Hepatitis virus in-vitro culture model as well as construction method and application thereof
A hepatitis virus, in vitro culture technology, applied in the direction of virus/phage, virus, retro DNA virus, etc., can solve the problems of low infectivity, high homogeneity, instability, etc., to achieve good repeatability, simple method, scalable applied effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
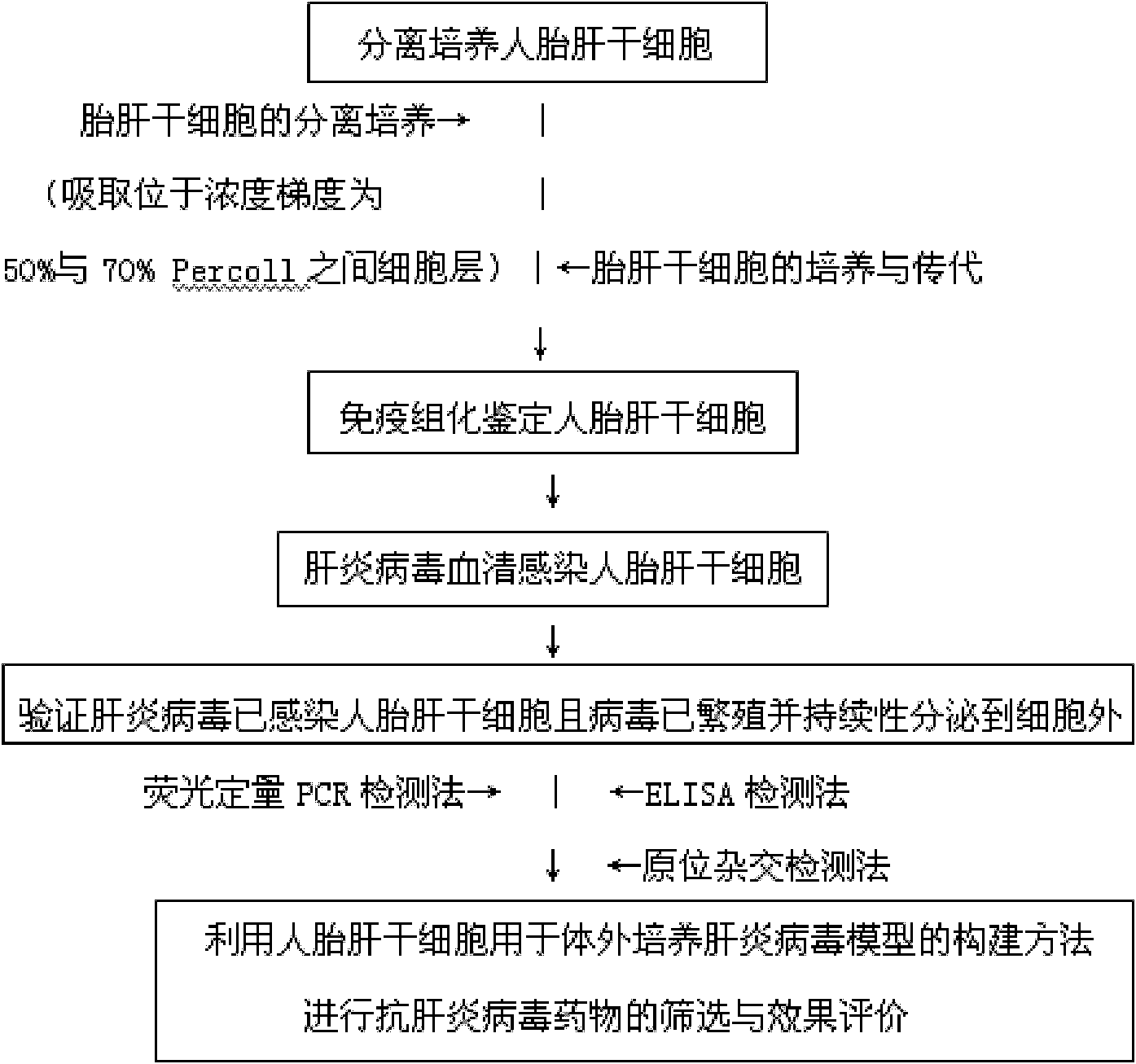
[0067] Embodiment 1 constructs hepatitis virus in vitro culture model such as Figure 1-Figure 4 shown
[0068] I. Isolation and culture of human fetal liver stem cells:
[0069] (1). Isolation and culture of fetal liver stem cells: Perfuse the liver with collagenase in situ, stop the perfusion when the liver turns grayish white, carefully peel off the liver cell suspension with a small spatula, filter through a 100-mesh screen, blow with a pipette to fully disperse the cells . The cell suspension was centrifuged in D-Hank's solution at 2000r / min, 4°C for 5min. Discard the supernatant, suspend the precipitated cells with 2ml DMEM medium, add 50ml DMEM medium containing 0.1% Pronase E and 0.005% DNaseI, and incubate at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 30min. Then the cells were transferred to a centrifuge tube and placed on ice for 20 min to precipitate the cells by using the hepatic stem cell adhesion. The cell suspension was removed, and the pelleted cells were centrifuged at 4°C, 2000r / ...
Embodiment 2
[0098] I.HCV high copy positive serum infects human fetal liver stem cells: HCV (10 5 -10 7 Copies) serum 100ul was inoculated into six-well plate cells in 1ml DMEM / F12 culture medium (serum-free); after incubation at 37°C for 24h, the supernatant was sucked out, and the cells were cultured in DMEM / F12 culture medium (10% FBS). HCV can be obtained by taking the supernatant within 48 hours, which can be sampled continuously for 5 times.
[0099] II. Verify that hepatitis C virus has infected human fetal liver stem cells and multiplied and continuously secreted outside the cells:
[0100] Detection of virus titers in cell supernatants at different times by fluorescent quantitative PCR
[0101] (1). RNA extraction: RNA was extracted using the Hepatitis C virus nucleic acid quantitative detection kit and stored at -20°C. The negative and positive quality control samples were treated in the same way for later use.
[0102] (2). Fluorescent quantitative PCR amplification: using t...
Embodiment 3
[0111] Example 3 as Figure 6 As shown, the difference with embodiment 1 is as follows:
[0112] I. Isolation and culture of human fetal liver stem cells: Isolation and culture of fetal liver stem cells: perfuse the liver with collagenase in situ, stop the perfusion when the liver turns grayish white, carefully peel off the liver cell suspension with a small spatula, filter it through a 100-mesh sieve, and blow it with a pipette Disperse the cells thoroughly. The cell suspension was centrifuged in D-Hank's solution at 2000r / min, 4°C for 5min. Discard the supernatant, suspend the precipitated cells with 2ml DMEM medium, add 50ml DMEM medium containing 0.1% Pronase E and 0.005% DNase I, and incubate at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 30min. Then the cells were transferred to a centrifuge tube and placed on ice for 20 min to precipitate the cells by using the hepatic stem cell adhesion. The cell suspension was removed, and the pelleted cells were centrifuged at 4°C, 2000r / min for 10min. Cel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com