A method of remediating contaminated water and apparatus for the same
A technology of polluted water and equipment, applied in the field of remediation of polluted water, which can solve problems such as complex storage technology, reduced permeability/water flux, and expensive treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
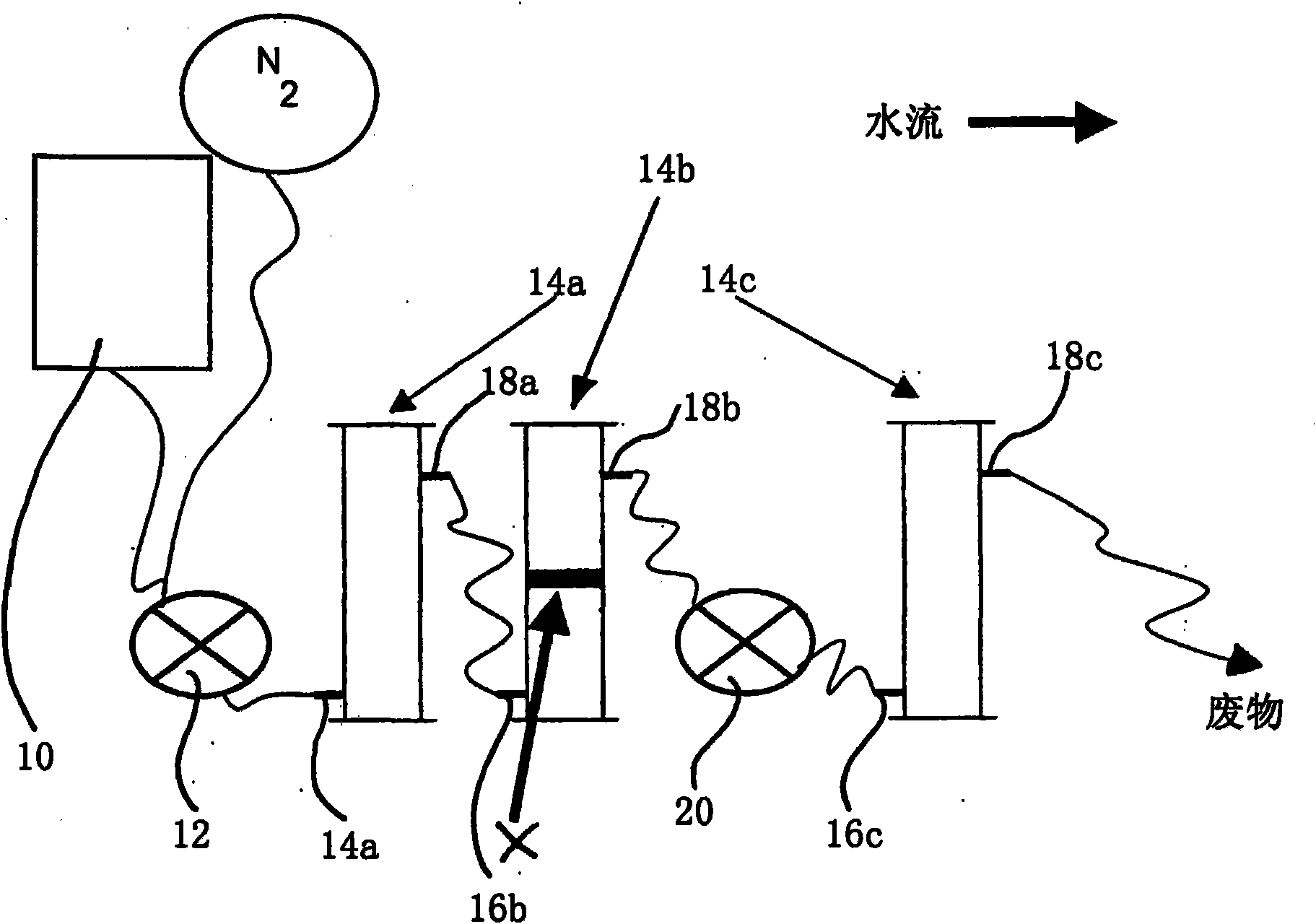
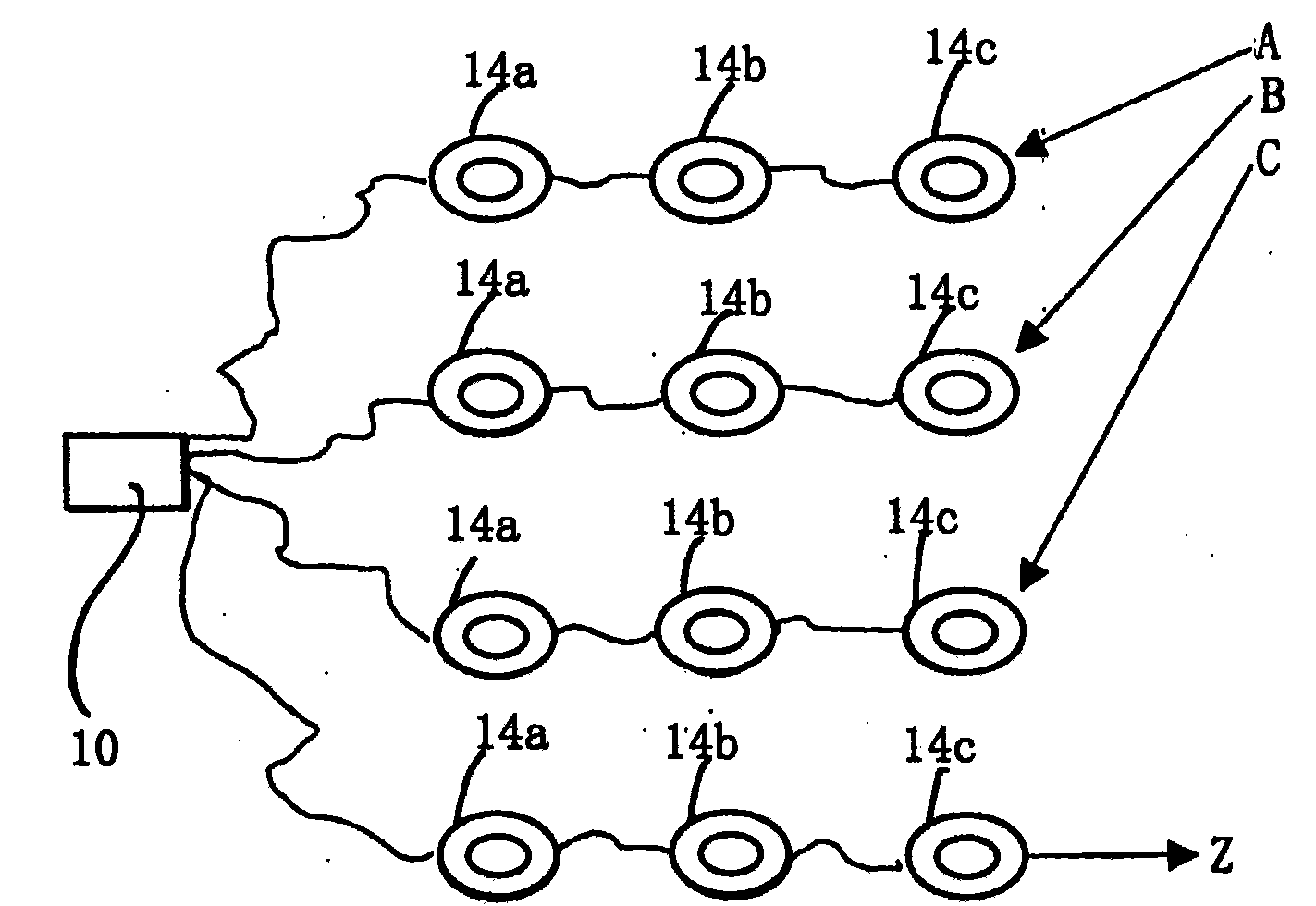
[0031] according to figure 1 Schematic design of the treatment train for the flow of water through the system is shown. A 20L reservoir 10 containing autoclaved distilled water was connected by PTFE tubing to a peristaltic pump 12 connected to three series-connected stainless steel columns 14a, 14b and 14c. Cylinders 14a, 14b and 14c consist of a stainless steel core with a diameter of 76 mm and a height of 300 mm and a stainless steel cap. Inlets 16a, 16b, and 16c and outlets 18a, 18b, and 18c were placed 20 mm from the top and bottom of each cylinder 14a, 14b, and 14c, and equipped with fine wire mesh ( figure 1 not shown) to prevent particle clogging. A further pump 20 is arranged between the outlet 18b and the inlet 16c. In each trial, three treatment series (labeled A, B, and C) and one control series (no treatment, labeled series Z) were run simultaneously, as figure 2 shown schematically.
[0032] The first and third columns (14a and 14c, respectively) of each ser...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Such as figure 2 As shown, treatment series A, B, C and Z were set up as described in Example 1 above. The experiment was carried out as described in Example 1 above, but with the water storage tank 10 free of contaminants, only distilled water. Instead, TCE is introduced directly by injection at inlet 16b, and only the sample analysis at points (iii) and (iv) described above is performed. The purpose of transmitting TCEs in this way is to characterize "source" TCEs, eg from direct spills or memory leaks.
