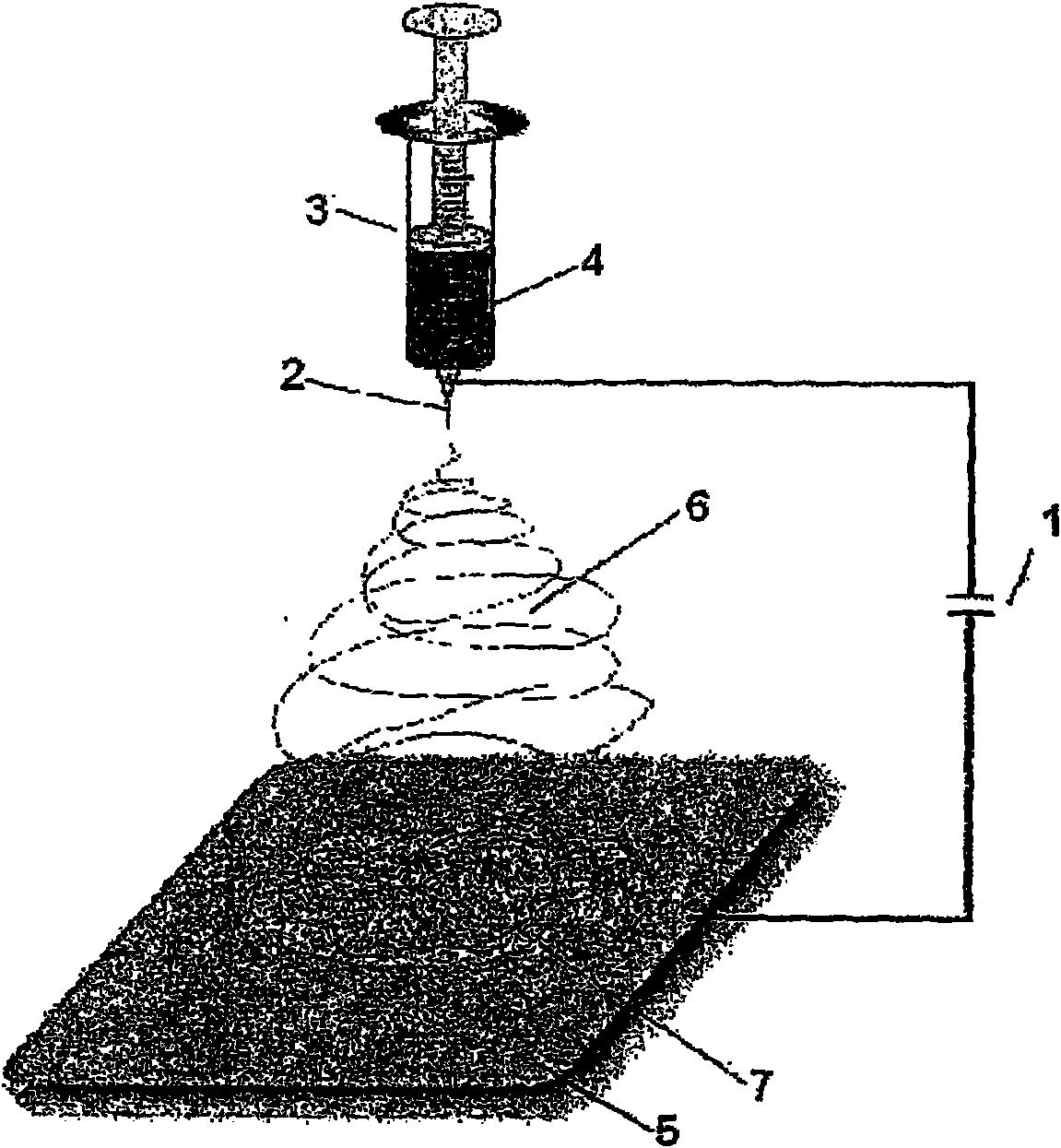
Polyethylenimine nanoparticle-containing microbicidal electrospun polymer fibers for textile applications
A technology of polyethyleneimine and nanoparticles, which can be used in textiles and papermaking, chemical post-treatment of synthetic polymer artificial filaments, textiles, etc., and can solve problems such as non-inclusion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0068] 1. Production of polyethyleneimine nanoparticles
[0069] According to "Mission Accomplished" polyethyleneimine nanoparticles were produced. In this case, 1,5-dibromopentane was used as crosslinker in the first reaction step. In the second reaction step, the alkylation of the crosslinked PEI, 2-bromooctane was used. In the third reaction step - quaternization of the second and third amino groups of PEI, methyl iodide in tetrahydrofuran was used.
[0070] 2. Production of PVB-based antibacterial nanofibers
[0071] Polyvinyl butyral (PVB, trade name Mowital), a polymer soluble in ethanol, was used.
[0072] Repeating unit of polyvinyl butyral:
[0073]
[0074] First, polyvinyl butyral (Mw=19640, Mn=159000, Mw / Mn=1.23) was dissolved in ethanol by stirring at room temperature. The concentrations of the prepared solutions were 10% by weight and 15% by weight. In order to provide the fibers with an antimicrobial coating, in each case 2% by weight of quaternized PEI...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com