Method for measuring propagation time of stress wave in wood and nondestructive test system
A travel time, non-destructive testing technology, applied in the direction of using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves to analyze solids, can solve the problem of non-destructive rapid detection and continuous detection, etc., to improve detection efficiency and accuracy, reduce errors, improve The effect of precision and reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
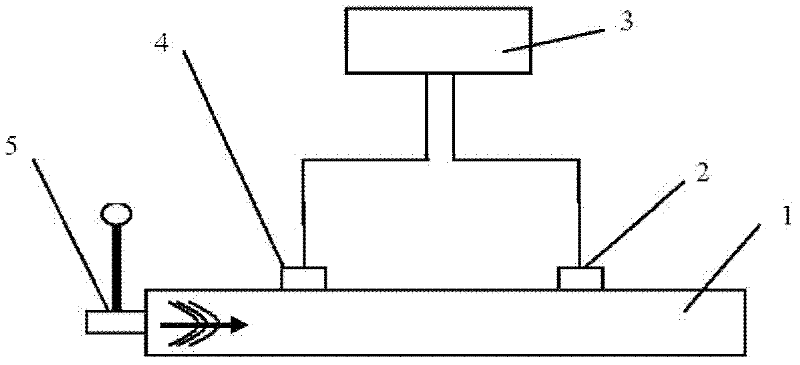
[0048] Example 1 (see figure 1 )
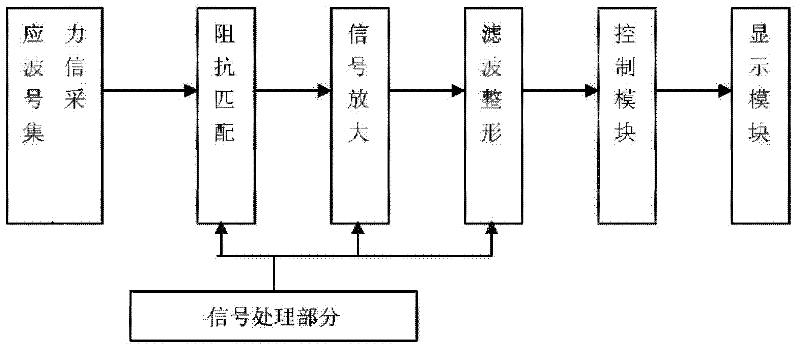
[0049] In the first step, two screws are embedded in the wood sample 1 to be tested, the start sensor 4 is connected with the start screw and the pulse hammer 5, the end sensor 2 is connected with the terminal screw, and the data cable and the detection system ( That is, the signal processing part 3) in the figure is connected.
[0050] The second step is to turn on the power switch of the detection system and set up the test environment. Including wood species, test sequence number, test sequence length (i.e. number of moving average items), wood density, distance between sensors (distance between screws), etc. After the test environment is set up, the system proceeds to the test waiting stage.
[0051] In the third step, the tester uses a pulse hammer to hit the screw at the start end to generate a stress wave that propagates inside the wood (the arrow in the figure indicates the direction of propagation). The start sensor collects the...
Embodiment 2
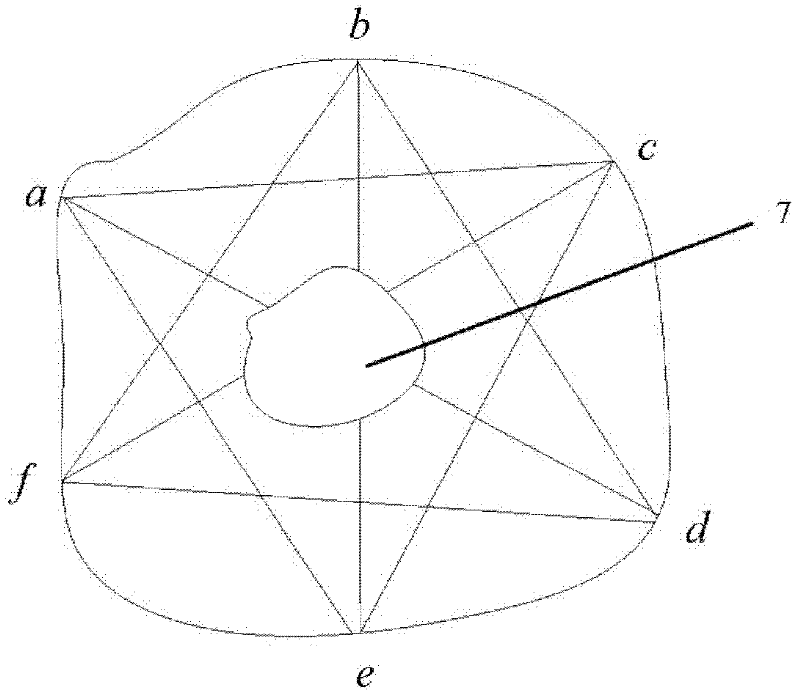
[0052] Example 2 (see figure 2 )
[0053] In order to accurately locate the internal defects of wood, it is necessary to perform multiple measurements on the wood sample from multiple directions to obtain test results from different directions, so as to more accurately determine the position and degree of defects within the wood. figure 2 represents the cross-section of the tested wood, where a, b, c, d, e, f Respectively represent six detection points (3 start sensors and 3 end sensors are respectively installed), and the central part 7 in the figure represents internal decay. The user conducts inspections from 9 directions in turn to obtain different stress wave propagation velocities and wood elastic modulus. According to these measurement results, the size and location of wood internal defects can be determined more accurately.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com