Method for analysis of metallic material
An analysis method and technology of metal materials, applied in the direction of testing metal components, analyzing materials, testing metals, etc., can solve problems such as no size classification analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
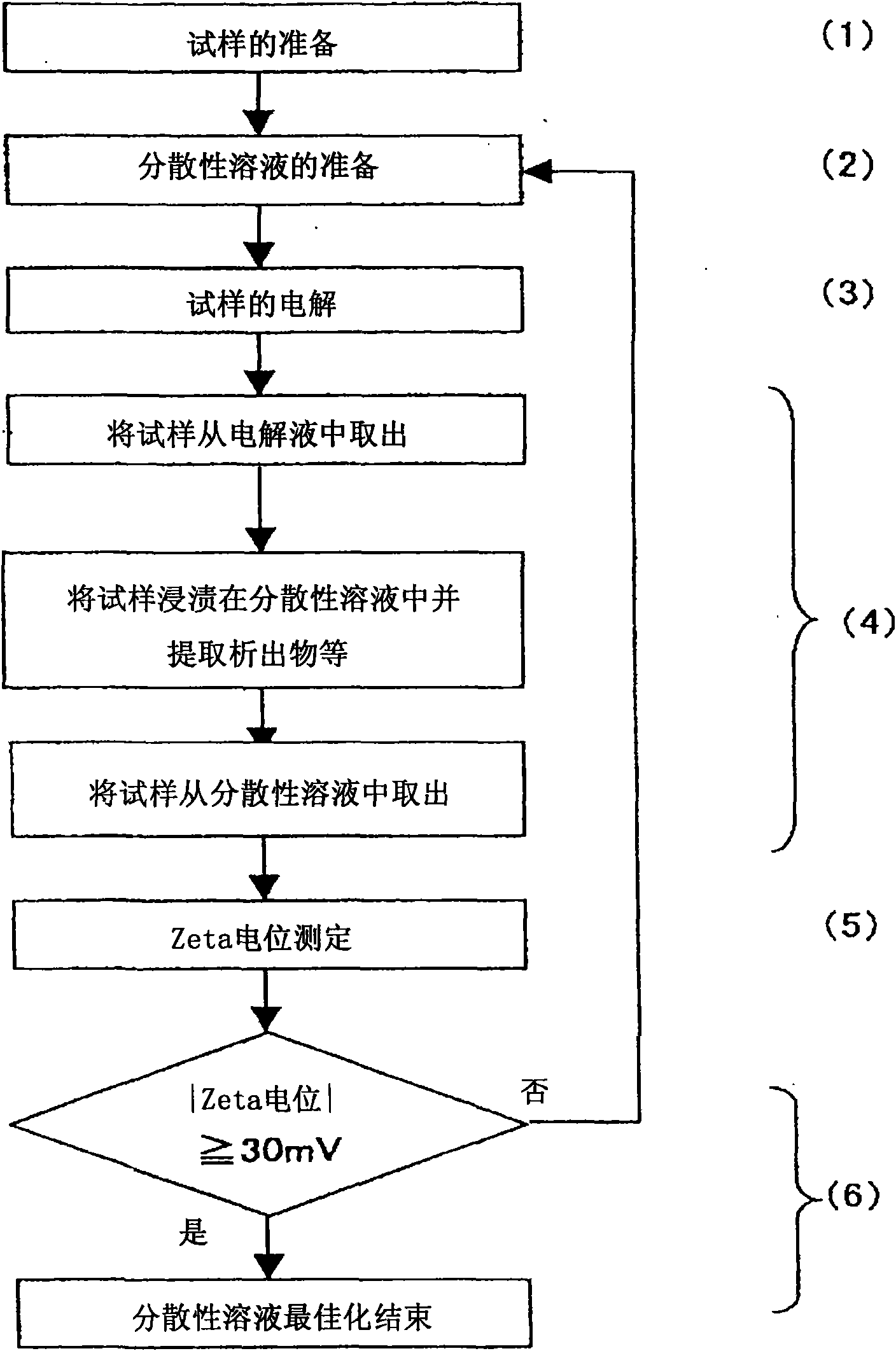
[0106] according to figure 1 In the order of (1) to (6) shown, the relationship between the titanium content in precipitates and the like and the zeta potential was examined. The specific conditions of each operation are as follows, but the present invention is not limited to the specific conditions described below.
[0107] Titanium-added carbon steel was used as a metal sample, and its chemical composition was: C: 0.09% by mass, Si: 0.12% by mass, Mn: 1.00% by mass, P: 0.010% by mass, S: 0.003% by mass, Ti: 0.18 Mass%, N: 0.0039 mass%.
