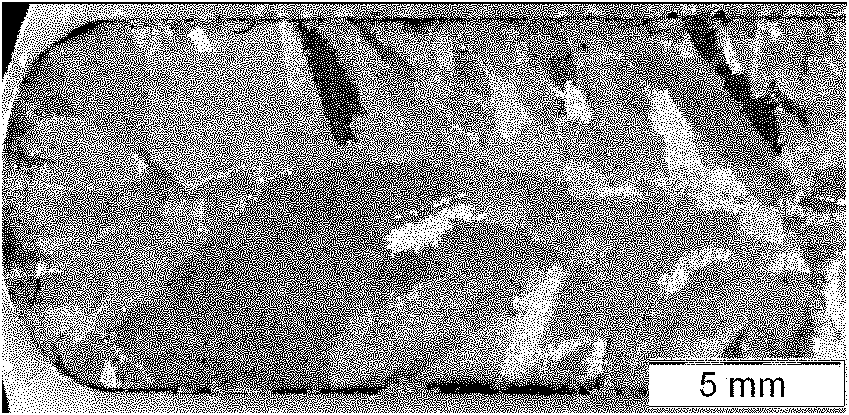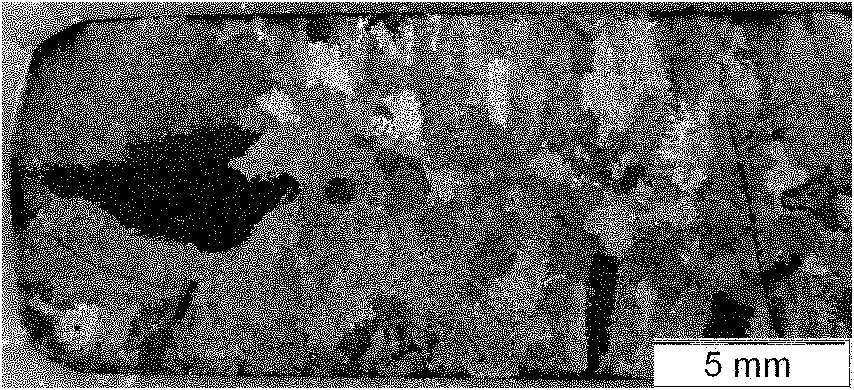Method for preparing in-situ deformation Cu-Ag composite material by using magnetic field
A composite material and in-situ deformation technology, applied in the field of materials, to achieve the effect of reducing solid solution scattering, reducing solid solubility, and increasing effective strengthening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Using oxygen-free copper and electrolytic silver as raw materials, Cu-Ag alloy liquid is produced after smelting. The composition of Cu-Ag alloy liquid is Ag 6% by weight percentage, and the balance is Cu;
[0030] Put the Cu-Ag alloy liquid in a vacuum resistance furnace, heat the Cu-Ag alloy liquid to 1200 ° C, keep it for 1 hour, and then cool it with the furnace to obtain the cast Cu-Ag alloy; during the process of heat preservation and cooling with the furnace, Apply a steady magnetic field with a magnetic induction intensity of 1T to the vacuum resistance furnace;
[0031] The as-cast Cu-Ag alloy is kept at 850°C for 0.5 hours, and then hot forged at 650~850°C to make a deformed Cu-Ag alloy, and the area reduction rate is controlled to 10%;
[0032] Draw the deformed Cu-Ag alloy at room temperature, keep the drawing direction perpendicular to the hot forging direction, and make a deformed Cu-Ag composite material, and control the total area reduction rate to 65%; ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Oxygen-free copper and electrolytic silver are used as raw materials, and Cu-Ag alloy ingots are made by cooling after smelting; the composition of Cu-Ag alloy ingots is Ag 14% by weight percentage, and the balance is Cu;
[0038] Place the Cu-Ag alloy ingot in a vacuum resistance furnace, heat the Cu-Ag alloy ingot to 980°C, hold it for 0.3 hours, and then cool it with the furnace to obtain the cast Cu-Ag alloy; during the process of heat preservation and cooling with the furnace, Apply a steady magnetic field with a magnetic induction intensity of 20T to the vacuum resistance furnace;
[0039] The as-cast Cu-Ag alloy was kept at 800°C for 0.8 hours, and then hot forged at 650-850°C to produce a deformed Cu-Ag alloy with a controlled area reduction rate of 9%;
[0040] Draw the deformed Cu-Ag alloy at room temperature, keep the drawing direction perpendicular to the hot forging direction, and make a deformed Cu-Ag composite material, and control the total area reductio...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Oxygen-free copper and electrolytic silver are used as raw materials to produce Cu-Ag alloy liquid after smelting. The composition of Cu-Ag alloy liquid is Ag25% by weight percentage, and the balance is Cu;
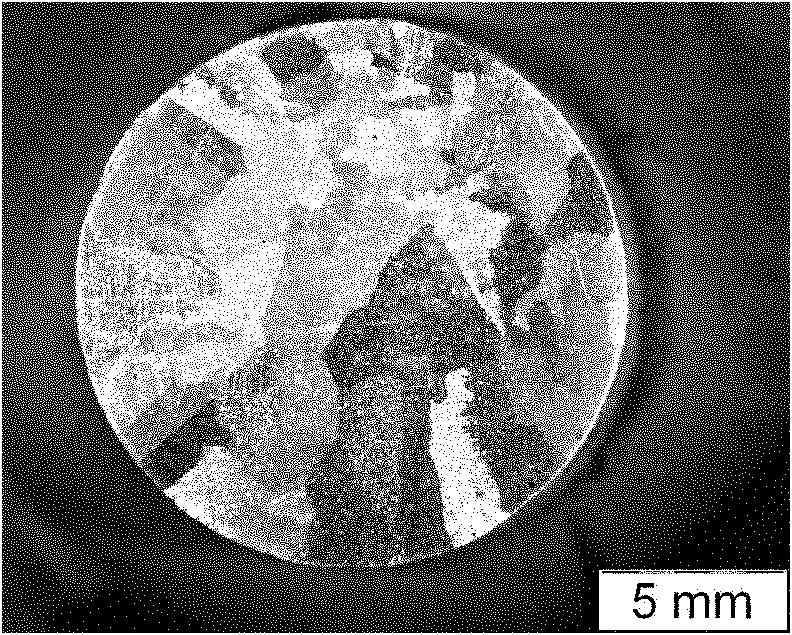
[0046] Put the Cu-Ag alloy liquid in a vacuum resistance furnace, heat the Cu-Ag alloy liquid to 960°C, keep it for 0.05 hours, and then cool it with the furnace to obtain the cast Cu-Ag alloy; during the process of heat preservation and furnace cooling, Apply a steady magnetic field with a magnetic induction intensity of 12T to the vacuum resistance furnace; the macroscopic photo of the cast Cu-Ag alloy is as follows figure 2 shown;
[0047] Keep the cast Cu-Ag alloy at 750°C for 1 hour, then hot forge at 650-850°C to make a deformed Cu-Ag alloy, and control the area reduction rate of the deformed Cu-Ag alloy to 5%;
[0048] Draw the deformed Cu-Ag alloy at room temperature, keep the drawing direction perpendicular to the hot forging direction, and make a deform...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com