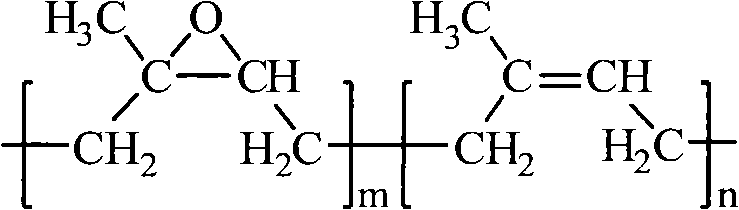Modified polylactic acid, preparation method and application thereof
A technology of polylactic acid and polylactic acid materials, applied in medical science, prosthesis, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption and inability to improve thermal stability, and achieve low consumption, simple operation process, and wide sources Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
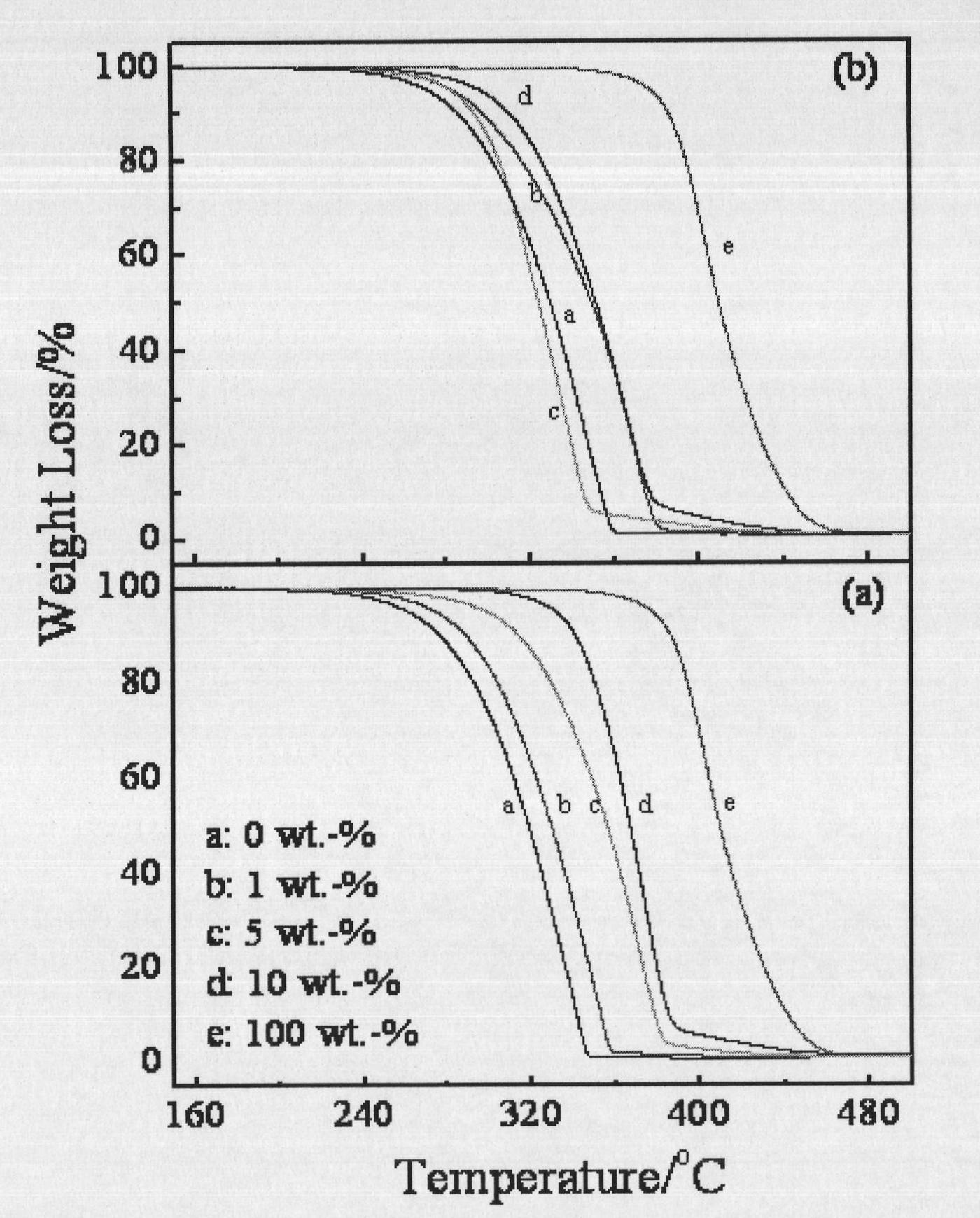
[0047] The impact of the content of embodiment 1, ENR-50 on the thermal stability of linear polylactic acid (abbreviated as PLA)
[0048] Mix PLA with different weights of ENR-50, dissolve in chloroform at 55°C, stir magnetically until it is completely dissolved, and cast a film. The mixture film was obtained by vacuum drying for 3 days under the condition of 90° C., and then annealed at 90° C. for 5 hours to obtain the modified polylactic acid provided by the present invention.