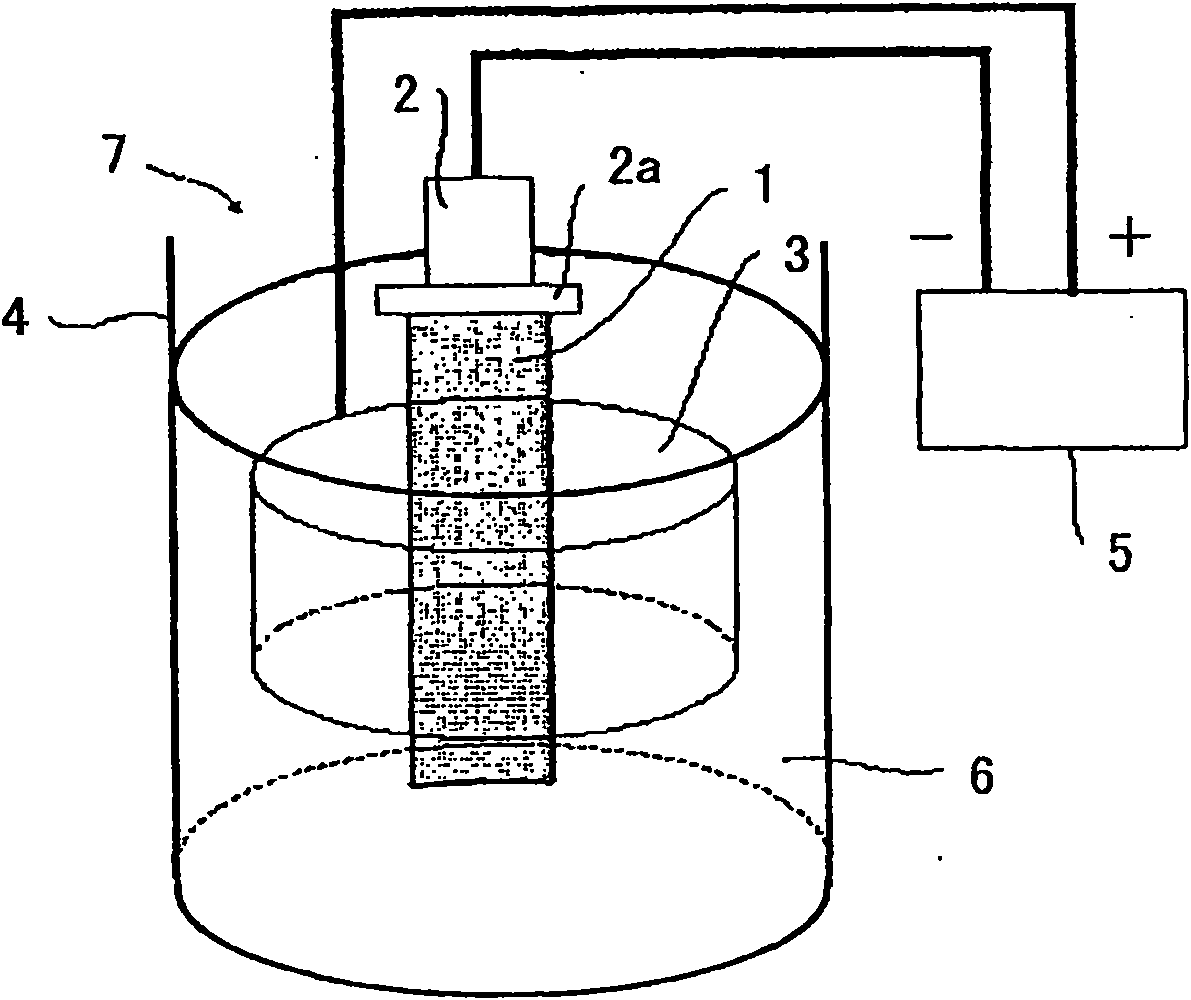
[0108] electrolytic operation through image 3 The device structure shown was carried out, and about 300 ml of 10% AA-based electrolyte solution (10 volume % acetylacetone-1 mass % tetramethylammonium chloride-methanol) was used as the electrolyte solution.
[0109] As a dispersive solution, an aqueous solution of sodium hexametaphosphate (hereinafter abbreviated as SHMP) was used, and the concentration of SHMP was changed in seven steps...
Embodiment 2
[0115] In Example 2, the analysis method of the present invention (examples of the present invention) and the methods of Non-Patent Document 1 and Patent Document 3 (Comparative Examples 1 and 2) were used to analyze the titanium content in precipitates and the like in steel. Specific instructions.
[0116]A steel ingot having the composition shown in Table 1 was cut into three pieces to obtain sample A, sample B, and sample C. Sample A was heated at 1250°C for 60 minutes and then water-cooled. Samples B and C were heated at 1250°C for 60 minutes and then rolled at a finishing temperature of 950°C, and then heat treated under the conditions shown in Table 2. . After natural cooling, sample A, sample B, and sample C are all cut into appropriate size and the surface is fully ground, using the analytical method of the present invention (example of the present invention), the method of non-patent literature 1 (comparative example) 1) The method of Patent Document 3 (Comparative ...
