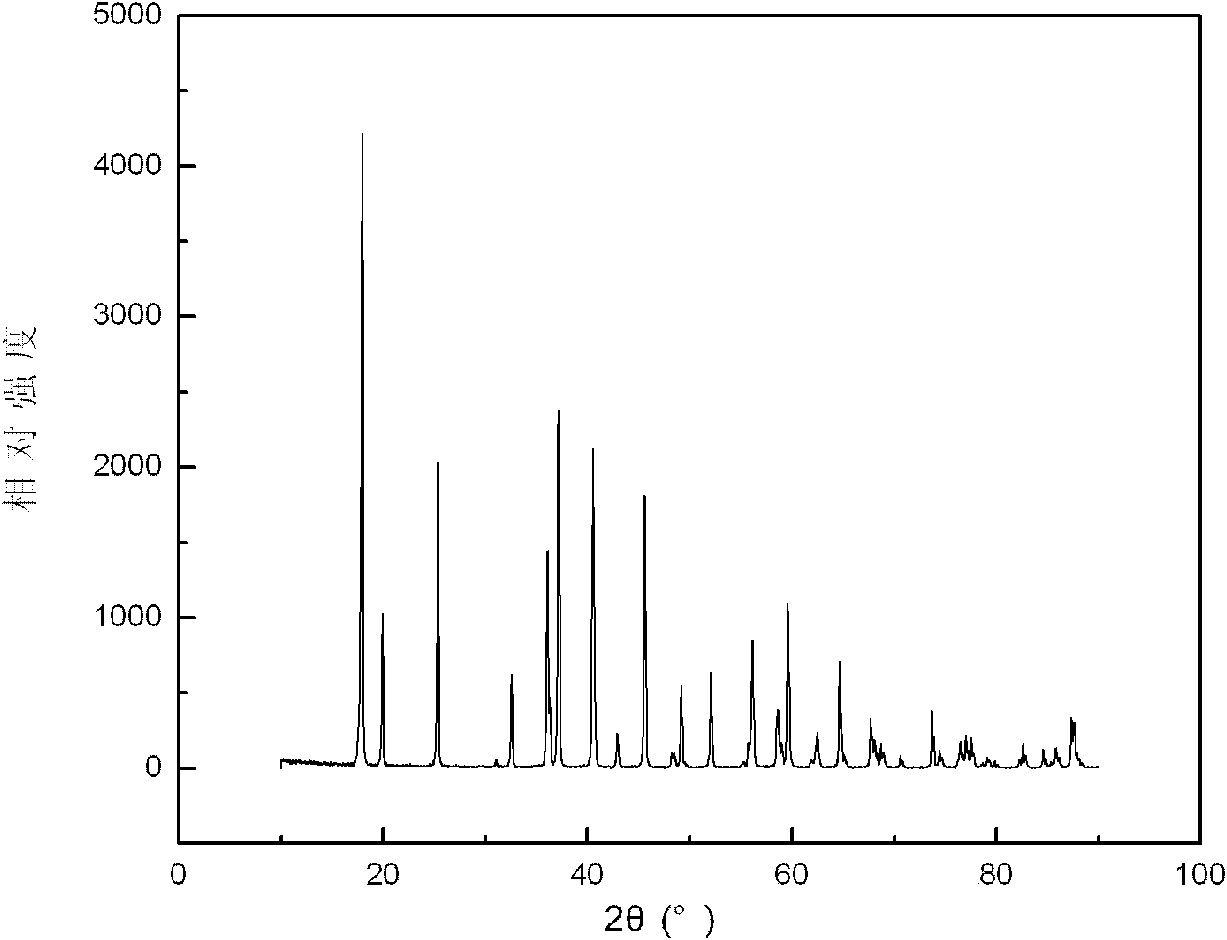
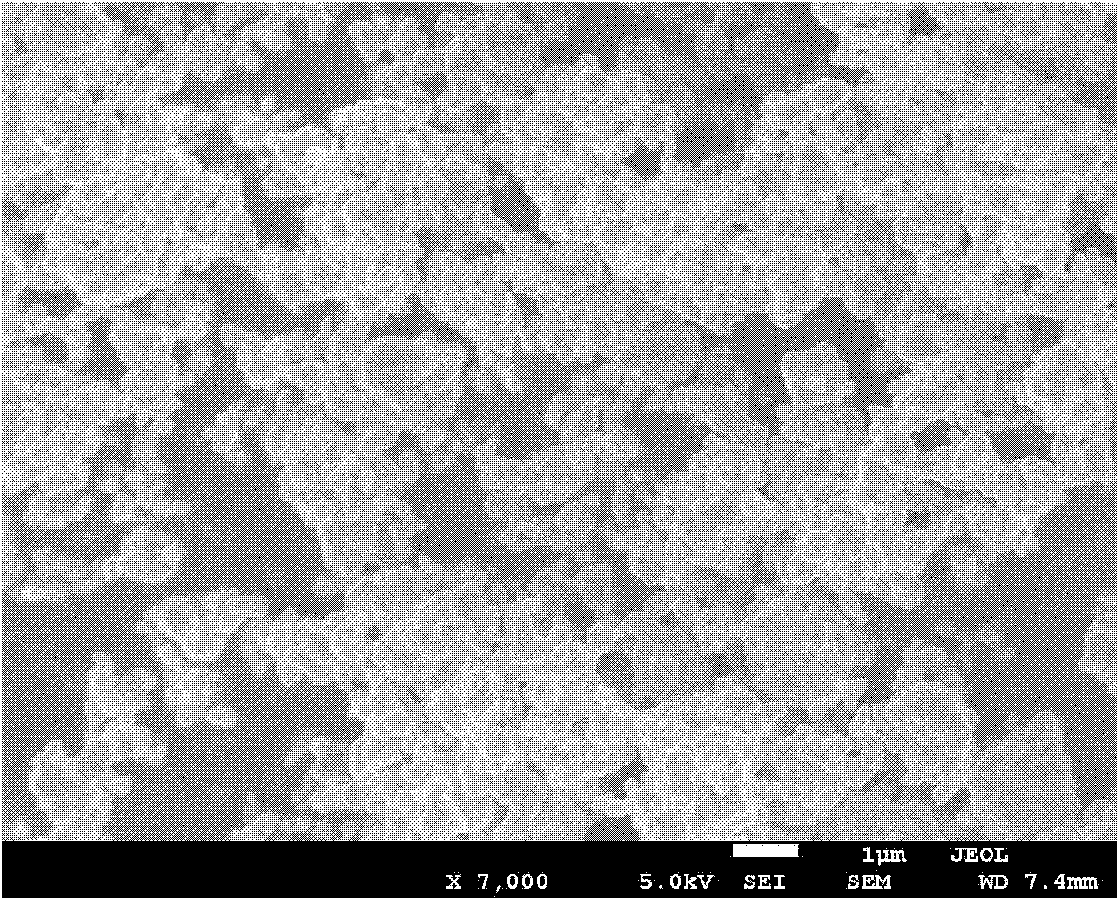
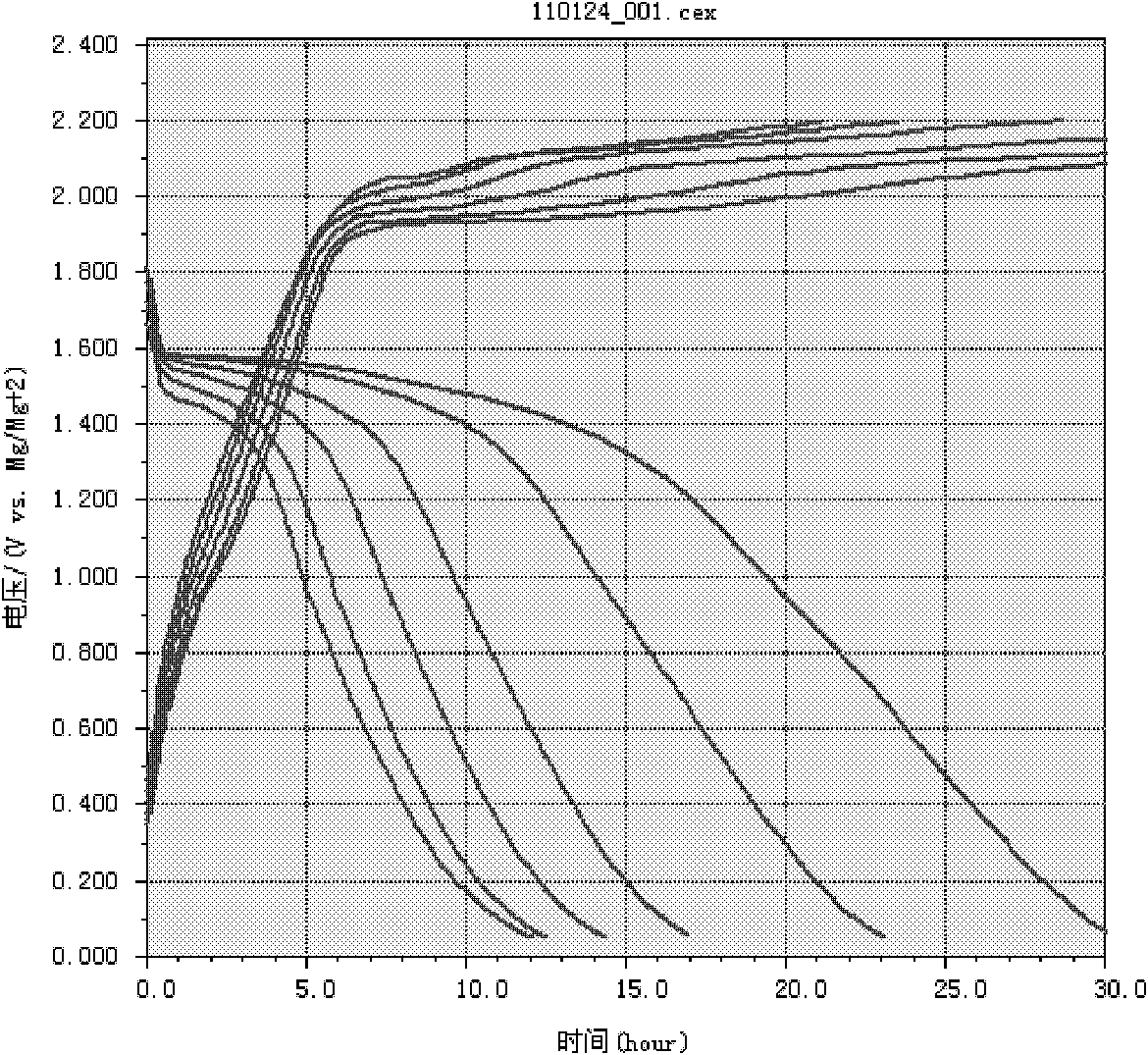
Modified positive pole material of magnesium secondary battery and preparing method thereof
A technology for magnesium secondary batteries and positive electrode materials, applied in electrode manufacturing, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of harsh preparation conditions, small ionic radius, and large charge density, and achieve simple and easy preparation methods, low cost, The effect of high specific capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The tetravalent magnesium molybdate Mg of embodiment 1 heteropolyacid modification 1+x MoO 3 (x=0.03) Preparation
[0022] (1), adopt magnesium carbonate, molybdenum trioxide, activated carbon as raw material, the consumption of raw material is Mg according to the molar ratio of atom: Mo: C=1.03: 1: 1 ratio weighs; First raw material is fully ground, after mixing uniformly Rapidly heat up to 500°C in argon, burn for 6 hours, then cool naturally, grind, put the ground powder into the furnace, protect with argon, control the heating rate of 5°C / min, heat up to 820°C and burn For 18 hours, finally control the cooling rate to 5°C / min, and cool down to 200°C to obtain tetravalent magnesium molybdate powder;
