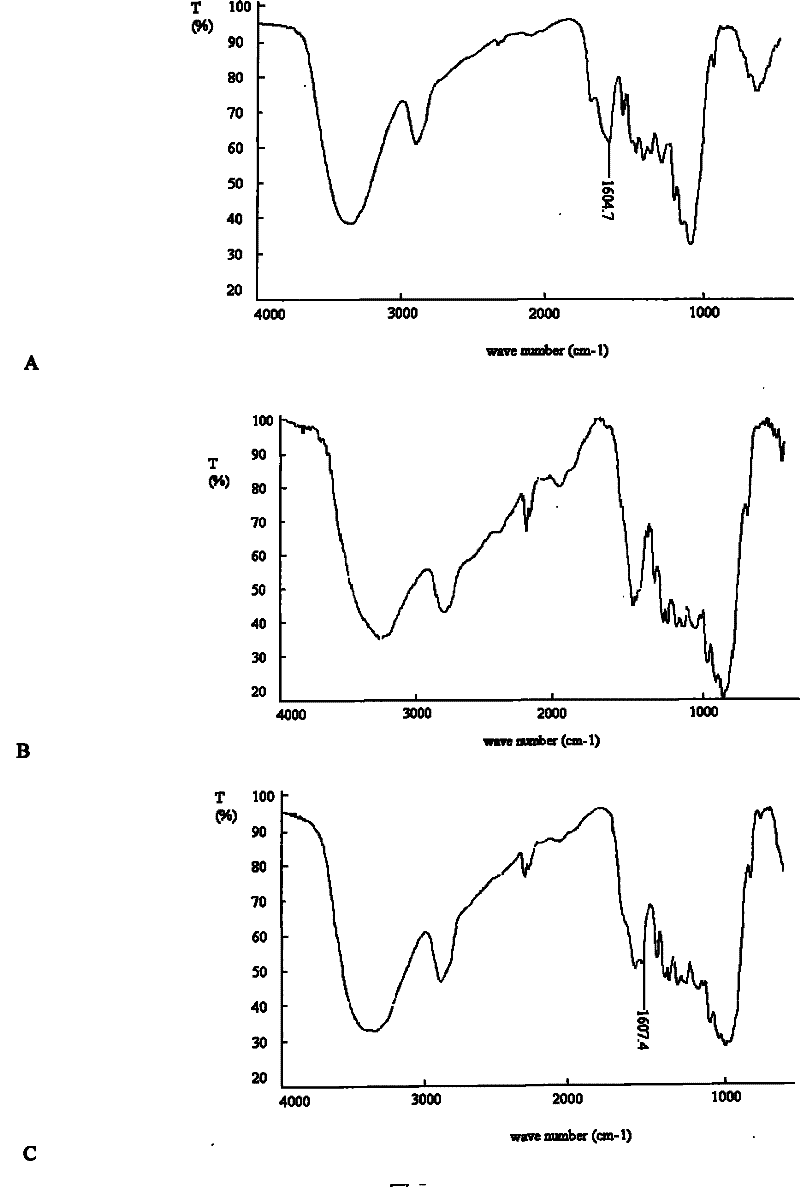
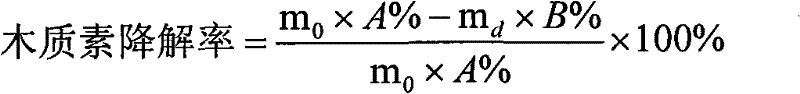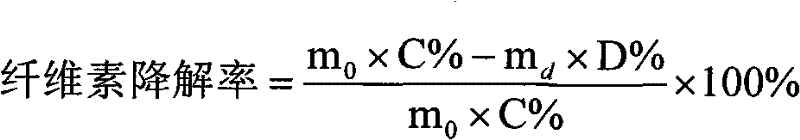Method for removing lignin by combined treatment of straws and laccase
A delignification and pretreatment technology, which is applied in the field of straw laccase combined pretreatment to remove lignin, can solve the problems of low accessibility of enzymes and raw materials, large enzyme amount, etc., and improve the moistening ability and removal rate High, increase the effect of adsorption performance and specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030]Corn stalks (13.42% moisture, 33.24% cellulose, 26.43% hemicellulose, 14.58% lignin, 7.24% ash) were cut into 10 mm long blocks, placed in a steam explosion device, and maintained at 1.5 MPa for 5 minutes. The pressure is suddenly released, and the obtained steam explosion material is separated from the solid and liquid by a screw extruder to obtain the washing liquid and the solid residue respectively. Dry in an oven at 60°C to obtain steam-exploded straw. The contents of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in steam-exploded straw were determined to be 45.28%, 10.21% and 18.43%, respectively. Take 20g of this steam-exploded straw, after crushing, add the basidiomycetes MyceliaSterilia laccase solution according to the laccase concentration of 0.55U / g substrate, adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 6.5, then add water to adjust the solid-liquid ratio to 1:20, mix well and place React in a water bath at 30°C for 4 hours, filter after the reaction, and weigh 17.6 g o...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Corn stalks (13.42% moisture, 33.24% cellulose, 26.43% hemicellulose, 14.58% lignin, 7.24% ash) were cut into 20 mm long blocks, placed in a steam explosion device, and the pressure was maintained at 2.0 MPa for 4 min. The pressure is suddenly released, and the obtained steam explosion material is separated from the solid and liquid by a screw extruder to obtain the washing liquid and the solid residue respectively. Place in an oven at 60°C to dry to obtain steam-exploded straw. The contents of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the steam-exploded straw were determined to be 48.41%, 7.04% and 19.17% respectively; 20 g of the steam-exploded straw was taken, crushed According to the laccase concentration of 2.0U / g substrate, add versicolor versicolor laccase solution, adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 4.5, then add water to adjust the solid-liquid ratio to 1:20, mix well and place it in a water bath at 30°C for 6 hours. After the reaction was completed, the fi...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Wheat straw (12.62% moisture, 32.16% cellulose, 25.63% hemicellulose, 10.36% lignin, 6.52% ash) was cut into 50 mm lengths, placed in a steam explosion device, maintained at 1.2 MPa for 6 minutes, and suddenly released The obtained steam explosion material is separated from solid and liquid by a screw extruder to obtain washing liquid and solid residue respectively. After the solid residue is soaked in water according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1:2, it is extruded for the second time. The solid residue is placed in Dry in an oven at 60°C to obtain steam-exploded straw. The contents of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the steam-exploded straw were determined to be 40.38%, 9.12% and 9.72%, respectively. Take 20g of this steam-exploded straw, after pulverizing, add the basidiomycete Mycelia Sterilia laccase solution according to the laccase concentration of 1.0U / g substrate, adjust the pH of the reaction solution to 8.0, then add water to adjust the solid-liquid rat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com