Method for removing O2, N2 and dimethyl ether from olefin streams
A technology of dimethyl ether and logistics, applied in chemical instruments and methods, purification/separation of hydrocarbons, hydrocarbons, etc., can solve the problems of large cooling capacity consumption of demethanizer, affecting product quality, and large loss of olefins, etc., to achieve Guaranteed ethylene recovery rate, reduced desiccant consumption, and stable deep drying effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Wash the compressed olefin stream in the water washing tower, perform oxygenate washing at a gauge pressure of 1.6MPa and 40°C according to the mass ratio of washing water and feed 2.5:1, feed the olefin stream and the top gas phase of the water washing tower after washing The composition of the stream and the bottom liquid phase stream (weight percent composition) is shown in Table 1.
[0044] Table 1
[0045]
Embodiment 2
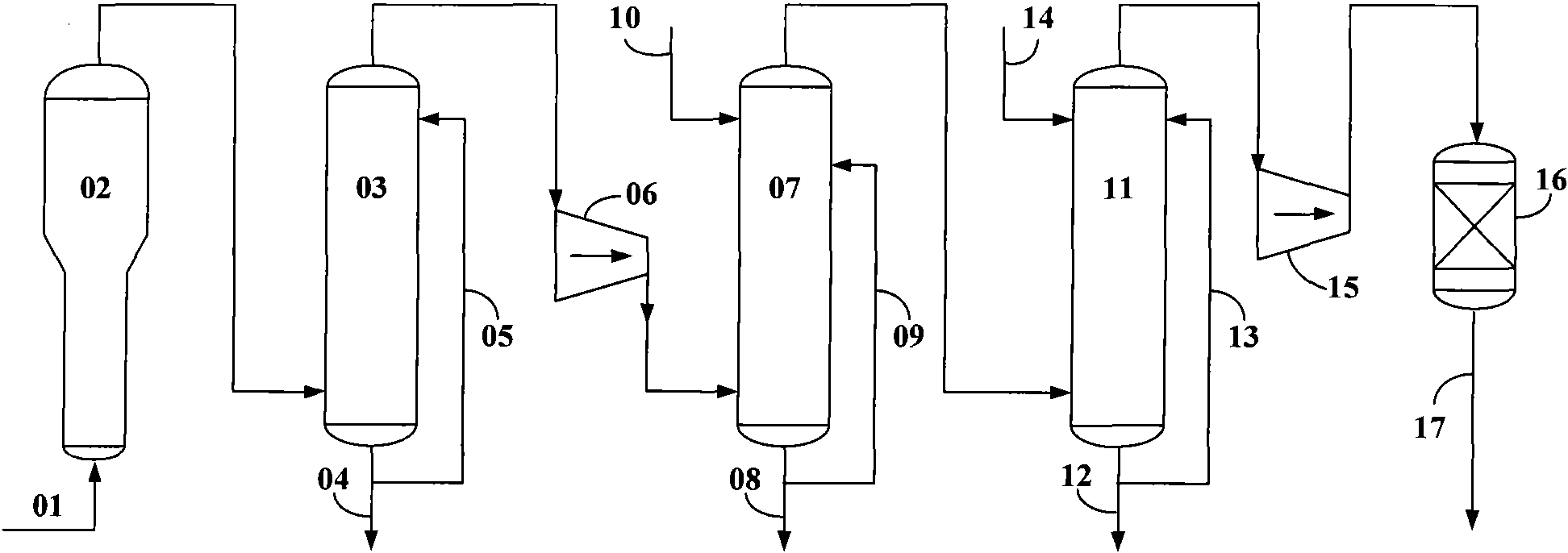
[0047] according to figure 1As shown, using the process flow of the present invention, the olefin stream with a gauge pressure of 1.65MPa, 40°C, and 50 tons / hour is washed with water under the same conditions as in [Example 1], washed with alkali at a gauge pressure of 1.55MPa, and 40°C, and further compressed To a gauge pressure of 3.8MPa and cooled to 15°C, the liquid water was separated and then dried.
