Phosphate material having mesoporous structure for lithium secondary batteries and preparation method thereof
A technology of mesoporous structure and mesoporous materials, applied in secondary batteries, electrode manufacturing, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of low electrode density and poor rate characteristics, achieve high power density, improve rate performance, and reduce consumption Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
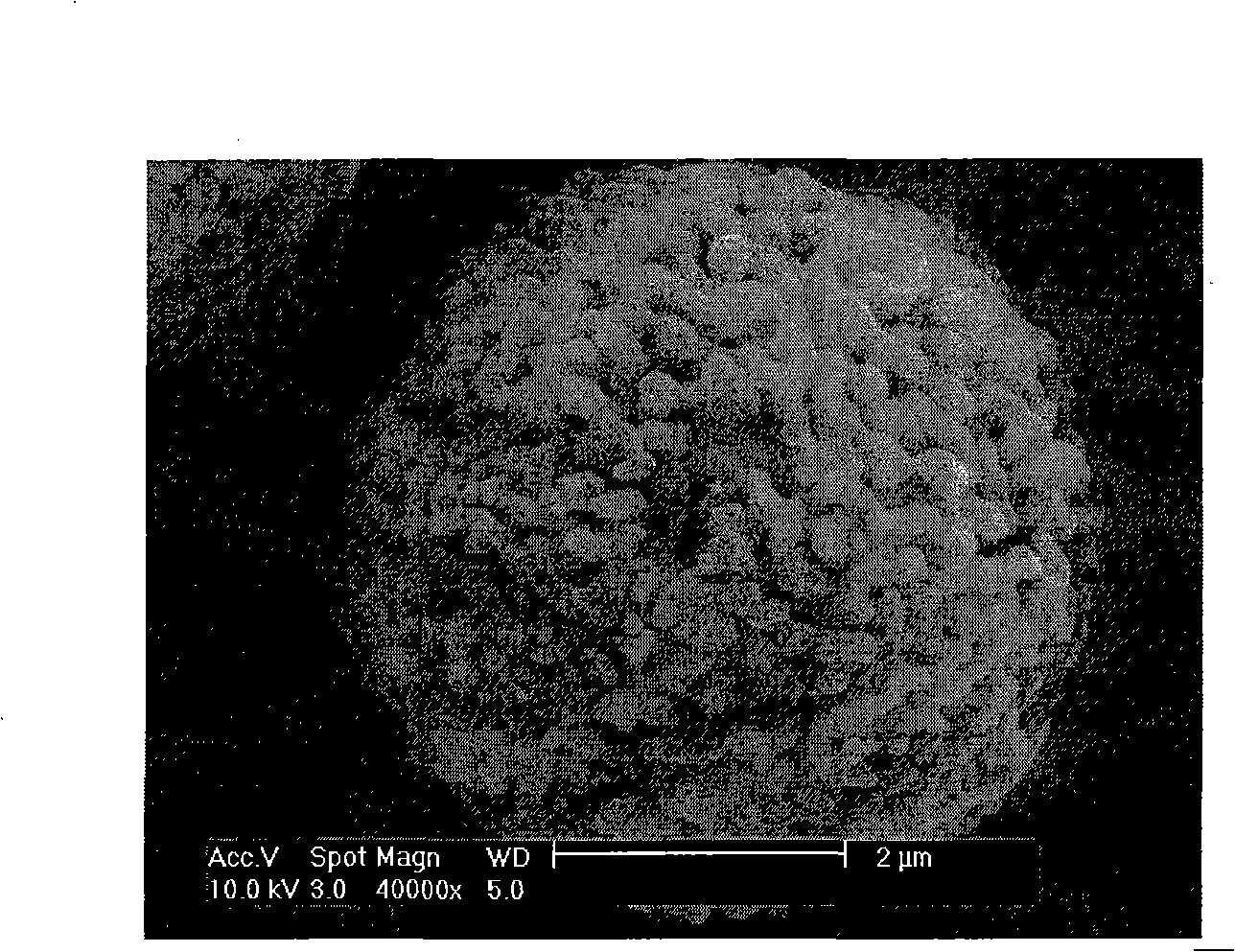
[0043] Embodiment 1, prepare the mesoporous structure pure phase LiFePO that is used for secondary lithium battery of the present invention , prepared this sample reference as attached figure 1 and 2 .
[0044] The mesoporous structure pure phase LiFePO4 of this embodiment can be prepared by the following steps. First, weigh 1.02g of LiAc 2H2O, 2.48g of Fe(Ac)2 4H2O and 0.98g of H3PO4, add them into a beaker filled with 200ml of ethylene glycol, and stir for 30 minutes with a magnetic stirrer until uniformly dispersed. Add NH4·H2O to adjust the pH value to 7-8, continue magnetic stirring for 0.5 hours until a sol is formed, and heat-treat the sol in high-purity Ar gas (the heat treatment step is: heat the sol at 120°C for 3 hours, then raise the temperature to 140°C ℃ until it becomes a xerogel), and the xerogel is sintered under the protection of high-purity Ar gas (the sintering step is: take 3 hours to heat up from room temperature to 700 ° C, keep the temperature at 700 ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2. Preparation of the mesoporous cathode material LiCoPO4 for secondary lithium batteries of the present invention. The prepared sample is referred to as attached image 3 and 4 .
[0049] Mesoporous cathode material LiCoPO4 can be prepared by the following steps. First, weigh 1.05g of LiAc 2H2O, 2.51g of Co(Ac)2 4H2O and 0.98g of H3PO4, add them into a beaker containing 80ml of ethylene glycol, stir for 30 minutes with a magnetic stirrer until uniformly dispersed, Add NH4·H2O to adjust the pH value to 7-8, continue magnetic stirring for 0.5 hours until a sol is formed, and heat-treat the sol in air (the heat-treatment step is: heat the sol at 120°C for 1 hour, then raise the temperature to 140°C until it becomes into a xerogel), and sinter the xerogel in air (the sintering step is: take 3 hours to heat up from room temperature to 700°C, keep the temperature at 700°C for 12 hours, and then cool to room temperature for 5 hours). The scanning electron microgra...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3, mesoporous structure doped lithium iron phosphate material
[0054] Doped lithium iron phosphate Li0.99Na0.01FePO4 can be prepared by the following steps. First, weigh 1.02g of LiAc·2H2O, 2.46g of Fe(Ac)2·4H2O, 0.035g of NaAc·3H2O and 0.98g of H3PO4, add them to a beaker containing 50ml of ethylene glycol, and use a magnetic stirrer Stir for 1 hour until uniformly dispersed, add NH4·H2O to adjust the pH value to 7-8, continue magnetic stirring for 1.5 hours until a sol is formed, and heat-treat the sol in high-purity Ar gas (the heat treatment step is: heat the sol at 150°C for 5 hours, and then heated up to 170°C until it becomes a xerogel), the xerogel is sintered under the protection of high-purity Ar gas (the sintering step is: use 2 hours to heat up from room temperature to 700°C, and keep the temperature at 700°C for 12 hours , and cooled to room temperature for another 3 hours). The obtained mesoporous structure Li0.99Na0.01FePO4 has an average prima...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com