Laser machining method, laser cutting method, and method for dividing structure having multilayer board
A technology of laser processing method and cutting method, which is applied in manufacturing tools, metal processing, stone processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of laser beam difficult to reach the lower glass plate, metal film damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0105] The laser medium is titanium sapphire crystal (center wavelength 780nm), the pulse width is 150 femtoseconds, and the output energy is above 1μJ. In addition, the object of processing was Corning Eagle 2000, which is a glass substrate, with a thickness of 700 μm. These parameters are common to all Examples unless there is a description different from this in each Example.
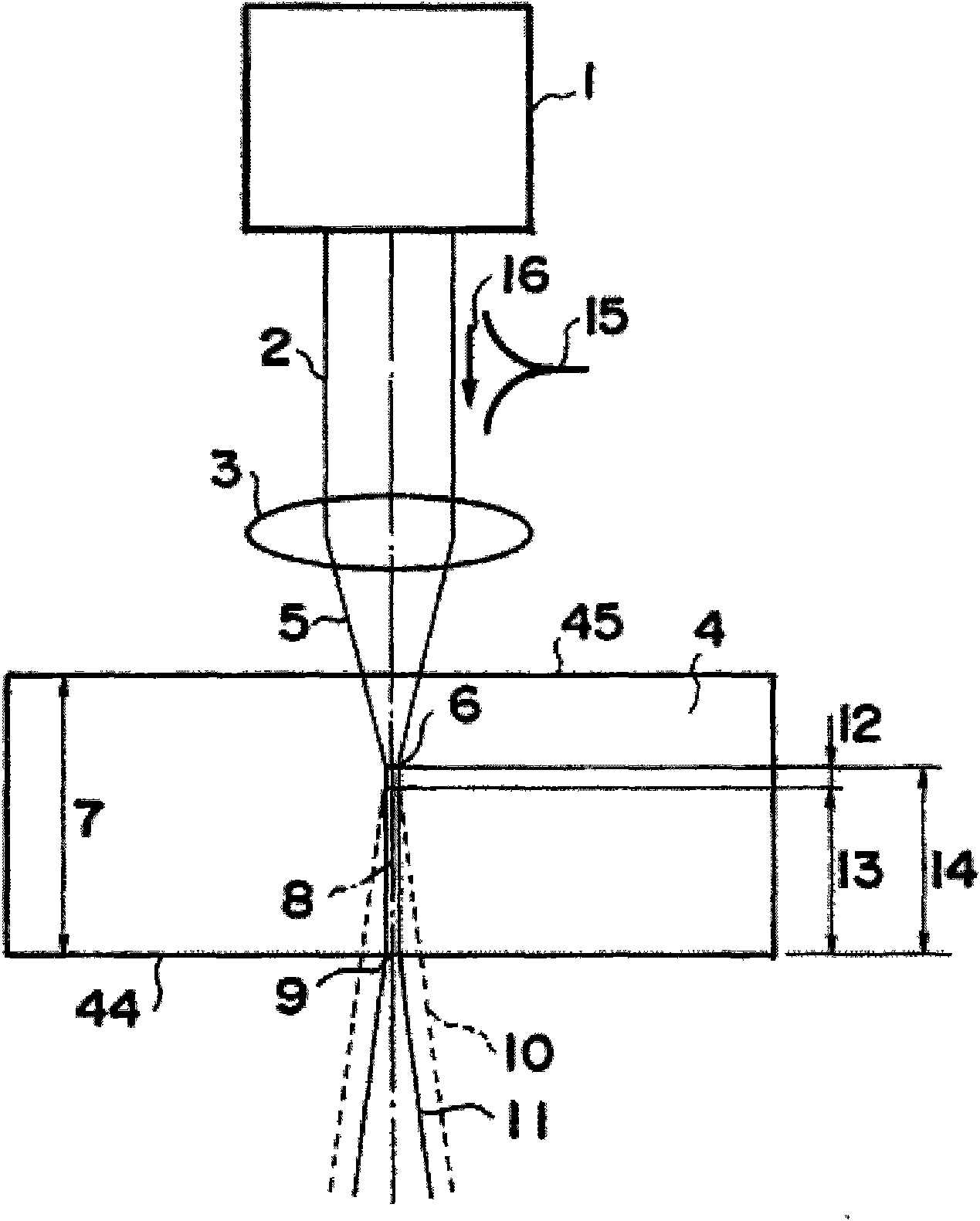
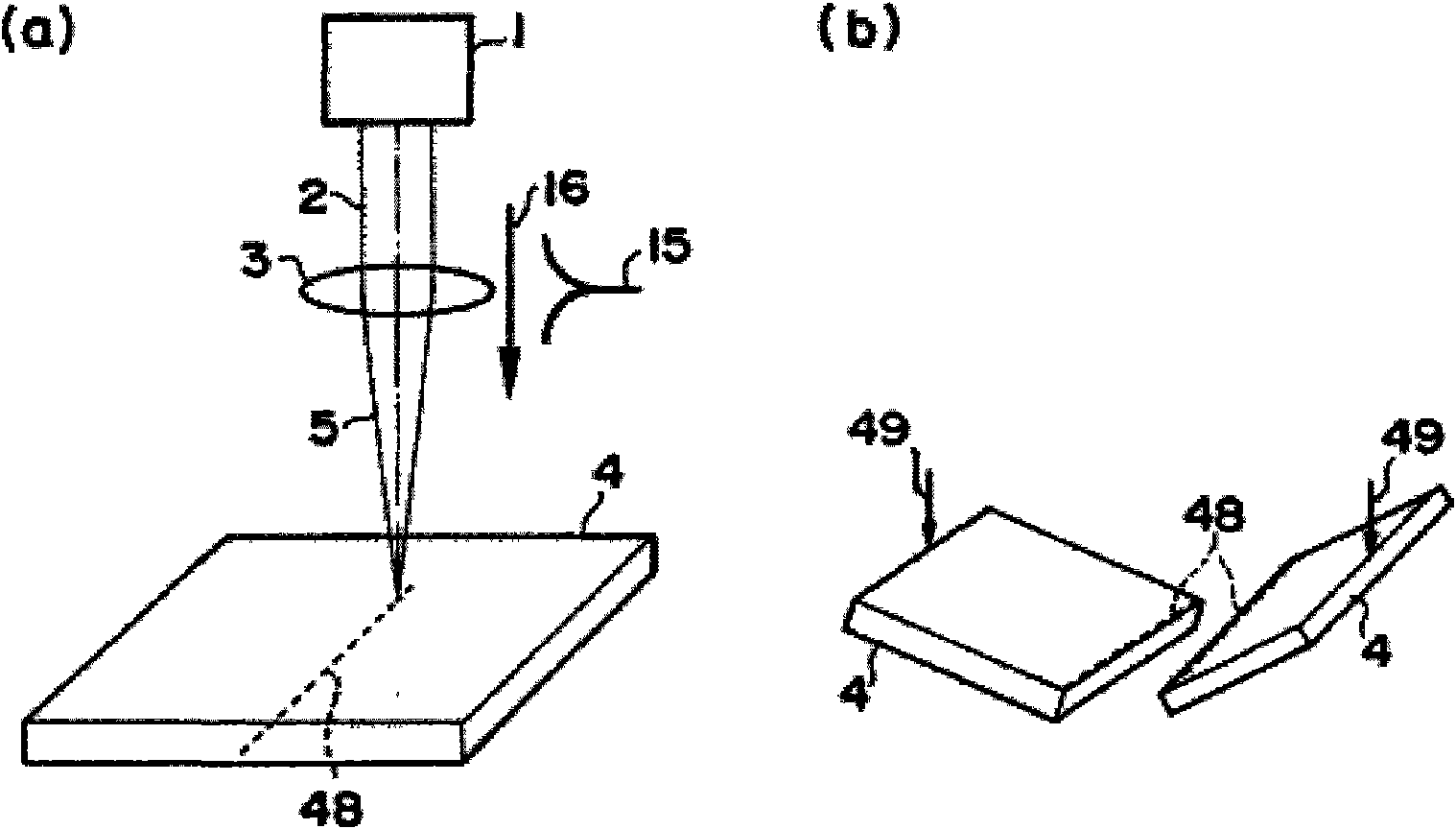
[0106] This example is figure 1 The configuration shown in is an experimental example to verify the principle of this processing method by observing changes in the object to be processed when the laser beam irradiating the object is moved from the surface to the inside.
[0107] exist Figure 10 as well as Figure 11 , shows a microscope photograph of a cross-sectional view in which changes occurring in a processed object are observed. Figure 10 shows the surface 45 of the substrate as the object to be processed, Figure 11 The vicinity of the rear face 44 is shown. for figure 1In this config...
