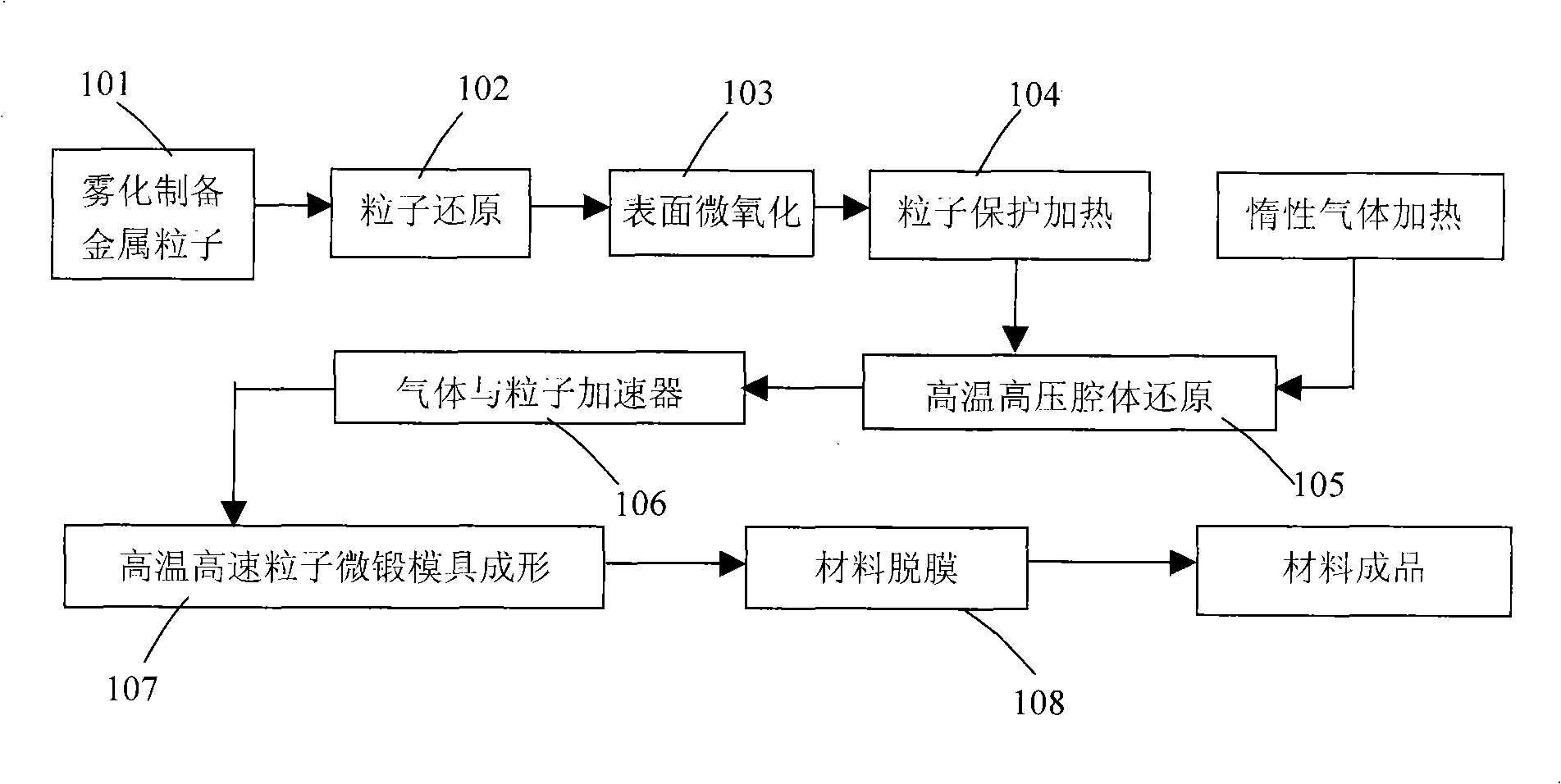
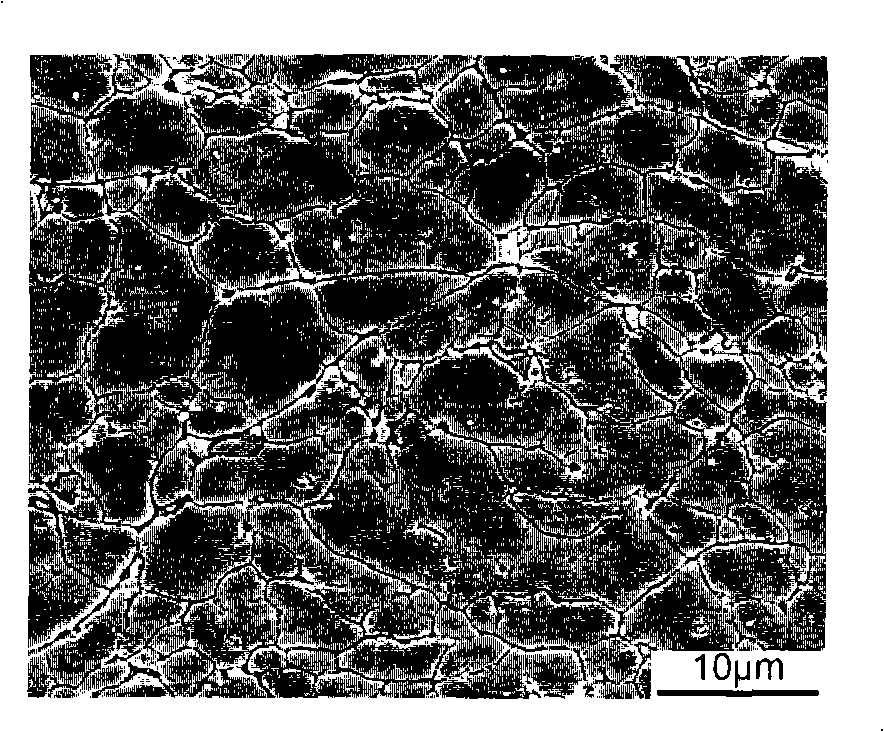
Reduced metal particle high speed micro-forging forming process
A metal particle and forming process technology, which is applied in the field of high-speed micro-forging forming process for reducing metal particles, can solve the problems of low deposition rate, high energy consumption, and inability to eliminate oxygen, and achieve simple operation, strong reducing ability, and easy control of fluidity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Copper alloy threads are prepared on the inner wall of the steel pipe. Using gas atomized copper alloy particles, the melting point of the particle material is 1050°C, and the average particle size of the particles is 35 microns. The copper alloy particles are fully reduced by the method of ammonolysis reduction, and the internal oxygen is eliminated. The particles were passed through in an air environment at 400° C., and the particle temperature was equalized for 5 seconds to obtain micro-oxidized copper alloy particles on the surface. The oxygen content is 3%. The micro-copper oxide alloy particles were rapidly heated to 500°C under nitrogen protection, and sent to a nitrogen-hydrogen mixed high temperature and high pressure reduction chamber with a hydrogen content of 1%. The temperature in the reduction chamber was 600°C and the pressure was 25 bar. Then, it is introduced into the accelerator, accelerated to 1.5 times the speed of sound, and formed by integral mic...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A streamlined aluminum-magnesium alloy composite structural skeleton is prepared in the cavity of the composite material structure. Aluminum-magnesium alloys are notoriously difficult to prepare and process. In this experiment, aerosolized