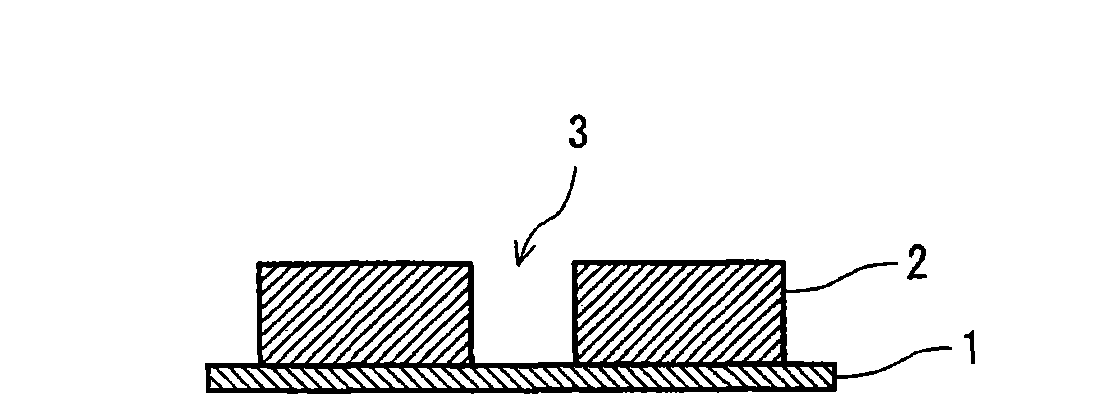
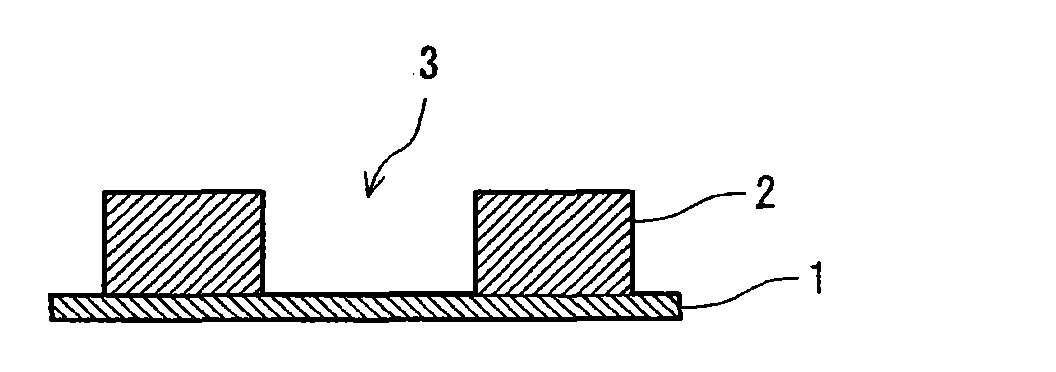
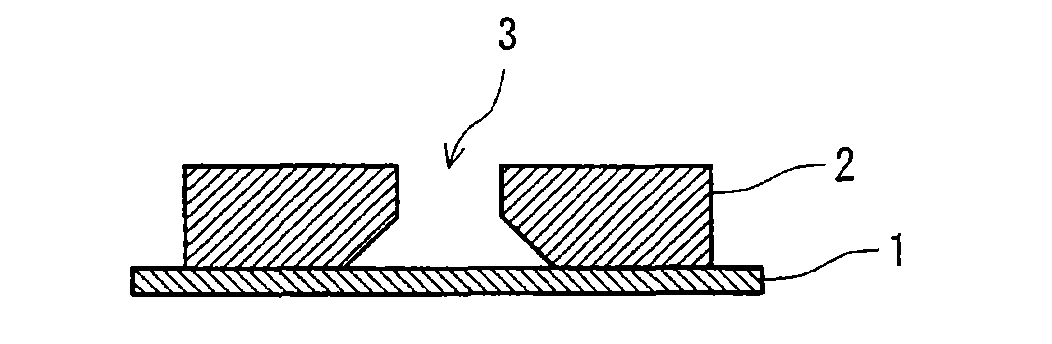
Positive radiation sensitive composition, interlayer insulation film and forming method thereof
A radiation-sensitive technology, which is applied in the field of positive-type radiation-sensitive compositions, can solve the problems of prolonging the development time and reducing the developability and pattern formation, and achieves fine and detailed patterns, excellent development and pattern formation, and responsiveness high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Synthetic example 1
[0285] In a flask with a condenser tube and a stirrer, 7 parts by mass of 2,2'-azobis(2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile) and 200 parts by mass of diethylene glycol ethyl methyl ether were added. Then, add 5 parts by mass of methacrylic acid, 40 parts by mass of 1-ethoxyethyl methacrylate, 5 parts by mass of styrene, 40 parts by mass of glycidyl methacrylate, 10 parts by mass of 2-methacrylic acid Hydroxyethyl ester and 3 parts by mass of α-methylstyrene dimer were replaced with nitrogen, and then slowly stirred. The temperature of the solution was raised to 70° C., and the temperature was maintained for 5 hours to obtain a polymer solution containing the polymer (A-1). The polystyrene-equivalent mass average molecular weight (Mw) of the polymer (A-1) was 9,000. In addition, the solid content concentration (the ratio of the mass of the polymer contained in the polymer solution to the total mass of the polymer solution; the same applies hereinafter) of the polymer solution obtained her...
Synthetic example 2
[0287] In a flask with a condenser tube and a stirrer, 7 parts by mass of 2,2'-azobis(2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile) and 200 parts by mass of diethylene glycol ethyl methyl ether were added. Then, add 5 parts by mass of methacrylic acid, 40 parts by mass of tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl methacrylate, 5 parts by mass of styrene, 40 parts by mass of glycidyl methacrylate, 10 parts by mass of methyl 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and 3 parts by mass of α-methylstyrene dimer were replaced with nitrogen, and then slowly stirred. The temperature of the solution was raised to 70° C., and the temperature was maintained for 5 hours to obtain a polymer solution containing the polymer (A-2). The polystyrene-equivalent mass average molecular weight (Mw) of the polymer (A-2) was 9,000. In addition, the solid content concentration of the polymer solution obtained here was 31.3 mass %.
Synthetic example 3
[0289] In a flask with a condenser and a stirrer, 7 parts by mass of 2,2'-azobis(2-methylpropionate) and 200 parts by mass of propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate were added. Next, 67 parts by mass of 1-n-butoxyethyl methacrylate, 23 parts by mass of benzyl methacrylate, and 10 parts by mass of methacrylic acid were added and replaced with nitrogen, followed by slow stirring. The temperature of the solution was raised to 80°C, and the temperature was maintained for 6 hours to obtain a polymer solution containing the polymer (a-1). The polystyrene-equivalent mass average molecular weight (Mw) of the polymer (a-1) was 9,000. In addition, the solid content concentration of the polymer solution obtained here was 30.3 mass %.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com