Method for producing low-aromatics solvent oil by hydrogenation
A technology of solvent oil and hydrogenation treatment, which is applied in the petroleum industry and the treatment of hydrocarbon oil, etc. It can solve problems such as difficult to guarantee the operation cycle, easy to be poisoned and deactivated, and unable to meet the quality index requirements of high-grade low-aromatic solvent oil, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
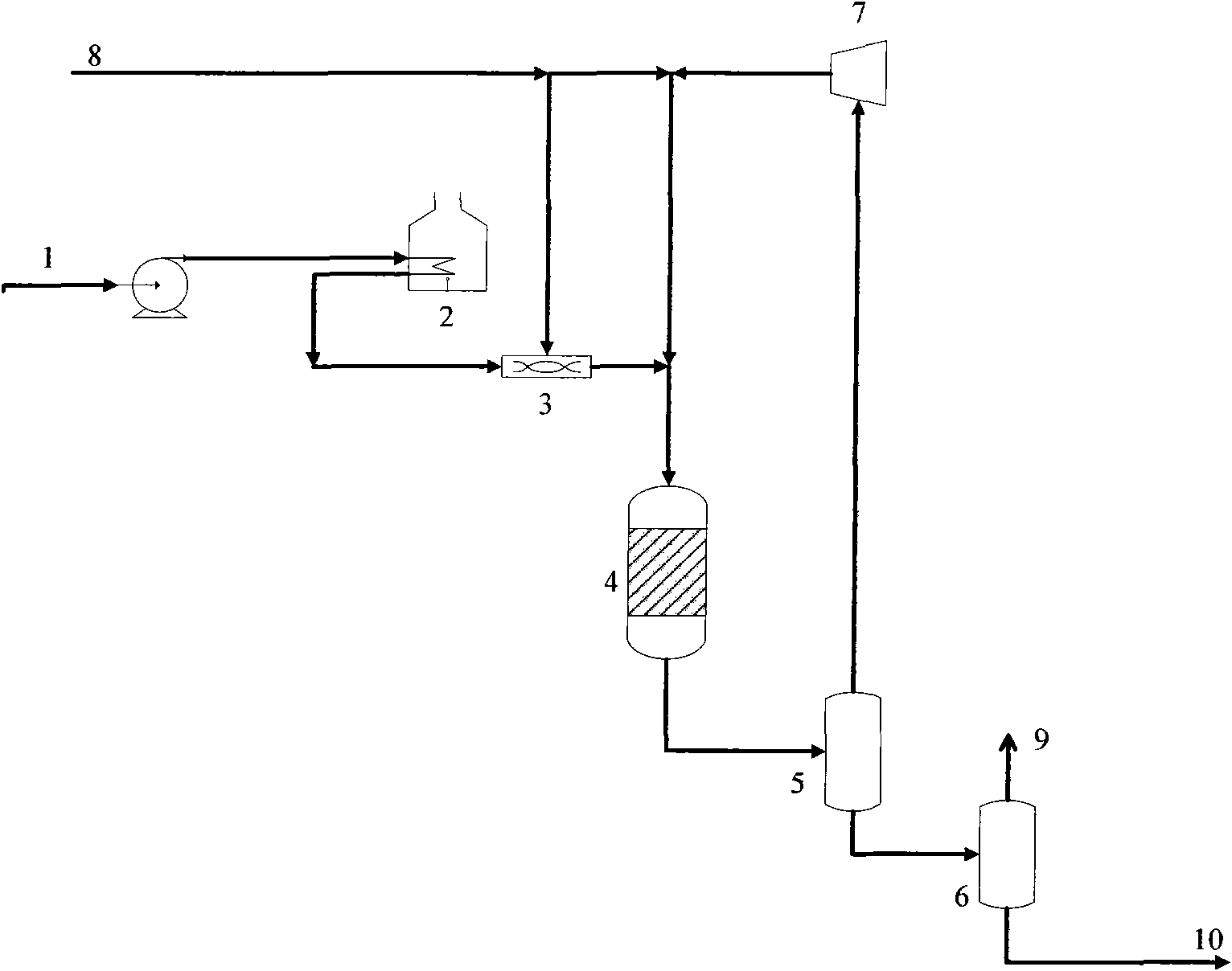
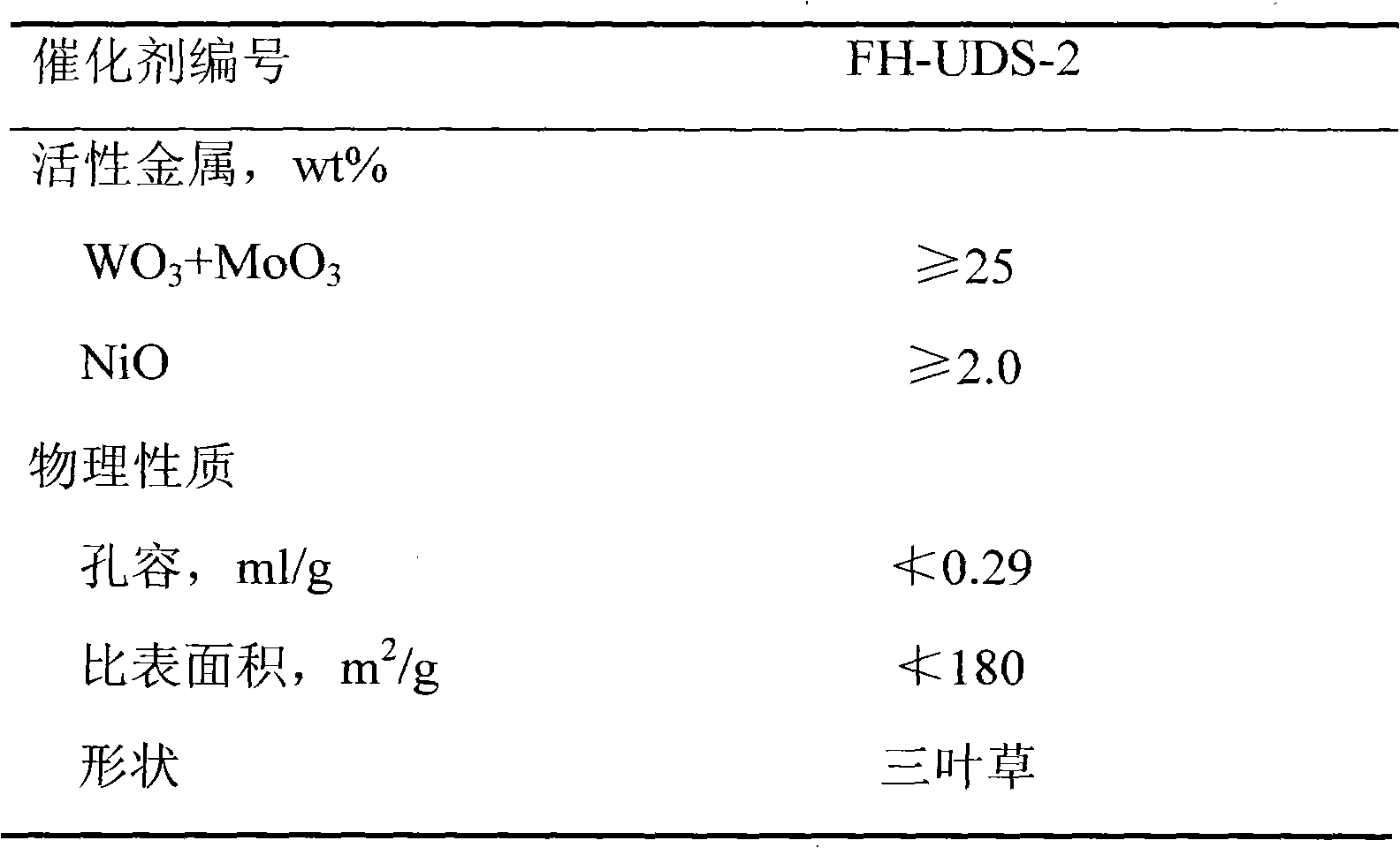
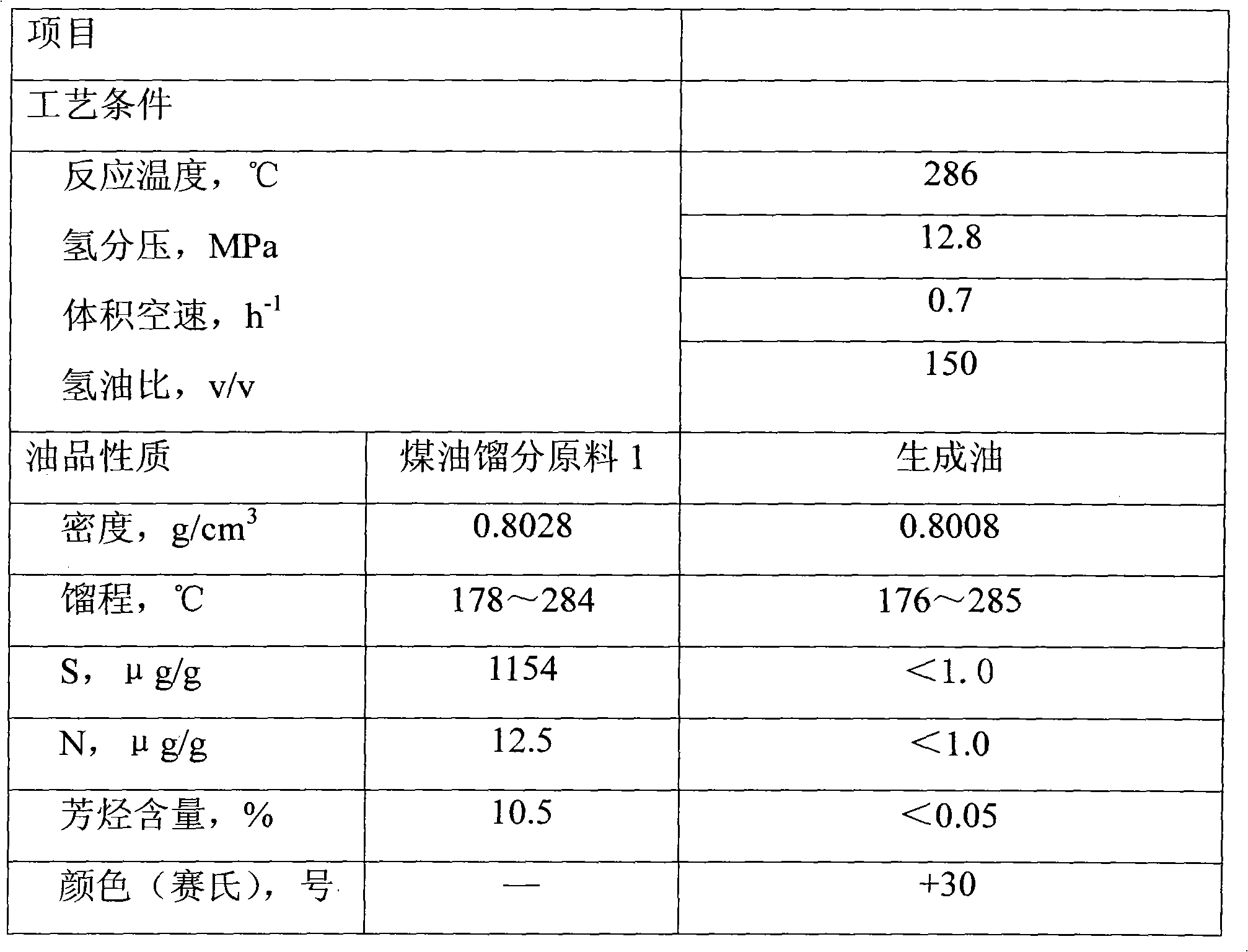
[0028] The kerosene fraction raw material 1 goes through the heating furnace to reach the required temperature and fully mixes and dissolves the hydrogen in the SH-type static mixer, and then enters the hydrogenation reactor. The reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 12.8MPa, volume space velocity 0.7h -1 , The reaction temperature is 286° C., and the volume ratio of hydrogen to oil is 150:1. The raw material oil properties and product properties are listed in Table 2.