aluminum-magnesium alloy particles were used, the melting point of the particle material was 760 °C, and the average particle size of the particles was 75 microns. The aluminum-magnesium alloy particles were reduced by the hydrogen reduction method, and the internal oxygen was eliminated. The particles were passed through in an air environment at 300°C, and the particle temperature was equalized for 3 seconds to obtain micro-alumina-magnesium alloy particles on the surface. The oxygen content is about 2.5%. Under the protection of helium, the micro-alumina-magnesium alloy particles are rapidly heated to 350 ° C, and sent to a nitrogen-hydrogen mixed high temperature and high pressure reduction chamber with a hydrogen content of 1%. ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Preparation of stainless steel profiled rolling die. Use water atomized stainless steel powder. The melting point of the particle material was 1750° C., and the average particle diameter of the particles was 30 μm. The stainless steel particles are fully reduced by the method of ammonolysis reduction, and the internal oxygen is eliminated. The particles were passed through in an air environment at 700° C., and the particle temperature was equalized for 5 seconds to obtain micro-oxidized stainless steel particles on the surface. The oxygen content is 5%. Under nitrogen protection, the micro-oxidized stainless steel particles are rapidly heated to 600°C, and sent to a nitrogen-CO mixed high temperature and high pressure reduction chamber containing 6% CO. The temperature in the reduction chamber is 800°C and the pressure is 30bar. Then, it is introduced into the accelerator, accelerated to 2.0 times the speed of sound, and formed by integral micro-forging. A stainless...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com