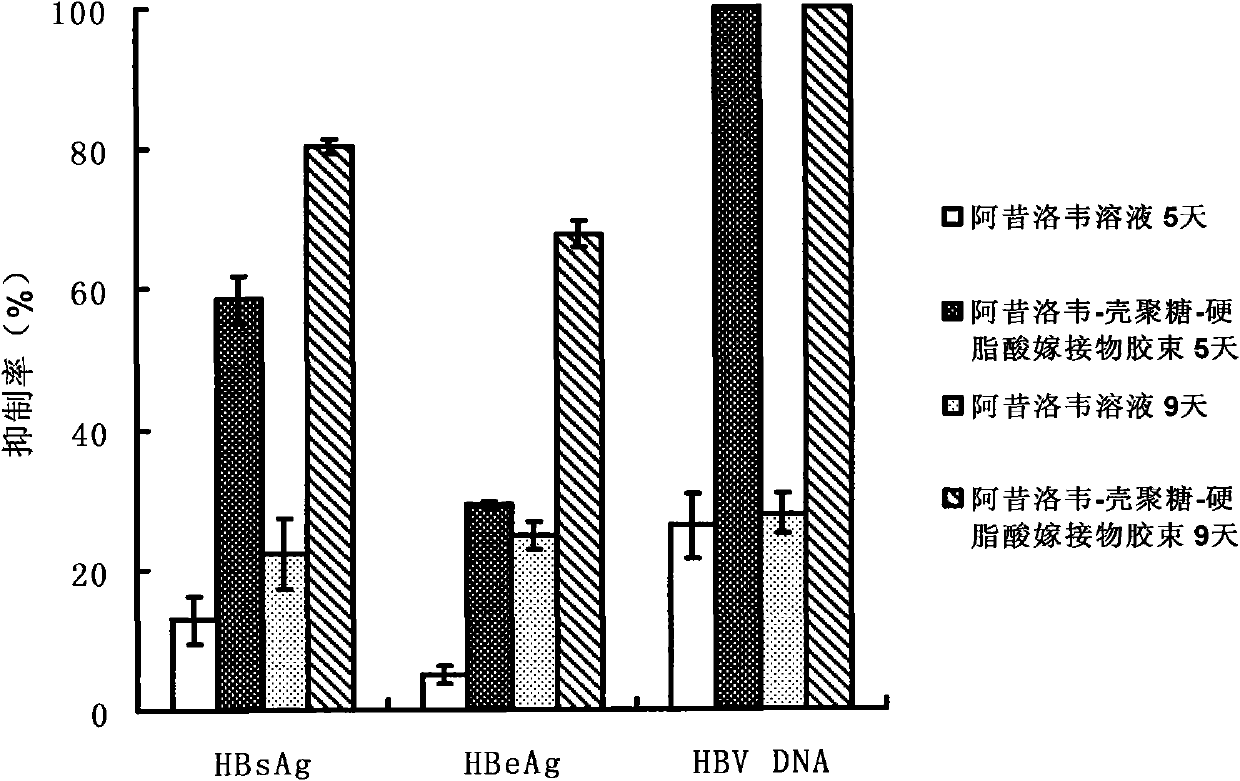
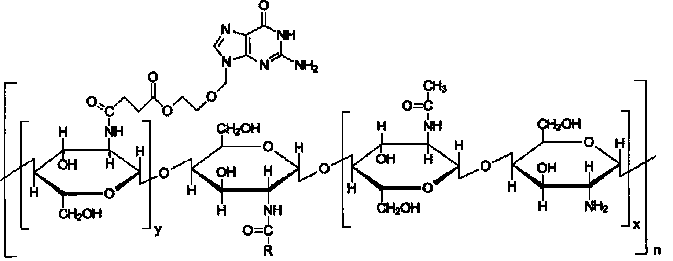
Acyclovir-chitosan-stearic acid grafting, synthetic method and application thereof
A technology of stearic acid and chitosan, which is applied in the application field of preparing anti-hepatitis B virus drugs, can solve the problems of limited drug loading capacity and difficult loading, and achieve the effects of increasing drug concentration, increasing intake, and reducing toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of acyclovir-chitosan-stearic acid graft
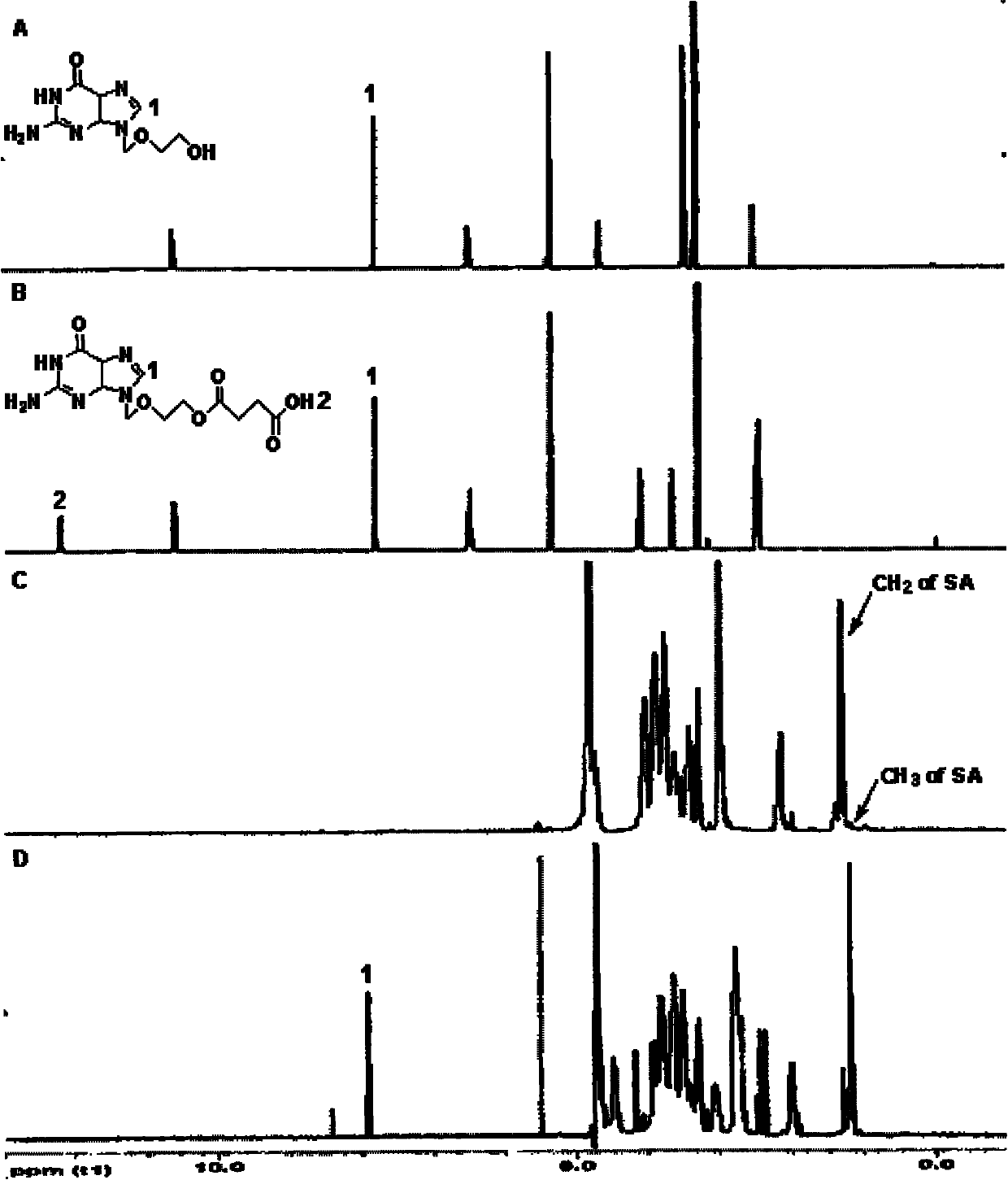
[0021] (1) Synthesis of acyclovir-succinic acid intermediate: 562.5mg (2.5mmol) acyclovir, 500.0mg (5.0mmol) succinic anhydride and 0.355mL triethylamine were dissolved in 37.5mL dry N , N-dimethylformamide, 60 ℃ water bath reaction 21h. After the reaction solution was cooled, most of the volatile components were evaporated under reduced pressure, 25 mL of ice water was added, and 2N hydrochloric acid was added to adjust the pH to 2. The white precipitate was collected by filtration, washed thoroughly with ice water, and dried at 40°C. Put the white precipitate into a round-bottomed flask, add a small amount of methanol, stir in a water bath at 70°C, reflux with a condenser, slowly add methanol dropwise until the solids are completely dissolved, let stand overnight at room temperature, filter with suction to obtain white crystals, and dry at 40°C to obtain Acyclovir-succinic acid intermediate.
[...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of acyclovir-chitosan-stearic acid graft
