GaN-based light emitting diode chip and preparation method thereof
A technology of LED chips and electrodes, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of high equipment cost and low yield rate, and achieve the reduction of production cost, increase of yield rate, brightness improvement effect and stability effect. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
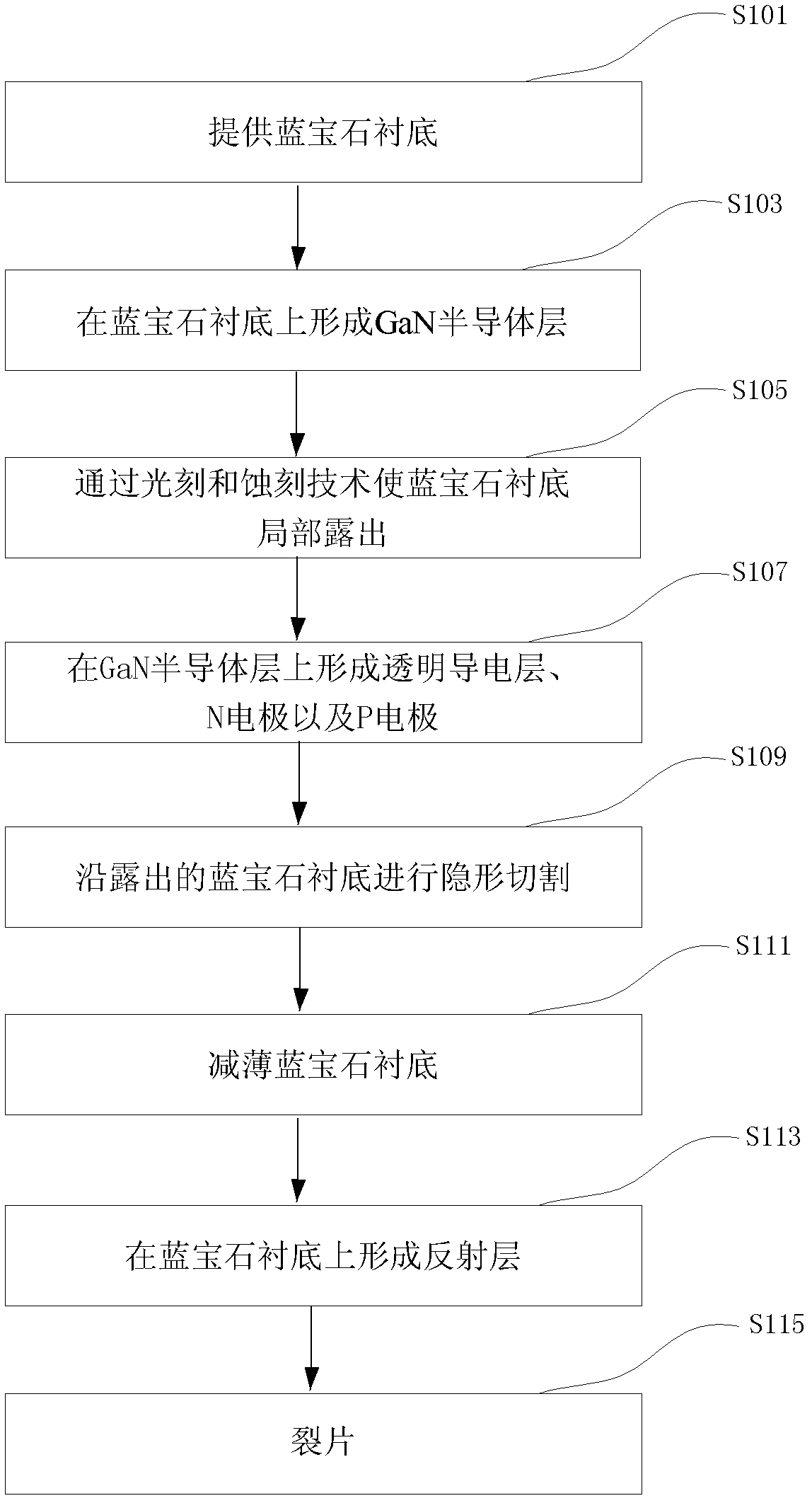
[0025] figure 1 It is a schematic flow chart of preparing a GaN-based LED chip according to the method for manufacturing a GaN-based LED chip according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Such as figure 1 Shown, described preparation method comprises the steps:
[0026] S101, providing a sapphire substrate;
[0027] S103, forming a GaN semiconductor layer on the sapphire substrate;
[0028] S105, partially exposing the sapphire substrate by photolithography and etching techniques;
[0029] S107, forming a transparent conductive layer, an N electrode and a P electrode on the GaN semiconductor layer;
[0030] S109, performing invisible cutting along the exposed sapphire substrate;
[0031] S111, thinning the sapphire substrate;
[0032] S113, forming a reflective layer on the sapphire substrate; and
[0033] S115, lobes.
