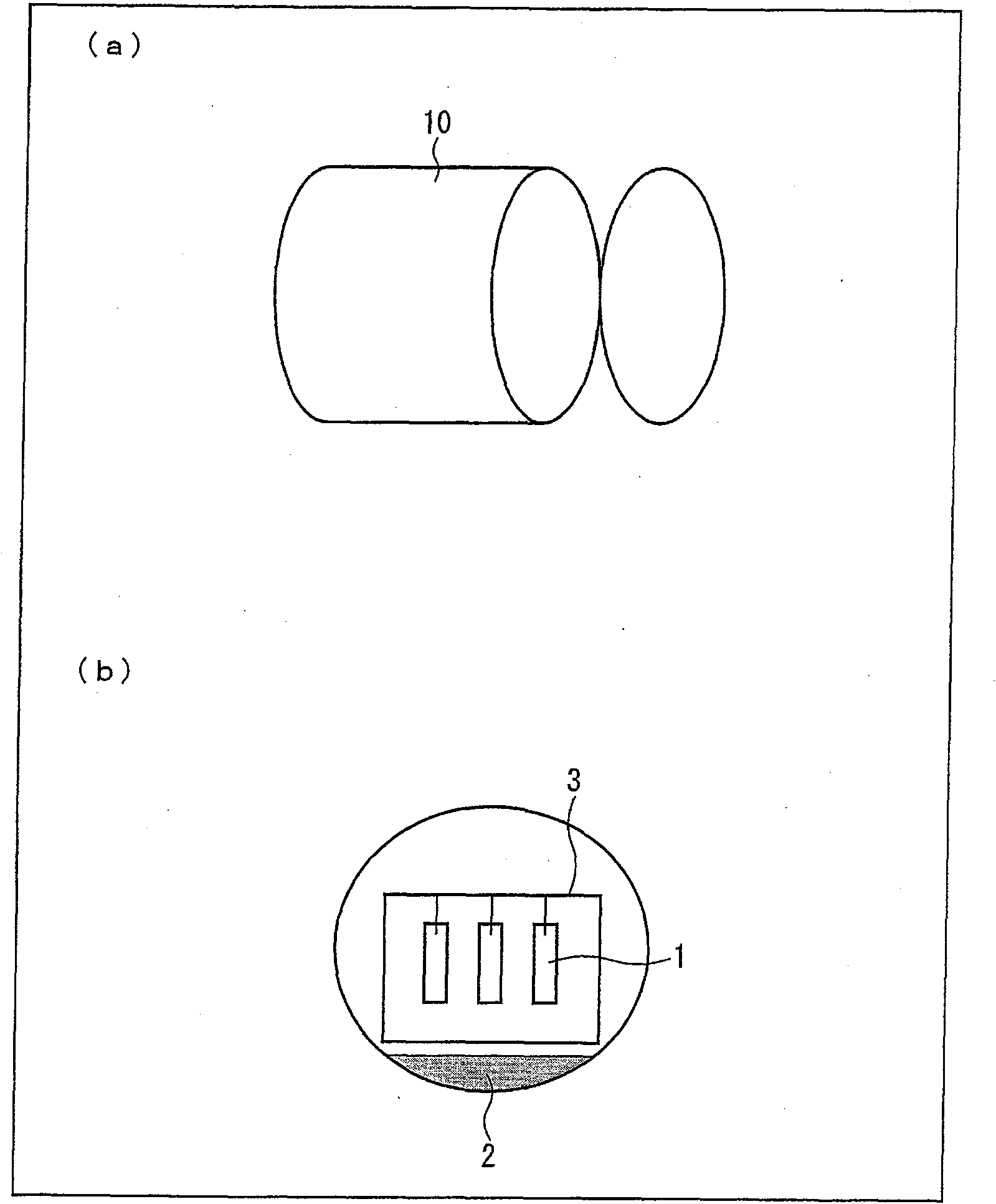
Magnesium alloy material, and method for treatment of surface of magnesium alloy material
A surface treatment, magnesium alloy technology, applied in the field of magnesium alloy materials, can solve the problems of reduced compactness, easy peeling of coating layers, oxidation of magnesium alloy materials, etc., to achieve improved reaction efficiency, good impact resistance and corrosion resistance, The effect of good corrosion and impact resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
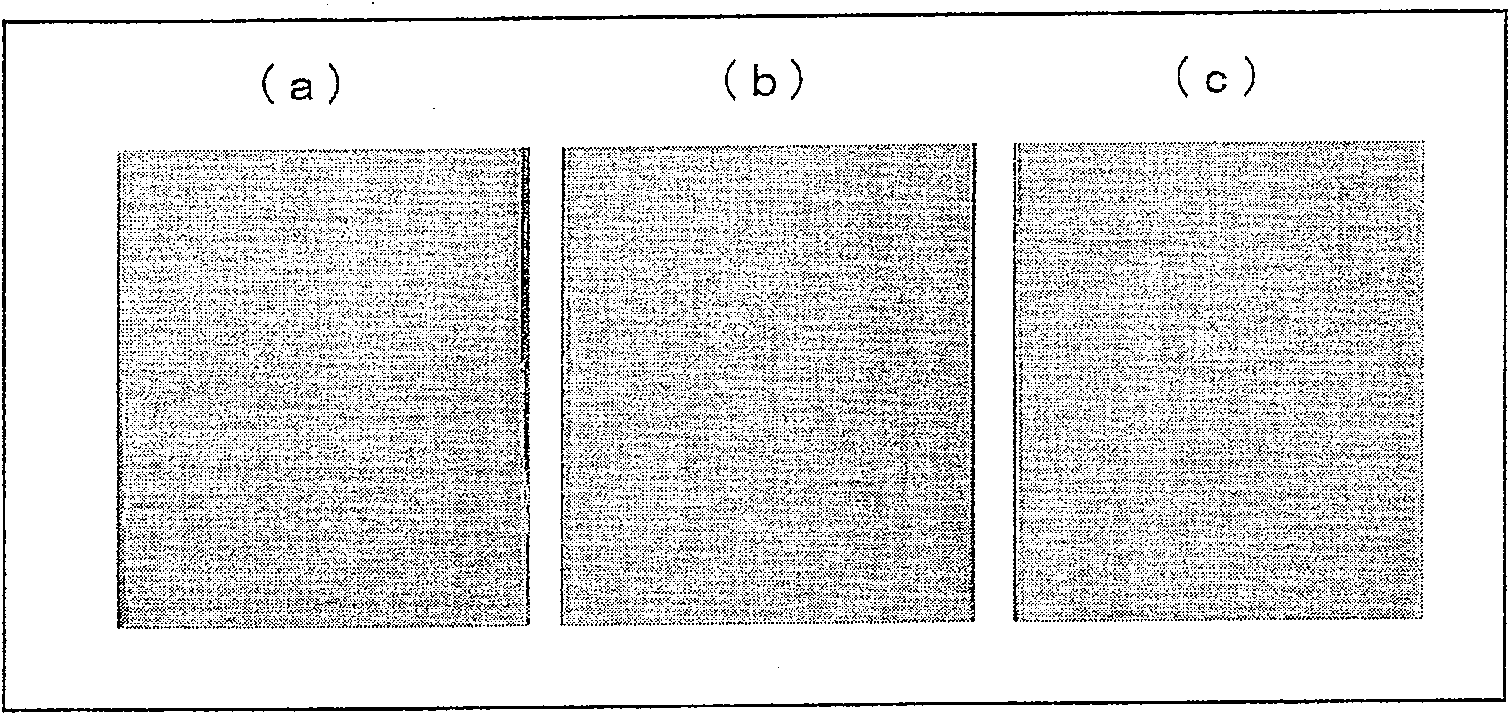
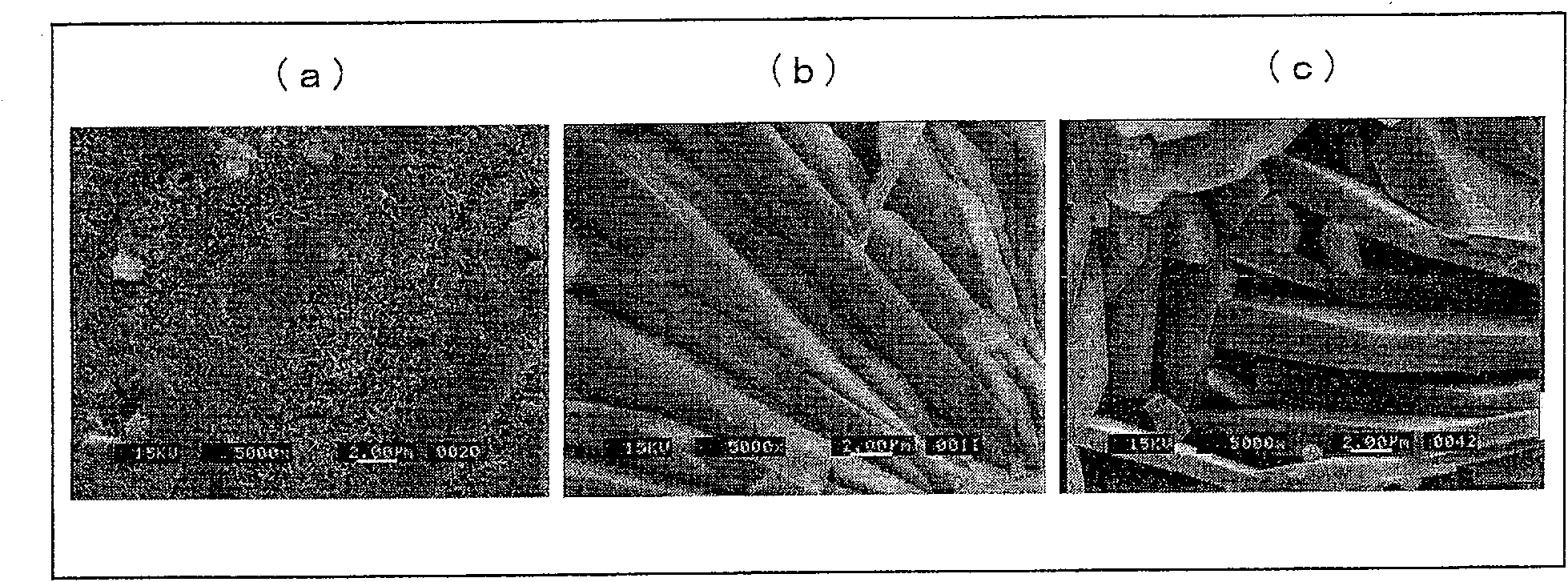
[0115]Put the magnesium alloy material into a steam curing device at 140° C., and treat it with 20% diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution for 24 hours. Table 1 shows the film thickness, hardness, and corrosion resistance after the treatment. Samples soaked in saline solution such as figure 2 (a) shown. The SEM observation results of the samples after steam curing are as follows: image 3 (a) shown. like