[0029] It can be seen from Table 2 that the sulfur and nitrogen content of the solvent oil product can be reduced to below 1 μg / g, and the aromatic hydrocarbon content is less than 0.05%.
Embodiment 2
[0031] The kerosene fraction raw material 2 is fully mixed with hydrogen and enters the hydrogenation reactor after passing through the heating furnace. The gas-liquid mixer adopts SK type static mixer. The reaction conditions are: hydrogen partition pressure 12.5MPa, volume space velocity 0.6h -1 , The reaction temperature is 281° C., and the volume ratio of hydrogen to oil is 140:1. The raw material oil properties and product properties are listed in Table 3.
[0032] It can be seen from Table 3 that the sulfur and nitrogen content of the solvent oil product can be reduced to less than 1 μg / g, and the aromatic hydrocarbon content is less than 0.05% by using this process technology.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The kerosene fraction raw material 3 is fully mixed with hydrogen and enters the hydrogenation reactor after passing through the heating furnace. The reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 13.6MPa, volume space velocity 0.8h -1 , The reaction temperature is 304°C, and the volume ratio of hydrogen to oil is 170:1. Half of the hydrogen is mixed with the raw materials through the SL gas-liquid mixer, and the other half is directly fed into the reactor through the pipeline. The raw material oil properties and product properties are listed in Table 4.
[0035] It can be seen from Table 4 that the sulfur and nitrogen content of the solvent oil product can be reduced to less than 1 μg / g, and the aromatic hydrocarbon content is less than 0.05%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com