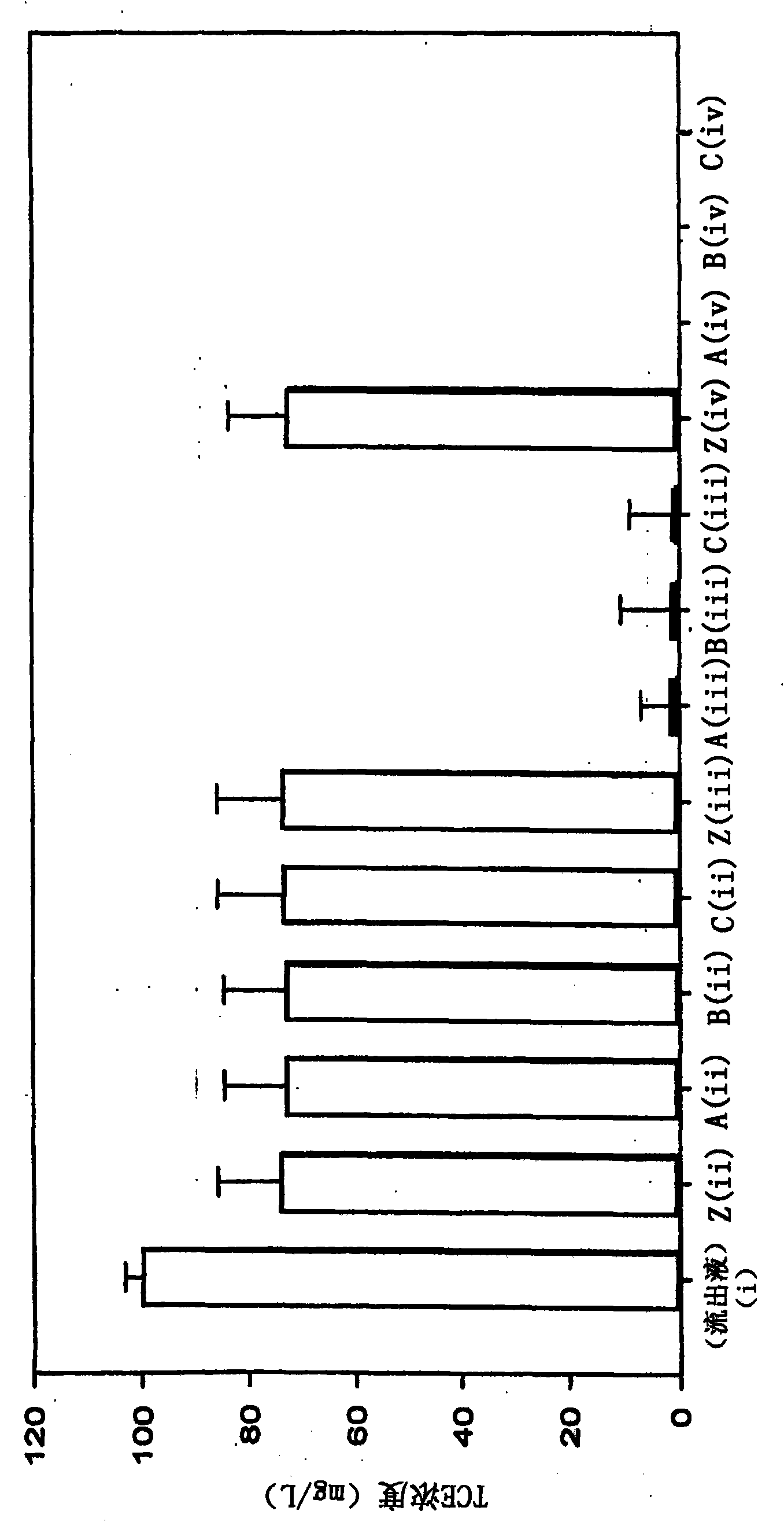
[0038] The TCE concentrations of the extracted samples are shown in Figure 4 middle. The concentration of the effluent from series Z was assigned 100%, ie the effluent was not subjected to debris treatment and passed through only three sand-filled cylinders. The final effluent had a TCE concentration of 1460 mg / L and the amount of TCE removed by residue treatment in series A, B and C was expressed as a percentage of this value.
[0039] Figure 4 It was shown...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Treatment series A, B, C and Z were set up as described above for Example 1. The experiment was carried out as described in Example 1 above, but wherein the storage tank 10 contained 6 different CAH pollutants, each at a concentration of 100 mg / L (PCE, TCE, dichloroethylene (DCE), carbon tetrachloride (CT), chloroform (CF) and trichloroethane (TCA)). Artificial groundwater samples were taken at points (i), (iii) and (iv) as described in Example 1.
[0042] The CAH concentrations of the extracted samples are shown in Figure 5 Middle (from left to right are the displayed results of PCE, TCE, DCE, TCA, CT and CF in each sample group). The results showed that the concentration of all six pollutants in series A, B and C showed significant reduction (P ≤ 0.05) compared with series Z. The greatest reduction in concentration was in samples containing CT and TCA, where a reduction of greater than 90% was recorded at all sampling points. The concentration of TCE was reduced ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com