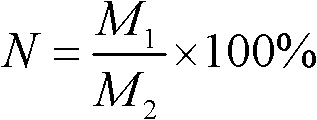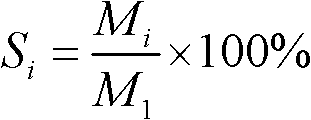Method for preparing catalyst for hydrogenation reaction of dimethyl oxalate and product
A technology of dimethyl oxalate and hydrogenation reaction, which is applied in the preparation of organic compounds, chemical instruments and methods, preparation of hydroxyl compounds, etc., can solve the problems of unutilization, low conversion rate of dissociation and fermentation, etc. The conditions are simple and are conducive to the effect of industrial application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Weigh 3g copper nitrate (Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O) solid, dissolved in 300ml deionized water, then add 7.47g urea, after dissolving, add dropwise 60g of silica sol with a silicon dioxide weight percentage content of 25%, stir for 4h, move the above mixture into a hydrothermal kettle, and heat at 60°C Keep the conditions for 24h, then keep at 120°C for 24h, then filter, wash with water, dry at 120°C, and roast at 450°C for 4h to obtain the catalyst precursor; use the catalyst precursor in a fixed-bed reactor 50mL / min H 2 After reduction at 350° C. for 3 h, a copper catalyst with a loading of 5% was obtained.
[0028] In the reaction of hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to produce methyl glycolate, at a temperature of 200°C and a pressure of 2 MPa, the ratio of hydrogen to dimethyl oxalate is 200, and the liquid volume space velocity is 0.8h -1 Under the above conditions, the conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate is 82%, and the selectivity of methyl glycolate is 92%.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Weigh 6.34g copper nitrate (Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 O) solid, be dissolved in 300ml deionized water, then add 7.87g urea. After dissolving, add 60g of silica sol with a weight percentage of 25% silica dropwise, and stir for 4 hours; transfer the above mixture into a hydrothermal kettle, keep it at 60°C for 48h, and then keep it at 90°C for 24h; other conditions are the same In Example 1, a copper catalyst with a loading of 10% was obtained.
[0031]In the reaction of hydrogenating dimethyl oxalate to produce methyl glycolate, at a temperature of 195°C and a pressure of 2 MPa, the ratio of the amount of hydrogen to dimethyl oxalate is 200, and the liquid volume space velocity is 1.0h -1 Under the above conditions, the conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate is 90%, and the selectivity of methyl glycolate is 87%.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Weigh 9.51g copper nitrate (Cu(NO 3 ) 2 ·3H 2 (0) Solid, dissolved in 200ml deionized water, then add 7.1g urea, after dissolving, add dropwise 40g silica sol with a silicon dioxide weight percentage content of 25%, and stir for 4h; The conditions were maintained for 36 hours; other conditions were the same as in Example 1, and a copper catalyst with a loading capacity of 20% was obtained.
[0034] In the reaction of hydrogenation of dimethyl oxalate to ethylene glycol, at a temperature of 200°C and a pressure of 2 MPa, the ratio of hydrogen to dimethyl oxalate is 200, and the liquid volume space velocity is 1.0h -1 Under the conditions, the conversion rate of dimethyl oxalate is 100%, and the selectivity of ethylene glycol is 99%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com