Refining method for long-chain binary acid
A long-chain dibasic acid and refining method technology, which is applied in the field of long-chain dibasic acid refining, can solve the problems of high content of protein and other impurities, failure to meet the requirements of polymer grade products, and uneven crystal particle size, so as to save drying costs. Steam consumption, easy washing and filtering, coarse and uniform crystals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
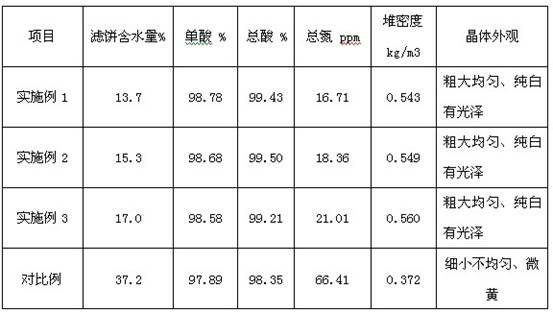
[0018] Embodiment 1: Purify long-chain dibasic acid according to the following steps
[0019] Step 1: The pH of the fermented liquid produced by microbial fermentation to produce dodecanedibasic acid is adjusted to 8.5, heated to 60°C to break the emulsion, and filtered through a ceramic membrane to remove alkanes, bacteria, other macromolecular proteins, and pigment impurities to obtain a clear liquid;
[0020] Step 2: Add pure water to the clear liquid obtained in step 1 to adjust the salinity to 8%, add 0.1% activated carbon of the clear liquid mass for decolorization for 30 minutes, plate and frame press filter and wash the filter cake, dilute the decolorized clear liquid with pure water to control the salinity 4%;
[0021] Step 3: 6000ml of the decolorized clear liquid obtained in step 2 and dilute sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 30% are subjected to rapid mixing and reaction crystallization on the molecular scale through a T-shaped microchannel reactor to form...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: Purify long-chain dibasic acid according to the following steps
[0026] Step 1: adjust the pH of the fermented liquid to 8.8 after microbial fermentation to produce tridecanedibasic acid, heat to 75°C to break the emulsion, and filter through a ceramic membrane to remove alkanes, bacteria, other macromolecular proteins, and pigment impurities to obtain a clear liquid;
[0027] Step 2: Adjust the salinity of the clear liquid obtained in step 1 to 10%, add 0.3% activated carbon of the clear liquid mass for decolorization for 30 minutes, plate and frame press filter and wash the filter cake, dilute the decolorized clear liquid with steam condensate, and control the salinity to 5 %;
[0028] Step 3: 6000ml of the decolorized clear liquid obtained in step 2 and dilute sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 40% are passed through a Y-type microchannel reactor for rapid mixing and reaction crystallization on the molecular scale to form a homogeneous mixture ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: Purify long-chain dibasic acid according to the following steps
[0033] Step 1: adjust the pH of the fermented liquid produced by microbial fermentation to tetradecanedibasic acid to 9.0, heat to 90°C to break the emulsion, and filter through a ceramic membrane to remove alkanes, bacteria, other macromolecular proteins, and pigment impurities to obtain a clear liquid;
[0034] Step 2: adjust the salinity of the supernatant obtained in step 1 to 12%, add 0.5% of the mass of the supernatant to decolorize with activated carbon for 30 minutes, plate and frame press filter and wash the filter cake, dilute the decolorized supernatant with purified water, and control the salinity to 6% ;
[0035] Step 3: 6000ml of the decolorized clear liquid obtained in step 2 and dilute sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 50% are subjected to rapid mixing and reaction crystallization on the molecular scale through a T-shaped microchannel reactor to form a homogeneous mi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com