Process for extracting iron from an aqueous acid solution
An acidic aqueous solution, an aqueous solution technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, mining wastewater treatment, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable microbial activity, and achieve excellent sediment performance, high biomass concentration, fast and effective iron remove effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
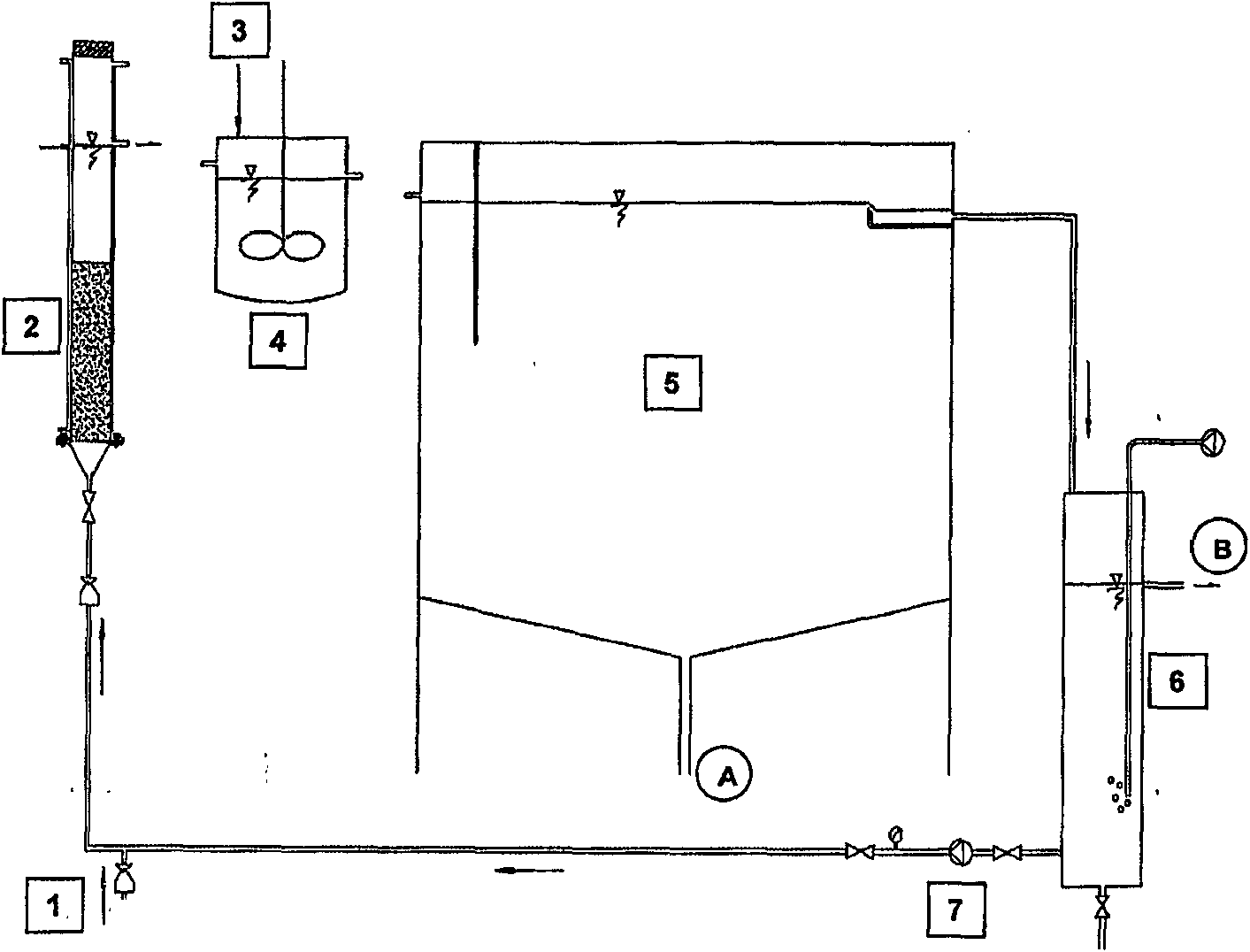
[0086] In laboratory-scale experiments, a fluidized bed was used comprising activated carbon (CalgonCarbon Filtrasorb 200) as a support and iron-oxidizing biomass Leptospira siderophilum on the surface of the activated carbon. The temperature of the reactor was 37°C, the total capacity of the fluidized bed reactor was 500 ml, and the capacity of the fluidized bed during fluidization was 340 ml. The residence time in the fluidized bed was 2 hours. A pH adjustment unit with a capacity of 4.5 l is connected to the fluidized bed. After a residence time of 7 minutes in the conditioning unit, the solution was sent to the precipitation unit. The capacity of the precipitation unit was 40 1 and the residence time of the solution to be precipitated in said unit was 1 hour. The device operates continuously.
