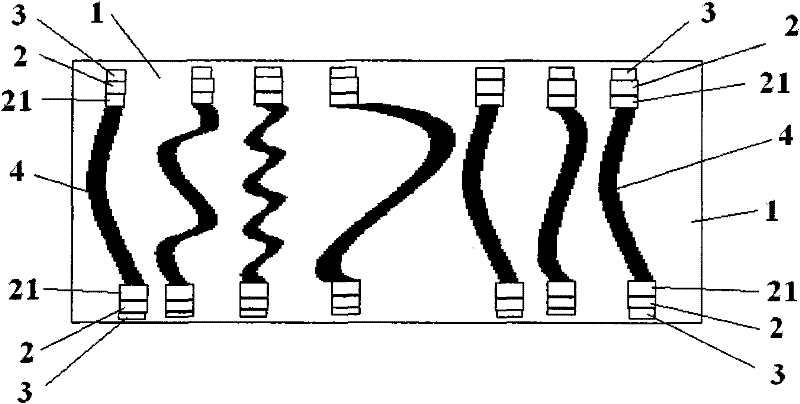Thermal interface material
A thermal interface material and metal technology, applied in the direction of heat exchange materials, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of poor contact, increased interface thermal resistance, large interface thermal resistance, etc., and achieve tight contact and small contact thermal resistance. , the effect of reducing thermal resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
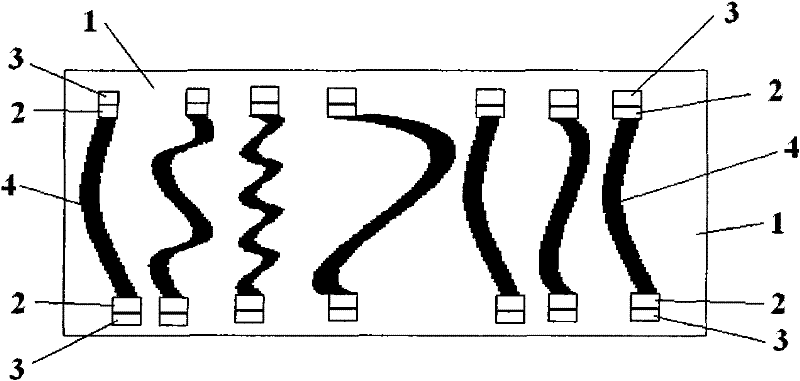
[0023] A thermal interface material, comprising a low-melting point metal and a carbon nanotube array formed by directional arrangement of carbon nanotubes, the preparation method of the carbon nanotube array is described below, wherein the average length of the carbon nanotubes in the carbon nanotube array is 1-150 Micron (before bending), for example can be selected as: 1 micron, 10 micron, 25 micron, 40 micron, 50 micron, 75 micron, 90 micron, 100 micron, 115 micron, 120 micron, 150 micron, described low melting point metal is Sn-lead alloys, tin-bismuth alloys, tin-silver-copper alloys, tin-zinc alloys and other alloys with a melting point below 400 degrees Celsius. Carbon nanotubes are single-walled or multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes refer to carbon nanotubes with more than 2 walls. Nanotubes can be 3, 5, 6, 8 walls, etc. The volume occupied by carbon nanotubes accounts for 1-50% of the total volume of carbon nanotube arrays, usually 5-20%, for...
Embodiment 2
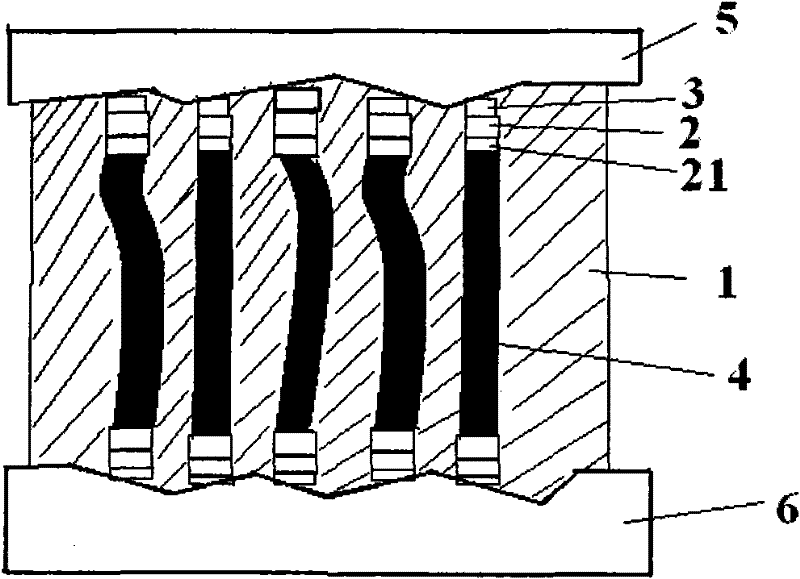
[0028] The preparation method of the thermal interface material described in Example 1 includes the following steps. The first step is to prepare a carbon nanotube array on the growth sheet. The carbon nanotubes used are the same as in Example 1. The preparation method of the carbon nanotubes is described below. The second The first step is to deposit a metal wetting layer and a metal transition layer on both ends of the carbon nanotube: deposit a metal wetting layer on the free end surface (necessary plasma cleaning before this) and a metal transition layer, such as: Ti / Cu / Au, or Ti / Ni / Au, or W / Cu / Au, or W / Ta / Au, or Al / Ni / Au, or Cr / Cu / Au, or Ti / W / Au, and then transfer the carbon nanotube array to another On the substrate, the same metal wetting layer and metal transition layer are deposited on the other end face of the carbon nanotube array. The deposition method is magnetron sputtering, and the deposition rate is 80-120 Angstroms / min. Choose to use the aforementioned micro...
Embodiment 3
[0030] A thermal interface material, including low-melting-point metal SAC305 and a carbon nanotube array formed by directional arrangement of carbon nanotubes, the preparation method of the carbon nanotube array is as follows, wherein the average length of the carbon nanotubes in the carbon nanotube array is 75 microns , the carbon nanotubes are aligned in parallel, the carbon nanotubes are multi-walled carbon nanotubes, and the volume occupied by the carbon nanotubes accounts for 4.5% of the total volume of the carbon nanotube arrays. The carbon nanotube array is elastically bent in the solidified low-melting point metal, and the two ends of the carbon nanotubes are provided with a metal wetting layer, and the metal wetting layer is titanium. It can also be seen from the SEM topography in the attached drawing Wetting well with the carbon nanotubes can significantly reduce the contact thermal resistance between the low-melting point metal and the carbon nanotubes, and the thic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com