[0034] The following combination Figure 1 to Figure 11 A method of manufacturing a GaN-based LED chip according to Embodiment 1 of the present i...
Embodiment approach 2
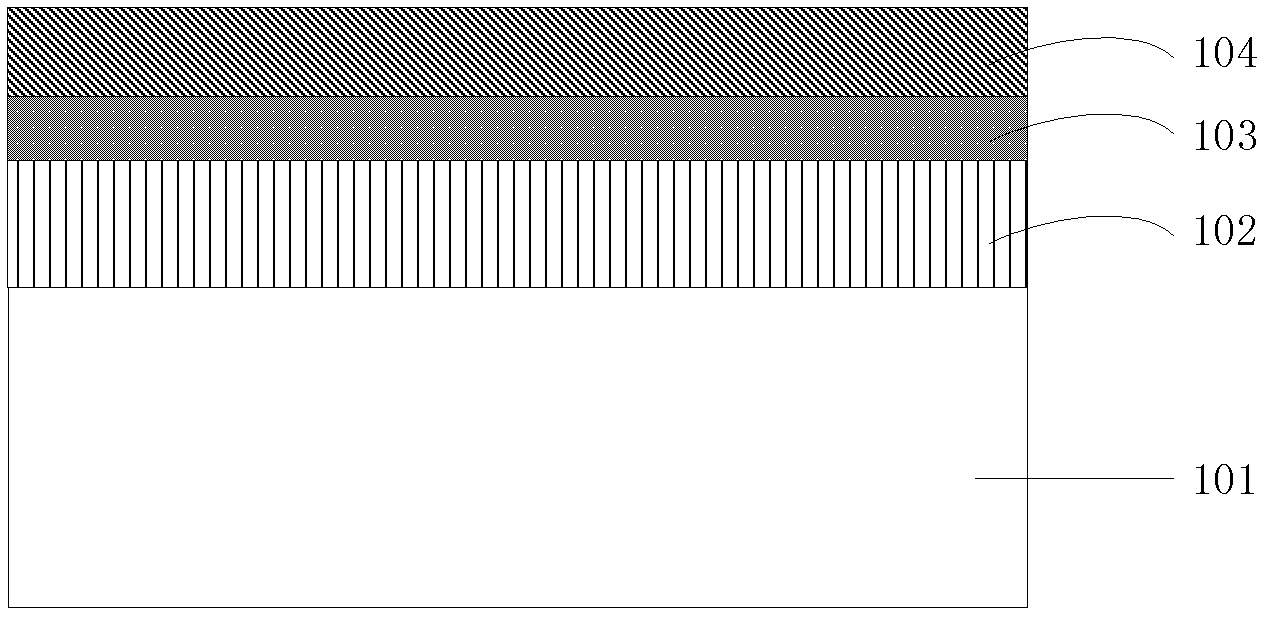
[0043] In Embodiment 1, step S105 is first performed, that is, the flat sapphire substrate 101 is partially exposed by photolithography and etching techniques, and then step S107 is performed to form a transparent conductive layer 106, an N electrode 107 and a P electrode 108 . In this embodiment, after forming the transparent conductive layer 106, the N electrode 107 and the P electrode 108 on the GaN semiconductor layer, the GaN semiconductor layer is etched by photolithography and etching techniques, so that the flat sapphire substrate 101 is locally Exposure is equivalent to exchanging the execution order of steps S105 and S107 in the first embodiment. The remaining parts are the same as those in Embodiment 1 and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment approach 3
[0045] In Embodiment 1, step S105 is first performed, that is, the flat sapphire substrate 101 is partially exposed by photolithography and etching techniques, and then step S107 is performed to form a transparent conductive layer 106, an N electrode 107 and a P electrode 108 . In this embodiment, the flat sapphire substrate 101 can be partially exposed during the formation of the transparent conductive layer 106, the N electrode 107 and the P electrode 108, or it can be formed after the transparent conductive layer 106 is formed, or after the N electrode 107 is formed. After that, or after the P electrode 108 is formed, the flat sapphire substrate 101 is partially exposed. The remaining parts are the same as those in Embodiment 1 and will not be repeated here.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com