[0048] Table 2
[0049]
Embodiment 3
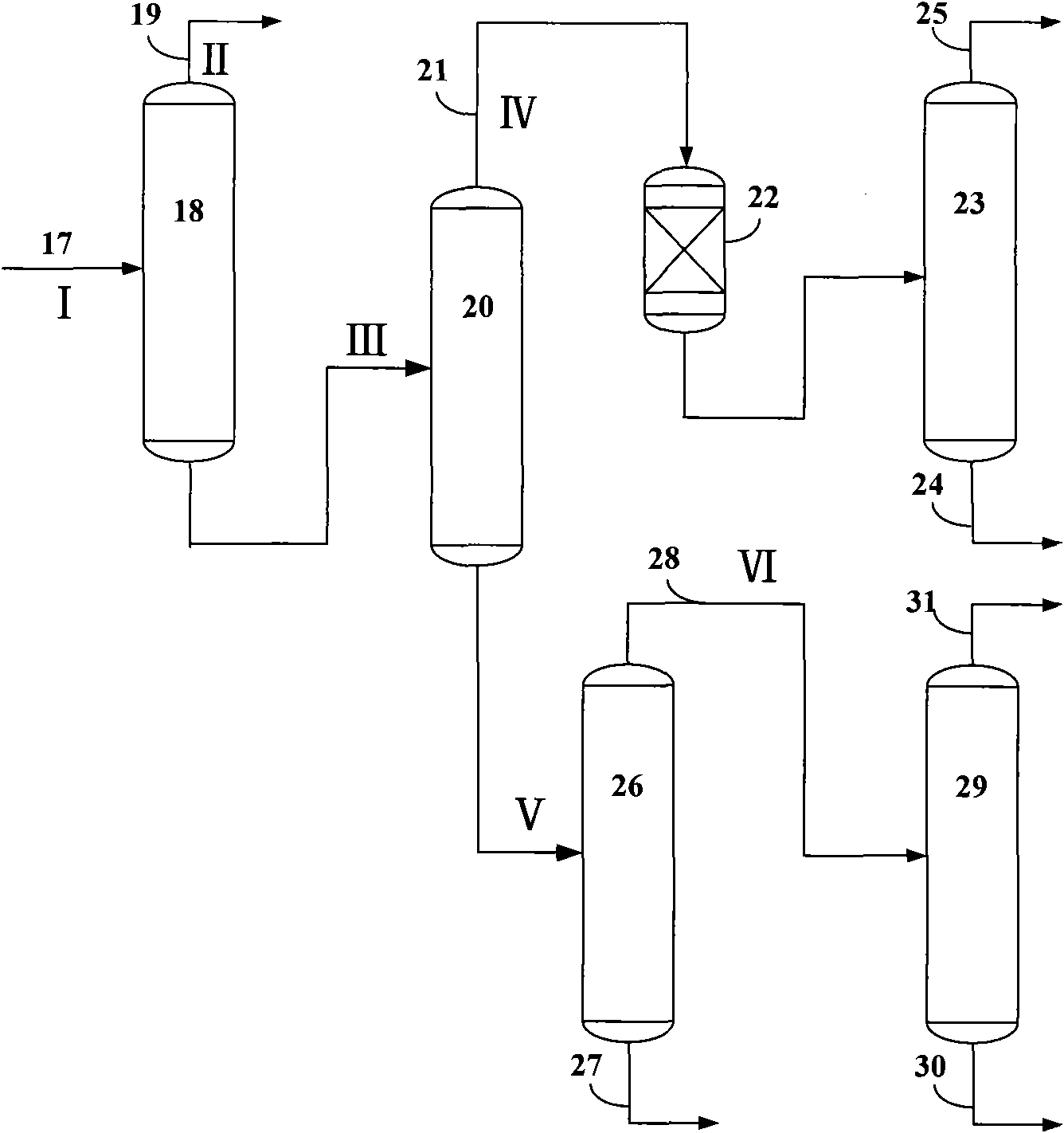
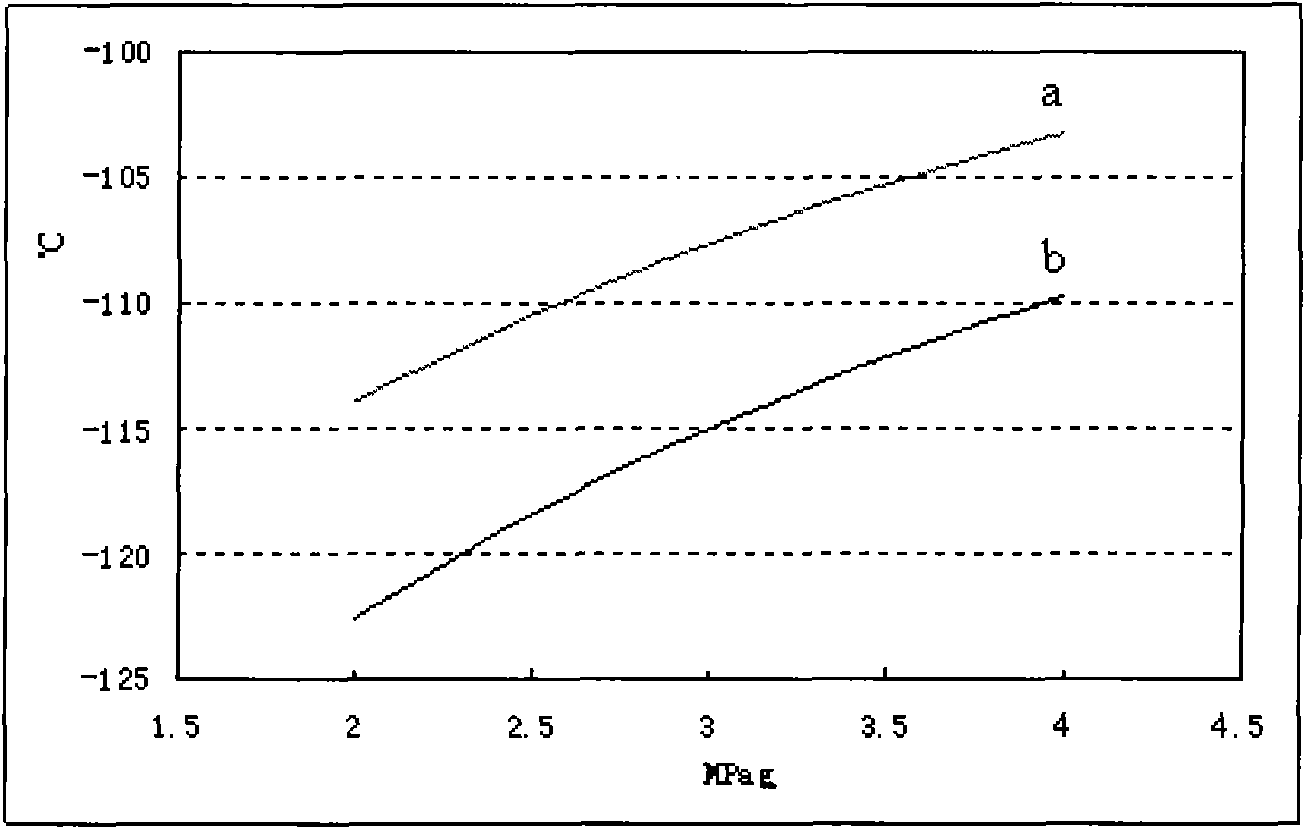
[0051] use figure 2 Process flow, the olefin stream obtained from the treatment in [Example 2] is further subjected to distillation and separation. The composition of the separated stream 19, stream 21, stream 28 and stream 27 is shown in Table 3. The operating conditions of the demethanizer are as follows: the pressure is 2.75MPa in gauge pressure, the temperature at the bottom of the tower is 12°C, and the temperature at the top of the tower is -65°C. The condensation temperature at the top of the tower is -110°C, the reflux ratio is 30, and the dew point of the stream at the top of the tower is -109°C. The operating conditions of the deethanizer are as follows: the pressure is 1.6MPa in terms of gauge pressure, the temperature at the bottom of the tower is 48°C, and the temperature at the top of the tower is -35°C. The operating conditions of the depropanizer are as follows: the pressure is 0.85 MPa in terms of gauge pressure, the temperature at the bottom of the tower i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com