[0049] In this method, the weight ratios of PLA and ENR-50 used are: 99:1, 95:5 and 90:10, respectively. In addition, as a control, PLA and ENR-50 were also subjected to solution film formation in the same manner as above.
[0050] figure 1 (a) and (b) are the thermal degradation curves of PLA, ENR-50 and their mixtures with different weight ratios without annealing treatment and after annealing at 90℃ for 5h, respectively. pass figure 1 It can be seen that the introduction of ENR-50 can improve ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2, the influence of the degree of epoxidation of additive ENR on the tensile properties of PLA
[0052] Blank experiment: Dissolve 1.2g PLA in chloroform at room temperature, stir magnetically until it is completely dissolved, and cast a film. After evaporating the solvent at room temperature, dry it in vacuum for 3 days at a vacuum degree of -0.1M Pa and a temperature of 30°C. The obtained film was annealed in an oven at 90°C for 5 hours to obtain a polylactic acid film, and its tensile properties are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the elongation at break of polylactic acid is very low and the toughness is poor.
[0053] 90 parts by weight of PLA and 5 parts by weight of ENR with different epoxidation degrees (the epoxidation degrees of the ENR are respectively 25% and 50%, as shown in ENR-25 and ENR-50 in Table 1) were mixed, 55 Dissolve in chloroform at ℃, stir magnetically until completely dissolved, cast film, volatilize the solvent ...
Embodiment 3
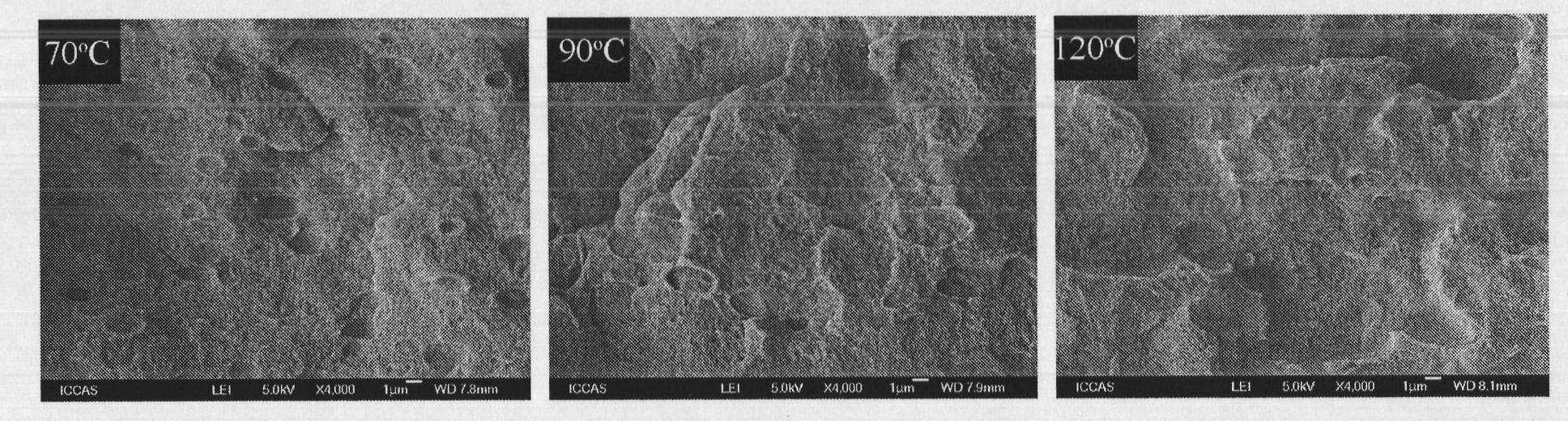
[0055] Example 3, the influence of annealing temperature on the tensile properties and phase separation of PLA and its blended film with ENR-50
[0056] Blank experiment: Dissolve 1.2g PLA in chloroform at room temperature, stir magnetically until it is completely dissolved, and cast a film. After evaporating the solvent at room temperature, vacuum-dry it for 3 days at a vacuum degree of -0.1M Pa and a temperature of 30°C. The resulting film was annealed in an oven at different temperatures for 5 hours to obtain a polylactic acid film, and its tensile properties are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that as the annealing temperature increases, the tensile strength of PLA increases, but the toughness decreases significantly.
[0057] Mix 90 parts by weight of PLA and 10 parts by weight of ENR-50, dissolve in chloroform at 55°C, stir magnetically until completely dissolved, and then cast the film. Vacuum drying under the same conditions for 3 days to obtain a film o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com