Regenerative dehumidification heat exchange device
A heat exchanger, regenerative technology, applied in household heating, heating methods, lighting and heating equipment, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable desiccant dehumidification/regeneration, reduced operating efficiency, waste of energy, etc., to improve indoor air. The effect of quality, low equipment investment cost and simple production process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
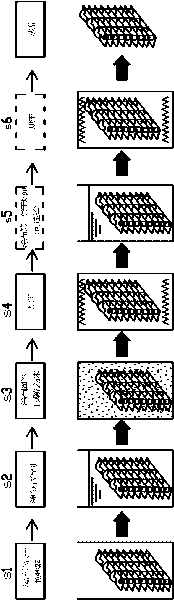
[0042] The manufacturing method of the regenerative dehumidification heat exchanger involved in this embodiment is as follows: figure 1 , 3 Shown:
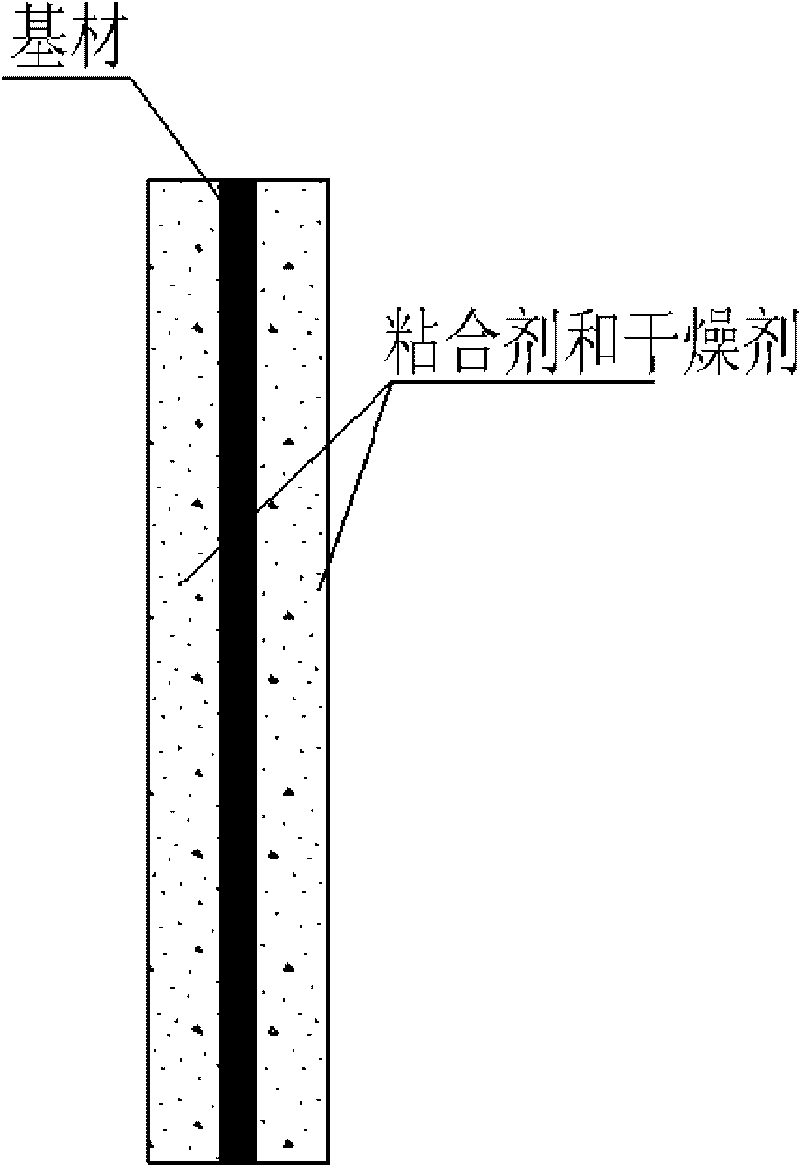
[0043] In the cleaning and drying process (S1), the tube-fin heat exchanger 1 with a specification of 202×168×25mm and a fin spacing of 1mm and the tube-fin heat exchanger 2 with a specification of 202×168×25mm and a fin spacing of 0.5mm Clean it and dry it with an electric constant temperature blast drying oven at a drying temperature of 40°C ± 0.2°C. After drying, the masses of heat exchanger 1 and heat exchanger 2 are 483.58g and 513.78g, respectively. After the dried tube-fin heat exchanger is placed in the room to cool naturally, in the adhesive coating process (S2), it is coated with adhesive, and after coating, the excess adhesive is removed with a compressed air machine In order not to block the heat exchange air passage, a uniform thin layer of adhesive with a thickness of about 0.1 mm is formed on the surface of the tu...
Embodiment 2
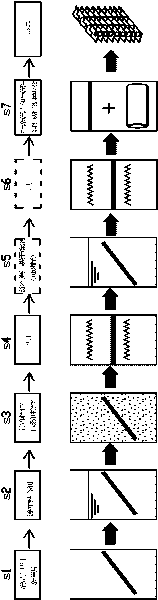
[0048] The manufacturing method of the regenerative dehumidification heat exchanger involved in this embodiment is as follows: figure 2 .3 shows:
[0049] In the cleaning and drying process (S1), the metal sheet with a thickness of about 0.2mm and a mass of 1.00g is cleaned and dried in an electric constant temperature blast drying oven at a drying temperature of 40°C±0.2°C. Put the dried tube-fin heat exchanger in the room to cool naturally, and then carry out the adhesive coating process (S2), and then use a compressed air machine to remove the excess adhesive to form a uniform layer on the surface of the metal sheet. A thin layer of adhesive with a thickness of approximately 0.1 mm. Expose the metal sheet after the process of coating the adhesive (S2) to the air for about 10 minutes to evaporate part of the moisture in the adhesive, and then carry out the process of coating the solid desiccant powder (S3), and the silica gel solid powder Evenly sprinkled on the adhesive,...
Embodiment 3
[0055] The regenerative dehumidification heat exchanger involved in this embodiment has a specific structure such as Figure 4 As shown, the cooling system is a cooling tower system 1, and the heating system is a solar collector system 2.
[0056] This embodiment includes: a cooling tower system 1, a solar collector system 2, and a dehumidification and heat exchange system 3, wherein the dehumidification and heat exchange system 3 is further divided into a regeneration area 33 and a treatment area 32, and the three systems are connected by water pipes.
[0057] The cooling tower system 1 includes: a cooling tower 4 , a water pump 5 , a sprinkler 6 , a water pump 7 , a valve 8 , and a cold water tank 9 . The connection relationship is: one end of the water pump 5 is connected to the cold water tank 9 through a water pipe, the other end of the water pump 5 is connected to the cooling tower 4, the other end of the cooling tower 4 is connected to the valve 8, and the other end of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com