[0023] (2), the heteropolyacid (H 3 PMo 12 o 40 ) was dissolved in deionized water, adding vacuum-dried graphite and metal magnesium powder to form a solution, in the solution by mass ratio, heteropoly acid was 3%, graphite was 0.1%, metal magnesium powder was 0.1%...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 Heteropoly acid modified tetravalent magnesium molybdate Mg 1+x MoO 3 (x=0.1) Preparation
[0035] (1), adopt magnesia, molybdenum trioxide, gac to be raw material, the consumption of raw material is the ratio of Mg:Mo:C=1.1:1:1 according to the mol ratio of atom to take by weighing; First raw material is fully ground, after mixing uniformly Rapidly heat up to 500°C in argon, burn for 6 hours, then cool naturally, grind, put the ground powder into the furnace, protect with argon, control the heating rate of 5°C / min, heat up to 850°C and burn For 20 hours, finally control the cooling rate to 5°C / min, and cool down to 200°C to obtain tetravalent magnesium molybdate powder;
[0036] (2), the heteropolyacid (H 4 PMo 11 VO 40 ) was dissolved in deionized water, adding vacuum-dried graphite and metal magnesium powder to form a solution, in the solution by mass ratio, heteropoly acid was 2%, graphite was 0.2%, metal magnesium powder was 0.2%, deionized Water...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3 Heteropoly acid modified tetravalent magnesium molybdate Mg 1+x MoO 3 (x=0.05) Preparation
[0039] (1), adopt magnesium acetate, molybdenum trioxide, activated carbon as raw material, the consumption of raw material is Mg according to the molar ratio of atom: Mo: C=1.05: 1: 1 ratio takes by weighing; First raw material is fully ground, after mixing uniformly Rapidly heat up to 500°C in argon, burn for 6 hours, then cool naturally, grind, put the ground powder into the furnace, protect with argon, control the heating rate of 5°C / min, heat up to 800°C and burn For 12 hours, finally control the cooling rate to 5°C / min, and cool down to 200°C to obtain tetravalent magnesium molybdate powder;
[0040] (2), the heteropolyacid (H 3 PW 12 o 40 ) is dissolved in deionized water, adding vacuum-dried graphite and metal magnesium powder to form a solution. In the solution, by mass ratio, heteropolyacid is 4%, graphite is 0.2%, metal magnesium powder is 0.2%, and dei...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com