Pichia farinose strain FL7 capable of dissolving inorganic phosphorus compounds and application thereof
A powdery Pichia pastoris and compound technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of affecting phosphorus dissolving ability, loss, and failure to show the effect of increasing production, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1, can dissolve the separation and screening of inorganic phosphorus compound bacterial strain
[0026] (1) Weigh 10g of agricultural waste compost samples (collect the agricultural waste compost samples from the experimental base of Tianjin Forestry and Fruit Research Institute), put them into a 250mL triangular flask (with glass beads) filled with 90mL sterile water, and let it stand After 20 minutes, place it in a 200rpm shaking incubator and shake it fully for 30 minutes to fully disperse the cells and make a bacterial suspension;
[0027] (2) Use a 5mL pipette to draw 5mL of the supernatant of the bacterial suspension obtained in the above step (1) into 45mL sterile water, mix well and carry out 10-fold decreasing dilution; take 10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 Each 100 μL of three dilutions of bacterial suspension was spread on Pikovskaya medium (glucose 10 g, yeast powder 0.5 g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.5g, NaCl 0.3g, KCl 0.3g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2, bacterial strain FL7 utilizes the ability of cellulose
[0033] Strain FL7 was treated with 1% glucose, 1% soluble starch, 1% sucrose, 1% sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 1% cellulose, 1% sodium carboxymethylcellulose+0.01% glucose, 1% cellulose+0.01 % glucose as carbon source, all can grow, but the growth status is different. As shown in Table 1, the strain FL7 can rapidly grow and reproduce by utilizing glucose, but has poor utilization effects on soluble starch and sucrose. The strain FL7 also has a certain decomposing effect on sodium carboxymethylcellulose and cellulose, but the growth and reproduction of the strain FL7 is slow when it is used as the sole carbon source. it is good.
[0034] Table 1 The growth of strain FL7 using various carbon sources
[0035]
[0036] Note: The "+" sign in the table indicates the growth of the colony, and the more + signs, the larger the colony and the faster growth and reproduction.
Embodiment 3
[0037]Embodiment 3, the tolerance of bacterial strain FL7 to temperature, pH value, NaCl concentration, ammonium ion concentration
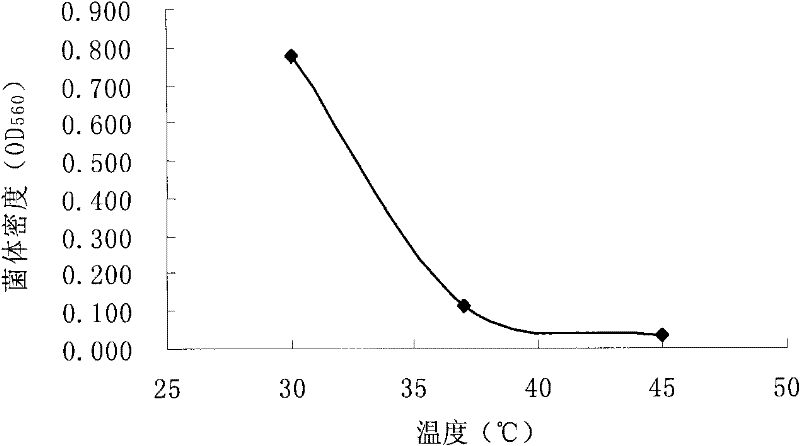
[0038] (1) Inoculate powdery Pichia farinosa strain FL7 on YEPD solid slant medium, culture at 30°C for 48 hours, so that the bacterial cells are in the logarithmic growth phase, and then transfer them by streaking on the plate Put it on the YEPD plate, culture it at different temperatures (28°C, 30°C, 35°C, 40°C, 45°C, 48°C, 50°C) for 7 days, observe the growth of the strain (see Table 2), and determine its growth potential. The highest temperature, indicating that the strain can still grow at 45°C.
[0039] By comparing the size of the cell density of the fermentation broth at different temperatures, it can be known ( image 3 ), the high temperature environment will inhibit the growth of the strain FL7, and the growth of the strain FL7 is better at a temperature of about 37°C.
[0040] (2) Then, the YEPD solid medium was adjusted to pH=5, pH...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com