[0027] (1) Synthesis of acyclovir-succinic acid intermediate: 562.5mg (2.5mmol) acyclovir, 500.0mg (5.0mmol) succinic anhydride and 0.355mL triethylamine were dissolved in 37.5mL dry N , N-dimethylformamide, 60 ℃ water bath reaction 21h. After the reaction solution was cooled, most of the volatile components were evaporated under reduced pressure, 25 mL of ice water was added, and 2N hydrochloric acid was added to adjust the pH to 2. The white precipitate was collected by filtration, washed thoroughly with ice water, and dried at 40°C. Put the white precipitate into a round-bottomed flask, add a small amount of methanol, stir in a water bath at 70°C, reflux with a condenser, slowly add methanol dropwise until the solids are completely dissolved, leave it at room temperature overnight, filter with suction to obtain white crystals, and dry at 40°C to obtain Acyclovir-succinic acid intermediate.
[0...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of acyclovir-chitosan-stearic acid graft
[0037] (1) Synthesis of acyclovir-succinic acid intermediate: 562.5mg (2.5mmol) acyclovir, 500.0mg (5.0mmol) succinic anhydride and 0.355mL triethylamine were dissolved in 37.5mL dry N , N-dimethylformamide, 60 ℃ water bath reaction 21h. After the reaction solution was cooled, most of the volatile components were evaporated under reduced pressure, 25 mL of ice water was added, and 2N hydrochloric acid was added to adjust the pH to 2. The white precipitate was collected by filtration, washed thoroughly with ice water, and dried at 40°C. Put the white precipitate into a round-bottomed flask, add a small amount of methanol, stir in a water bath at 70°C, reflux with a condenser, slowly add methanol dropwise until the solids are completely dissolved, let stand overnight at room temperature, filter with suction to obtain white crystals, and dry at 40°C to obtain Acyclovir-succinic acid intermediate.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com