Cognitive routing protocol for heterogeneous wireless return network
A backhaul network and routing protocol technology, applied in wireless communication, advanced technology, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as increased end-to-end delay, decreased throughput, and inability to adjust
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
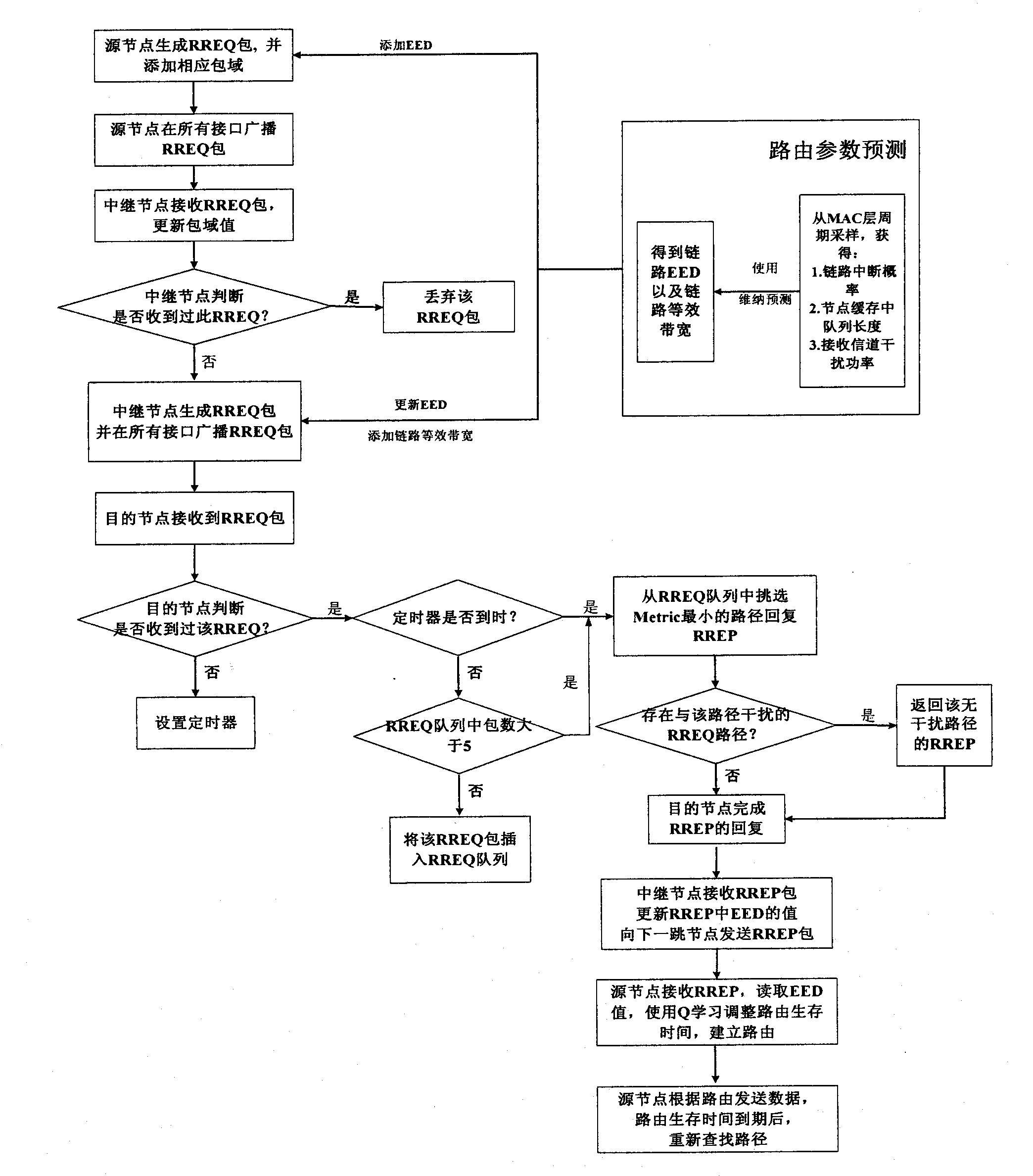
[0073] The present invention is a cognitive routing protocol for heterogeneous wireless backhaul network, see figure 1 As shown in the process diagram, the specific steps are as follows:
[0074] Step 1: Considering that each node is equipped with multiple radios, add the channel_num field to the routing table to record which interface to send data from each node.
