Method for preparing terpene resin
A technology of terpene resin and pinene, which is applied in the field of preparation of terpene resin, can solve the problems of hydrogenation catalyst poisoning, difficult industrial production, and high cost of hydrogenation, and achieve the effect of easy product, easy preparation, and no corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
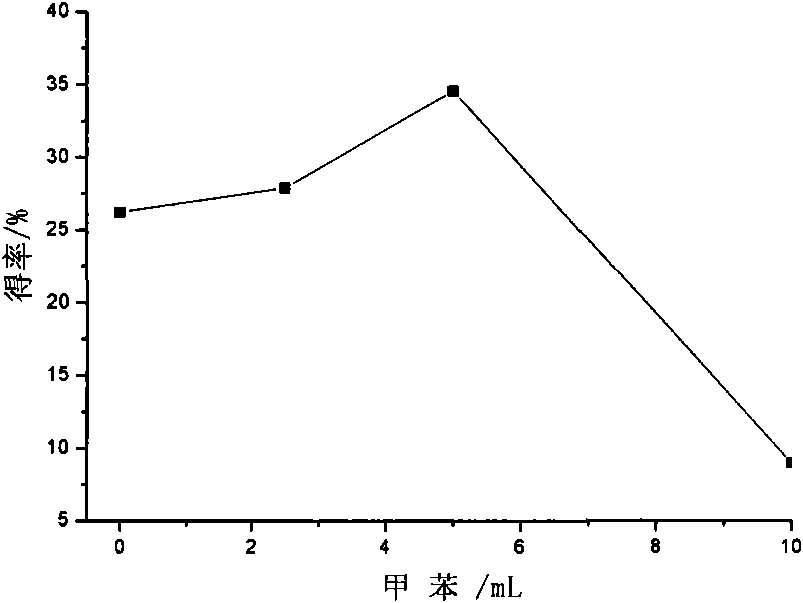
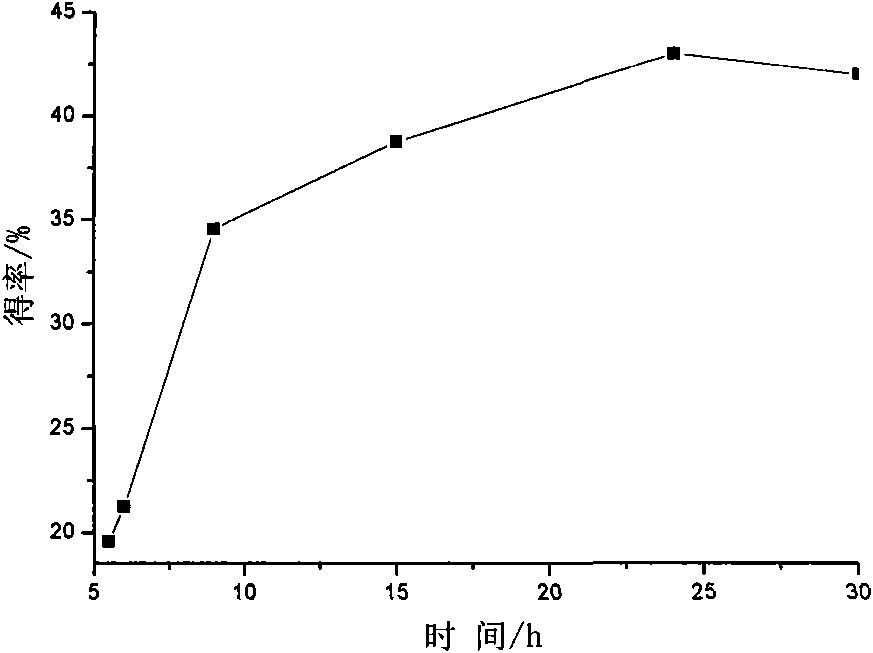
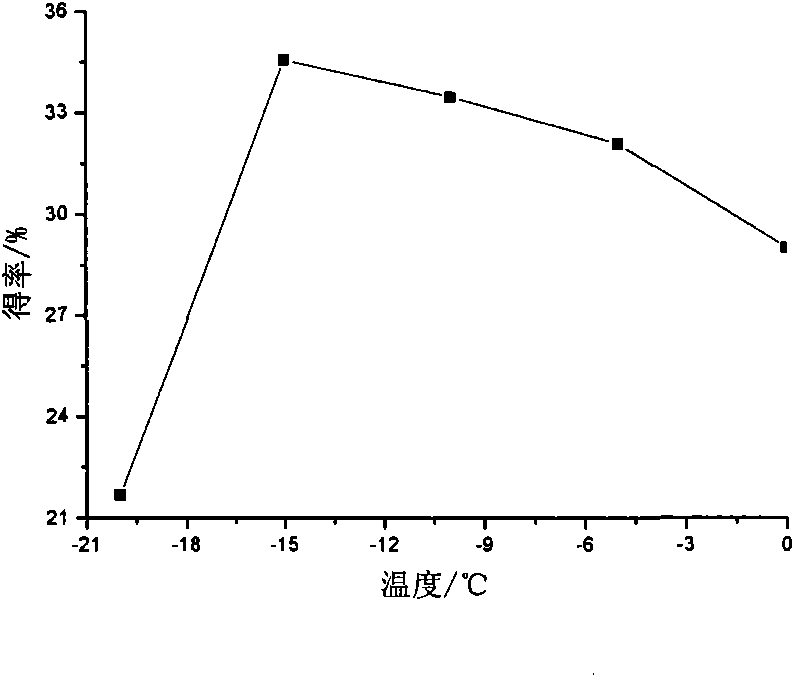
[0055] Add 0.30g of activated phosphotungstic acid to a dry three-necked flask, control the bath temperature between -17°C and -15°C, then add 5ml of toluene, and then take 5mL of β-pinene into a dry dropping funnel , Slowly drop into the reaction flask, about 1h drop. After mechanical stirring for 9 hours, methanol terminated the reaction. Filter the reaction mixture to recover the catalyst, wash a small amount of residual catalyst with an appropriate amount of ethanol, recover the solvent, unreacted monomer raw materials and oligomers by distillation, and vacuum-dry the residue at 50-80°C to obtain terpene as a colorless solid Vinyl resin. Resin yield: 34.56%.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Add 0.30g of activated phosphotungstic acid to a dry three-necked flask, control the bath temperature between -12°C and -10°C, then add 5ml of 1,2-dichloroethane, and then take 5mL of β-pinene In a dry dropping funnel, slowly drop it into the reaction flask, and drop it in about 1 hour. After mechanically stirring the reaction for 18 hours, the reaction was terminated with methanol. Filter the reaction mixture to recover the catalyst, wash a small amount of residual catalyst with an appropriate amount of ethanol, recover the solvent, unreacted monomer raw materials and oligomers by distillation, and vacuum-dry the residue at 50-80°C to obtain terpene as a colorless solid Vinyl resin. Resin yield: 60.85%
Embodiment 3
[0059] Add 0.30g of activated phosphotungstic acid to a dry three-necked flask, control the bath temperature between 10°C and 12°C, then add 5ml of dichloromethane, and then take 5mL of α-pinene into a dry dropping funnel , Slowly drop into the reaction flask, about 1h drop. After mechanical stirring for 9 hours, methanol terminated the reaction. Filter the reaction mixture to recover the catalyst, wash a small amount of residual catalyst with an appropriate amount of water, distill and recover the solvent, unreacted monomer raw materials and oligomers, and dry the residue under vacuum at 50-80°C to obtain terpene as a colorless solid Vinyl resin. Resin yield: 69.97%
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com