Embodiment 2
[0110] In this embodiment, laser scanning is performed while forming the cavity channel near the back surface to form the cutting surface of the cavity channel.
[0111] In the case of filamentary cavities that form self-bunching effects, such as Figure 12 As shown in the figure inside, a funnel-shaped part 43 may be formed together on the back side. The funnel-shaped part 43 has overlapping adjacent parts, and the filamentary cavity and the channel 8 are respectively formed at the same position. By scanning the ultrashort laser pulse relatively along the back surface 44 of the object to be processed, the depth of processing along the scanning direction can be reduced. A plurality of filamentary cavities juxtaposed are formed on the winding wire 46 . exist Figure 12 The middle control shows a photomicrograph of the cut surface of the thus formed filamentary cavities. In this example, after scanning with laser pulses at a scanning speed of 3 mm / s, the section was observed ...
Embodiment 3
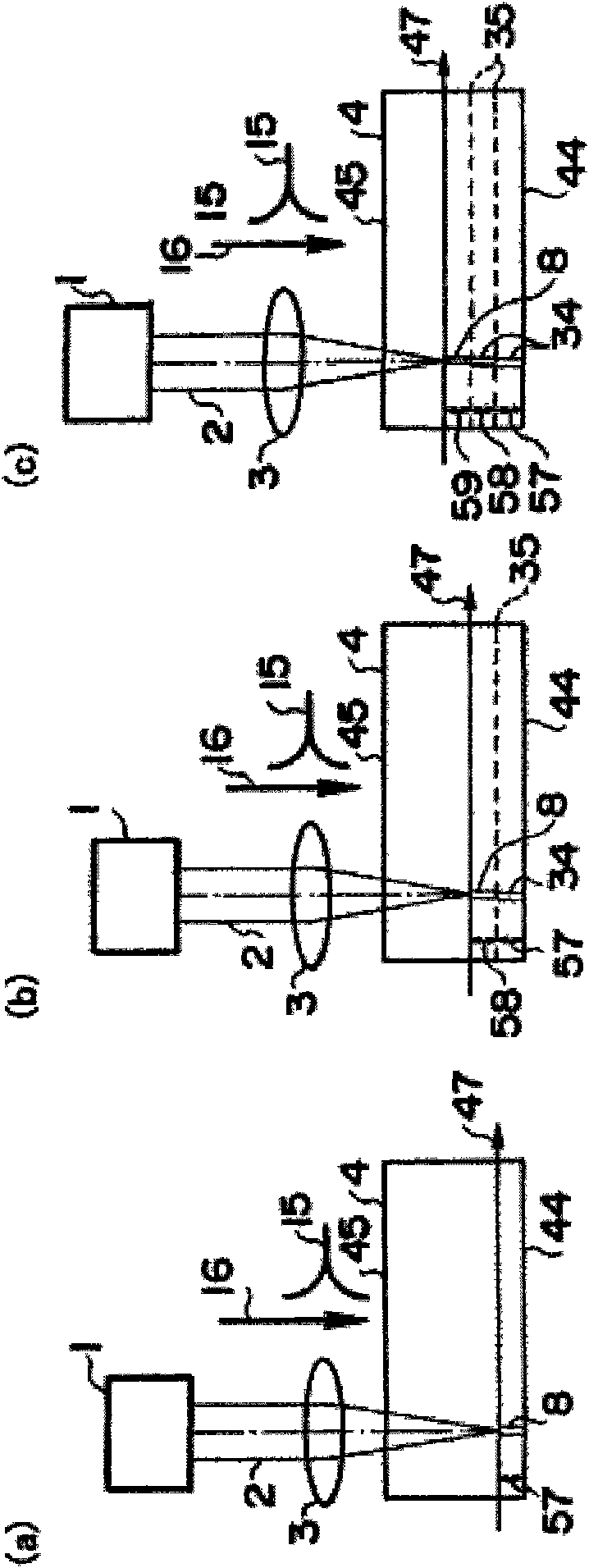
[0113] by image 3 In the configuration shown in , the height of the beam waist is changed, multiple scans are performed, and the vicinity of the back side is processed. Figure 15 The cross section in the case where the number of scans is 4, the pulse energy is 10 μJ, and the pulse width is 2 ps is shown. By reducing the pulse energy and optimizing the pulse width, a high-quality processed region 36 can be formed near the back surface.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pulse width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pulse width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com