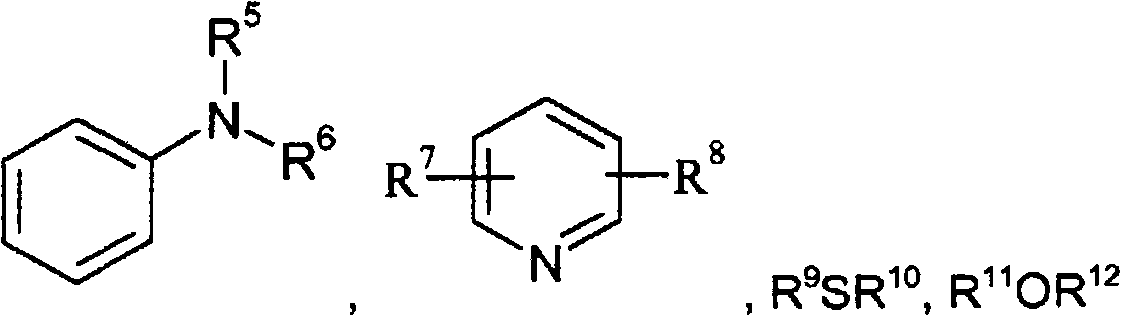
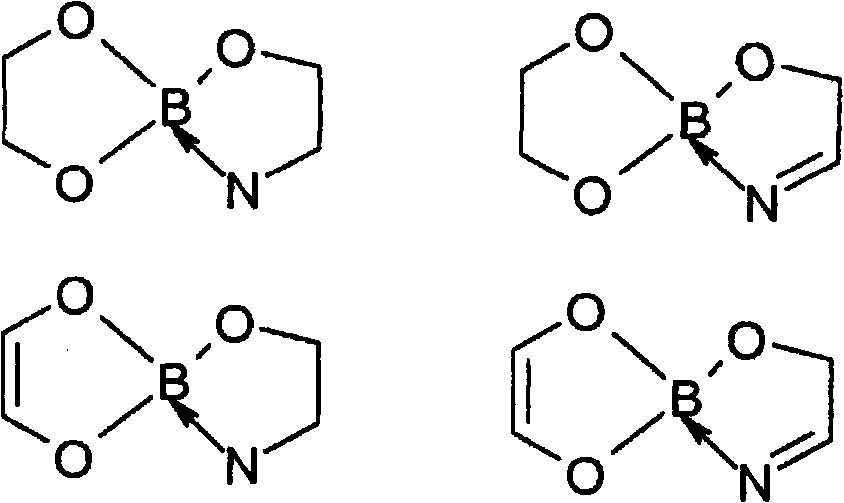
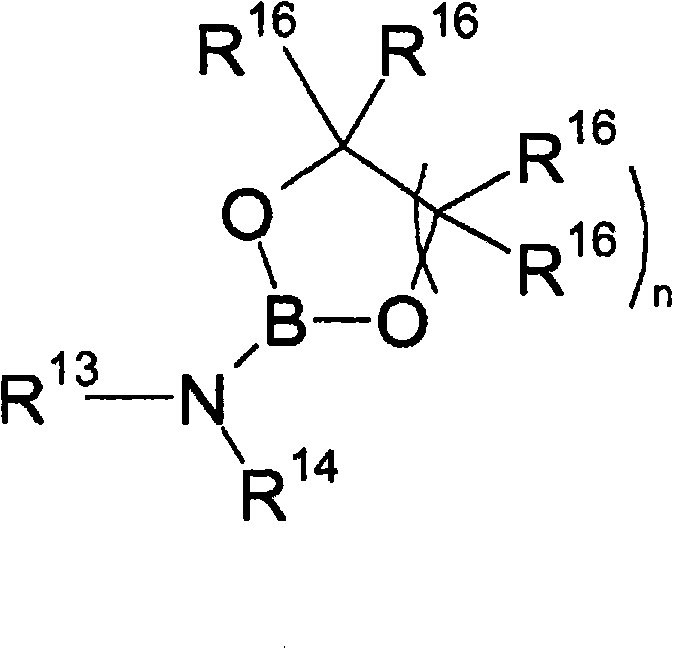
Accelerated reduction of organic substances with boranes
An organic substrate, borane technology, applied in organic chemistry methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic reduction, etc., can solve problems such as chiral oxazolborane catalysts that cannot be obviously tried
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Process Example 1: Reduction of Esters and Amides at 50°C
[0068] The reactor was charged with 200 ml dry THF and 0.1 mol ester or amide and heated to 50°C under 20 psi nitrogen pressure with a back pressure regulator (BPR) set at 25 psi. DEANB (number of moles, substrate dependent) was added subsurface at 30 psi over 1 hour while maintaining a reaction temperature of 50°C. Completion of the reaction is determined by the disappearance of the carbonyl stretching vibration (wavenumber, depending on the substrate). After all data were collected and analyzed, the reaction was quenched with 50 ml of MeOH at 7-10°C.
Embodiment 2
[0069] Process Example 2: Reduction of Esters and Amides at 85°C
[0070] The reduction at 85°C was performed in a pressure vessel with a nitrogen pressure of 30 psi, a BPR of 35 psi and a feed pressure of 40 psi. Concentration and addition time are the same as in Process Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0071] Process Example 3: Reduction of the matrix in glassware at 50°C
[0072] Shielding reactions on a smaller scale are done in glassware. equipped with a lead to N 2 Add 0.05 mol of ethyl butyrate or ethyl benzoate and 10 ml of THF to a 100 ml three-neck round bottom flask (clean, oven-dried) of the bubbler condenser, shielding plate and thermocouple and stir for 15 minutes. After heating the flask to 50°C, a mixture of 0.05 mol of DEANB (with or without additives) was slowly added to the flask. To determine the reduction time, a 1 ml sample was hydrolyzed with 0.5 ml methanol, and the carbonyl stretching vibration (1734-1654 cm -1 , depends on the disappearance of the matrix).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com