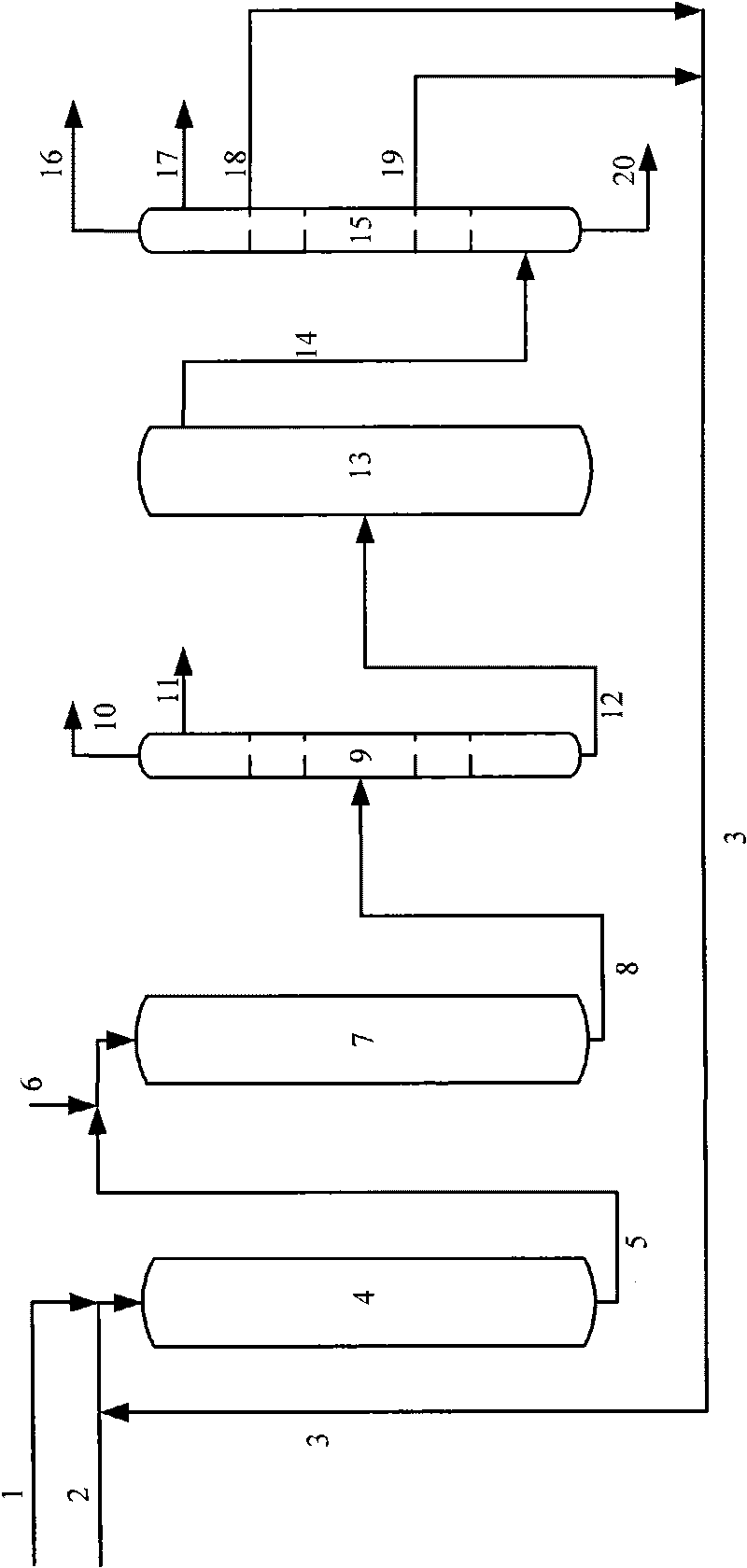
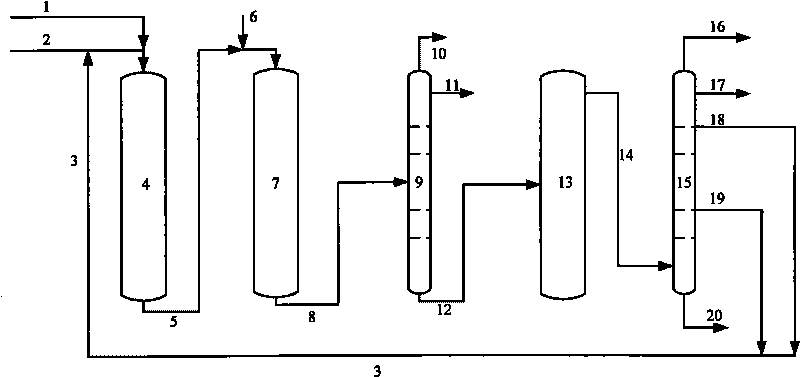
Method for producing light olefins and monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from heavy hydrocarbons
A technology for low-carbon olefins and single-ring aromatics, which is applied in the treatment of hydrocarbon oil, the petroleum industry, and hydrotreating processes. It can solve the problems of increasing the production of high-value target products, and achieve the effects of improving properties and improving the removal rate of impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1 adopts the method provided by the present invention:
[0047] The first hydrogenation reaction zone (first reaction) is filled with 200ml of wax oil hydrogenation refined preparation A, and the second hydrogenation reaction zone (second reaction) is filled with catalysts B, C and D from top to bottom, a total of 400ml, and the filling volume The ratio is 5:45:50. The mixed oil of wax oil and heavy cycle oil (mass ratio 9:1) is first passed through the first reactor for hydrorefining at a flow rate of 320g / h, and mixed with the residual oil at the outlet of the first reactor at a flow rate of 80g / h, and then enters the second reactor for adding Hydrogen reaction. The reaction pressure of the first reactor and the second reactor is 10.0 MPa, and the reaction temperature is 370°C. The effluent after the reaction is cooled and separated, the hydrogen-containing gas is recycled, and the liquid product enters the fractionation system. Here, gas and a small amount...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2 adopts the method provided by the present invention:
