Method for determining biomass of hyphae of edible fungi in substrate by detecting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) concentration
A technology for concentration measurement and edible fungus, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, color/spectral characteristic measurement, etc. It can solve the problems of not being able to know the error range, not being able to accurately quantify, and not being able to rule out the effects of the results, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of solving inaccurate measurement, simple method and short time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
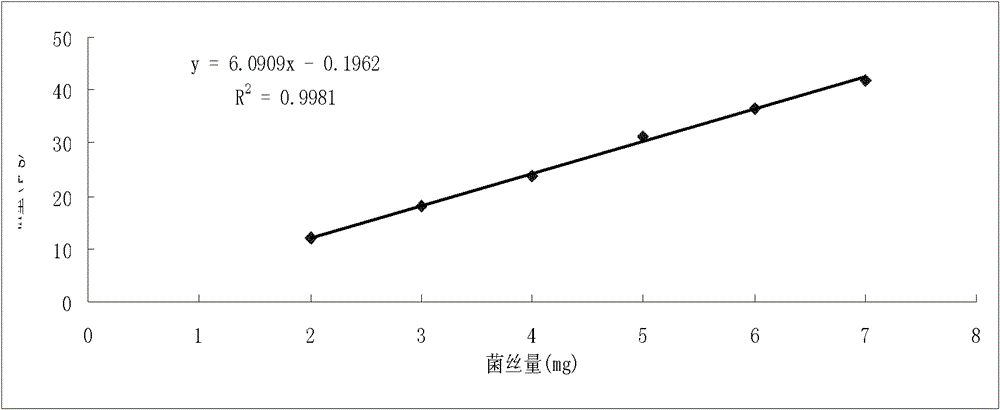
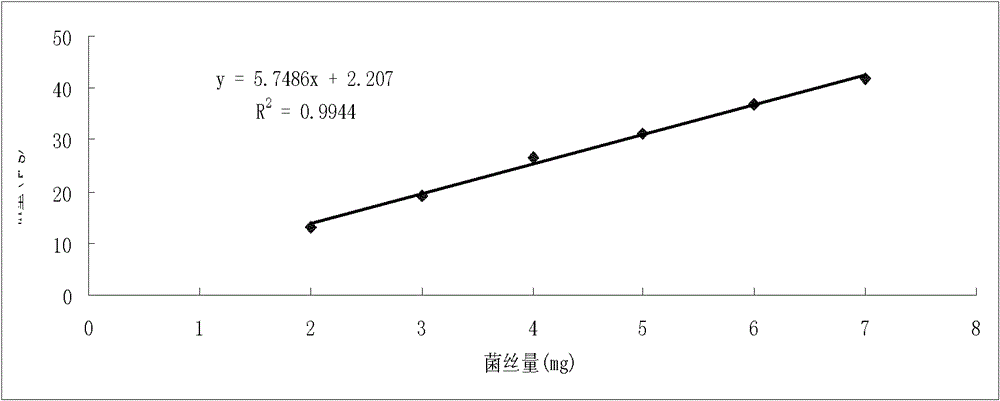
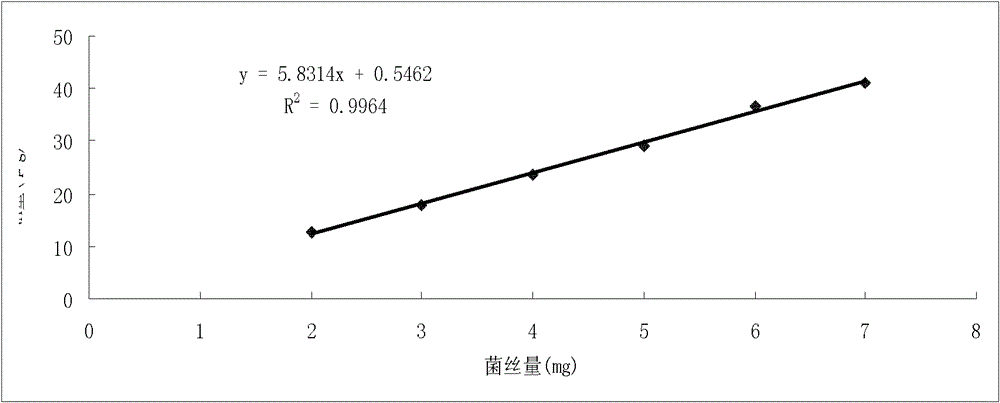
[0040] The present invention sets forth the specific steps by taking the biomass of shiitake mushroom 135 mycelium in the shiitake mushroom 135 mycelial culture as the conventional substrate of sawdust as an example:
[0041] (1) Cultivate the standard hyphae of Lentinus edodes 135 with standard PDB liquid medium
[0042] After the mushroom 135 mycelium on the solid PDA medium is activated, break it up with a homogenizer at high and low intervals for 30 seconds, insert it into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 90mL of fresh standard liquid PDB (produced by U.S. BD Company) medium, and rotate at 120rpm. At 25°C, cultivate for 14 days until the mycelium is stable. A batch of mycelium was cultured every other day, and 5 bottles were cultured in each batch, and 3 batches were cultured in total for the construction of a standard curve.
[0043] (2) Mycelia treatment
[0044] Filter the mycelia with non-woven fabric, rinse with sterile water, then blot excess water with sterile ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com