[0087] The ferrous ion content in the solution introduced into the reactor was 14 g / l, and the rate at which the solution was pumped to the reactor was 0.17 l / h. The total amoun...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Under pilot plant conditions, a fluidized bed comprising activated carbon (Calgon Carbon Filtrasorb 200) as support and iron-oxidizing biomass Leptospira ferrophilum on the surface of the activated carbon was used. The temperature of the reactor was 37°C, the total capacity of the fluidized bed reactor was 14 1, the capacity of the fluidized bed during fluidization was 9.3 1. The residence time of the solution in the fluidized bed was 3 hours. A pH adjustment unit with a capacity of 70 1 was connected to the fluidized bed, and the residence time of the sludge in said unit was 4.3 minutes. The solution is delivered from the pH adjustment unit to a 2.9m 3 capacity of the precipitation unit, the residence time of the solution in said unit was 2.9 hours.
[0092] The ferrous ion content in the solution introduced into the reactor was 7 g / l and the pumping rate of said solution to the reactor was 3.2 l / h. The total amount of solution passing through the fluidized bed was ...
Embodiment 3
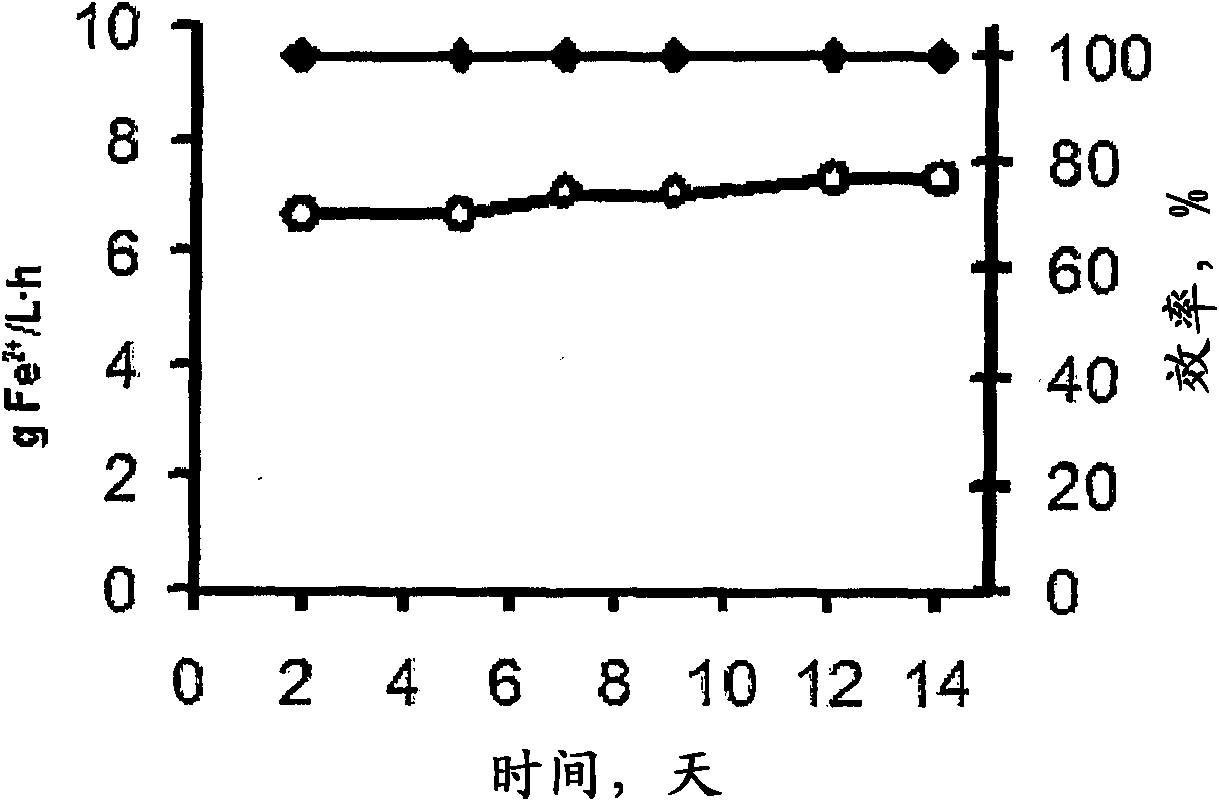
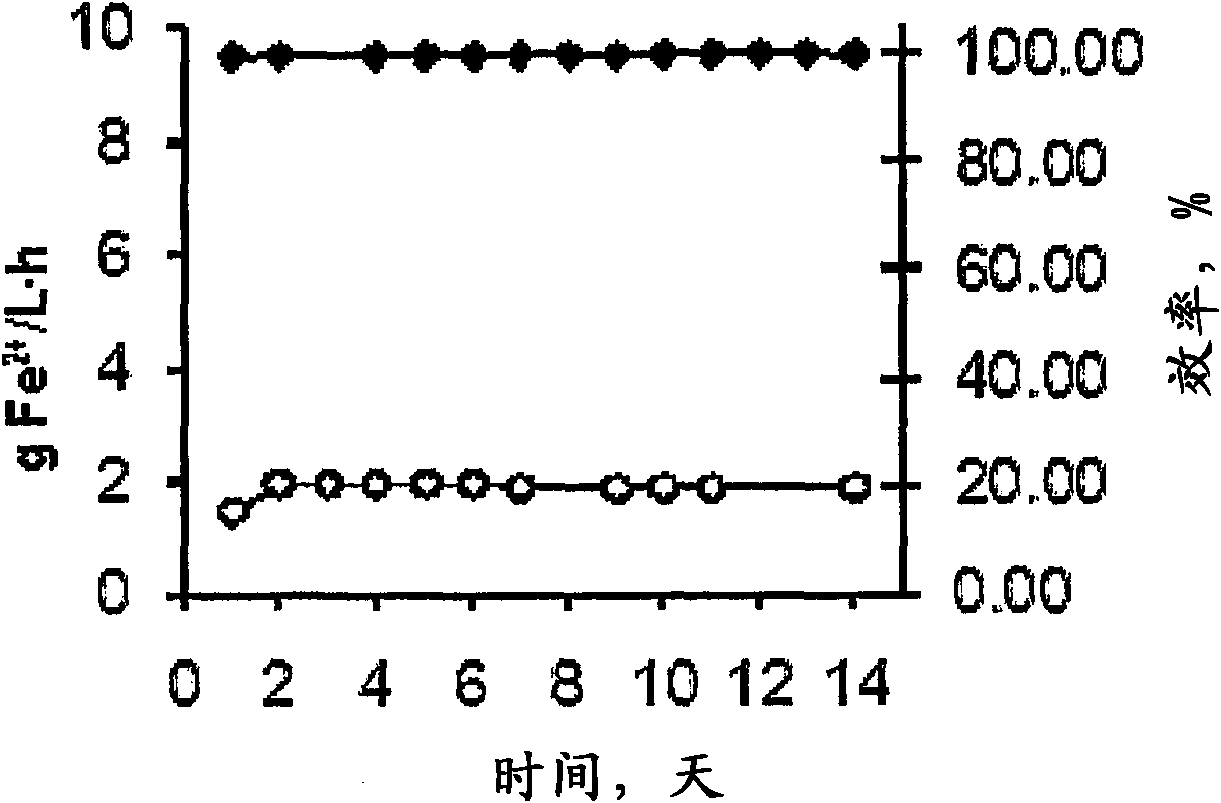
[0095] With the experimental configuration of Example 1, when using CaCO 3 When adjusting the pH of the solution, we get figure 2 The oxidation rate and oxidation efficiency of ferrous ions shown in .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com