[0057] The first reactor is filled with 250ml of wax oil hydrofining preparation A, and the second reactor is filled with catalysts B, C, D and E from top to bottom, a total of 400ml, and the filling volume ratio is 5:45:45:5. After wax oil, heavy cycle oil and light cycle oil are mixed in a mass ratio of 320:32:48, the mixed oil is first passed through a reactor at a flow rate of 400g / h for hydrorefining, and blended at a flow rate of 80g / h at the outlet of the first reactor. After the residual oil, enter the second reactor for hydrogenation reaction. The reaction pressure is 9.0MPa, the first reaction temperature is 365°C, and the second reaction temperature is 380°C. The effluent after the reaction is cooled and separated, the hydrogen-containing gas is recycled, and the liquid product enters the fractionation system. Here, hydrogen sulfide and a small amount of light distillate are fractionally disti...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3 adopts another form of the method provided by the present invention:
[0061] The first reactor is filled with 250ml of wax oil hydrofining preparation A, and the second reactor is filled with catalysts B, C, D and E from top to bottom, a total of 400ml, and the filling volume ratio is 5:45:45:5. After wax oil, heavy cycle oil and light cycle oil are mixed in a mass ratio of 320:24:36, the mixed oil is first passed through a reactor at a flow rate of 380g / h for hydrorefining, and blended at a flow rate of 100g / h at the outlet of the first reactor. After the residual oil mixed oil enters the second reactor for hydrogenation reaction, the composition of the used residual oil mixed oil is residual oil: heavy cycle oil: light cycle oil=80:8:12 (mass ratio). The reaction pressure is 9.0MPa, the first reaction temperature is 365°C, and the second reaction temperature is 380°C. The effluent after the reaction is cooled and separated, the hydrogen-containing gas is r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com