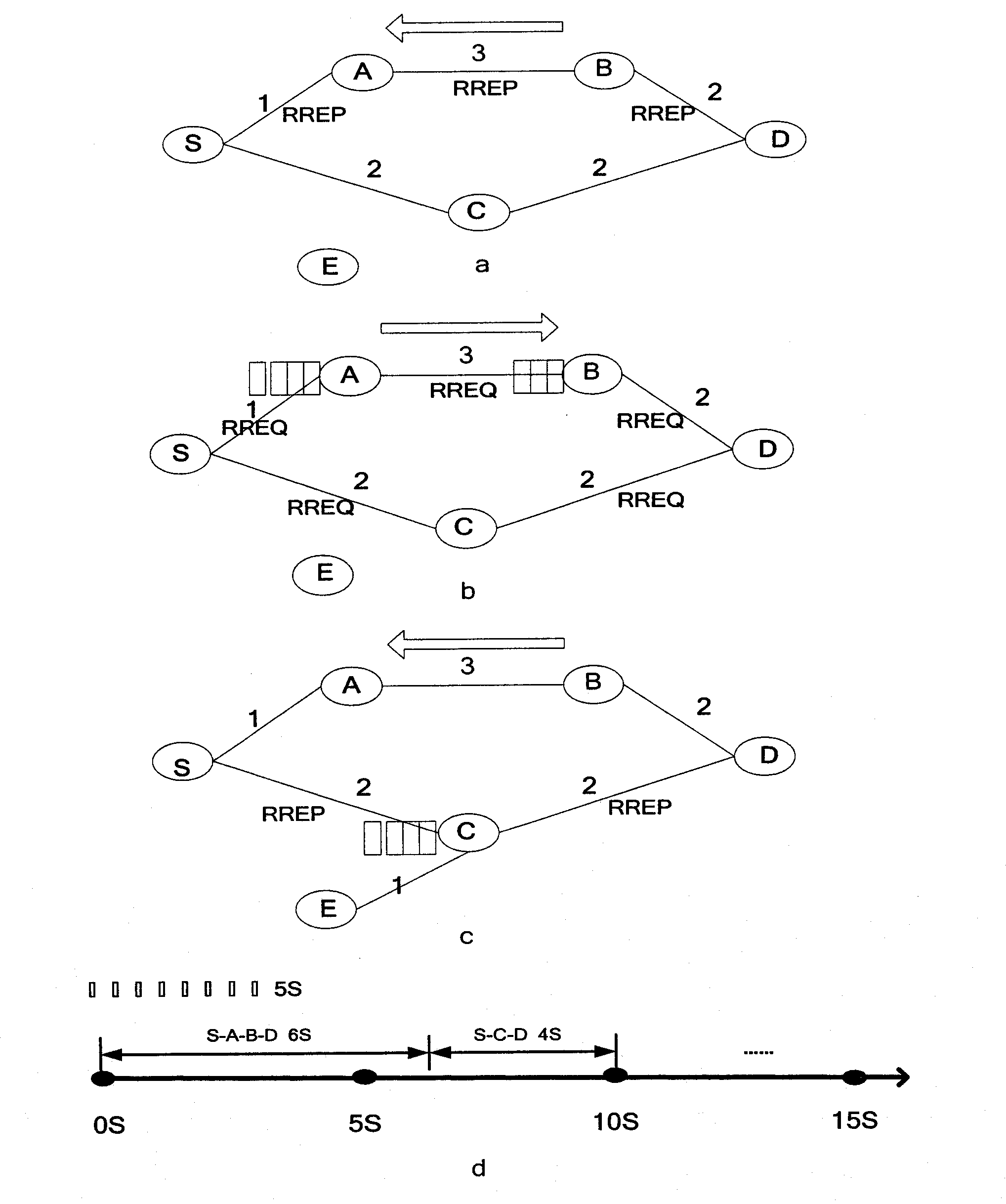
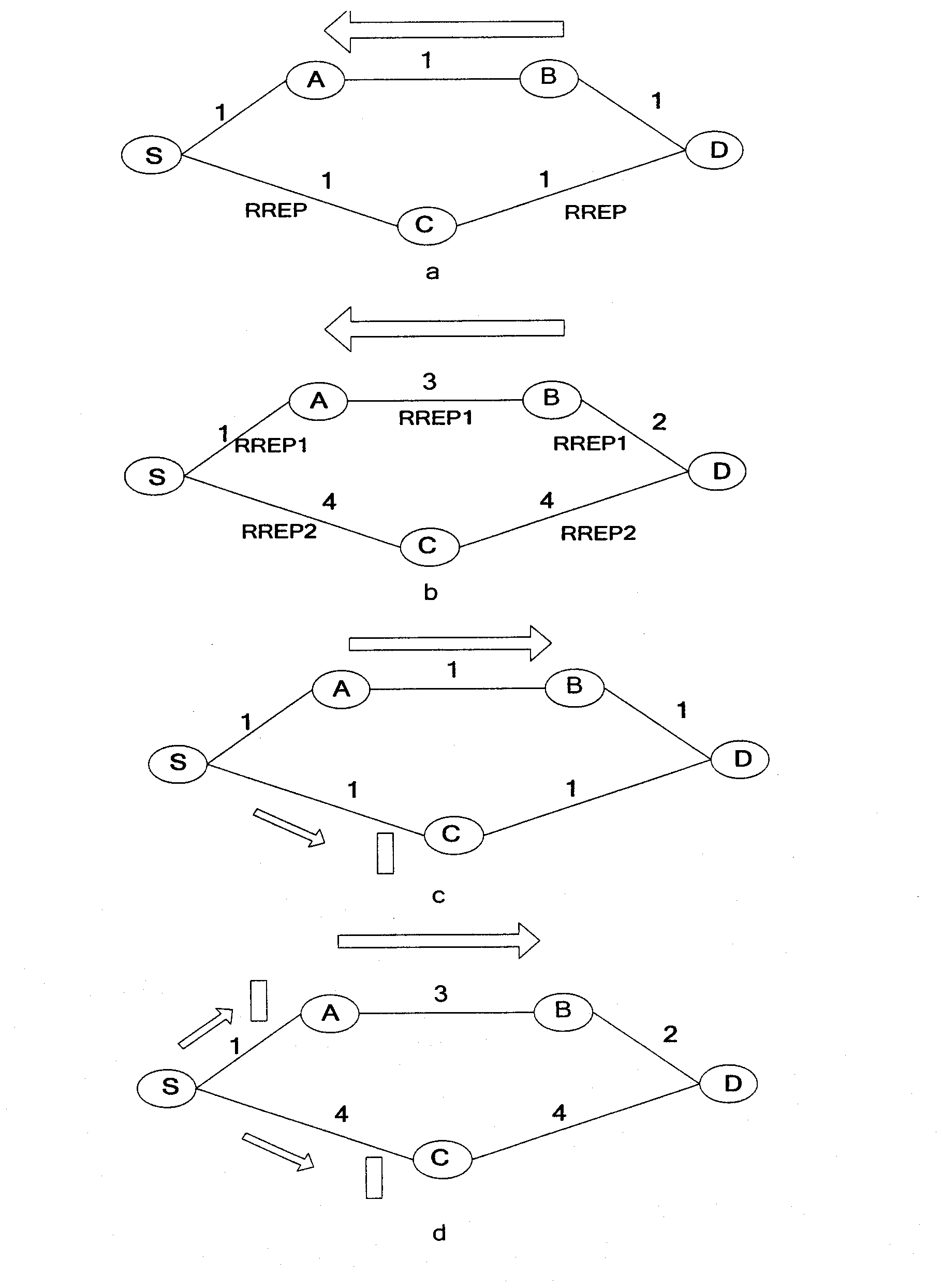
[0075] Add the EED_record field in the RREQ packet, which is used to record the transmission delay sum of each intermediate node on the path through Wiener prediction, for the destination node to use for routing; add the channel_num field, which is used to record which interface each node uses to receive and send RREQ package; add the ABITF_record field, which is used to record the equivalent bandwidth of each link, for the destination node to consider interference and frequency diversity factors to select routes; add the interference_record field to record the neighbor nodes that have the same channel as the node ...
Embodiment 2
[0091] The protocol method is the same as in embodiment 1, and the specific routing parameter calculation process in step 2 includes:
[0092] 2a. The node periodically counts the number of bits lost by the MAC layer at the MAC layer, divides it by the number of bits input by the MAC layer, calculates the packet loss rate of the MAC layer, and uses it as the link interruption probability p i estimate.
[0093] 2b. The network layer periodically reads the network layer queue length of the node and the packet loss rate of the MAC layer from the MAC layer, and calculates the routing metric EED value of the node.
[0094] p i is the link outage probability read from the MAC layer; T i Indicates the service time of the packet on link i; K indicates the maximum number of retransmissions; W j Indicates the contention window size of the jth backoff; L indicates the packet length; B indicates the link bandwidth, then on the wireless link, the expected service time E[T i ] is repres...
Embodiment 3
[0104] The protocol method is the same as in embodiment 1-2, and the specific routing parameter calculation process in step 2 includes:
[0105] 3a. The network layer obtains the sampling value of the interference power from the MAC layer, and infers the interference power P according to the Wiener prediction method in step 2.1c i The future value of P i (t+τ).
[0106] 3b. Let i represent the directed link i used by node u to send to node v; B i Indicates the physical bandwidth of link i; inter-flow interference ratio IDR i (uv) is the ratio of the interference power actually received by node v to the maximum interference power allowed by node v:
[0107] IDR i ( uv ) = P i ( t + τ ) P max ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com