image 3 As shown in (a), tiny crystals can be seen after steam curing. also, Figure 4 In the shown X-ray diffraction figure, the peak of tiny Dittmarite can be seen clearly, and the peak of magnesium hydroxide ( Figure 4 A). In addition, according to Figure 5 As a result of elemental analysis shown in (a), it was found that phosphorus (P) was contained at a mass concentration of 1.5%.
Embodiment 2
[0117] The magnesium alloy material was soaked in 10% diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution at 120°C for 2 hours, then placed in a steam curing device at 140°C, and treated with 20% diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution for 24 hours. Table 1 shows the film thickness, hardness, and corrosion resistance after the treatment. Samples soaked in saline solution are shown in figure 2 (b). The SEM observation results of the samples after steam curing are displayed in image 3 (b). like image 3 As shown in (b), plate-like crystals can be seen after steam curing. from Figure 4 In the X-ray diffraction figure shown, can clearly see the peak of Dittmarite and the peak of magnesium hydroxide ( Figure 4 B).
Embodiment 3
[0119] The magnesium alloy material was soaked in 20% diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution at 120°C for 2 hours, then placed in a steam curing device at 140°C, and treated with 20% diammonium hydrogen phosphate solution for 24 hours. Table 1 shows the film thickness, hardness, and corrosion resistance after the treatment. Samples soaked in saline solution are shown in figure 2 (c). The SEM observation results of the samples after steam curing are displayed in image 3 (c). like image 3 As shown in (c), plate-like crystals can be seen after steam curing. from Figure 4 In the X-ray diffraction figure shown, can clearly see the peak of Dittmarite and the peak of magnesium hydroxide ( Figure 4 C). according to Figure 5 As a result of elemental analysis shown in (b), it was found that phosphorus (P) was contained at a mass concentration of 27.4%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com