Embodiment 3
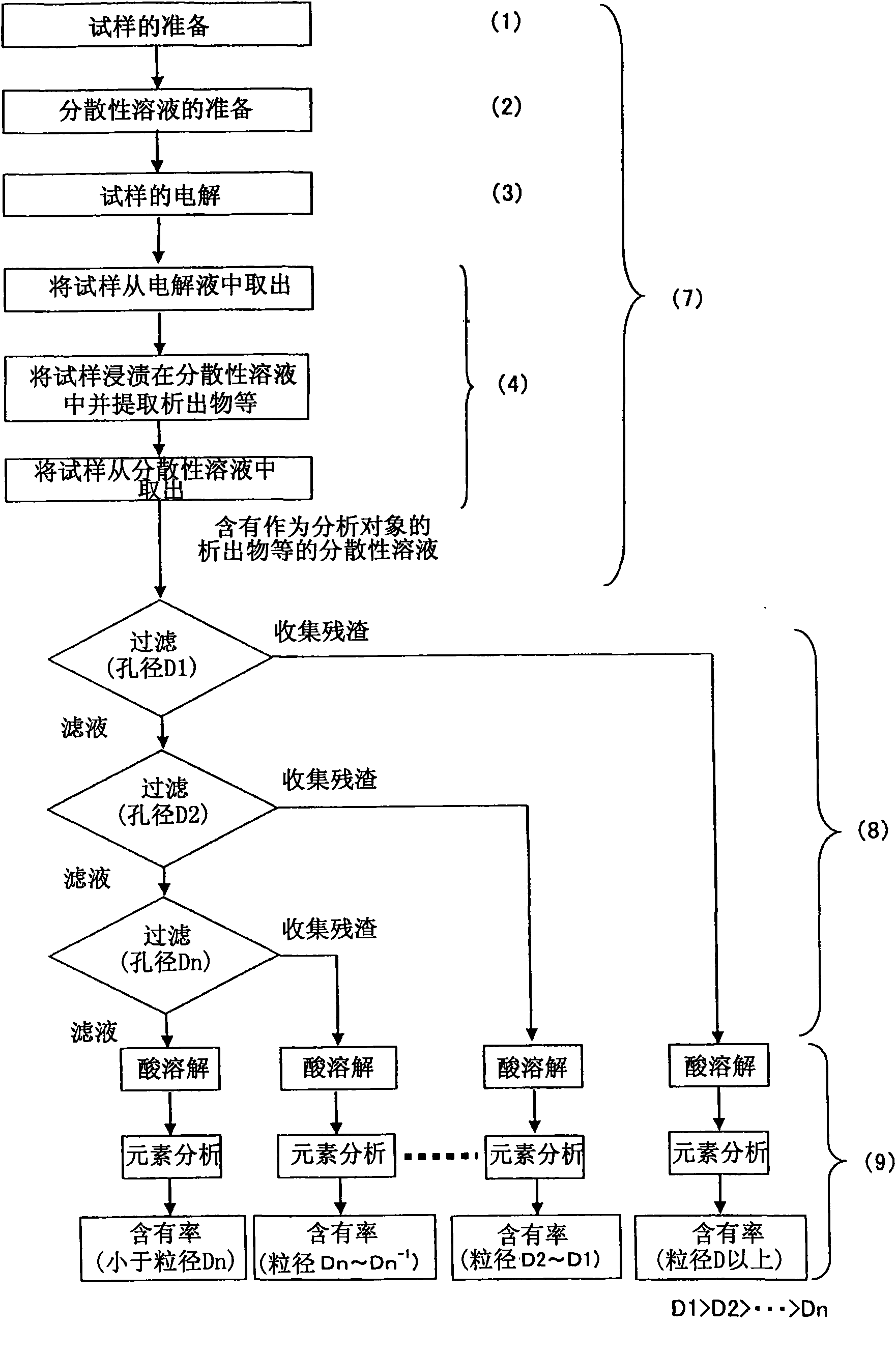
[0142] according to figure 2 The particle size distribution measurement was performed in the order of (1) to (4) shown.
[0143] Carbon steel was used as a metal sample, and its chemical composition was: C: 0.10% by mass, Si: 0.2% by mass, Mn: 1.0% by mass, P: 0.024% by mass, S: 0.009% by mass, Cr: 0.03% by mass, Ti : 0.05% by mass. Then, these steels were cut into a size of 20 mm x 50 mm x 1 mm, and used as samples for electrolysis.
[0144] electrolytic operation through image 3 The device structure is carried out, and 500ml of 10% AA-based electrolyte is used as the electrolyte. The amount of electrolysis was performed at 0.1 g each time, and (3) to (4) were repeated 10 times. Sacrificial electrolysis (sacrificial electrolysis) for decontamination of the surface layer was performed only once before the electrolysis operation.
[0145] As the dispersion solution, a sodium hexametaphosphate aqueous solution having a concentration of 500 mg / l was used, and 50 ml was pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com